Med Term Final
1/397
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
398 Terms
emesis
vomiting
pepsia
digestion
phagia
eating, swallowing
ptsis
spitting
rrhage, rrhagia
bursting forth (of blood)
rrhaphy
suture
rrhea
flow, discharge
spasm
involuntary contraction of muscles
stasis
stopping, controlling
stenosis
narrowing, tightening
contrast medium
substance that x-ray cannot penetrate
lower gastrointestinal series (barium enema)
x-ray image of the colon & rectum obtained after injection of barium into rectum
upper gastrointestinal series
x-ray images of the esophagus, stomach, & small intestine obtained after adminstering barium by mouth
cholangiography
x-ray examination of the biliary system performed after injection of contrast into the bile ducts
fecal transplant
transfer of stool from a healthy donor into the gastrointestinal tract of a recipient
C. difficile
harmful bacteria that cause diarrhea & colitis
bariatric surgery
procedures used to achieve weight loss in people with severe obesity
sleeve gastrectomy
visual examination of the gastrointestinal tract using an endoscope
laparoscopy
visual (endoscopic) examination of the abdomen with a laparoscopic inserted through small incisions in the abdomen
nasogastric intubation
insertion of a tube through the nose into the stomach
paracentesis (abdominocentesis)
puncture to remove fliud from the abdomen
BE
barium enema
EGD
esophagogastroduodenscopy
ERCP
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
G tube
gastrostomy tube → feeding tube
GERD
gastroesophageal reflux disease
GI
gastrointestinal
J-tube
jejunostomy tube → feeding tube
NG tube
nasogastric tube
NPO
nothing by mouth
PEG tube
presutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy tube → feeding tube
abdominal cavity
space below the chest containing organs such as the liver, stomach, gallbladder & intestines
also called peritoneal cavity
cranial cavity
spead in the head containing the brain & surrounding by the skull
cranial means pretaining to the skull
diaphragm
muscles separating the abdominal & thoracic caitives
moves up & down & aids in breathing
dorsal (posterior)
pertaining to the back
mediastinum
centerally located space outside of & between the lungs
pelvic cavity
space below the abdomen containing portions of the intestines, rectum, urinary bladder & reproductive organs
pelvic means pertaining to the pelvis - is composed of the hip bones surrounding the pelvic cavity
peritoneum
double-folded membrane surrounding the abdominal cavity
attaches abdominal viscera to muscles & functions as a prptective membrane around organs
pleura
double-folded membrane surrounding each lung
pleural means pertaining to ______
pleural cavity
space betnween the pleural layers
spinal cavity
space within the spinal column containing the spinal cord
thoracic cavity
space in the chest containing the heart, lungs, bronchial tubes, trachea, esophagus & other organs
ventral (anterior)
pertaining to the front
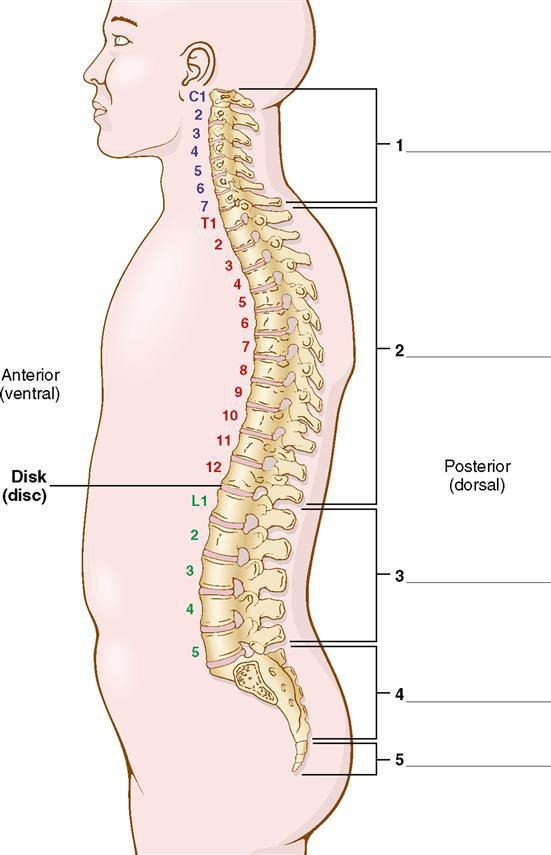
cervical - C
neck region
7 vertebrae
