3 Lec 18 (Exam 3): Malignant diseases of the jaws
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
ill-defined
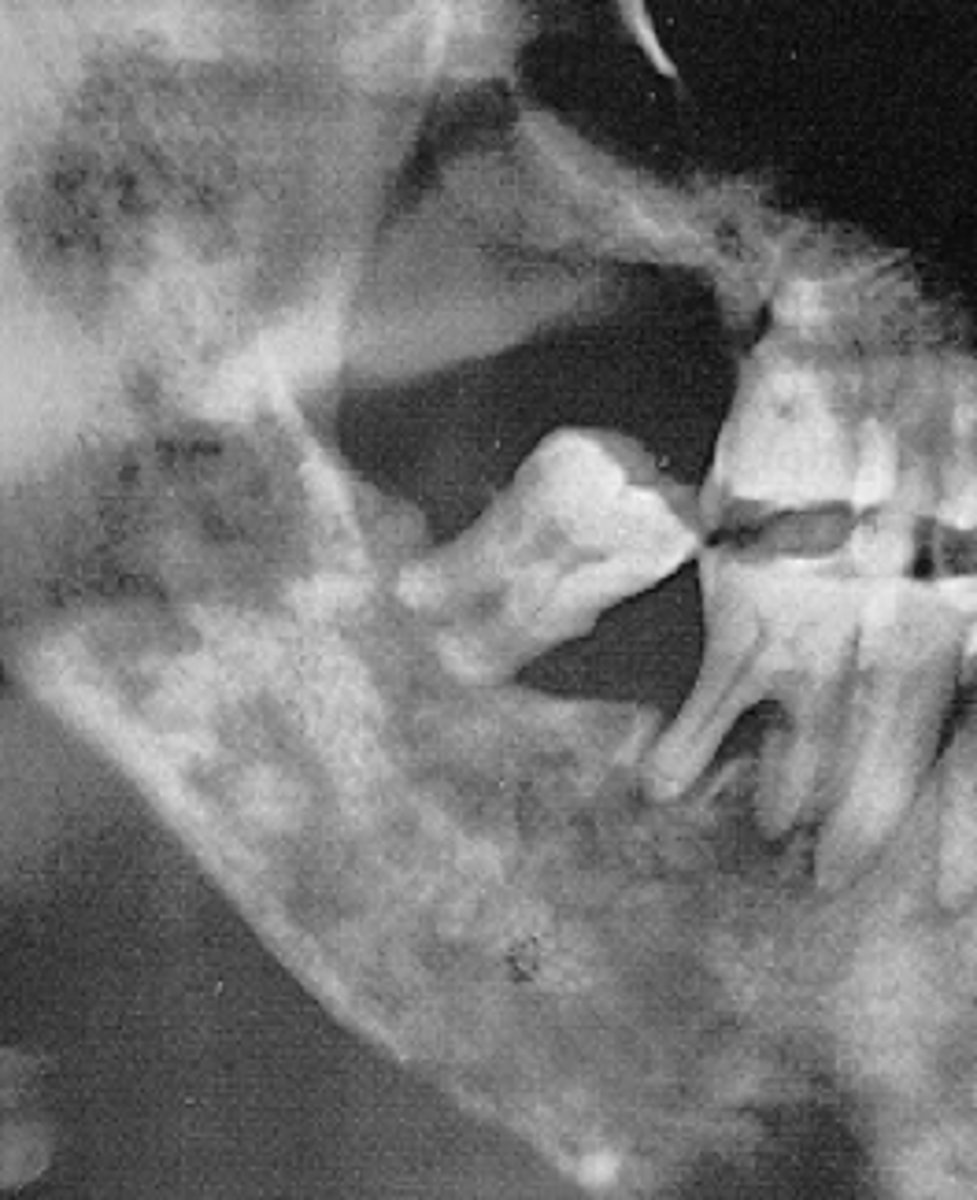
describe the periphery of this lesion:
radiolucent
MOST malignant lesions radiographically show up _______
floating teeth
what affect do malignant tumors have on tooth support?
widening
what affect do malignant tumors have on the PDL space?
spiked resorption pattern
what affect do malignant tumors have on tooth roots?
destruction
what affect do malignant tumors have on the IAN?
