Lec 37-38
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:24 AM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
What molecule is this
Histamine
2
New cards
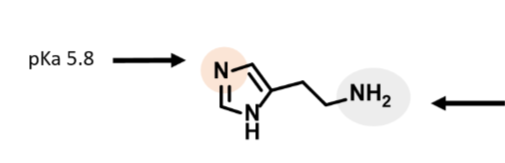
Know the pKa of the amines – i.e. which one is the most basic and which is least basic?
The most basic amine is the primary amine on the alkyl chain (9.4)
The ring amines have a pka of 5.8
The ring amines have a pka of 5.8
3
New cards
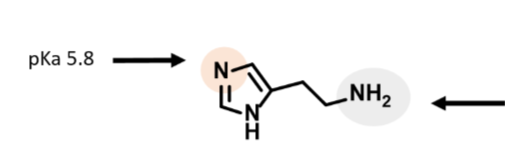
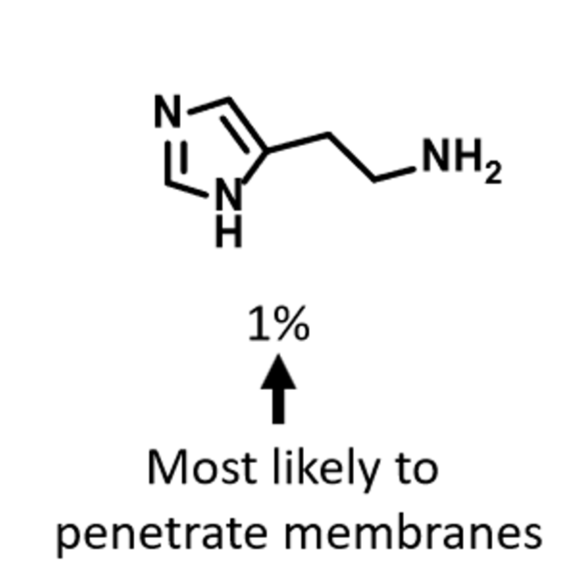
Know which form of histamine is most likely to penetrate membranes and why.
The unprotonated form (not a body pH)
4
New cards
How do H1 vs H2 antihistamines differ in what they are used to treat?
H1 antihistamines treat allergic inflammation
H2 antihistamines treat gastric hypersecretory disorder
H2 antihistamines treat gastric hypersecretory disorder
5
New cards
How many histamine receptors are known and are they G-coupled proteins or ion channels?
There are 4 receptors and they are G coupled protein receptors
6
New cards
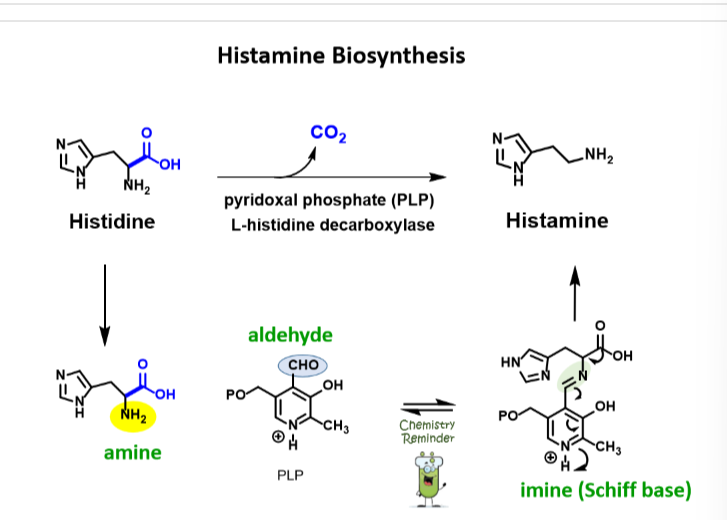
Understand histamine biosynthesis – what functional groups, co-enzyme and enzyme are involved?
Histidine is turned into Histamine via PLP L histidine decarboxylase
7
New cards
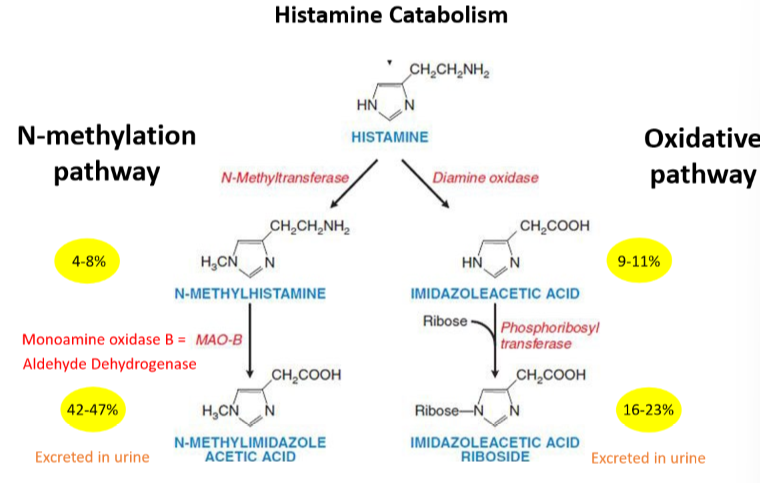
Histamine is broken down through two pathways – understand what are the major metabolites, and how are these metabolites excreted?
N methylation pathway:
Histamine → N methylhistamine→N methylimidazole acetic acid via N-methyltransferase and MAOB & aldehyde dehydrogenase
\
Oxidative pathway:
Histamine → Imidazoleatic acid →Imidazoleacetic acid riboside
via Diamine oxidase and phosphoribosyl transferase
Histamine → N methylhistamine→N methylimidazole acetic acid via N-methyltransferase and MAOB & aldehyde dehydrogenase
\
Oxidative pathway:
Histamine → Imidazoleatic acid →Imidazoleacetic acid riboside
via Diamine oxidase and phosphoribosyl transferase
8
New cards
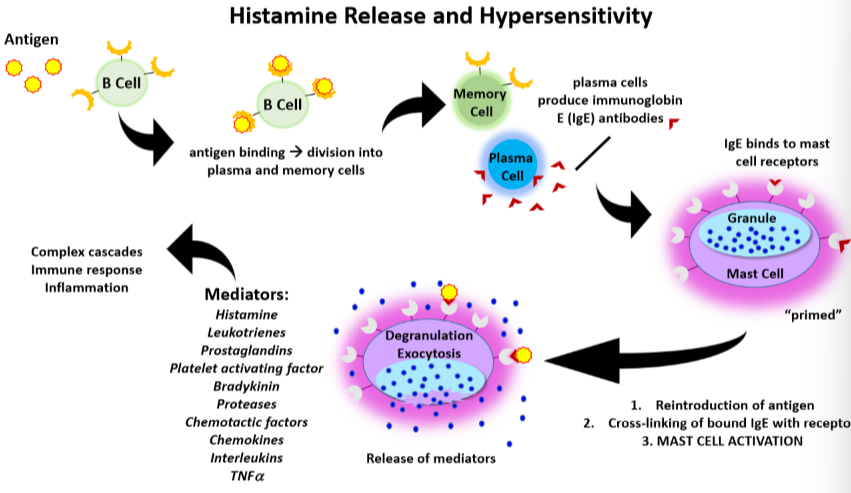
Understand the process of histamine release and hypersensitization.
1)B cells recognize an antigen then divide into memory and plasma cells
2)Plasma cells make antibodies
3)Antibodies bind to mast cells , mast cell is “primed”
4)Now, if we have antigen they bind to the antibodies leading to mast cell activation, leading to release of mediators (histamine) than go interact with other things that cause allergy symptoms
2)Plasma cells make antibodies
3)Antibodies bind to mast cells , mast cell is “primed”
4)Now, if we have antigen they bind to the antibodies leading to mast cell activation, leading to release of mediators (histamine) than go interact with other things that cause allergy symptoms
9
New cards
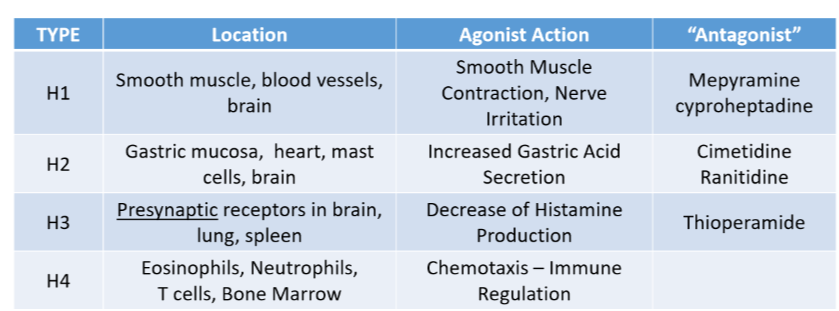
Know the result of agonist action on each histamine receptor type on the effectors and messengers.
finish later (table)
10
New cards
Cromolyn
Inhibitor of Histamine Release (Mast cell stabilizer)
Inhalation, eyes
Inhalation, eyes
11
New cards
Pemirolast
Inhibitor of Histamine Release (Mast cell stabilizer)
Eyes
Eyes
12
New cards
Nedocromil (Alocril) & Lodoxamide (Alomide)
Inhibitor of Histamine Release (Mast cell stabilizer)
ophthalmic solution
Season allergic conjunctivities
ophthalmic solution
Season allergic conjunctivities
13
New cards
How do first and second generation H1 receptor antihistamines differ from each other in terms of side effects. How do they generally work?
First generation- Sedation (get into CNS better)
\
Second generation- Non sedating, peripherally selective
\
Second generation- Non sedating, peripherally selective
14
New cards
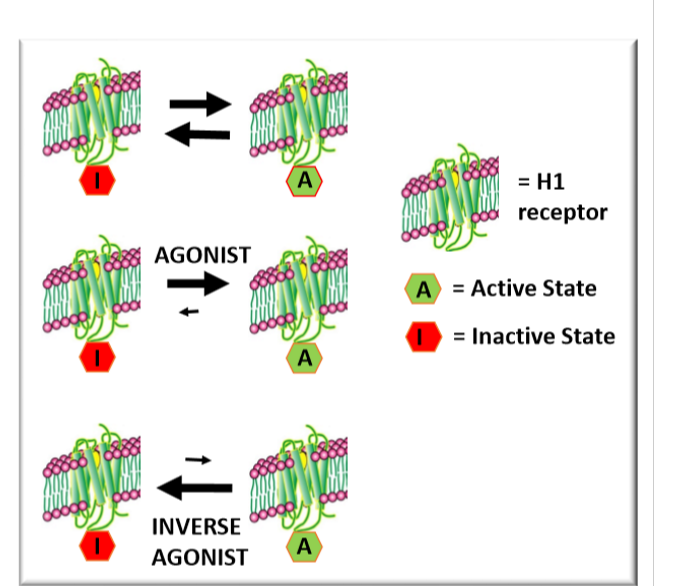
H1 receptor antihistamines MOA
inverse agonists
Produce the opposite response of an agonist
Produce the opposite response of an agonist
15
New cards
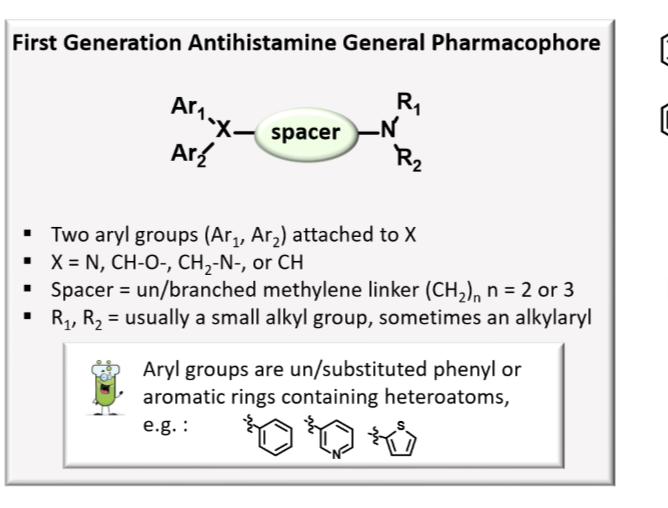
Know the pharmacophore of first generation H1 receptor antihistamines. This means that if you were given a lineup of structures (real or fictional) you can apply the rules to pick out an active vs inactive first generation H1 receptor antihistamine.
Two aryl groups
X = N, CHO, CH2N, CH
Spacer (CH2)
R1,R2= usually small alkyl group
X = N, CHO, CH2N, CH
Spacer (CH2)
R1,R2= usually small alkyl group
16
New cards
Understand that the pharmacophore of first generation H1 receptor antihistamines overlap with the pharmacophore of anticholinergics and why this is relevant.
We see anticholinergic effects associated with antihistamines because of this ( dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, urinary retention, constipation)
17
New cards
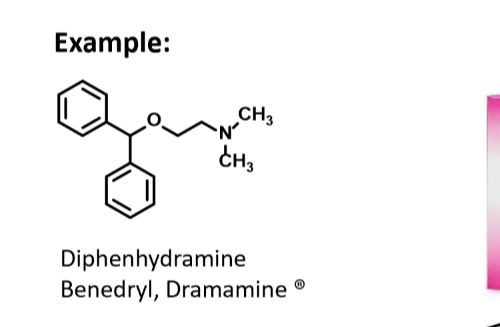
Recognize name/structure of benedryl
First gen H1 receptor antihistamine
Used for allergic conditions
Short half life
Wide safety margin
Sedation is a side effect
Used for allergic conditions
Short half life
Wide safety margin
Sedation is a side effect
18
New cards
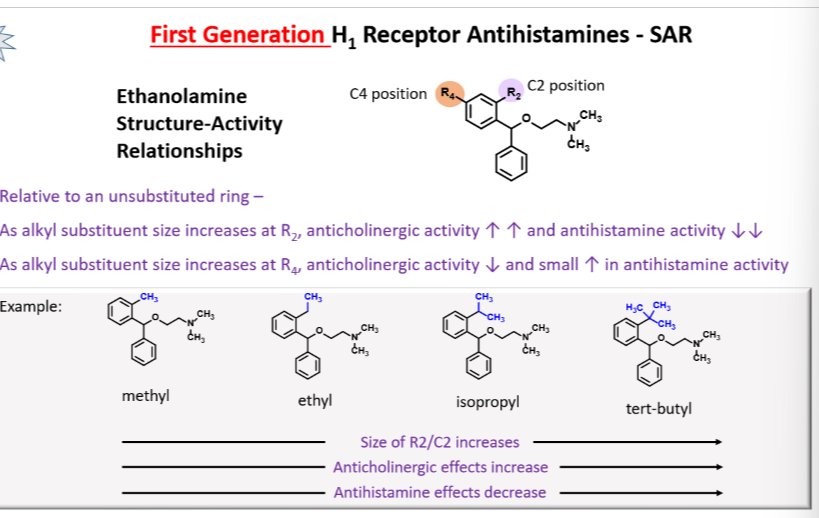
Understand the SAR of first generation H1 receptor ethanolamine-based antihistamines.
As the size of the R2 position increases the anticholinergic affects increase and the antihistamine effects decrease
19
New cards
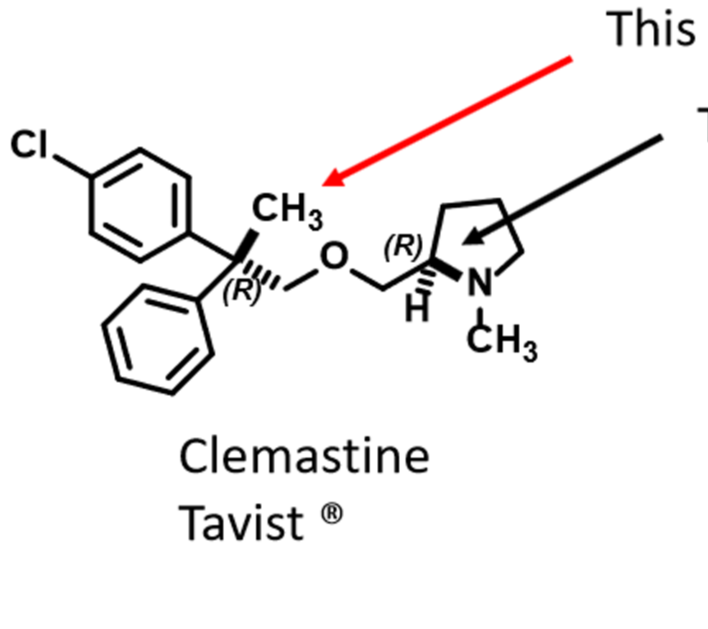
Recognize name/structure of clemastine
first generation H1 receptor ethanolamine based antihistamine
Relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis
Less sedative than diphenhydramine
R,R isomer is most potent
Relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis
Less sedative than diphenhydramine
R,R isomer is most potent
20
New cards
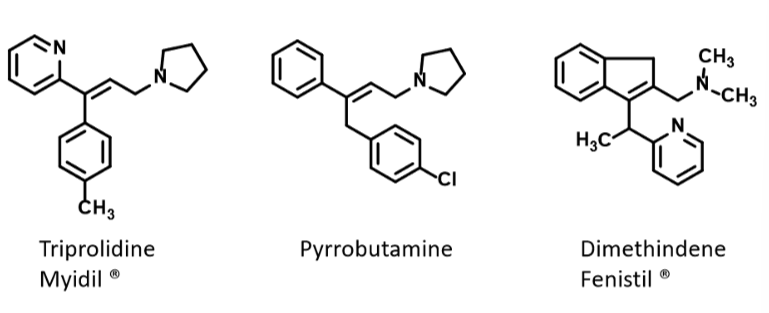
. Know what the alkylamines/propylamines are used for therapeutically and what advantages they possess over ethanolamine-based antihistamines (slide 17). Recognize the names/structures of these.
\
Triprolidine, Pyrrobutamine, Dimenthindene
\
Longer half lives
Extended duration of action
Fewer CNS side effects
Decrease anticholinergic effects
Decreased antiemetic effects
Triprolidine, Pyrrobutamine, Dimenthindene
\
Longer half lives
Extended duration of action
Fewer CNS side effects
Decrease anticholinergic effects
Decreased antiemetic effects
21
New cards
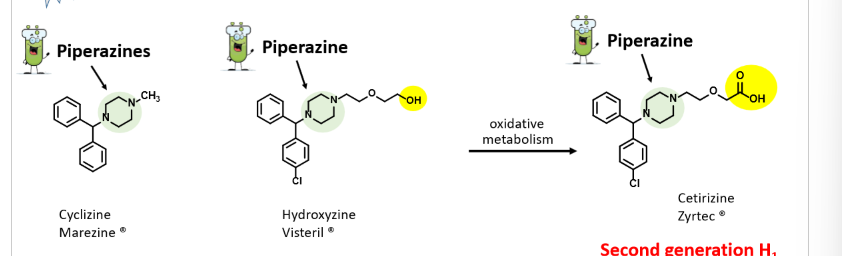
What are piperazine-based first generation H1 receptor antihistamines used for? Recognize structure/names for these.
Cyclizine, Hydroxytinze, Cetirizine
\
Vertigo, motion sickness
Significant antihistamine and anticholinergic effects
Drowsiness
hydroxyzine → itchy skin
\
Vertigo, motion sickness
Significant antihistamine and anticholinergic effects
Drowsiness
hydroxyzine → itchy skin
22
New cards
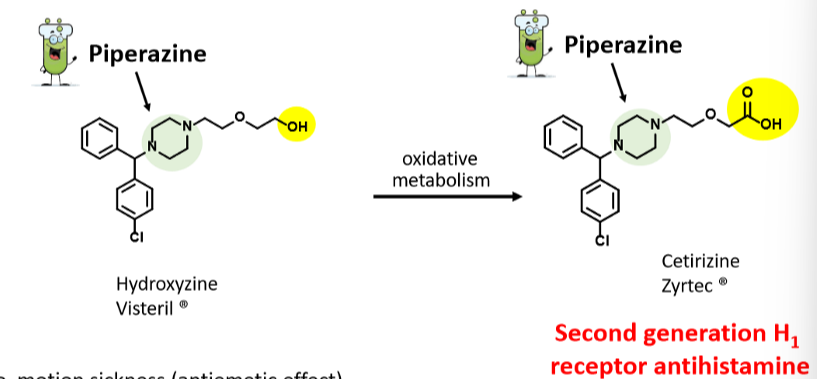
Know what functional group of Visteril is metabolized to give Zyrtec and what functional group results.
The hydorxy group on the end of the side chain is metabolized to a carboxylic acid
23
New cards
What is significant about Zyrtec in terms of its side effect profile compared to Visteril?
Second Generation H1 receptor antihistamine
“Nonsedating”
“Nonsedating”
24
New cards
Know the general pharmacophore of the tricylic antihistamines, how they are used, and examples by structure/name.
Promethazine: Sometimes combined with codeine for cough
Cyproheptadine: Appetite stimulating, used for anorexia nervosa
Cyproheptadine: Appetite stimulating, used for anorexia nervosa
25
New cards
Know the profile of second generation H1 receptor antihistamines vs first generation H1 receptor antihistamines.
Improved H1 selectivity
Decreased affinity for adrenergic and or serotonergic receptors
Act mostly in periphery
Little to no sedative effects
Decreased anticholinergic effects
May possess anti allergic effects apart from antihistamine activity
Vary widely in structure
Most are administered once daily
Decreased affinity for adrenergic and or serotonergic receptors
Act mostly in periphery
Little to no sedative effects
Decreased anticholinergic effects
May possess anti allergic effects apart from antihistamine activity
Vary widely in structure
Most are administered once daily
26
New cards
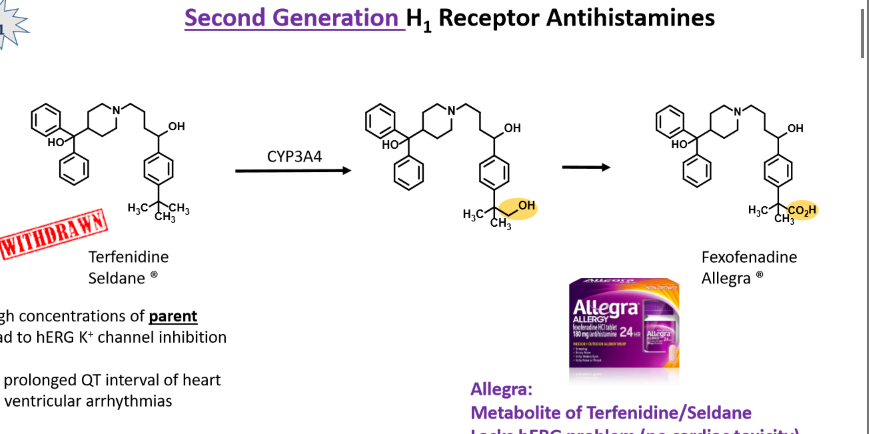
toxicity associated with terfenidine/Seldane.
\
Second gen H1 antihistamine
\
In presence of other CYP3A4 substrates high concentrations of parent drug can result leading to hERG K+ channel inhibition which leads to prolonged QT interval leading to ventricular arrhythmias
Second gen H1 antihistamine
\
In presence of other CYP3A4 substrates high concentrations of parent drug can result leading to hERG K+ channel inhibition which leads to prolonged QT interval leading to ventricular arrhythmias
27
New cards
How does hERG potassium channel inhibition effect heart rhythm?
prolonged QT interval of heart leading to ventricular arrhythmias
28
New cards
In the absence of CYP3A4 metabolism, does terfenidine/seldane have antihistamine activity?
No, its active metabolite is Allegra
29
New cards
. Recognize the structure/name of terfenidine and Allegra. What is the benefit of Allegra vs terfendiine/Seldane?
Allegra is not associated with hERG problem
Allegra is the metabolite of terfenidine
Allegra is the metabolite of terfenidine
30
New cards
Recognize Zyrtec as a second generation piperazines and what therapeutic advantage it has over its parent drug.
2nd gen H1 receptor antihistamine
“Nonsedating”
Active metabolite of hydroxyzine (1st gen)
“Nonsedating”
Active metabolite of hydroxyzine (1st gen)
31
New cards
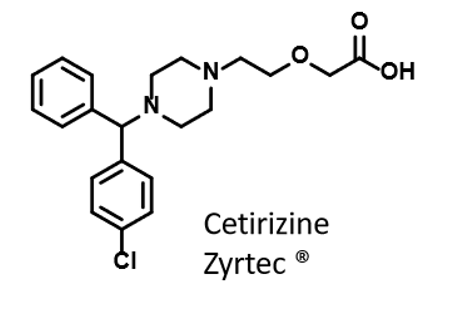
Zyrtec
2nd generation H1 receptor antihistamine
Acid metabolite of 1st gen antihistamine, hydroxyzine
No cardiotoxicity
Commonly combines pseudoephedrine
Acid metabolite of 1st gen antihistamine, hydroxyzine
No cardiotoxicity
Commonly combines pseudoephedrine
32
New cards
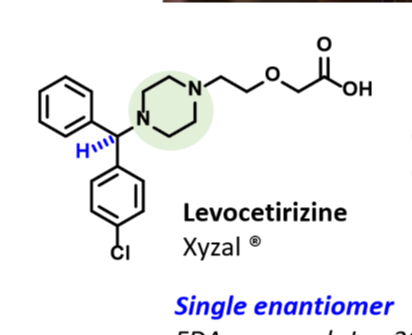
Know the origin of xyzal. Recognize the name/structure of xyzal and its use.
The enantiomer of zyrtec
33
New cards
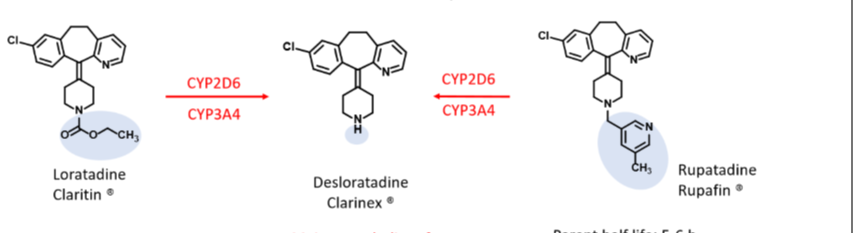
claritan, clarinex and rupafin
Second gen H1 antihistamines
Nonsedating, selective peripheral H1 inverse agonist activity
Long duration- once daily use
Clarinex is metabolite of claritin and rupafin
Nonsedating, selective peripheral H1 inverse agonist activity
Long duration- once daily use
Clarinex is metabolite of claritin and rupafin
34
New cards
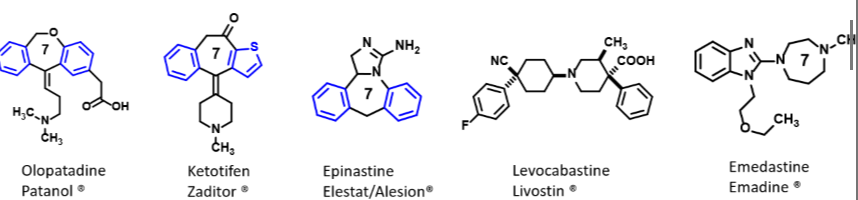
Recognize the structure/names of topical H1 receptor antihistamines and what they are used for.
Olopatadine, Ketotifen, Epinastine, Levocabastine, Emedastine
Eye drops
Eye drops
35
New cards
How are H2 receptor antihistamines used and what is their mechanism of action?
Alleviate over production of gastric acid
Inverse agonists
Inverse agonists
36
New cards
Understand the approaches to anti-ulcer agents summarized in class and how they work.
1) H2 receptor antihistamines
2) Proton pump inhibitors
3)Anticholinergics
4)Prostaglandin analogs
2) Proton pump inhibitors
3)Anticholinergics
4)Prostaglandin analogs
37
New cards
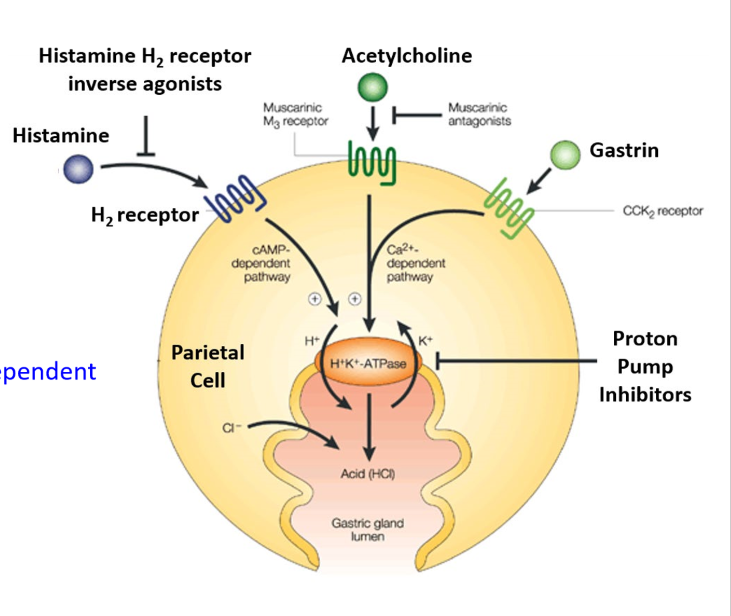
Know that the H2 receptor is cAMP dependent and that agonists increase cAMP production.
H2 receptor activation leads to a cAMP pathway that promotes the formation of HCL in the gastric lumen
38
New cards
What are the roles of prostaglandins in regulation of gastric acid secretion.
Balance the pro acidic mechanisms by:
1)Dampening the cAMP pathway in the parietal cells ti inhibit acid secretion
2)Increasing production of cytoprotective mucus and bicarbonate in superficial epithelial cells → pH 7
1)Dampening the cAMP pathway in the parietal cells ti inhibit acid secretion
2)Increasing production of cytoprotective mucus and bicarbonate in superficial epithelial cells → pH 7
39
New cards
How do NSAIDS affect ulcer formation?
Block Prostaglandin Production
Block Bicarbonate Production
Block Mucus Production
Block Bicarbonate Production
Block Mucus Production
40
New cards
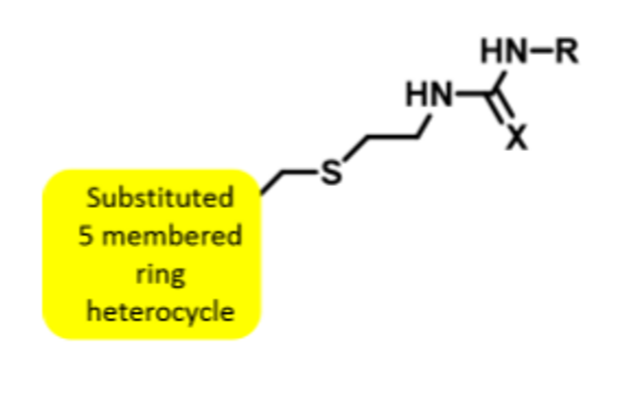
Recognize the structure/name of cimetidine, how it is used and the role of bioisoterism in its development.
Thiourea replaced with N cyanoguanidine (bioisosterism)
41
New cards
H2 receptor antihistamines
cimetidine, zantac and Pepcid AC
OTC used to treat gastric acid hypersecretion, acid indigestion, heartburn
OTC used to treat gastric acid hypersecretion, acid indigestion, heartburn
42
New cards
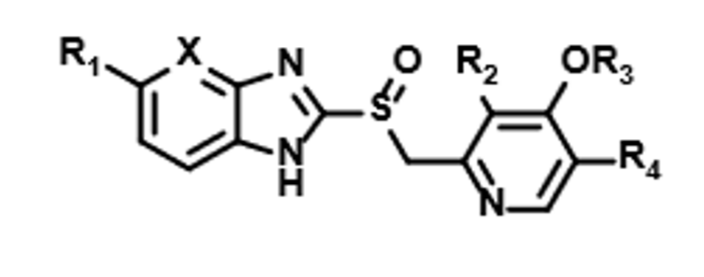
Prilosec, Nexium, prevacid, and protonix
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Treat gastric ulcers, GERD, gastric hypersecretion, erosive esophagitis
Treat gastric ulcers, GERD, gastric hypersecretion, erosive esophagitis
43
New cards
How do PPIs work
The PPI forms a disulfide bond with the proton pump which inactivates the pump
44
New cards
. What concern is there with prolonged use of proton pump inhibitors?
Increase risk of hip, wrist and spine fracture in patients of age 50 or older
\
Maybe bc:
PPIs interfere with absorption of iron, calcium , mg which are important to bone formation- inhibited pump is similar to pump in bone reabsorption
\
Maybe bc:
PPIs interfere with absorption of iron, calcium , mg which are important to bone formation- inhibited pump is similar to pump in bone reabsorption