Honors Bio - Final
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
How does science differ from other subjects?
It doesn’t give a 100% sure right answer, but instead uses many tests and evidence to give the best explanation to something
What is a hypothesis?
A specific and testable prediction or possible explanation for an observed phenomenon that can be proved wrong
What is data?
Raw, factual information ( EX. numbers, observations, or symbols ) collected through research, experiments, or measurements
What is a theory?
A well-supported, systematic explanation for observed phenomena made from tested facts, hypothesis, and laws.
What is the definition of biology?
The study of living organisms, divided into many fields
What is a controlled experiment?
A test where only one variable is changed, allowing researchers to see if that variable caused a specific effect
What are the three kinds of variables?
Independent
Dependent
Control
What is a control variable?
Any factor kept constant throughout an experiment to ensure a fair test
What is an independent variable?
The factor that is intentionally changed, manipulated, or controlled to observe its effect on the experiment
What is a dependent variable?
The factor, outcome, or response that is measured in an experiment
What are the characteristics of life?
All living things…
Are made of cells
Reproduce
Have a metabolism/use energy
Maintain homeostasis
Pass hereditary traits
Respond to their environment
Grow and develop
Adapt through evolution
What are the main 7 metric units?
Thousand - kilo
Hundred - hecto
Ten - deka
[UNIT]
Tenth - deci
Hundredth - centi
Thousandth - milli
What are the parts of an atom?
Protons and neutrons create the nucleus, electrons surround them
How many electrons in each electron ring?
First - 2
Second - 8
Third - 8
What is the atomic number of an atom?
The number of protons in the nucleus
What is the mass number of an atom?
The total count of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
What is an isotope?
An atom with a different number of neutrons than protons compared to other atoms of the same element
What are the characteristics of chlorine?
Green/yellow gas
Poisonous
Sharp smell
What are the characteristics of sodium chloride?
White
Strong water solubility
Edible and very common to put on food
AKA Table salt
What are chemical compounds?
Substances formed when two or more different chemical elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio (EX. Water and glucose molecules)
What are covalent bonds?
A strong chemical link where two atoms share pairs of electrons to get more stable outer electron rings
What are ionic bonds?
A strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, when one ion donates an electron to another
Is water polar or nonpolar?
Polar
What does it mean for a substance to be polar?
If it has an uneven charge distribution, making partial negative and positive ends. This is crucial for solubility.
What is a solution?
A homogeneous mixture where the solute is entirely dissolved in the solventA
What is a suspension?
A heterogeneous mixture where solid particles are dispersed in a liquid - the solute isn’t dissolved in the solvent
What is pH?
A scale measuring how acidic or basic a solution is, ranging from 1-14
What pH value does a substance need to be in order to be acidic?
1-7
What pH value does a substance need to be in order to be basic?
7-14
What is a carbohydrate?
Organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that are vital for energy and structural components
What is a lipid?
A diverse group of hydrophobic molecules, such as fats, oils, steroids, and waxes for storing energy
What is protein?
A large, complex molecule made up of amino acid chains. These chains fold into specific 3D shapes, and are vital for cell structure, function, and regulation
What are nucleic acids?
Macromolecules such as DNA that carry an organism’s genetic instructions
What is the reactant in a chemical reaction?
The substances that are used to start a chemical reaction
What is the product in a chemical reaction?
The substances that are made after a chemical reaction has occurred
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst that speed up specific chemical reactions in organisms
What is a catalyst
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction
What is it called when extreme temperature changes cause an enzyme to deform
Denatured
What is cell theory?
All living things are made up of cells
The cell is the basic unit of structure in living things
All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division
What are the pros of a compound light microscope?
Can view living things
Cheap
How does a compound light microscope work?
Uses light and glass lenses to magnify an image
What are the cons of a compound light microscope?
1000x magnification
Light refraction
What does SEM stand for?
Scanning electron microscope
What does TEM stand for?
Transmission electron microscope
What are the pros of scanning/transmission electron microscopes?
1,000,000x magnification
What are the cons of scanning/transmission electron microscopes?
Expensive
Can’t view living things
What is a prokaryote?
A single-celled organism without a membrane-bound nucleus. DNA is in its nucleoid
What is a eukaryote?