destruction
what affect do malignant tumors have on tooth corticla boundries?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
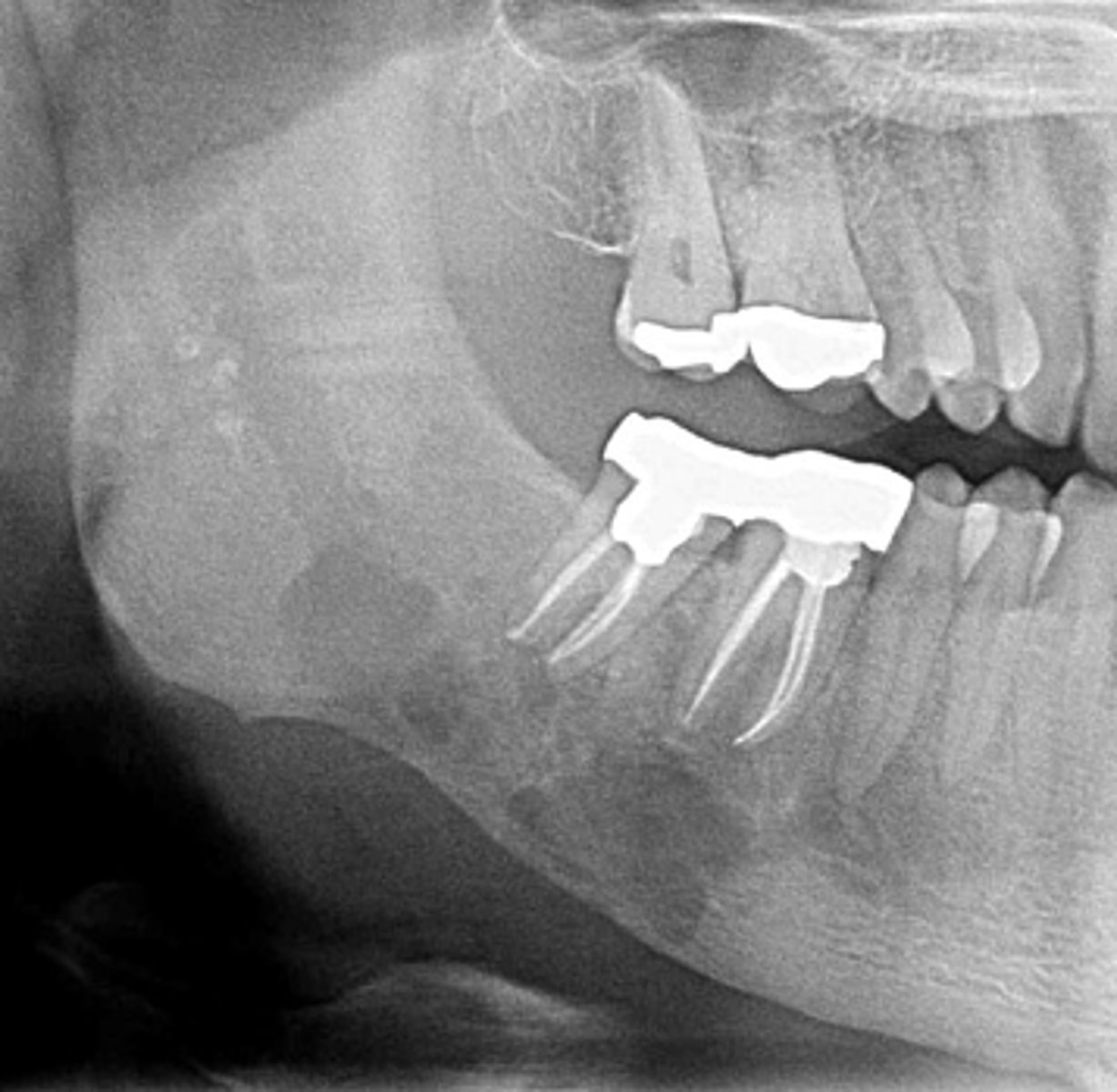
patient's radiograph shows, ill-defined, radiolucency on anterior mandible. Teeth appear to be "floating" due