NMJ
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the components of the CNS
Spinal cord, brain stem, brain
What are the components of the PNS
ANS and SNS
What are the components of the ANS
Sympathetic (flight or fight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest)
What are neurons
Basic unit of nervous system made of soma dendrites and axons
What are soma
Contains the nucleus and Nissl bodies formed by neurotubule and neurofilament
What are Nissl bodies
Ribosome + ER
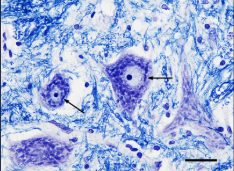
Soma
What are dendrites
Tree like branches of soma that form dendritic tree and is covered by dendritic spines
What are is the function of the dendrite in the PNS
Receive information and transfer to integrating region of sensory neuron
What are is the function of the dendrite in the CNS
Receive input from other neurons; important in memory formation and brain process
Axon function
Transmission of information as action potential/nerve impulse
What covers axons
Myelin sheaths
Myelin function
Speed up conduction of electrical signal and conserves energy
What is the myelinated cell in the CNS
oligodendrocyte
What is the myelinated cell in the PNS
Schwann cell
Kinesin function in axonal transport
Anterograde transport of MT and neurotransmitters from cell body to axon terminal at the PLUS end
Dynein function in axonal transport
Retrograde transport of growth factors/recycling of axon terminal component from axon terminal to cell body on the NEGATIVE end
Interneuron function
Connect neuron within the CNS
Afferent neuron function
Convey information from tissue and organ to CNS
Efferent neuron function
Convey information from CNS to effector cells
What are the characteristics of the afferent neuron
From peripheral to CNS; peripheral process axon in PNS to short process axon that enters CNS
What are the characteristics of the efferent neuron
From CNS to effector cells; cell body with many dendrites in the CNS, most axon in the PNS
What are the characteristics of the interneuron
Integrate and change signal; integrate groups of afferent/efferent neuron to reflex circuits; ONLY in CNS
What are synapse
Junction between two neurons where one alters the other chemically and electrically
Presynaptic neuron
Transmitting side (axon)
Postsynaptic neuron
Receiving side (dendritic/somatic sometimes axonal)
What are the CNS glia cells
Astrocyte, ependymal, microglia, oligodendrocyte
Astrocyte function
Neuronal migration in development, signal support in BBB
Ependymal cell function
Have ventricular space with adsorptive and secretory role for CSF
Microglia function
Immune response and synapse remodelling
Oligodendrocyte function
Myelinate CNS
PNS glia cells
Satellite and Schwann
Satellite cell function
Surround soma
Schwann cell function
Myelinate axon
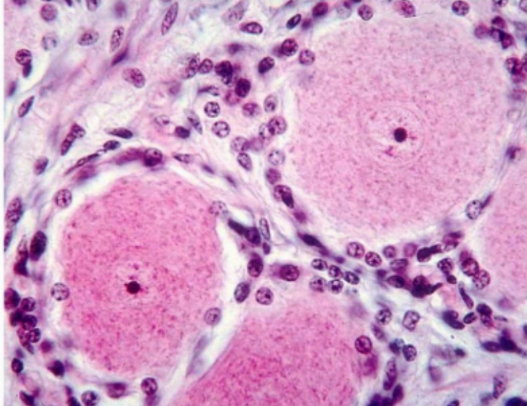
Satellite cells
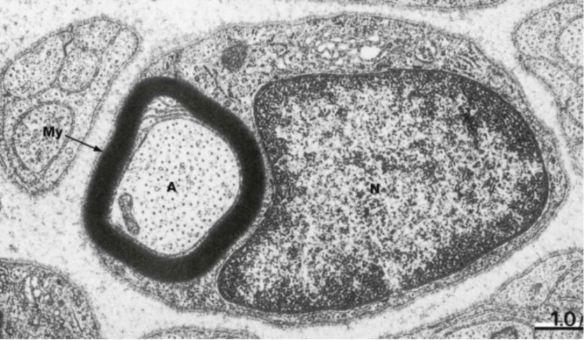
My = myelin, A = axon, N = Schwann cell
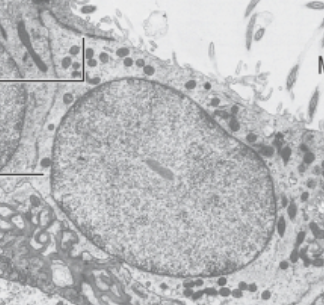
Ependymal cell
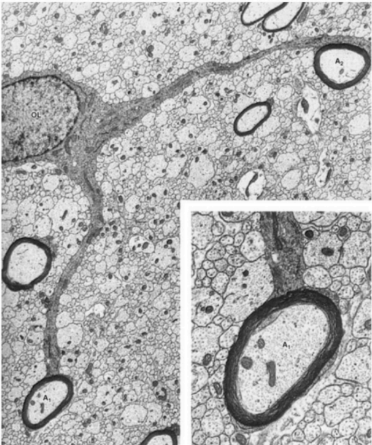
Gray is the oligodendrocyte
Curare mechanism
Bind to AchR and prevents binding
Botulinum mechanism
Prevent release of Ach
Lambert Eaton disease mechanism
Bind to Ca channel
Myasthenia gravis mechanism
Antibodies are produced against postsynaptic AchR
Postsynaptic dysfunction related disorders
Myasthenia gravis
Presynaptic dysfunction related disorders
Curare, botulinum, Lambert Eaton