BIOL 1001 Final.
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Define theory?
well-tested explanation whose unifies a broad range of observations
Define hypothesis?
a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
What is the difference between hypothesis and a theory?
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data.
What is the difference between evidence and proof?
Proof is a fact that demonstrates something to be real or true. Evidence is information that might lead one to believe something to be real or true. Proof is final and conclusive. Evidence is tentative
What is the difference between acceptance and belief?
Indeed it is clear that acceptance is voluntary and belief involuntary. It is also clear that from a subjective point of view acceptance is closed under deducibility, while belief is not, and that acceptance also needs to be compared with belief in regard to a number of other logical properties
What is the difference between function and purpose?
Function is what something does. Purpose it what something is designed for or intended to do
What is the difference between pattern and mechanism?
A mechanism is a system of causation-ally interacting parts and processes that produce one or more effects while a patten is a regular and intelligible forms or sequences that can be found throughout nature
Define anecdotal evidence?
Derived from personal observation and experience
What is "intelligent design"?
the theory that life, or the universe, cannot have arisen by chance and was designed and created by some intelligent entity.
What is theistic evolution?
The belief that God works through the natural process of evolution
What is empirical evidence?
Information from direct observation or experimental results
Who were the first major figures who globally each presented their own thoughts about evolution (in BCE)
- Anaximander (Greek)
- Zhuangzi (Chinese)
- Lucretius (Roman)
- Al-Jahiz (African/Arab)
Darwin presented his theories on natural selection and evolution between which two major conflicts?
French Revolution (1789) and The U.S. Civil War (1861)
Darwin's Idea of adaptation was influenced by which scientists before him? And what was their influential theory?
- Buffon (Organismal differences were related to the environments they inhabited)
- Lamarck (Proposed that species changed through time and said changes are passed onto offspring)
Lamrack and Buffon both suggested what about evolution?
- Populations change over time
- Importance of variation in natural populations
Darwin's Idea that gradual change had occurred and continued to occur was influenced by which scientists before him? And what was their influential theory?
- Hutton (Gradualism)
- Lyell (Uniformitarianism)
True or False: Hutton and Lyell were biologists who's theories influenced Charles Darwin?
False: Hutton and Lyell were geologists. They did influence Darwin though
What is gradualism?
The geological theory that the accumulation of small changes over long periods of time add up to big changes
What is uniformitarianism?
The geological theory that current geological processes occured in the pst at the rate as today (ie. the present is the key to the past and vice-versa)
Viewing what appears to be water erosion on mars by comparing it to water erosion on earth is a thought process derived from what geological theory?
Uniformitarianism
What are the two components of a scientific theory?
1. The Pattern
2. The Process
What is the "pattern" in a scientific theory?
The component that summarizes a series of observations. Represents the facts of how things truly are in nature
What is the "process" in a scientific theory?
The mechanism that produces the "pattern" or set of observations
What is a scientific revolution?
The overturning of an existing idea about how nature works and replaces it with another, radically different idea
What is typological thinking?
Species are unchanging and heavily segregated. Variations within species are unimportant or even misleading
Is Lamarckian Evolution progressive, regressive, or stagnant?
Progressive
Lamarck believed that species would always produce what?
Better and more complex versions of themselves over time
How did Lamarck describe evolution?
Individual's phenotypes (physical traits) would change in response to challenges posed by the environment. These changes were then passed on to offspring.
What is population thinking?
variation among individuals in a population was the key to understanding the nature of species
The opposite of population thinking is what?
Typological Thinking
As Darwin described what is "descent with modification"?
Species that lived in the past are the ancestors of the species that exist in present day
What is the "fossil record"?
A record of all the fossils that have been found on earth and described in scientific literature
What are extant species?
species that still exist today
What are sedimentary rocks?
Rocks formed by lithification (compact under pressure). Normally formed in layers. Pressure and temperature are responsible for formation.
Who discovered that the extensive time required for the formation of sedimentary rocks?
James Hutton
What is a geological time scale?
A sequence of named intervals known as; eons, eras, and periods. These intervals are represented by the major events that occurred in earths history
What is radiometric dating?
The process of determining the age of the fossils from radioactive isotopes
What 3 pieces of info are required for Radiometric Dating?