to bone destruction. PDL spaces of those roots are widened. What is the diagnosis?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
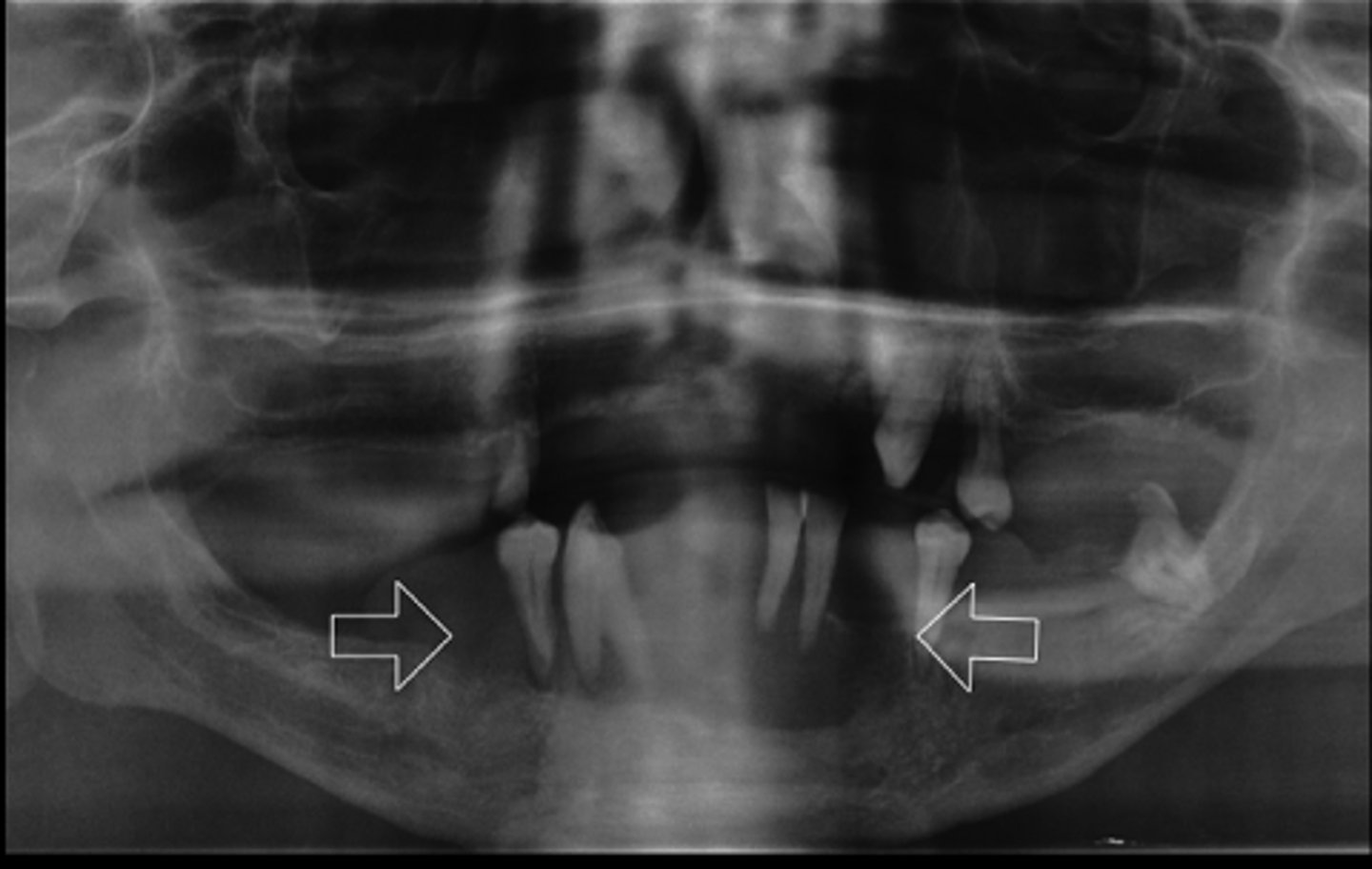
patient's radiograph shows, defined radiolucent lesion on the posterior mandible. IAN canal appears