lecture 20 - carbohydrates 2 - PoNF
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is glycolysis?
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
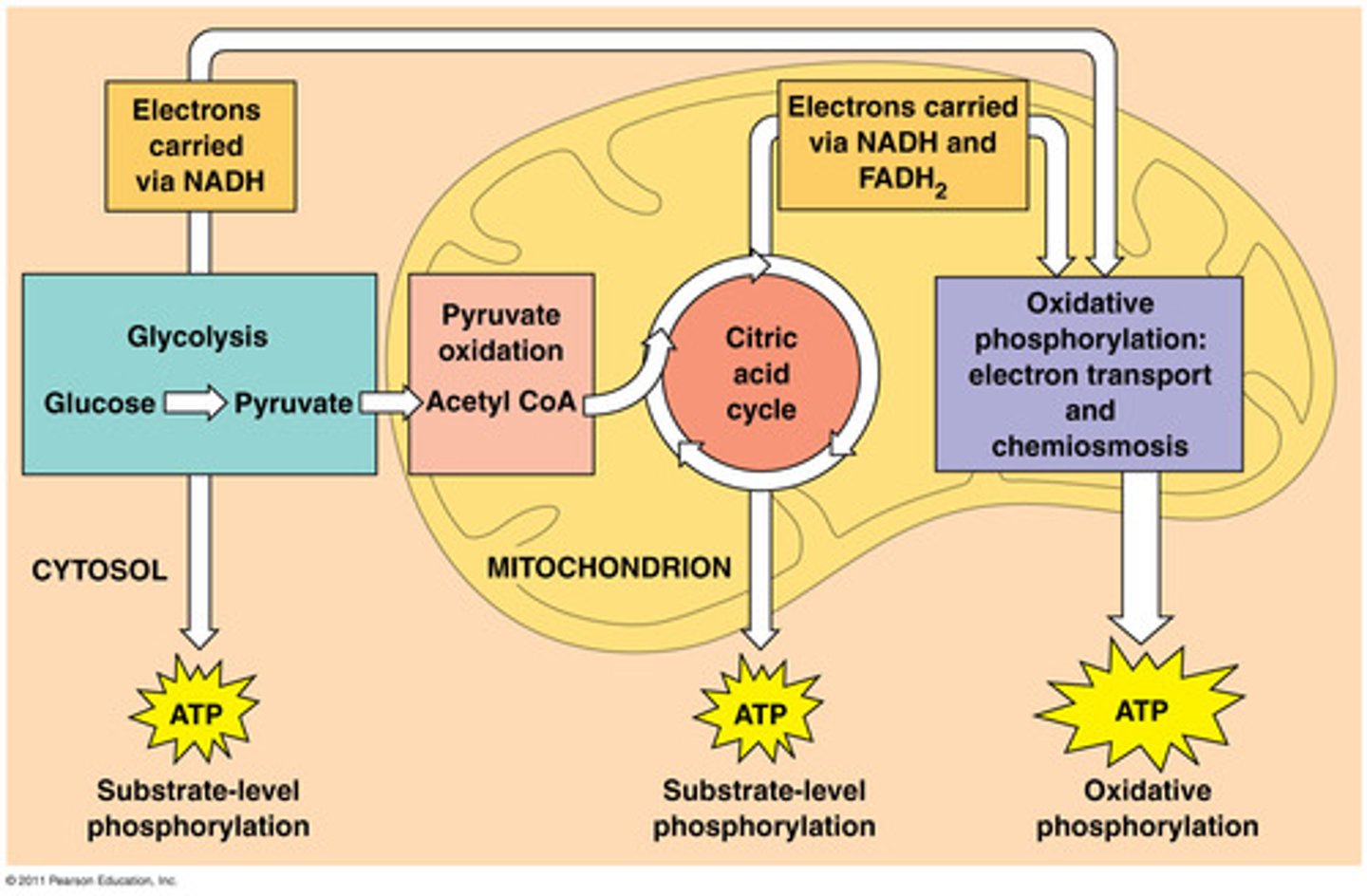
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytosol
2 phases of glycolysis
1. energy investment phase 2 ATP used
2. energy payoff phase - Net 2 ATP gain (4 gained altogether)
Step 1: Glycolysis
what is formed?
Enzyme used?
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
Glucose → G6P (phosphorylation)
hexokinase enzyme
ATP used
IRREVERISBLE
step 2 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
G6P→F6P (conversion)
phosphohexase isomerase
ATP and ADP used as it is REVERSIBLE due to free energy
step 3 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
F6P →F1,6BP (phosphorylation)
phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
none
IRREVERSIBLE - first committed step of glycolysis - cannot go back after this
step 4 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
cleavage of F1,6BP → DHAP + G3P (splitting part of glycolysis - 1 Glc into 2 triose sugars)
F1,6BP aldoase (aldoase for short)
REVERSIBLE
step 5 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
interconversion of triose sugars to form 2 G3P
triose phosphate isomerase
REVERSIBLE
what triose can only participate in glycolysis
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
step 6 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
oxidation of G3P to 1,3-biphosphate
dehydrogenase
2 NADH produced
REVERSIBLE
first energy payoff phase
step 7 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
transfer from 1,3-BiPG to ADP forms 3 PG
phosphoglycerate kinase
2 ATP produced
spontaneous
substrate level phosphorylation
REVERSIBLE
step 8 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
conversion of 3-PG to 2-PG
phosphoglycerate mutase
REVERSIBLE
step 9 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
dehydration of 2-PG to PEP
enzyme - enolase
REVERISBLE
step 10 of glycolysis
what is formed
enzyme used
ATP used?
irreversible or reversible
transfer of PEP to ADP
enzyme - pyruvate kinase
2 ATP produced
final step - produces pyruvate
IRREVERSIBLE
No NAD+ has what effect on glycolysis?
Inhibits it, NAD+ is required for glycolysis.
Fate of Pyruvate
Depends on oxygen availability.
- oxygen is present, pyruvate oxidised to acetyl-CoA, enters the citric acid cycle
- Without oxygen, pyruvate reduced in order to oxidise NADH back to NAD+ (2 lactate or 2 ethanol + CO2)
function of pyruvate dehydrogenase
converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA so it can enter citric acid cycle
Function of lactate dehydrogenase
changes lactate to pyruvate to enter citric acid cycle
Fate of blood lactate
cori cycle
- ATP made via substrate level phosphorylation producing lactate - converted to glucose in liver via gluconeogenesis
- liver repays O2 debt
What is gluconeogenesis?
production of glucose from amino acids
is glucose irreversible or reversible
irreversible
reactions A + B of gluconeogenesis
pyruvate --> oxaloacetate --> maltate --> outside mitochondria --> maltate --> PEP
substrates - pyruvate carboxylase
maltate dehydrogenase
PEP carboxykinase
reaction C of gluconeogenesis
checkpoint
irreversible
enzyme - fructose-1,6-phosphatase
F-1,6-BiP + H2O --> fructose-6-phosphate + Pi
reaction D of gluconeogenesis
3rd bypass
glucose-6-phosphatase
dephosphorylation
PEP --> pyruvate generates how many ATP
10
where is fructose metabolised
liver