thoracic - T
chest region
12 vertebrae
lumbar - L
loin (waist) or flank region (between the ribs & hip bone)
5 vertebrae
sacral - S
5 bones are fused to form 1 bone
coccygeal
the coccyx (tailbone) is a small bone composed of 4 fused pieces
anterior (ventral)
front side of the body
ex - forehead
posterior (dorsal)
back side of the body
ex - back of the head
deep
away from the surface
ex - stab wound
superficial
on the surface
ex - veins
proximal
near the point of attachment to the trunk or near the beginning of a structure
ex - femur is closer to the spine than the ulnar
distal
far from the point of attachment to the trunk or far from the beginning of a structure
ex - the foot is further away from the hip bone than the femur
inferior
below another structure
superior
above another structure
medial
pertaining to the middle or nearer the medial plane of the body
lareral
pertaining to the side
supine
lying on the back
prone
lying on the belly
frontal (coronal) plane
vertical plane dividing the body or struture into anterior & posterior portions
front & back slice
sagittal (lateral) plane
lengthwise vertical plane dividing the body or structure into right & left sides
the midsagittal plane divides the body into right & left havles
line cut through the sternum
transverse (axial) plane
horizontal (cross-sectional) plane running across the body parallel to the ground
divides body into upper & lower portions
slices body like bread
anatomical position
standard reference position of the body
standing with arms at the side & palms turned forward, with head & toes pointing forward
dorsum
back or posterior surface of a part
ex - in the foot it is the top of the foot
fowler’s
supine position with head higher than the feet
approsimately 45-60 degrees
mediolateral
going from the midline of a structure to the side of a structure
midline of the body
imaginary line created when the body is divided into equal right & left halves
midsagittal plane
plane that divides the body into right & left equal portions
semi fowler’s
supine position with head higher than feet
approximately 30 degrees
sims’
recumbent position with the patient lying on the left anterior side with the left leg extended & the right knee & thigh partially flexed
trendelenburg
supine position with the head tilted downward
lateromedial
going from the side of a structure towards the midline of the structure
lithotomy
a supine position with the knee & hip flexed & thighs abducted & rotated externally, supported by ankle supports
longitudinal plane
divided the body into right & left segments
planter
pertaining to the sole or bottom of the foot
decubitus
the patient is lying down & that the dentral ray is horizontal & parrallel with the floor
oblique
rotating the entire body or body part so that the coronal plane is not parallel with the IR
recumbent
general term refering to lying down in any position
coronal plane
divides the body into anterior & posterior segments
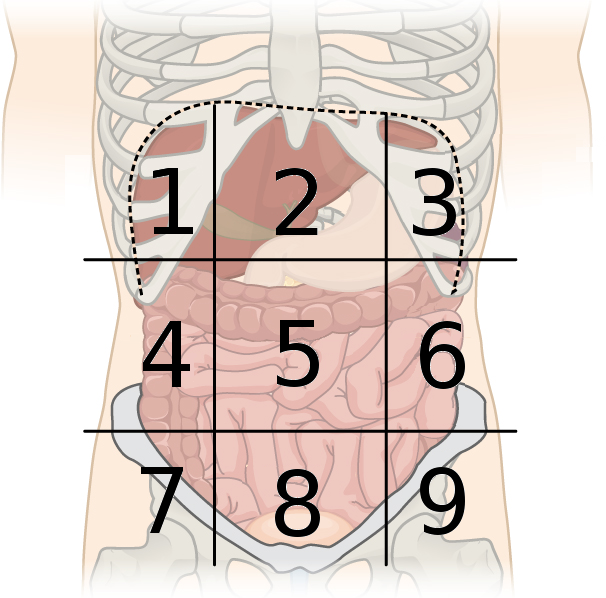
right hypochondriac region
what region is #1?
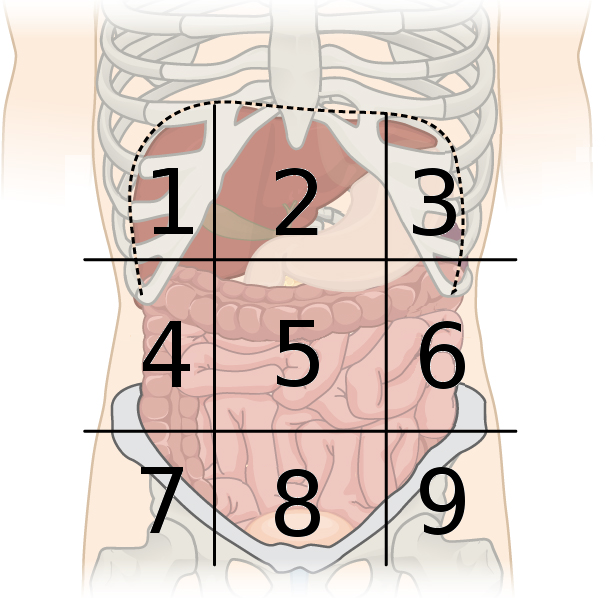
epigastric region
what region is #2?
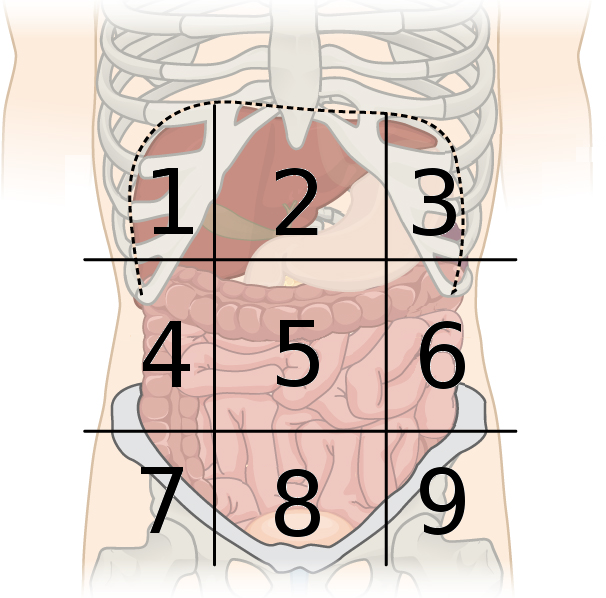
left hypochondriac region
what region is #3?
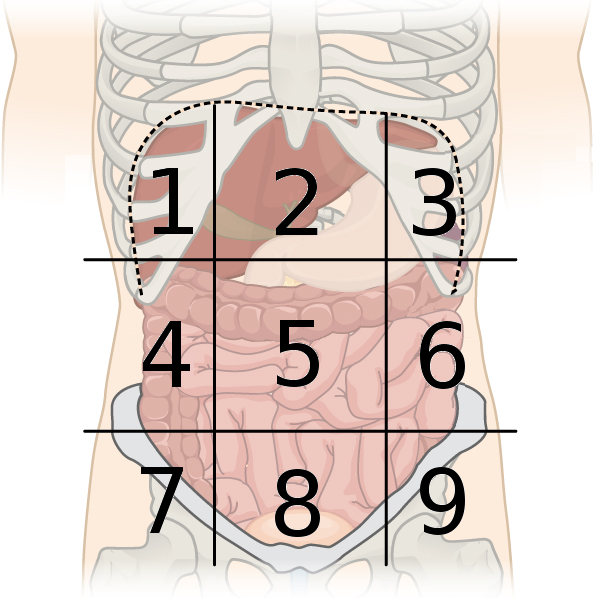
right lumbar region
what region is #4?