destroyed. Posterior teeth appear to be "floating" due to bone destruction.There is sudden mobility of #30, 31 for 1 month. There is no clinical evidence of peridontal disease. Patient experiences a dull ache. What is the diangosis?
Osteosarcoma
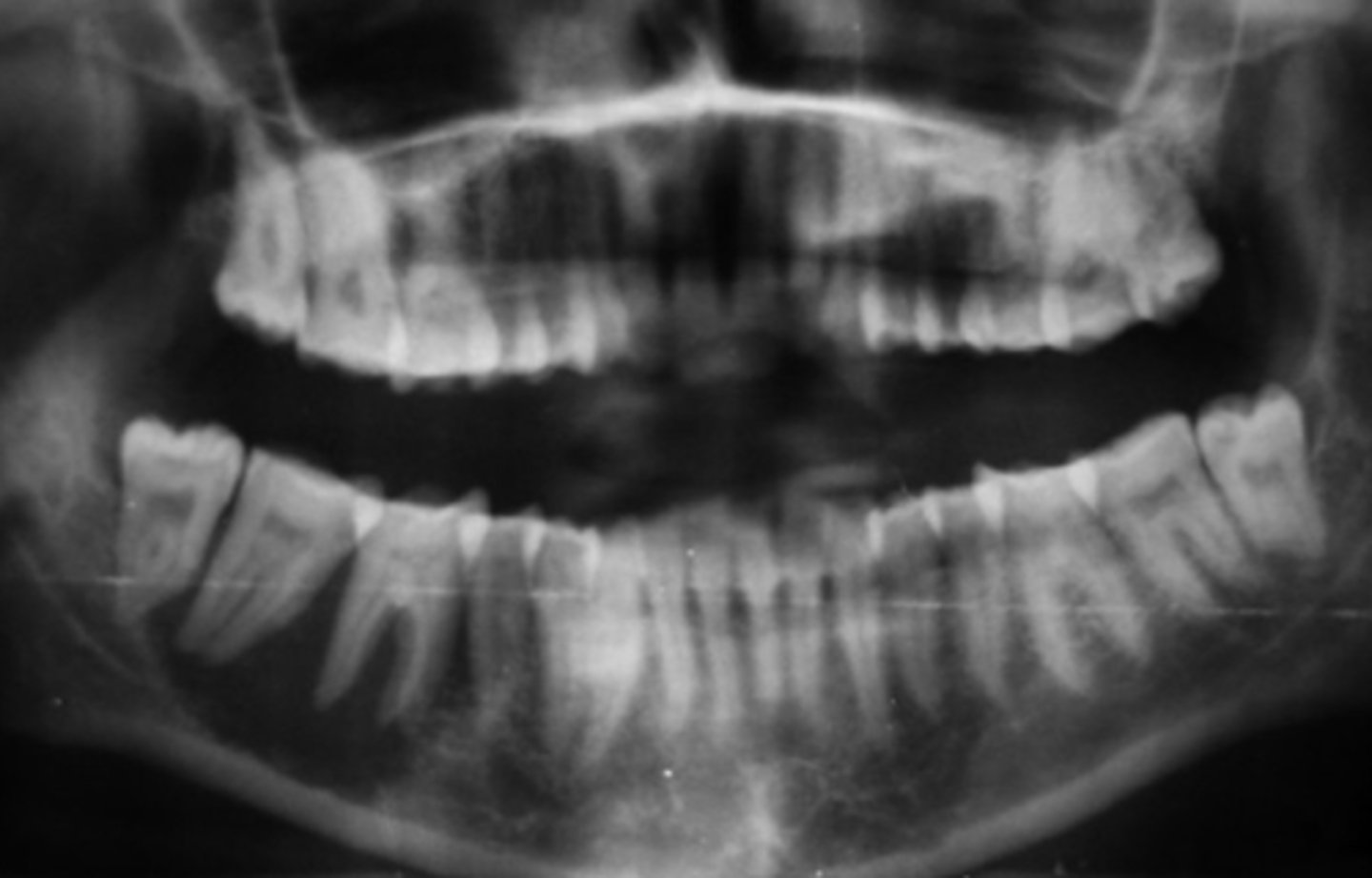