1. Observable decay rates of parent-daughter atoms
2. The ratio of parent-to-daughter atoms present in NEWLY FORMED ROCKS
3. The ratio of parent-to-daughter atoms present in a PARTICULAR ROCK SAMPLE
What is the difference between "Parent" atoms and "daughter" atoms?
Parent Atoms are unstable
Daughter Atoms are the stabilized atoms formed from the parent atoms
Who published the first analysis, detailing the intricacies that make up an "Extinct Species"
Baron Georges Curvier
According to recent analysis of the fossil record, what percentage of species that have ever lived are now extinct?
99%
What is the law of succession?
Fossils found in a certain geographic region frequently resemble the species currently living in that region. Meaning that the current species would have evolved from the fossilized species.
What is a transitional feature?
A trait(s) that is an intermediate stage of evolution between fossilized species and their most recent descendants
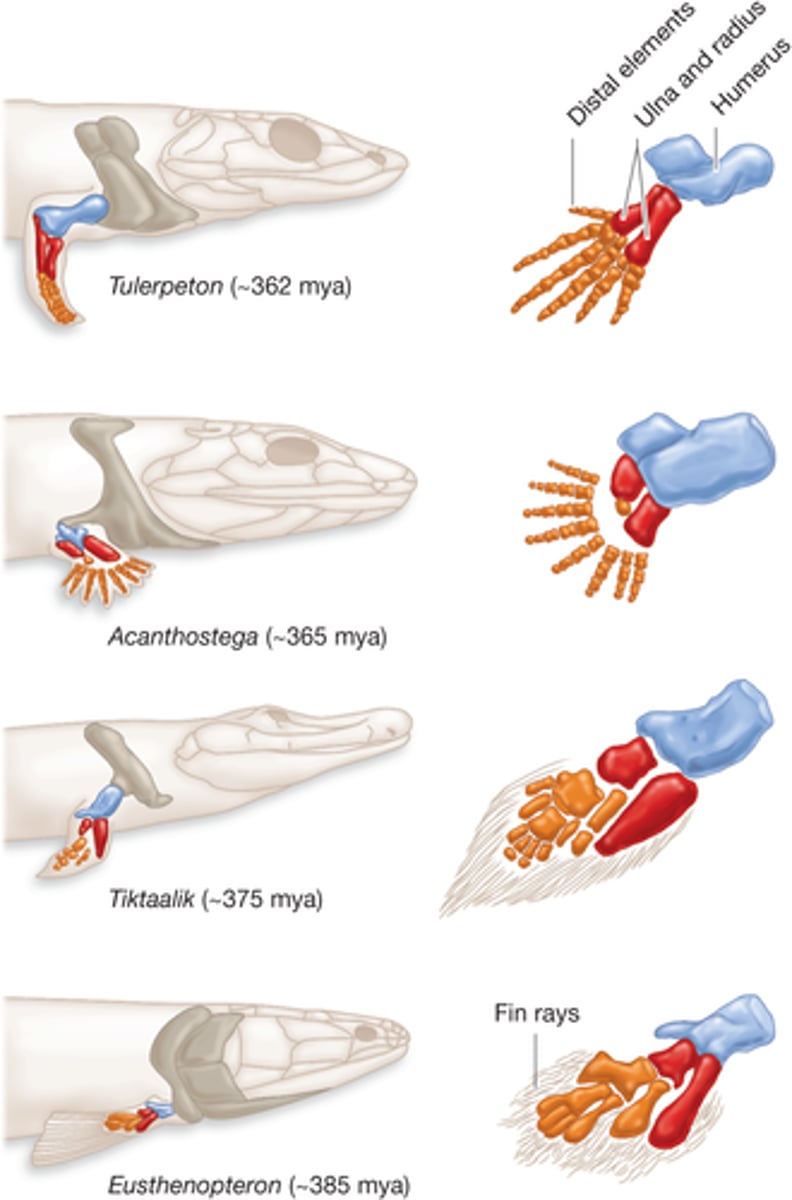
What is a vestigial trait?
A reduced or incompletely developed structure that has little to no function but is clearly similar to functioning organs or structures in closely related species
Vestigal Traits provide an inconsistency with which theory? and Why?
