Lab 3 - Freezing Point Depression
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
The Four Colligative Properties (fill in the blanks)
Osmotic _____
Lowering of _____________
Depression of _____________
Elevation of _______________
Osmotic pressure
Lowering of vapor pressure
Depression of freezing point
Elevation of boiling point
Molarity (M) is moles of solute divided by the number of _______ of the solution
Liters
Molality (m) is moles of solute divided by the _____ of solvent in ___
Mass in kg
1kg = ________ g
1000
What advantage does Molarity have over Molality?
Molarity is great for measuring exact volumes
What advantage does Molality have over Molarity?
Molality is temperature independent (i.e. concentration does not change with temp.)
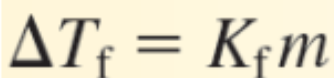
ΔTf is the difference between the initial freezing point of the solvent and the _____________
Final freezing point
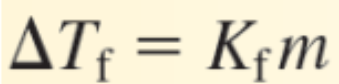
Kf is the ______________ for the solvent (°C/m)
Freezing point depression constant
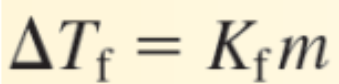
m is the concentration (mol solute/kg of solvent) of the solution in _________
Molality
Non-electrolytes do not _______ into “pieces” of the formula units.
Dissociate
Ex: Sugar will dissolve in water but won’t come apart into many pieces.
Sugar (a non-electrolyte) molecules will dissolve in water but will not come apart into many pieces in water. Therefore, one mole of sugar molecules in a solution will yield one mole of __________________.
dissolved sugar molecules
Van’t Hoff Factor (i) is the actual number of particles in solution after dissociation divided by the number of __________ initially dissolved in solution
Formula units
Using the van’t Hoff factor in the calculation accounts for the ____________ that go into solution when ionic compounds dissociate into their constituent cations and anions
multiple moles of ions
Adding a solute to a solvent will
Decrease the solvent’s __________
Increase the solvent’s ___________
Freezing point
Boiling point
The degree of freezing point depression is related to the identify of the __________, the molar mass of the _______, and the mass of the ________. This relationship is expressed as: 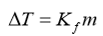
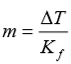
Identify of the solvent
Molar mass of the solute
Mass of the solution
What effect does adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent have on the solvent's freezing point?
a. No change
b. The freezing point increases
c. The freezing point decreases
d. The freezing point remains the same, but the boiling point decreases
The freezing point decreases
Why does the calculated molar mass of an ionic compound tend to be lower than its actual molar mass when using the freezing point depression method?
a. Ionic compounds dissociate into multiple particles in solution.
b. Ionic compounds increase the viscosity of the solution.
c. Ionic compounds do not dissolve in water.
d. Ionic compounds elevate the boiling point too much.
Ionic compounds dissociate into multiple particles in solution.
If 1 mol of a non-electrolyte solute is dissolved in 1 kg of water, causing the freezing point to decrease by 1.86°C, what is the freezing point depression constant (Kf) for water?
a. 1.86°C/m
b. 3.72°C/m
c. 0.5°C/m
d. 2.00°C/m
1.86°C/m
In the experiment, why is it important to stir the ice-water mixture in the polystyrene reaction vessel?
a. To increase the temperature of the mixture
b. To ensure uniform distribution of temperature
c. To prevent the solute from dissolving
d. To decrease the freezing point of water
To ensure uniform distribution of temperature
Which of the following would most likely result in the greatest decrease in freezing point?
a. Dissolving 1 mole of NaCl in 1 kg of water
b. Dissolving 1 mole of sucrose (C12H22O11) in 1 kg of water
c. Dissolving 1 mole of glucose (C6H12O6) in 1 kg of water
d. Dissolving 1 mole of CaCl2 in 1 kg of water (because it dissociates into three ions, Ca2+ and 2 Cl-)
Dissolving 1 mole of CaCl2 in 1 kg of water (because it dissociates into three ions, Ca2+ and 2 Cl-)