patient's radiograph shows the following:
•Garrington sign (widened PDL space)
•Ragged, ill-defined radiolucent/paque mixed area
•'sun ray' periosteal reaction
- spiked root resorption pattern
What is the diagnosis?
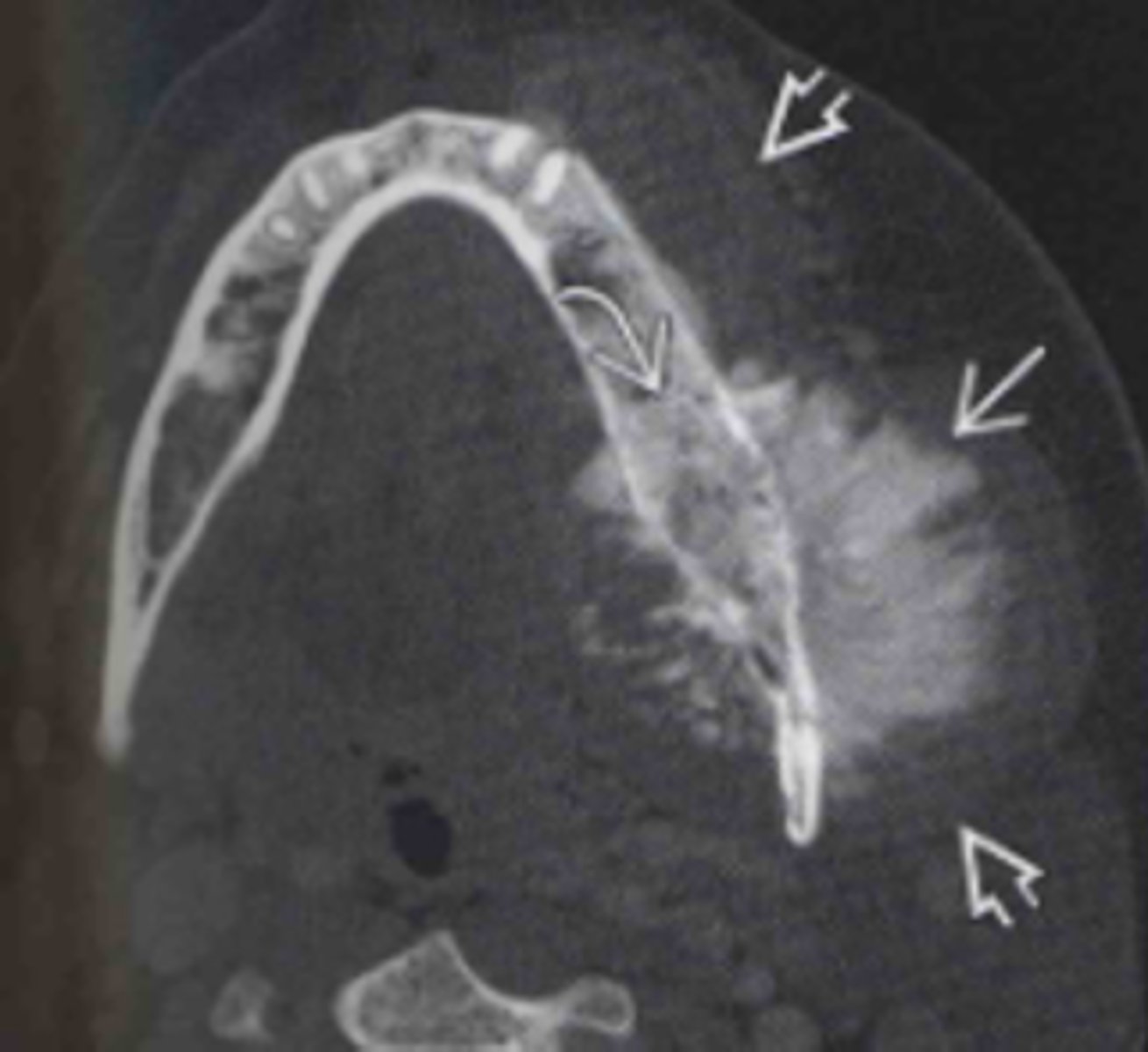
Osteosarcoma
ID the pathology:
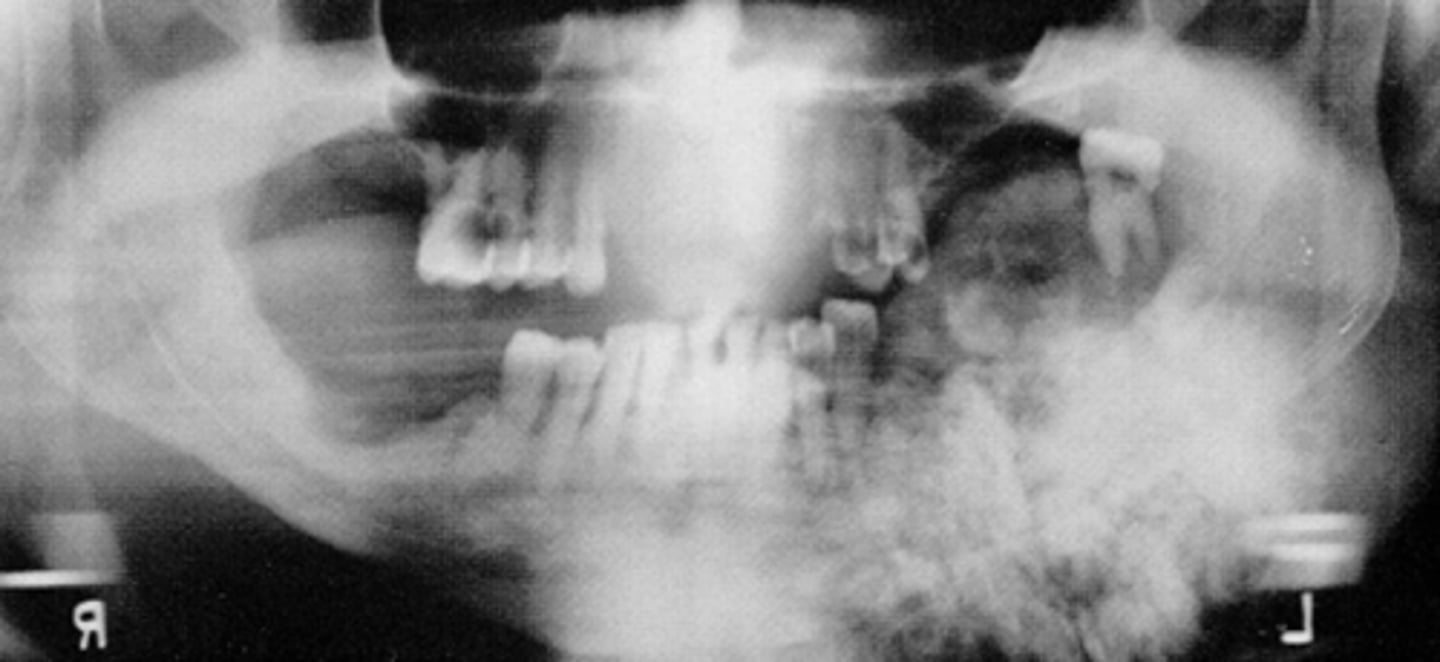
Osteosarcoma
ID the pathology:
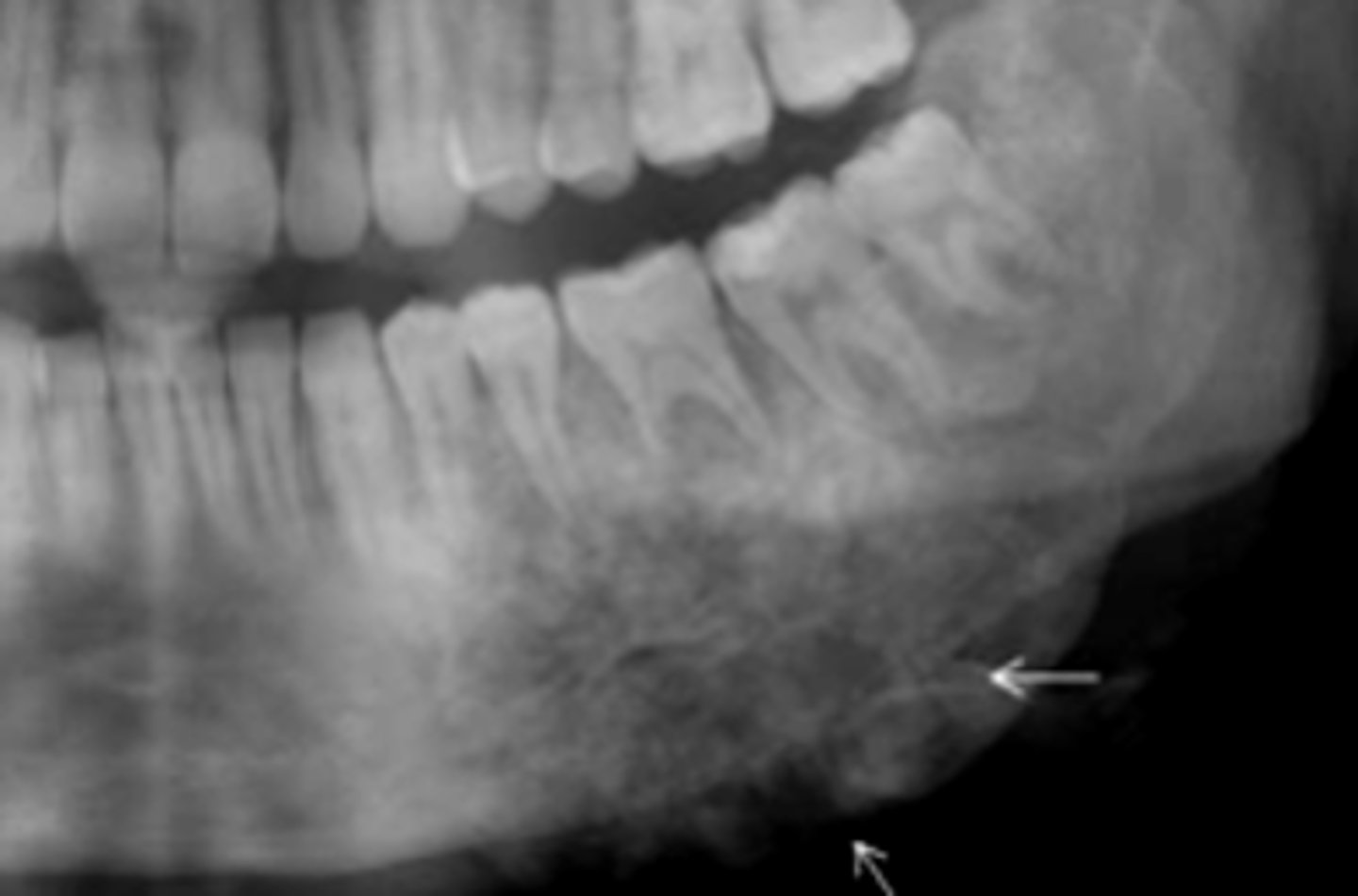
Osteosarcoma
ID the pathology:
-Lesion in left ramus, body
-Ill defined periphery
-Calcifications noted
-Expansion of ramus
-IAN destroyed
Osteosarcoma