An organism whose cells contain DNA in a nucleus
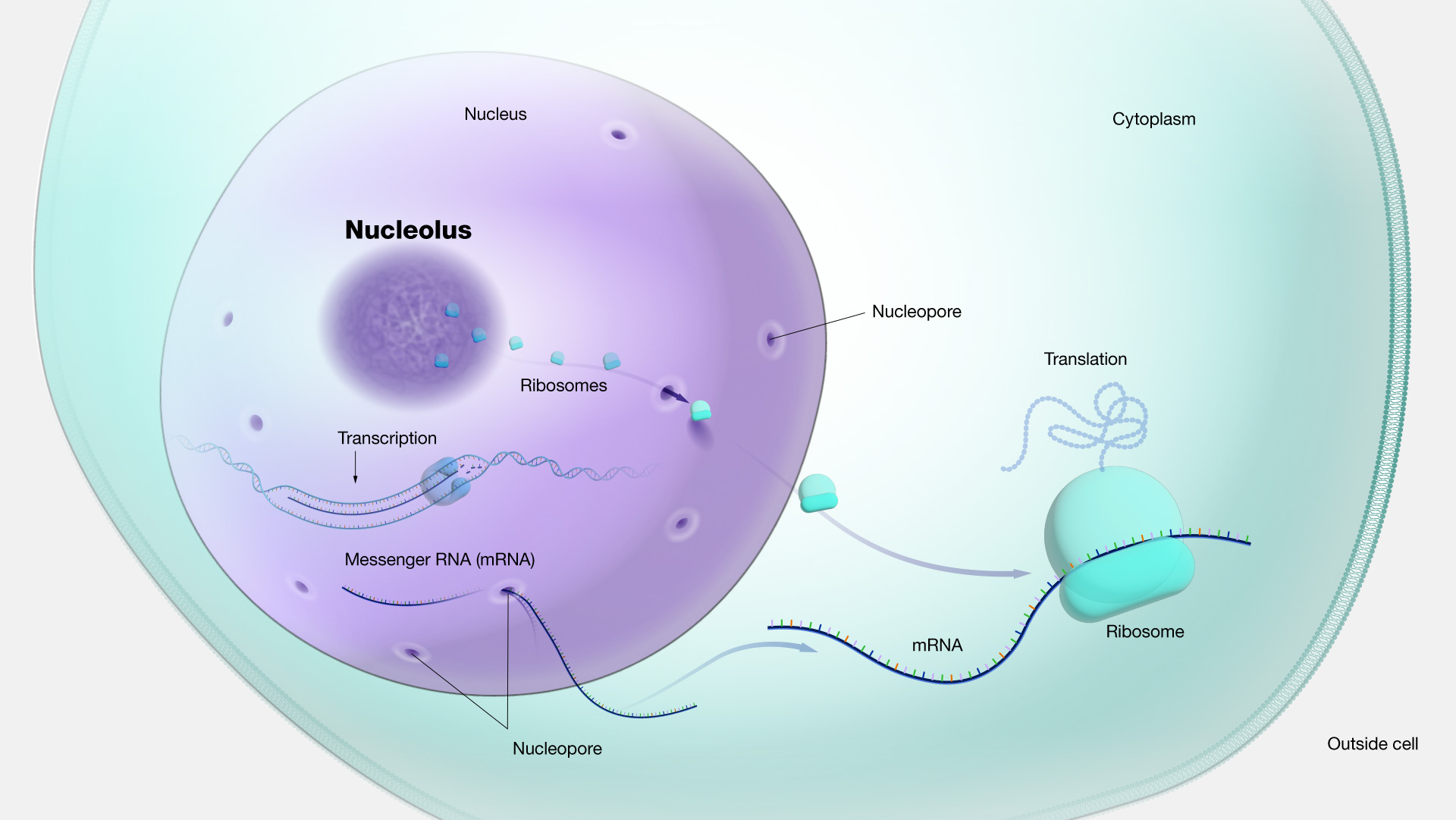
What is a nucleus?
Organelle in euk. cells that act as the control center, controlling growth, metabolism, reproduction, and protein synthesis
What are nuclear pores?
Large complexes in the nuclear envelope/membrane that are selective gateways for molecules such a as proteins, RNA, and ions form the cytoplasm
What does a nucleolus do?
Creates RNA and assembles ribosome subunits
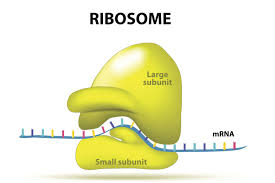
What does a ribosome do?
Synthesizes proteins into amino acid chains
What does a vacuole do?
A sac in a cell’s cytoplasm that stores water, nutrients, and waste
What is the vacuole in an animal like?
Many small with lots of nutrients
What is the vacuole in a plant like?
One large with lots of water
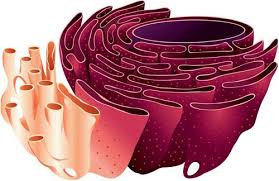
What does a rough E.R. do?
Modifies proteins
What does E.R. stand for?
Endoplasmic reticulum
What does a Golgi apparatus do?
Packages and sends proteins
What does a cell membrane do?
Regulates what enters or exits the cells through its phospholipid bilayer
What does a smooth E.R. do?
Makes lipids and detoxifies drugs
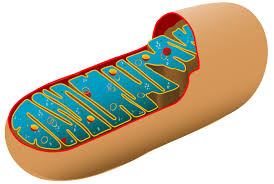
What does a mitochondria do?
Generate ATP by cellular respiration - converting nutrients into usable energy
What does a vesicle do?
Transports substances around a cell
What does a cytoplasm do?
Jelly-like substance in a cell
What does a lysosome do?
Breaks down waste materials and old cell parts using strong digestive enzymes
What does a cytoskeleton do?
Provides euk. cells with structure in the cytoplasm
What does a nucleus look like?
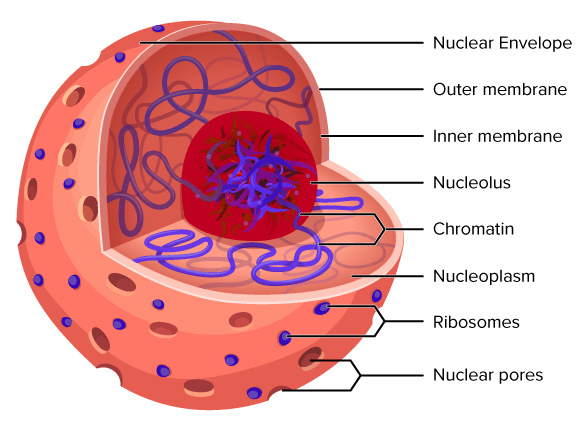
What does a nucleolus look like?
What does a ribosome look like?
What does a rough E.R. look like?
What does a Golgi apparatus look like?
What does a smooth E.R. look like?
What does a mitochondria look like?
What does a centriole look like?
How is a protein made?
Ribosome - makes proteins
Rough E.R. - modifies proteins
Golgi apparatus - packages and sends proteins
What is a cell membrane?
A semipermeable barrier surrounding every cell, mostly made of its phospholipid bilayer
What is a cell wall?
Rigid outer layer of the cell of plants, fungi, bacteria, and algae. It gives structural support and protection
What are protein pumps?
Specialized membrane proteins that use energy (ATP) to move specific molecules across the cell membrane from low to high concentration
What is diffusion?
The natural movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
What are the types of bulk transport?
Endocytosis & exocytosis
What is endocytosis?
Bringing substances like nutrients or large molecules into a cell by engulfing them with the cell membrane. This formed pocket buds off as an internal vesicle.
What is exocytosis?
Vesicles carrying substances fuse with the membrane and release contents outside the cell
What is osmosis?
The natural movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from high to low concentration
What does it mean when a solution is hypotonic?
The solution is less concentrated than the cell, and water enters the cell
What does it mean when a solution is hypertonic?
The solution is more concentrated than the cell, and water leaves the cell
What does it mean when a solution is isotonic?
The concentration of the solution is equal inside and outside of the cell
What is active transport?
Process of moving substances across a cell membrane AGAINST their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration) that REQUIRES ENERGY
What is cell specialization?
Process where unspecialized cells develop unique structures and functions for specific jobs
What are the levels of cell organization?
Cells → Tissue → Organs → Organ system → Organism
What is an autotroph?
An organism that creates its own food
What is a heterotroph?
An organism that eats other organisms for food
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
What is ATP?
The molecule that powers most cellular functions
What is ATP made of?
An adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups
How does ATP work?
It gives off energy when one of its phosphate bonds break, and gets the energy back when the broken bond is restored
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What is photosynthesis?
Process of plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create sugar for food
What is chlorophyll?
The pigment that gives plants/algae their green color and traps sunlight for photosynthesis
What color wavelengths of light can chlorophyll absorb and reflect?
Absorb: Red, blue, violets
Reflect: Green, yellow
What are the parts of a chloroplast?
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Stroma
Granums
Thylakoids
What is another name for light dependent reactions?
The ETC