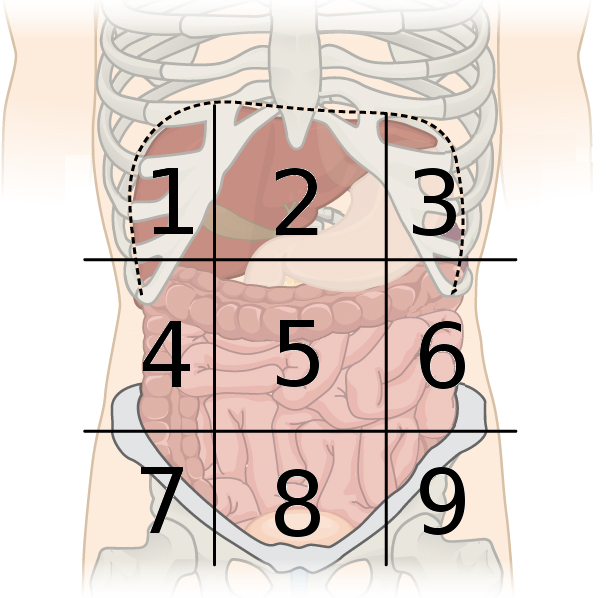
umbilical region
what region is #5?
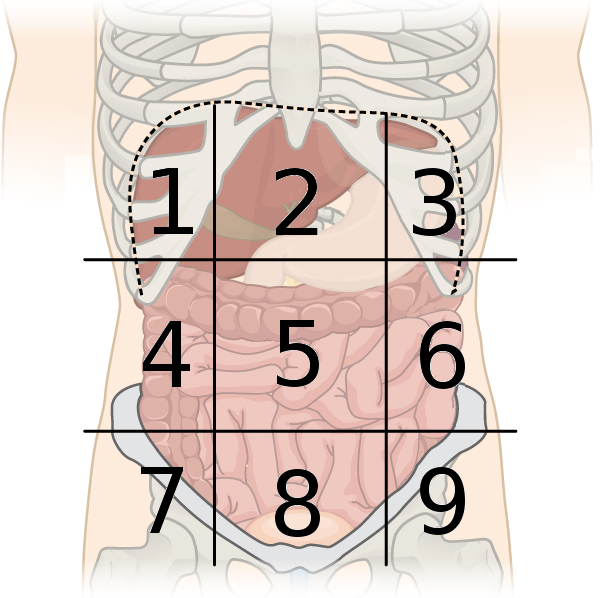
left lumbar region
what region is #6?
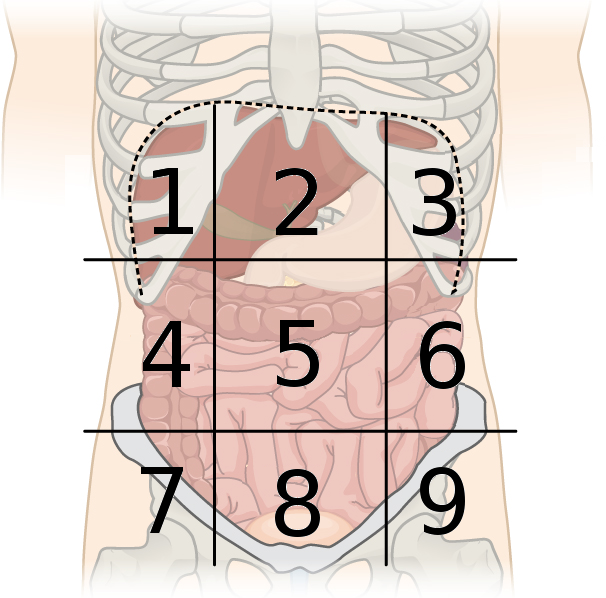
right inguinal region
what region is #7?
hypogastric region
what region is #8?
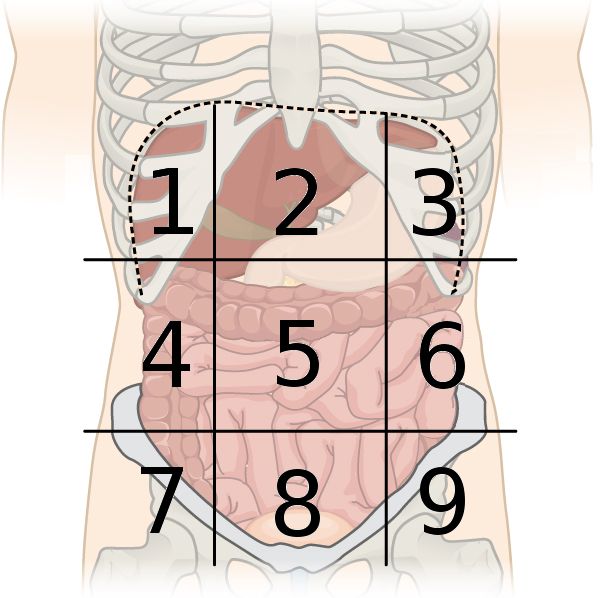
left inguinal region
what region is #9?
