The Endocrine System (Reproductive Hormones)
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reproductive Hormones
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What are the female reproductive organs & what hormones do they secrete
Ovaries are reproductive organs in females that produce ova (eggs)
Ovaries secrete the hormones oestrogen and progesterone that control ovulation and menstruation
Purpose of estrogen and progestrone (in-depth explanation not necessary for test)
Estrogen:
Development of female sexual characteristics (breast growth, widening of hips, development of reproductive organs)
Regulates menstrual cycle (thickening of uterine lining for pregnancy)
Stimulates ovulation
Maintains cardiovascular health, skin health, sex drive, bone health.
Progesterone:
Regulates the menstrual cycle, preparing uterus for implantation of a fertilised egg (thickens lining)
Maintains pregnancy, prevents uterine contractions, supports fetal development
Maintains bone density
Regulates thyroid stimulating hormone activity & sex drive.
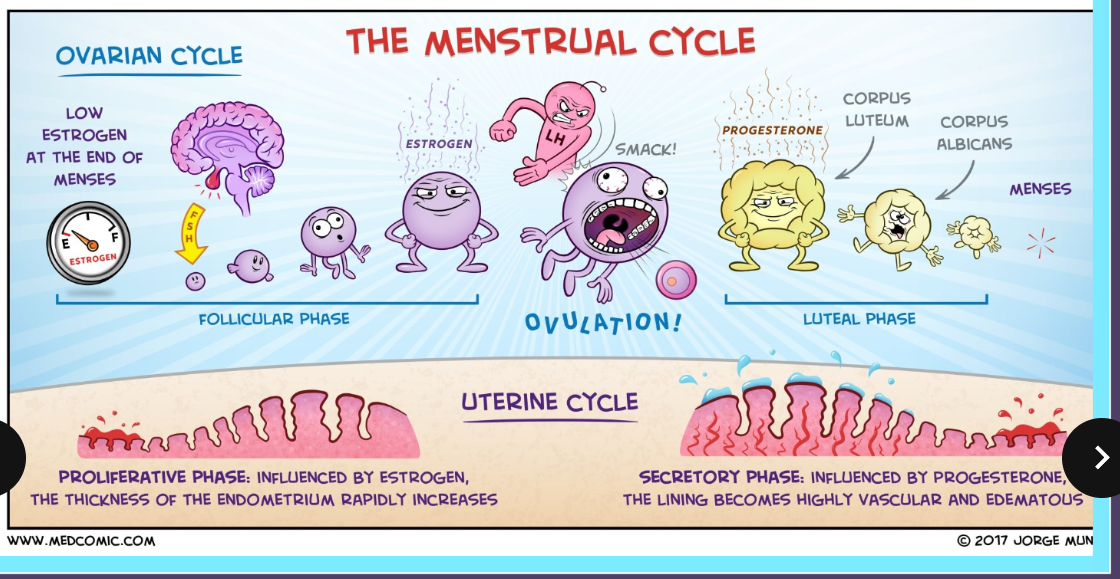
What are the four phases of the menstrual cycle?
Menstruation (Estrogen drops + Uterine lining shed)
Follicular Phase (Releasing estrogen + thick uterine lining))
Ovulation (Lots of estrogen = egg release)
Luteal phase (Progestrone + estrogene)
What animals have menstural cycles, which ones have oestrous cycles?
Only humans have menstrual cycles
Osestrous cycles vary in length
Polyoestrous Animals = throughout the year (cattle, pigs, mice, rats)
Seasonally Polyoestrous Animals = multiple cycles only during certain periods of the year (horses, sheep, goats, deer, cats)
Monstrous animals = animals with one oestrous cycle per year (dogs, wolves, foxes and bears)
Male Reproductive Organs & what controls production of hormones
Testes are the pair of reproductive organs in males that produce sperm
The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control the production of male hormones
Hormone messages are sent from these glands to the testes, where testosterone is produced, and sperm is made
The level of testosterone in the blood feeds back to the brain and when the level is low, more hormone messages are sent to increase the production
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) are messenger hormones made by the pituitary gland that act on the testes
LH is needed for cells in the testes to make testosterone that leads to the production of sperm
Testosterone
Important androgen (male sex hormone) in men
Needed for normal reproductive & sexual function, muscle and bone strength
Testosterone is important for the physical changes that happen during male puberty, such as development of the penis and testes, and for the ‘male’ characteristics typical of adult men such as facial and body hair
Testosterone also acts on cells in the testes to make sperm
Normal testosterone production varies widely in men
‘low’ testosterone levels = low energy levels, lowered libido, low mood, irritability, poor concentration, and reduced muscle
strength