It is inconsistent with the theory of special creation because species are supposedly "perfectly designed" but these vestigal traits not only provide an imperfection but are clear evidence of development from other species
What are some examples of vestigial traits in humans?
- Tailbone
- Goose Bumps
What is homology?
A similarity that exists in species due to shared ancestry
What is an example of a homologous trait?
Human Hair and Dog Hair
What are the three types of of homology that can be studied?
- Genetic
- Developmental
- Structural
Can hypothesis about homology be tested?
Not always, but yes there are some cases where they can be tested
Homology is a key concept in ____________ biology?
Contemporary
What is contemporary biology?
Study of major theories and principles of biology pertaining to cell and molecular biology, form and function of tissue and organ systems, and principles of ecology as they relate to animal and plant diversity and evolution
How does homology contradict the claims of special creation?
If species were created independently of one another as the theory of special creation dictates then these homologies would not occur as they are indicative of natural selection having occurred
What is speciation?
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
Speciation is strong evidence in support of what claim?
The claim that all organism are related by descent from a common ancestor
What is the most powerful evidence for any scientific theory?
Internal Consistency
What is an internal consistency?
The observation that data from independent sources agree in support in supporting predictions made by a theory
Darwin used what type of selection when he worked with pigeons?
Artificial Selection
How did Thomas Robert Malthus influence Darwin?
In his studies on human populations Malthus mentioned the idea that because more individuals are born than those that can survive there is a "Struggle For Existence". This idea was taken by Darwin and combined with his observation of his artificially selected pigeons
What are the 4 postulates of natural selection?
1. Variation in the population
2. Some forms of trait variation are heritable
3. Survival and reproduction are variable
4. Certain traits that increase fitness within the environment are why individuals survive, it is NOT randomized
What is the two part sentence that modern biologists use to condense Darwin's postulates?
Evolution by natural selection occurs when (1) heritable variation leads to (2) differential reproductive success
In M.turberculosis what gene mutates to create drug resistance?
rpoB
What type of mutation causes drug resistance in M.tuberculosis?
Point mutation in the gene rpoB
What is a natural experiment?
An experiment where the change in the independent var. is not brought about by the researcher but would have happened even if the researcher had not been there. The researcher records the effect on the dependent var.
In Grant's experiment on finches, why did majority of the survivors after the drought have deeper beaks?
Due to absent of seed sources (because of the drought) the primary source of food for the finches was a thick walled fruit that isn't within the usually diet of finches. The finches with the deeper and larger beaks had the strength and leverage to break open these fruits and get the to the seeds
In 1983 the environment surrounding the studied finches changed again. What was that change?
A 7-month long rainy season
During the excessive rainfall in 1983, which type of finch had the greater fitness and why?
Due to the rainfall small, soft seeds were being produced in the highest abundance. Individuals with shallow and small beaks had the greatest success harvesting this abundance of seeds and as such had the greatest fitness
Observing the finches in the Galapagos Islands it can be said that with every major environment change there was a subsequent change in what?
The characteristics of the representative population of finches on the islands
A major takeaway observed from the finches was that most traits are not inherently (1)__________ or (2)__________. A trait's (3)______________ value depends on the context of the environment and context can always (4)______________
1. Good
2. Bad
3. Adaptive
4. Change
What gene was a major determinant of the width and depth of adult finches?
Bmp4
A lower Bmp4 expression in a finch's embryo results in what?
Shallow Adult Beak
A higher Bmp4 expression in a finch's embryo results in what?
Deep Adult Beak
True or False: After further experimental testing with Bmp4, researchers discovered Bmp4 to be the strongest correlational gene determining beak depth?
False: Researchers did perform further experiments but discovered a CAUSATION relationship between beak depth and Bmp4 concentration
What is the gene recently discovered to be important in the regulation of beak shape in finches?
ALX1
What is acclimatization?
Changes in an individuals phenotypes (observable traits) in response to changes in environmental conditions
Do phenotypes formed via acclimitization get passed on to offspring?
No, acclimitization does not influence alleles and as a result does not play a role in evolution
Can the instinct for survival ever result in an individual's development of selectively beneficial traits?
No, which individuals have which selective traits is completely random.