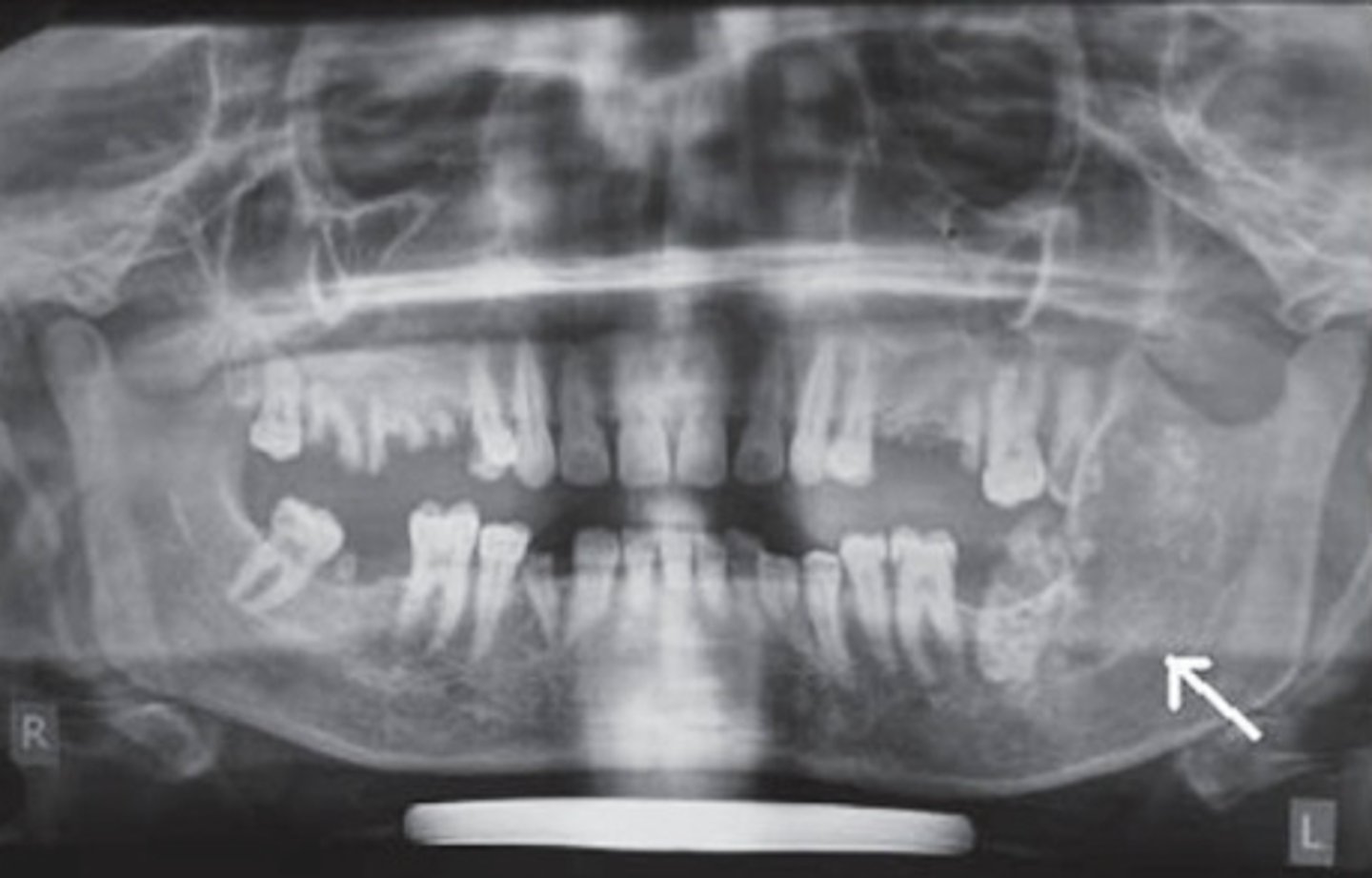
ID the pathology:
- Non-healing extraction site
- Ill-defined
- radioluceny, mixed
- resorption of roots
-distruction of lamina dura
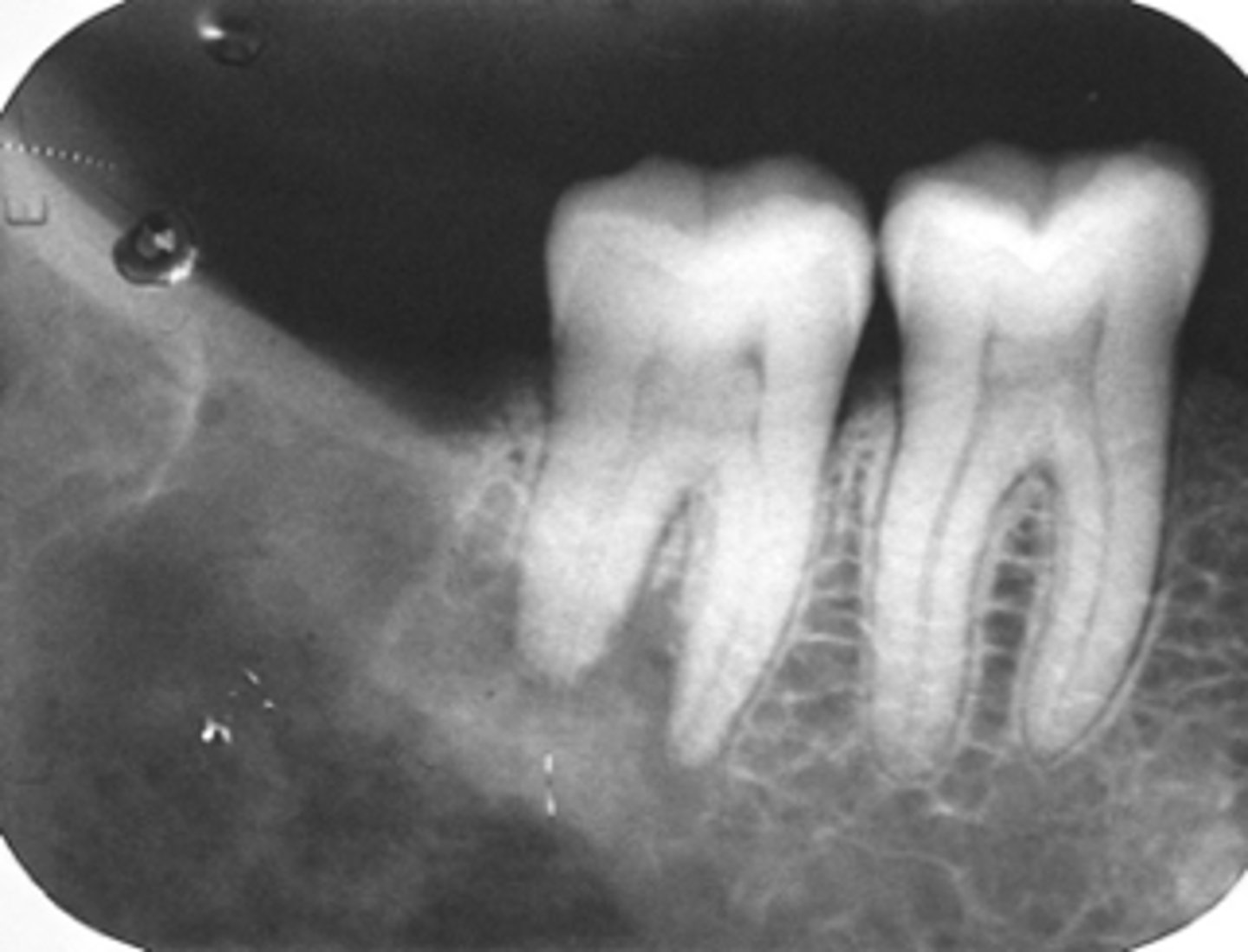
Multiple Myeloma
what is the most common malignancy in seniors/older patients?