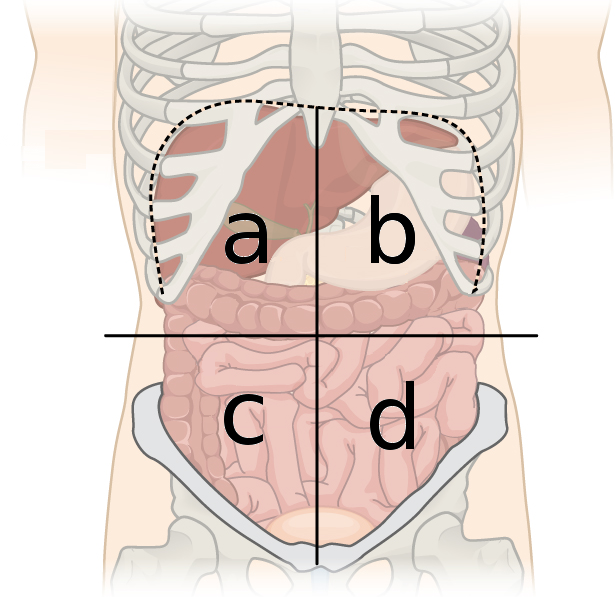
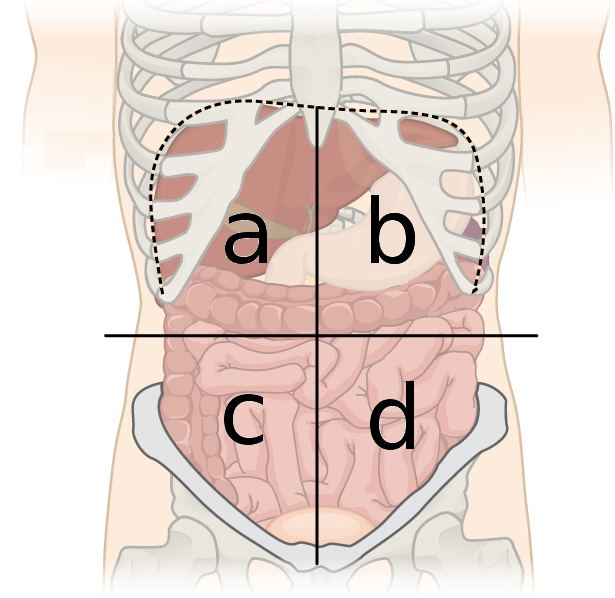
right upper quadrant
what quadrant is a?
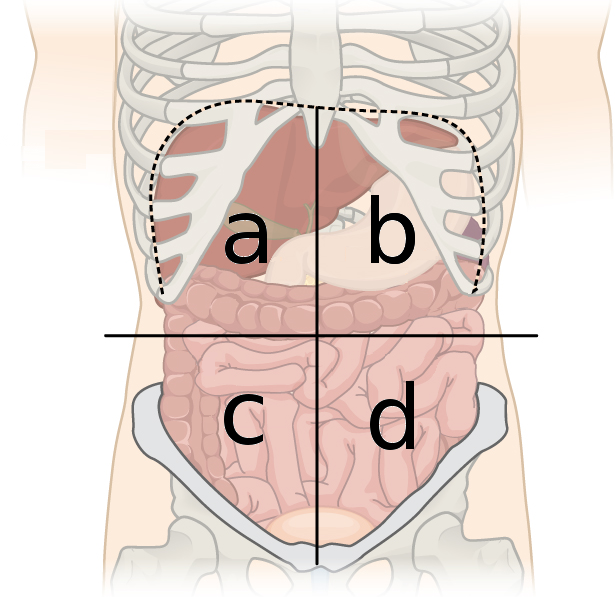
left upper quadrant
what quadrant is b?
right lower quadrant
what quadrant is c?
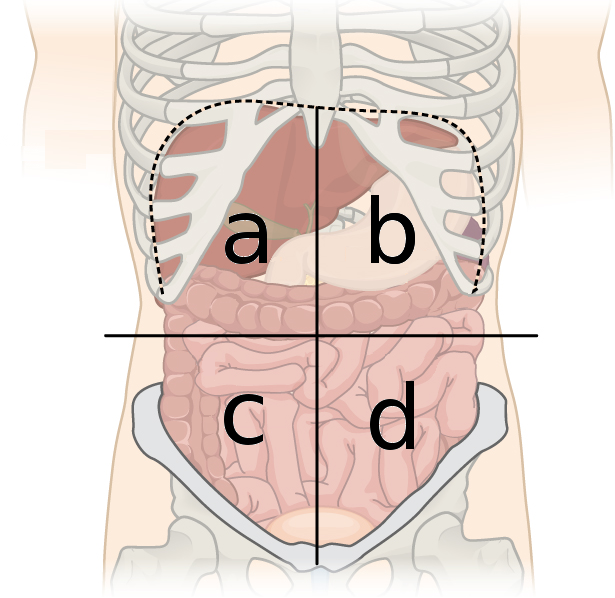
left lower quadrant
what quadrant is d?
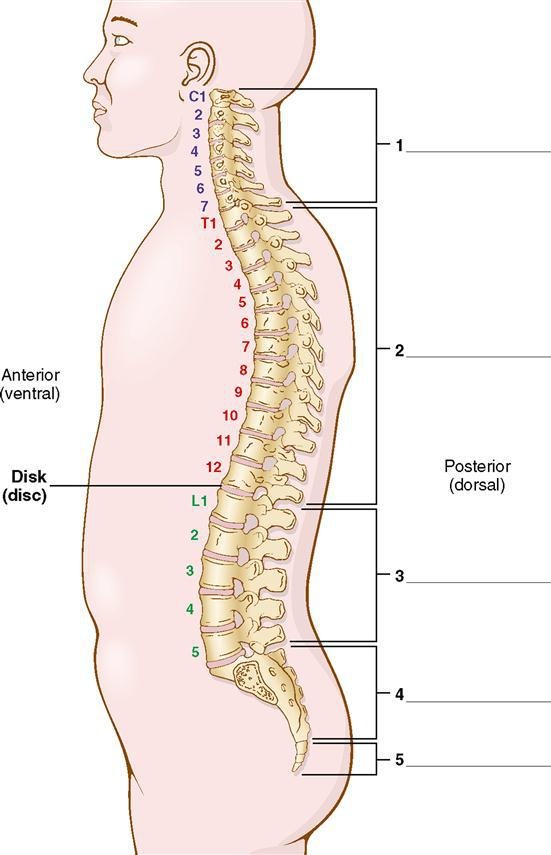
cervical
what is division #1?
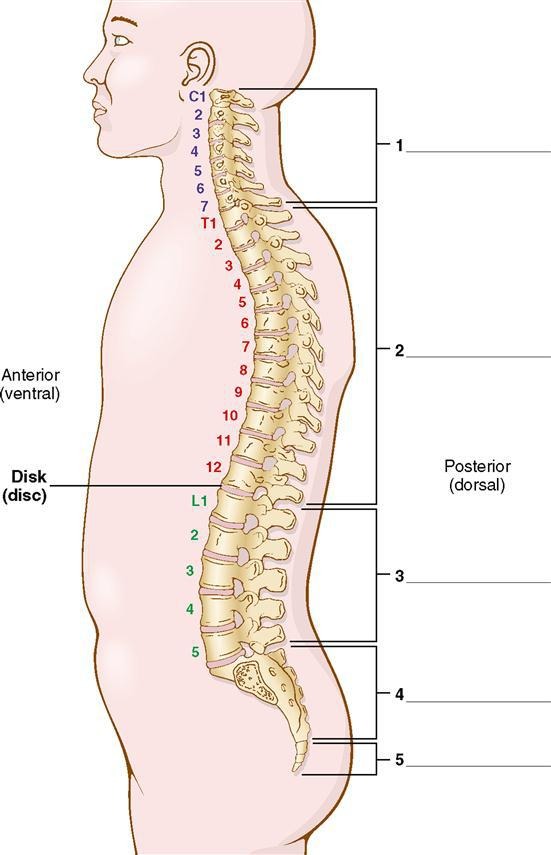
thoracic
what is division #2?
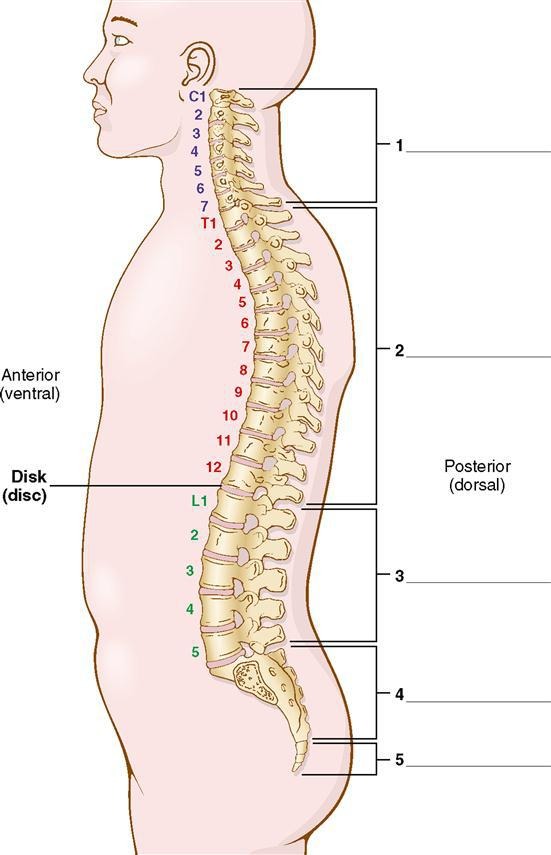
lumbar
what is division #3?
sacral
what is division #4?
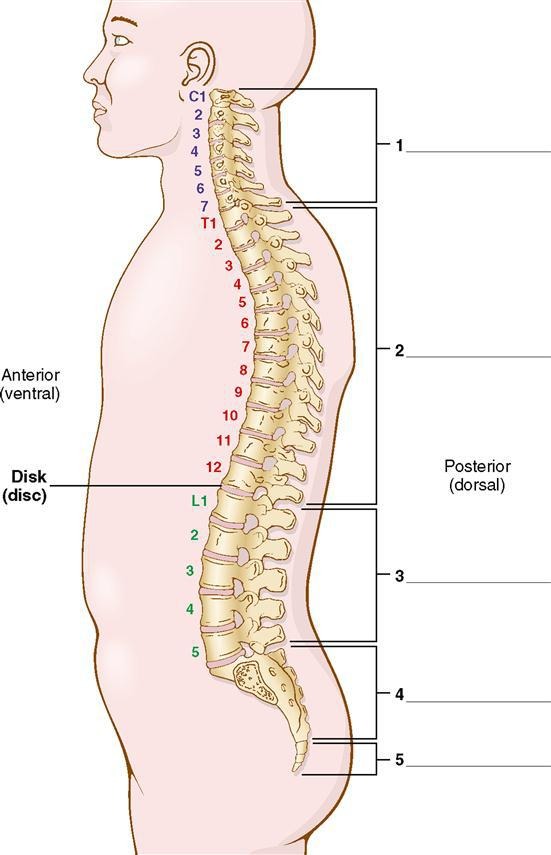
coccygeal
what is division #5?
RUQ - upper right quadrant
what quadrant contains the liver, gallbladder & part of the pancreas?
LUQ - lower upper quadrant
what quadrant contains the liver, stomach, spleen, part of the pancreas?