Hierarchies was a major difference between Darwin and Lamarck. Explain their differing opinions?
Lamarck believed that with each evolutionary advancement, a species got better and, as such, became a "higher" organism, those who had not evolved as much were seen as "lower" organisms. Darwin, however, disagreed with this idea and felt as though each evolved species was independent of those before it. No species was higher or lower than another simple species that survived that environment at that point
What is genetic correlation?
selection of alleles on one trait causes an increase in another trait
What is an example of genetic correlation in finches?
While Bmp4 has a causal relationship to beak depth, researchers also observed than an increase in Bmp4 additionally resulted in a wider beak
What is a fitness trade-off?
A compromise between traits that are unable to be optimized simultaneously
What is an example of a fitness trade-off with finches?
Finches of a larger body size had greater fitness due to their ability to better fend off smaller finches when fighting for food. However, these larger finches needed more food to feed their larger bodies. So while they had a better advantage of getting food over others, they required more and often died from starvation whenever the environment garnered a lower amount of food.
One of the limitations of natural selection is that all traits have evolved from (1)__________ (2)____________ traits
1. Previously
2. Existing
What are the 4 major limitation of natural selection (mentioned in the textbook)
1. Traits are not always adaptive (ie. vestigal traits)
2. Genetic Constraints
3. Fitness Trade-offs
4. Trait development is environmentally constrained
Define Evolution?
A change in allele frequencies (i.e., heritable traits) within a population over time
What are the 4 processes that govern evolution?
1. Natural Selection
2. Genetic Drift
3. Gene Flow
4. Mutation
True or False: Evolution can only occur when all 4 of its governing processes act on a population?
False: These processes may work in tandem but do not require the joint effort of all 4.
Which of the governing processes of evolution is able to act alone and still result in adaptation?
Natural Selection
What was/is the modern synthesis?
The Modern Synthesis is an era within the first few decades of the 1900s where biologists began to apply the findings of Mendel to Darwin's theory of evolution
True or False: G.H. Hardy and Wilhelm Wienberg were two biologists responsible for the creation of the Hardy-Weinberg Principle?
False: G.H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg were not biologists.
Hardy was a Mathematician and Weinberg was a doctor. They did however create the hardy-weinberg principle
What motivated Hardy and Weinberg to create their principle?
They curious as to what would happen when ALL the individuals within a populations (all possible genotypes) bred
Define genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
Who coined the term and idea of the "gene pool"?
Hardy and Weinberg
What is a gene pool?
all the genes in a population, brought into a single group
Given the following example, how would you check for a change in allele frequency using the Hardy-Weinberg-Principle?
Ex. Two alleles are present in a population, A1 and A2. In this gene pool, 70% of the population carries A1 and 30% carries A2.
Step 1: Set up equation (A1 = p) (A2 = q) -
(p + q = 1) then becomes (0.7 + 0.3) = 1
Step 2: Determine all possible genotypes and assign their subsequent variables-
Possible genotypes (A1A1 / A1A2 / A2A2)
A1A1 = p^2
A1A2 = 2pq
A2A2 = q^2
Step 3: Solve for the new allele frequency using new values-
Eq: p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
New Eq: 0.49 + 0.42 + 0.09 = 1
- Isolate A1:
p^2 + 1/2(2pq) = ?
0.49 + 1/2(0.42) = 0.7
- Isolate A2
q^2 + 1/2(2pq) = ?
0.09 + 1/2(0.42) = 0.3
Therefore: the allele frequencies of A1 and A2 did not change after random mating
What are the two fundamental claims of the Hardy-Weinberg Principle?
1. The alleles A1 and A2 and there frequency of genotypes are given by the equation (p^2 + 2pq + q^2=?)
2. When alleles are transmitted via meiosis and random combinations of gametes, their frequencies DO NOT change over time
True or false? The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that random mating is able to cause evolution?
False: the principle states the opposite, random mating alone is incapable of governing evolution, another factor must be involved.
True or False: nonrandom mating can cause genotype frequencies to change but not allele frequencies?
True
What type of hypothesis does the Hardy-Weinberg Principle serve as?
Null Hypothesis
What is a null hypothesis?
a null hypothesis states that two variables are not related.