Plasmocytoma
Singular lesion version of Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Myeloma
Metastatic lesions
These malignancy presents with multiple punched-out lesions of the scull:
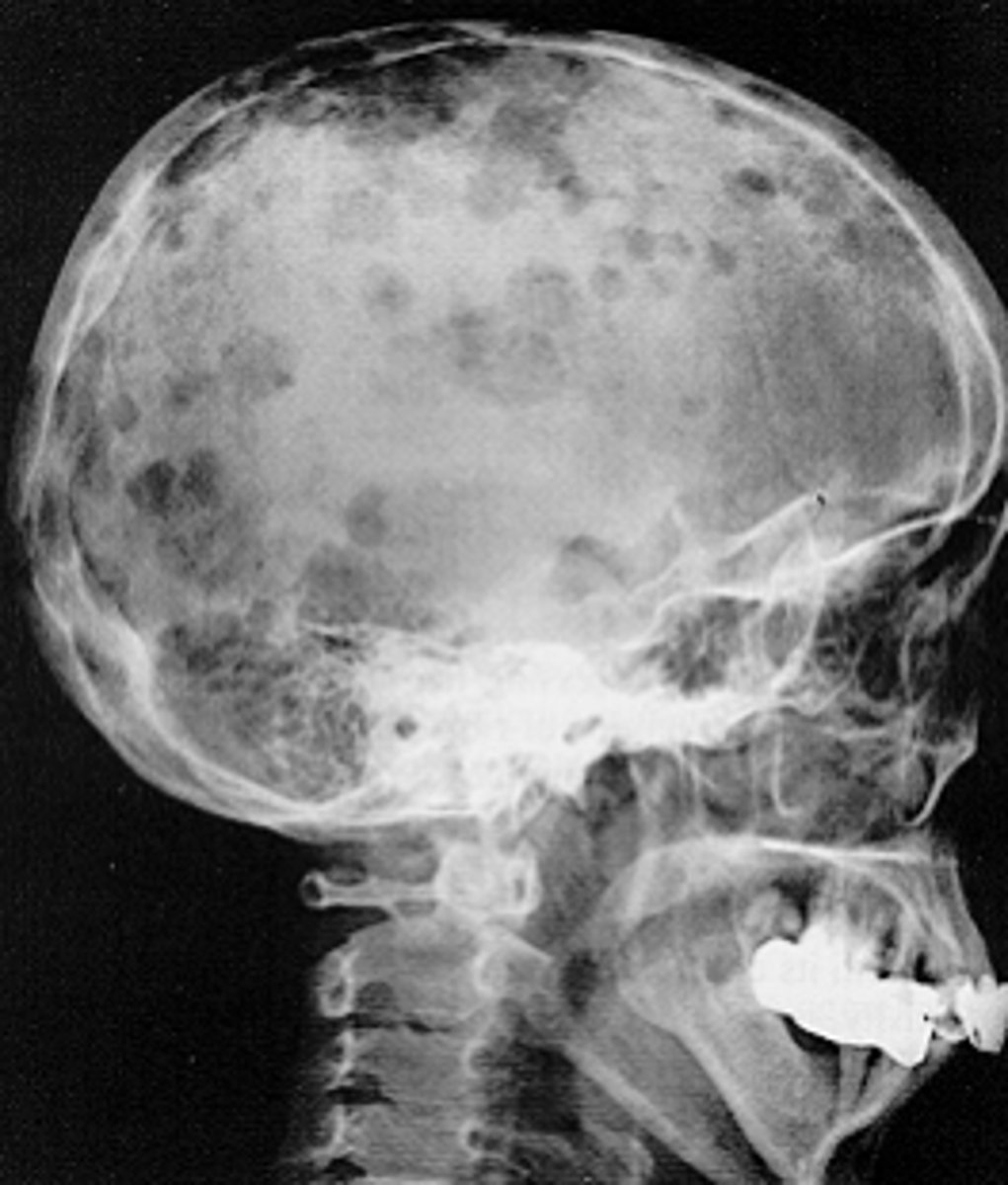
Multiple Myeloma
ID the pathology:
•Well defined , non-corticated, circular/oval radiolucent areas ('punched out' lesions)
•Lacks signs of bone reaction
Multiple Myeloma
ID the pathology: