Synapses and Neurotransmitters 1
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the sequence of events for transmission at a synapse
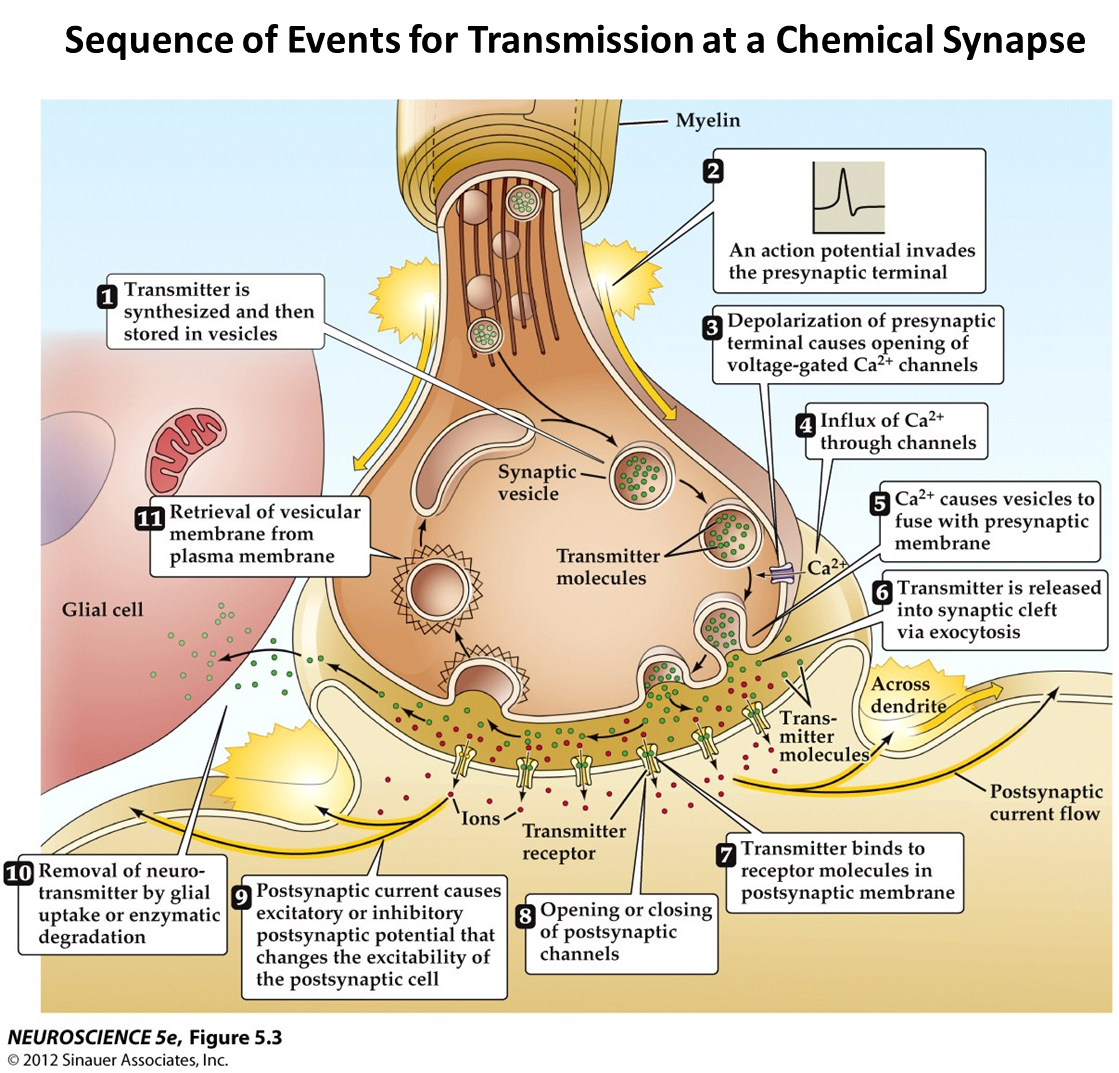
1) Neurotransmitters are made and stored in vesicles
2) Action Potential comes into the presynaptic terminal, depolarizing and opens voltage gated calcium channels
→ this triggers binding of vesicles and triggering exocytosis of neurotransmitters into the cleft
→ calcium is necessary for a postsynaptic response to occur
3) Transmitter binds to postsynaptic receptors leading to either excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic effect by depolarizing
→ after this occurs neurotransmitter is removed by reuptake into glial cells or enzymatic degradation
What are MEPPs?
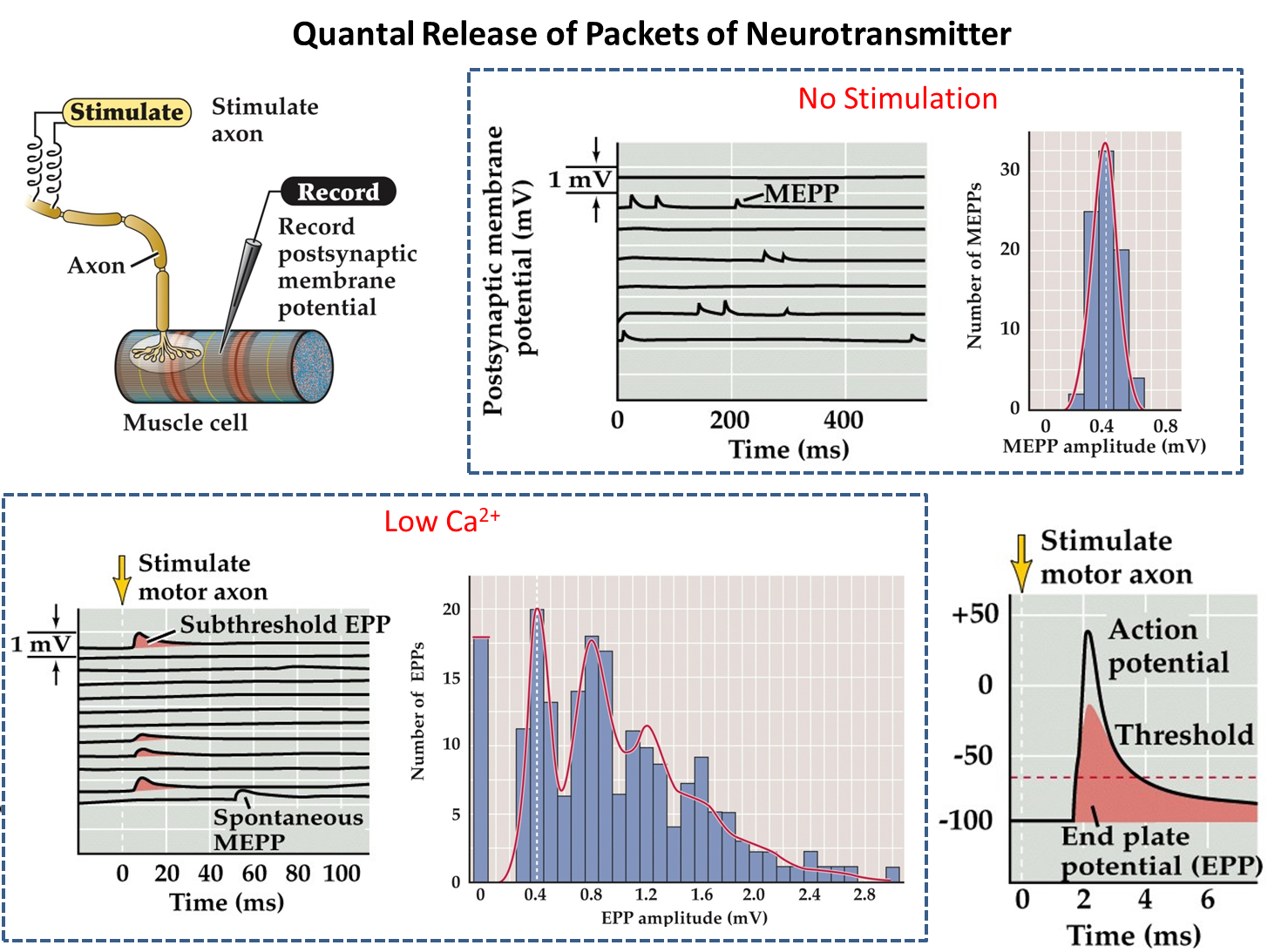
Miniature End Plate Potentials are the smallest activity that a NMJ creates when the muscle fiber is at rest
1) They are caused by the spontaneous release of a singular vesicle of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal
→ these occur without any nerve potential
→ occur as a result of random fluctuations in calcium levels in the presynaptic terminal
2) The existence of these MEPPs are proof for vesicles containing a consistent number of neurotransmitters (quantum)
Why can high levels of magnesium kill you?
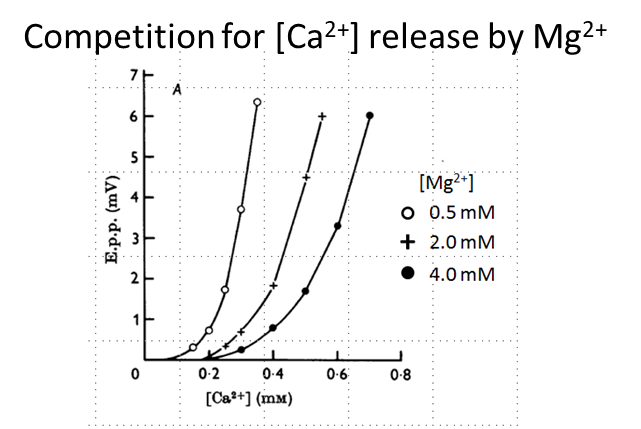
Magnesium, like calcium, is a divalent cation and is able to compete with calcium at the NMJ
→ this means that high levels of calcium prevent neurotransmitter release and can lead to death
What are SNAREs and Synaptotagmin?
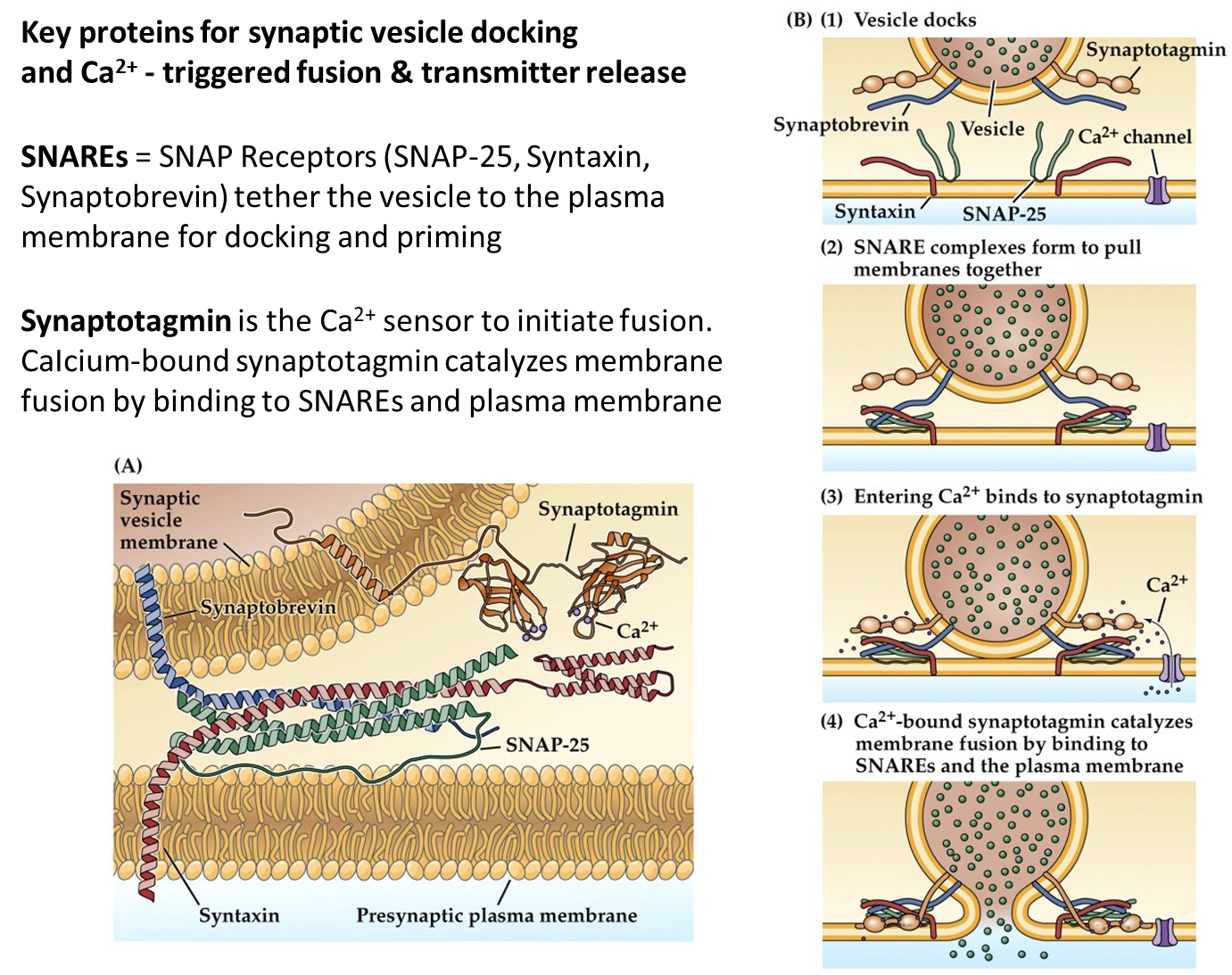
SNARE Proteins - family of proteins that pull synaptic vesicles and presynaptic membranes together in order to trigger neurotransmitter release
→ regulated by calcium binding to Synaptotagmin
Synaptotagmin - the calcium sensor for fast neurotransmitter release
→ binding of calcium to synaptotagmin will cause a conformational change triggering activation of SNARE complex
What are the three SNARE proteins?
SNARE Proteins form a complex that interacts with synaptotagmin in order to release neurotransmitters from vesicles
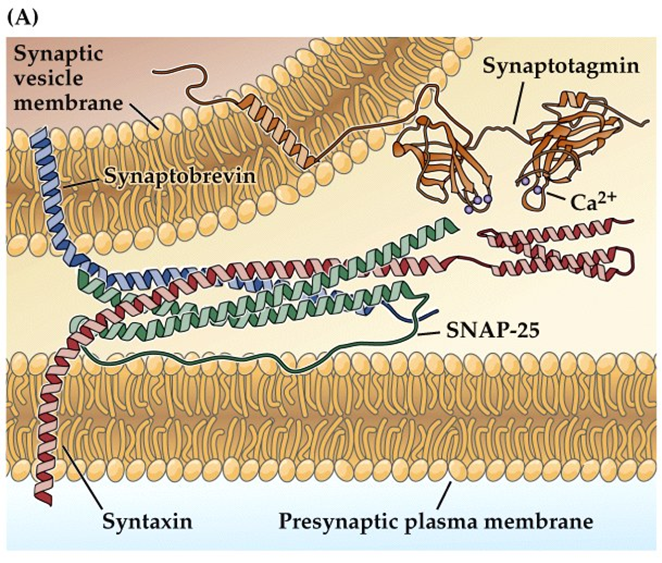
1) SNAP-25
→ located on the synaptic vesicle membrane
2) Syntaxin
→ located in the presynaptic plasma membrane
3) Synaptobrevin
→ located in the synaptic vesicle membrane
What are the two kinds of synapses?
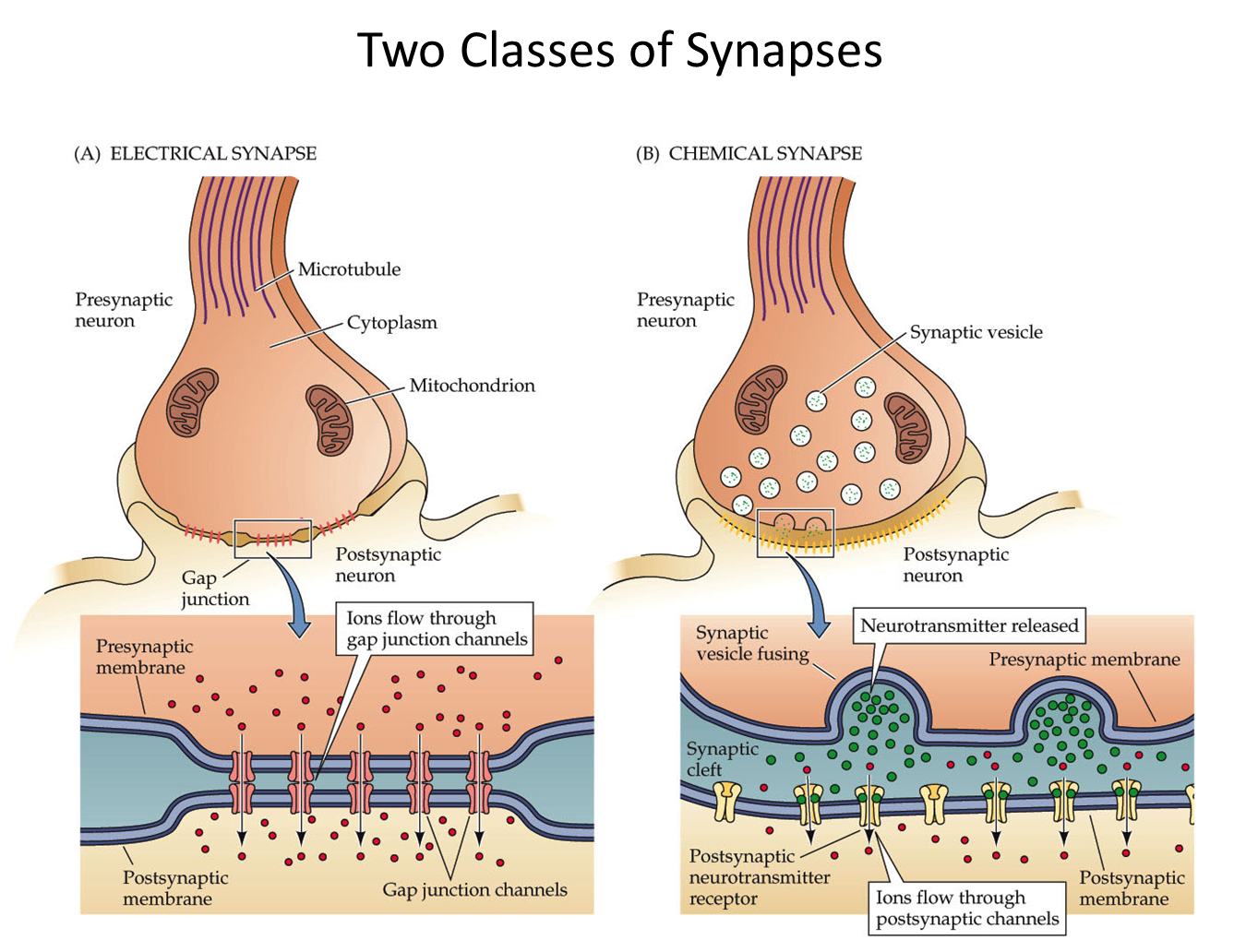
1) Electrical Synapses
→ utilize gap junctions created by connexons that allow passage of molecules across the presynaptic membrane to the post synaptic membrane
→ electrical synapses are much faster with the depolarization in the postsynaptic happening almost immediately after presynaptic depolarization
→ used often in synchronization and signaling is bidirectional
2) Chemical Synapses
→ use synaptic vesicles that release neurotransmitters that bind to the post-synaptic terminal, by far the most common
→ slower than the electrical synapse with unidirectional signaling
What are the two classes of neurotransmitter receptors for chemical synapses?
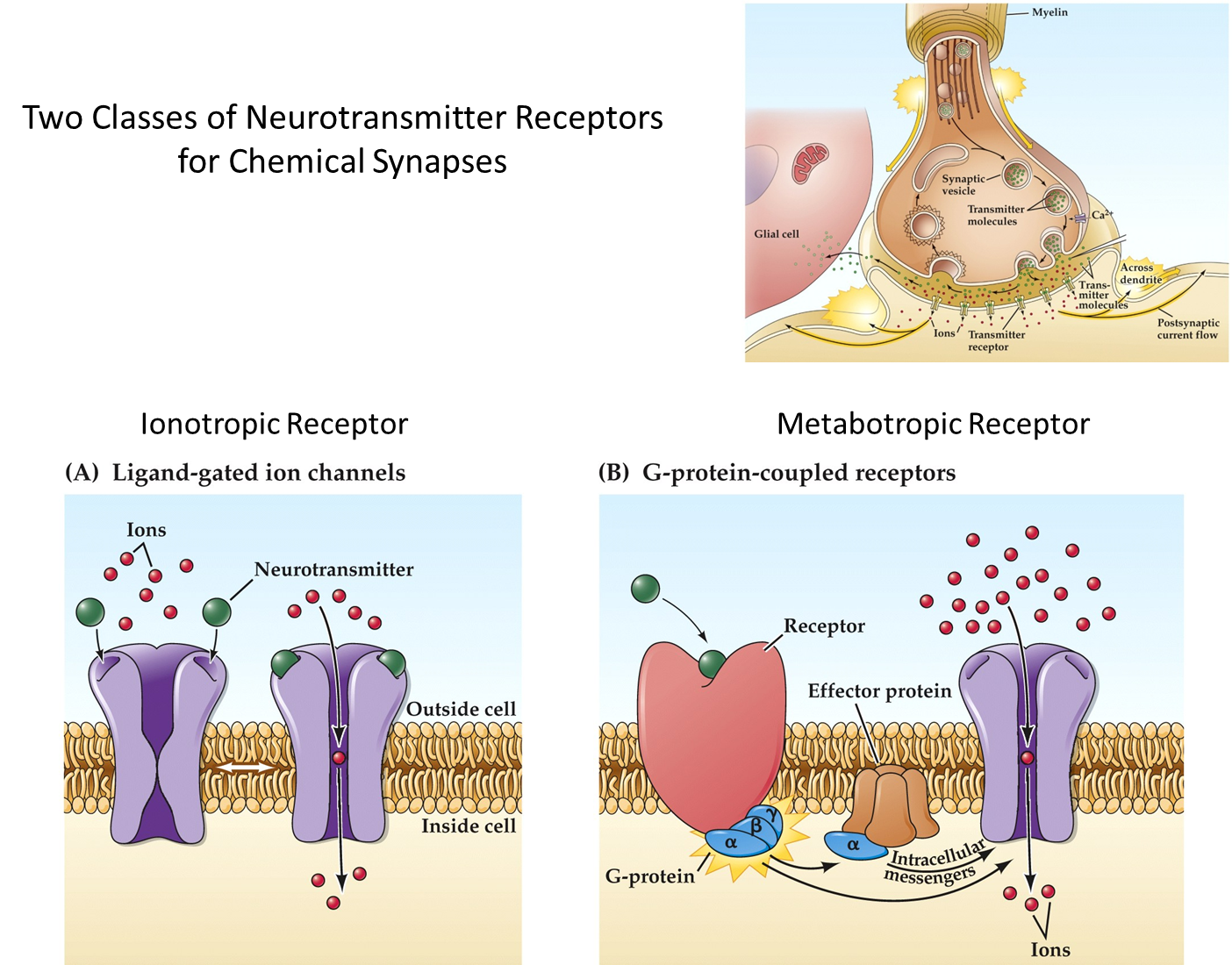
Ionotropic Receptor (Ligand Gated Ion Channels)
→ neurotransmitter binds changing conformation from closed to open, allowing entry of ions into the post-synaptic terminal
→ most ionotropic receptors are five subunits except the ones that interact with glutamate which are four subunits
Metabotropic Receptor (G-Protein Coupled Receptors)
→ neurotransmitter binds activating the G-protein modulating the activity of other channels by using secondary messengers
What is a reversal potential? How is it related to concentrations of ions and whether a channel is excitatory or inhibitory?
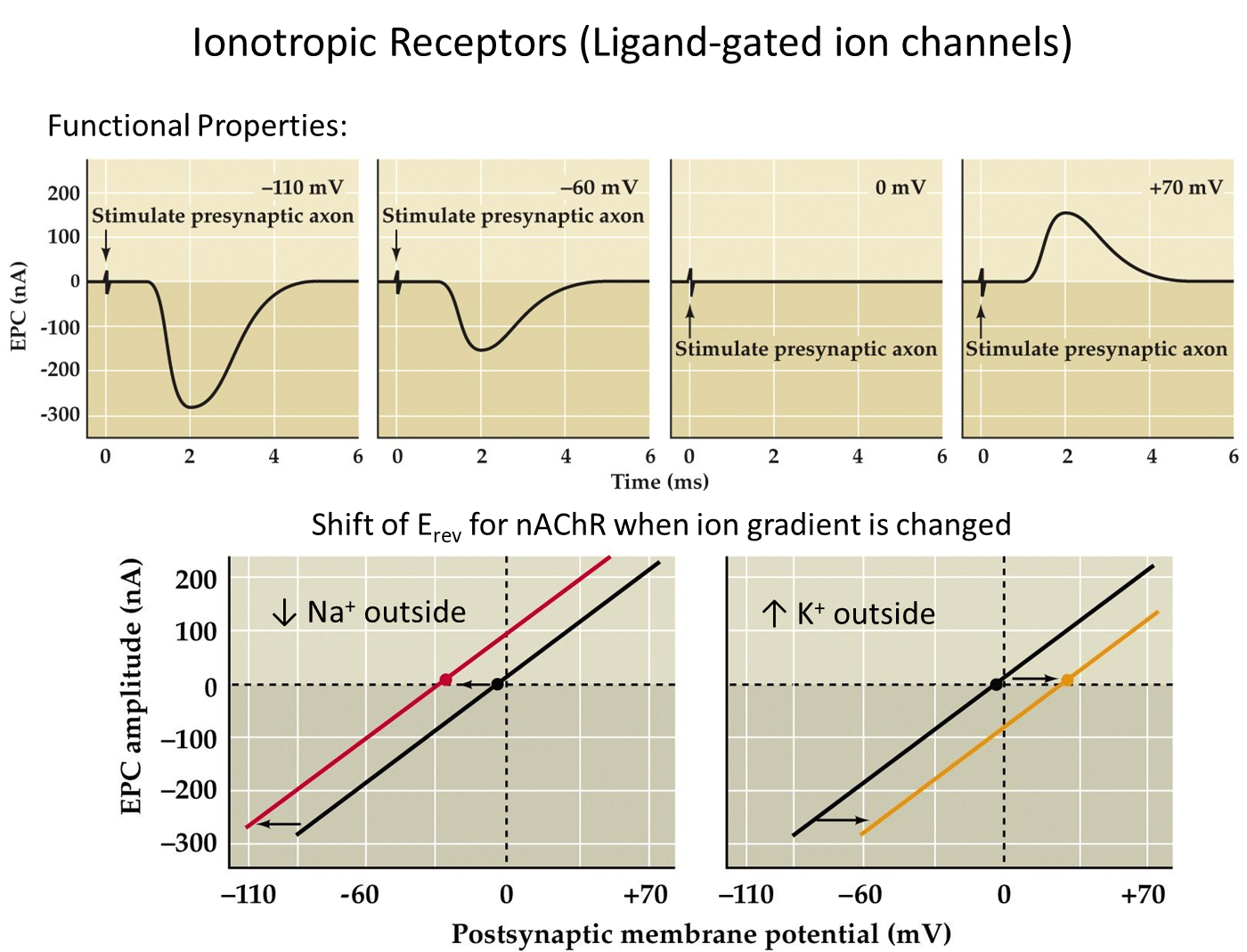
Reversal potential is the membrane voltage where opening a specific ion channel produces no net change in the membrane potential because the inward and outward fluxes are even
1) These matters because it tells us whether the opening of a channel will depolarize or hyperpolarize or do nothing
→ as seen in the example above, when the membrane is hyperpolarized, there is a tendency to depolarize during binding of the ionotropic receptors and vice versa
2) changing the relative concentrations of sodium or potassium will change the reversal potential
→ for example, lowering the amount of sodium outside decreases its driving force inside the cell
→ this leads to a more negative reversal potential
3) reversal potential determines whether a channel is excitatory or inhibitory
→ when Erev is positive than threshold opening the channel will depolarize the cell and make it excitatory
→ when Erev is negative than threshold opening the channel will hyperpolarize and make it inhibitory
What makes a substance a neurotransmitter?
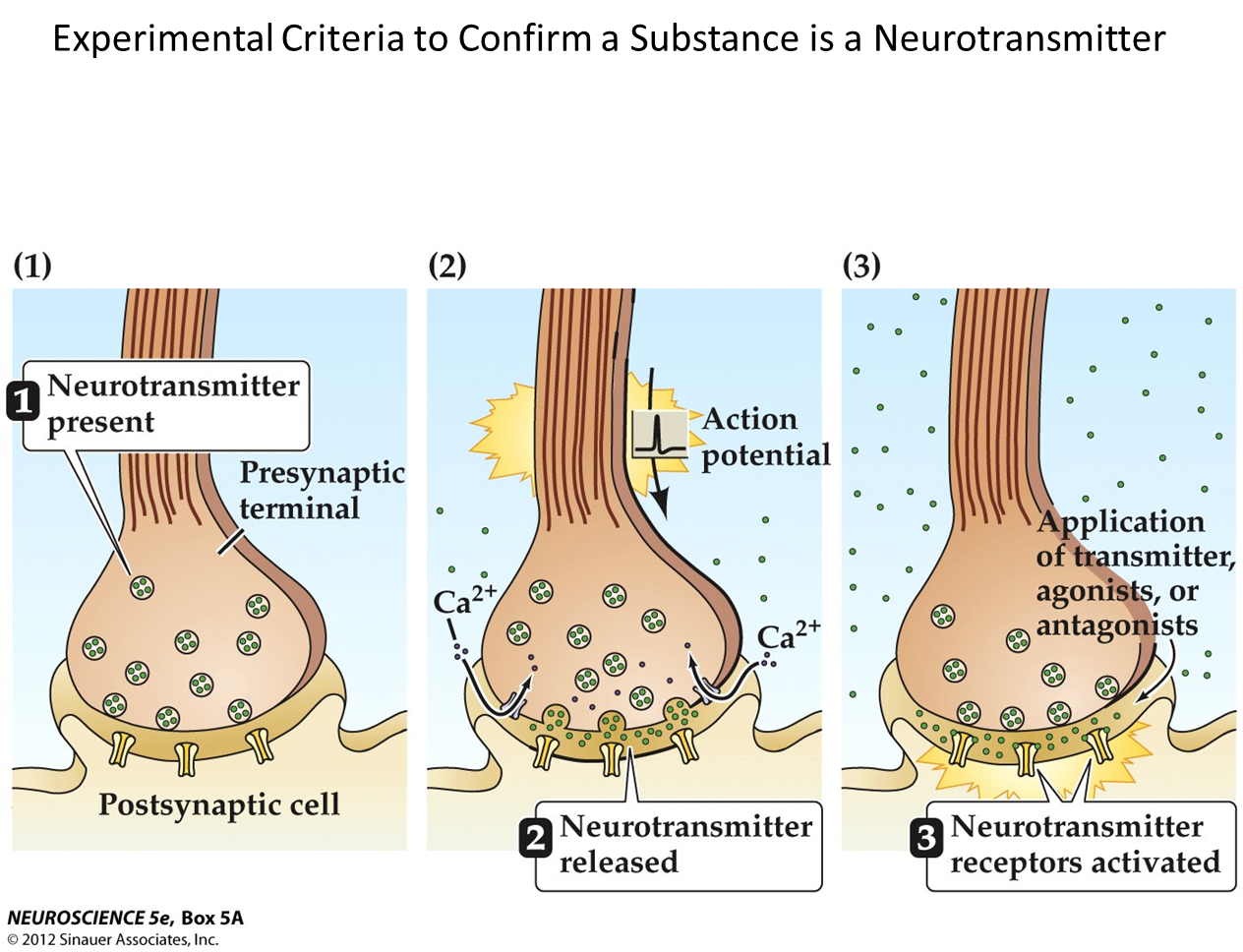
There are three experimental criteria to determine if a substance is a neurotransmitter
→ Neurotransmitter present in the presynaptic terminal
→ Neurotransmitter released when action potential occurs
→ Neurotransmitter receptors activated at post-synaptic terminal
What is Acetylcholine? (Enzyme, Removal, Importance)

Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that binds to both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
1) Rate limiting enzyme is done via choline acetyltransferase which takes acetyl group from Acetyl-CoA and attaches it to choline
2) removed by enzyme degradation from acetylcholinesterase
3) AchE inhibitors used to treat myasthenia gravis and Alzheimer
→ nerve gas agents are a form of irreversible AchE inhibitor
What is Glutamate? (Enzyme, Removal, Importance)
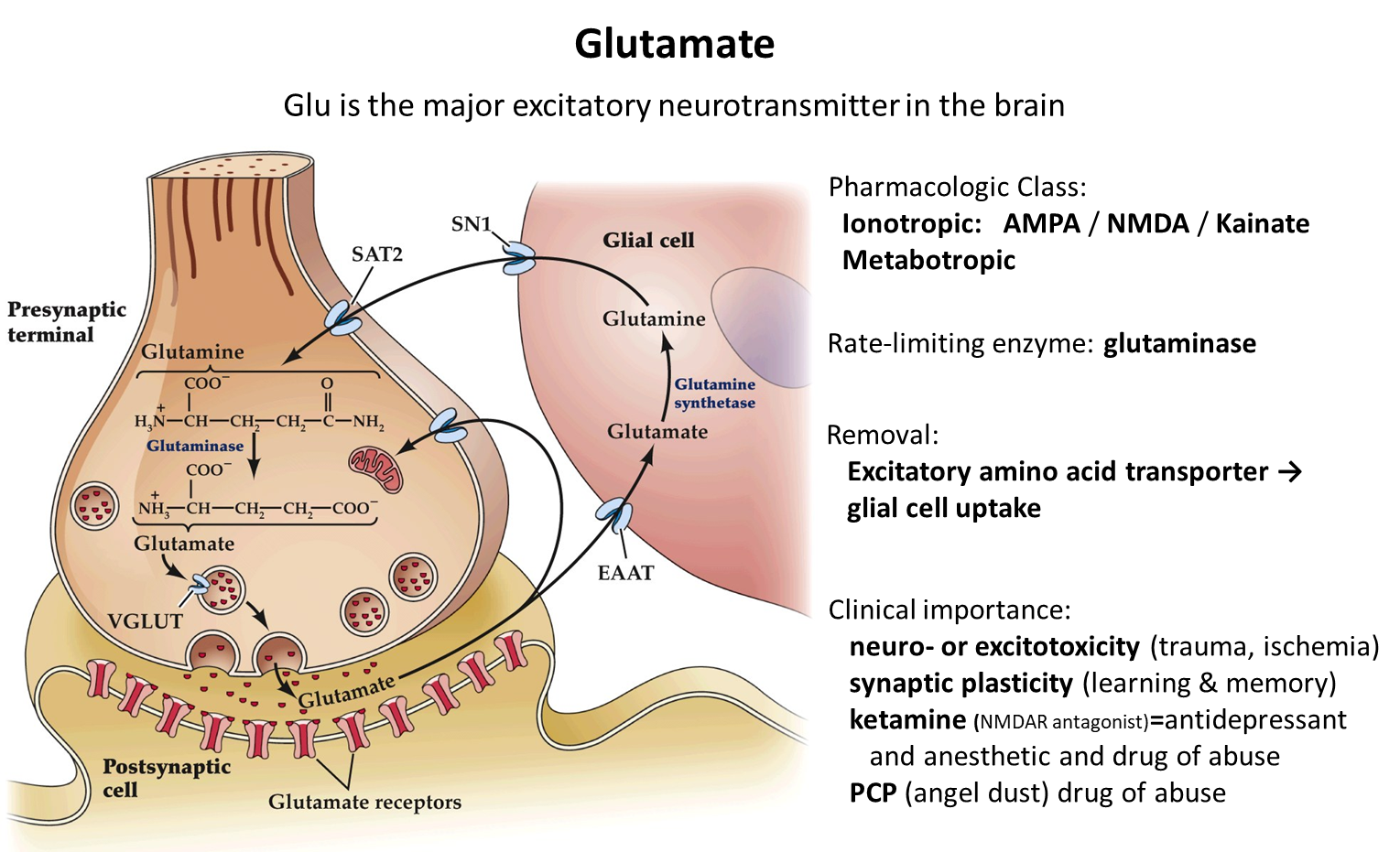
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter of the brain and binds to ionotropic (AMPA/NMDA) and metabotropic receptors
1) Made via the enzyme glutaminase
→ removed via the excitatory amino acid transporter which uptakes into glial cell
2) Neuro or Excitotoxicity is caused by massive release of glutamate
3) NMDA receptors which bind to glutamate are used in learning and memory
→ blocking these receptors via ketamine or PCP which made lead to psychotic activity