NURS 3444 - Exam 4 Study Guide on Cardiac Conditions
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
ASD Type of Defect
Increase PBF (acyanotic)
VSD type of defect
Increase PBF (acyanotic)
PDA type of defect
Increase PBF (acyanotic)
COA type of defect
obstruction
TOF type of defect
Decrease pulmonary blood flow (cyanotic)
HLHS type of defect
Mixed
What is ASD?
Abnormal opening between the atria
- L to R shunt because L arterial pressure is higher than R
- R atrium enlargement
ASD clinical manifestation
- Asymtomatic
- S/sx of HF seen with large ASD
- HF around age 30-40s if undiagnosed and pulmonary HTN
ASD Findings on Auscultation
Murmur and Split S2 (with larger sized ASD)
ASD Treatment
- Spontaneous closure by age 18-36 months
- Patch closure via cardiac cath for medium or large ASD
ASD Medication
- Preop: none unless S/sx of HF
- Postop: low dose ASA x 6 months
ASD Teaching points
- Developmentally appropriate prep for cardiac cath
- S/sx of HF
- ASA therapy
What is VSD?
Abnormal opening in between ventricles
- Blood shunts L to R
VSD Clinical Manifestation
- CHF symptoms
- May not be present initially at birth
- Associated with fetal alcohol syndrome, down syndrome, PDA, COA, preemies
- Slow weight gain
- Feeding difficulties
VSD auscultation findings
- Palpable thrill
- Diaphoresis, tachycardia, tachypnea with grunting
- Murmur at left sternal border
VSD treatment
- may close on own
- patch graft with cath
- closure restores normal A&P
VSD drugs
- Digoxin
- diuretics preop
- post op pain management
- possible ACE inhibitors
VSD Nursing Management
- cardiac assessment
- S/sx of HF
- sodium restriction
- monitor for ventricular dysrhythmias or AV block
What is PDA?
failure of DA to close
- L to R shunt since aortic pressure is higher than the low pulmonary artery
PDA clinical manifestations
- Asymtomatic up to age 40
- Seen commonly in preemies, COA, and VSD
- Resp distress / HF
- Fatigue and dyspnea on exerties
PDA findings
- Machine-like murmur
- Difficulty hearing S1 and S2
- Palpable thrill
- Decreased diastolic BP
- Bounding peripheral pulses
PDA Treatment
- Indomethasin or ibuprofen to close
- Thoracoscopic surgery
- Coil to occlude via cardiac cath
PDA meds
- Indomethacin
- Ibuprofen
- Digoxin
- Diuretics
Failure to close PDA risk
endocarditis
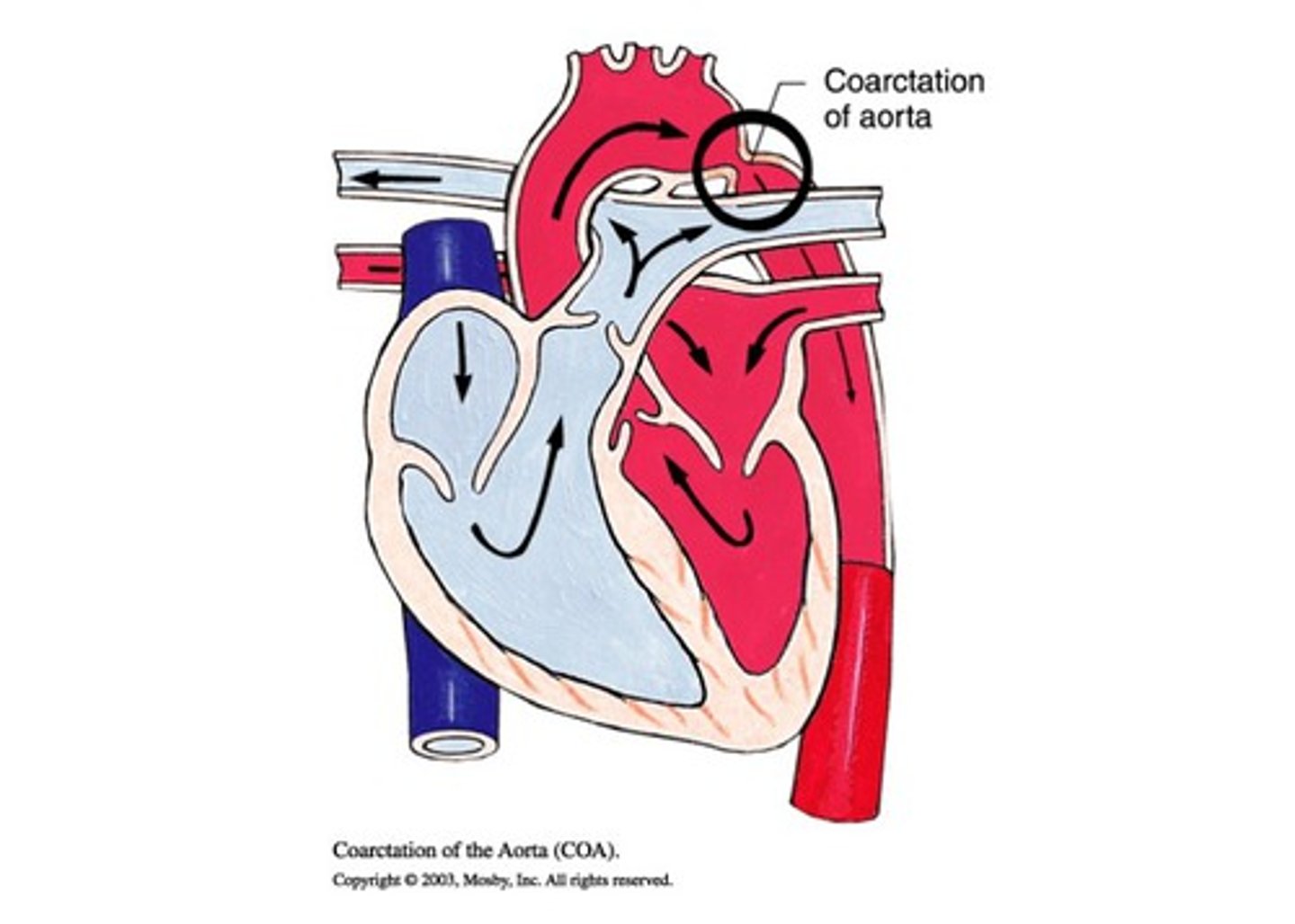
What is COA
narrowing of aortic arch
- causes decreased CO due to extra pressure on ventricles
COA clinical manifestations
- HF
- Dizziness, HA, fainting, tingling in lower extremities
COA assessment findings
- Pink upper extremities and pale and cool lower extremities
- Bounding upper pulses and weak lower pulses
- Murmur heard at base of heart
COA treatment
resection of coarted section with end-to-end anastomosis
- Angioplasty for older infants and children
COA medication
- Prostaglandins (critically ill)
- Digozin
- Diuretics
- O2
- Sedatives
- Antihypertensive meds
COA nursing assessment
- Cardiac assessment
- Monitor for s/sx of HF
- PVS assessment (BP all 4 extremities)
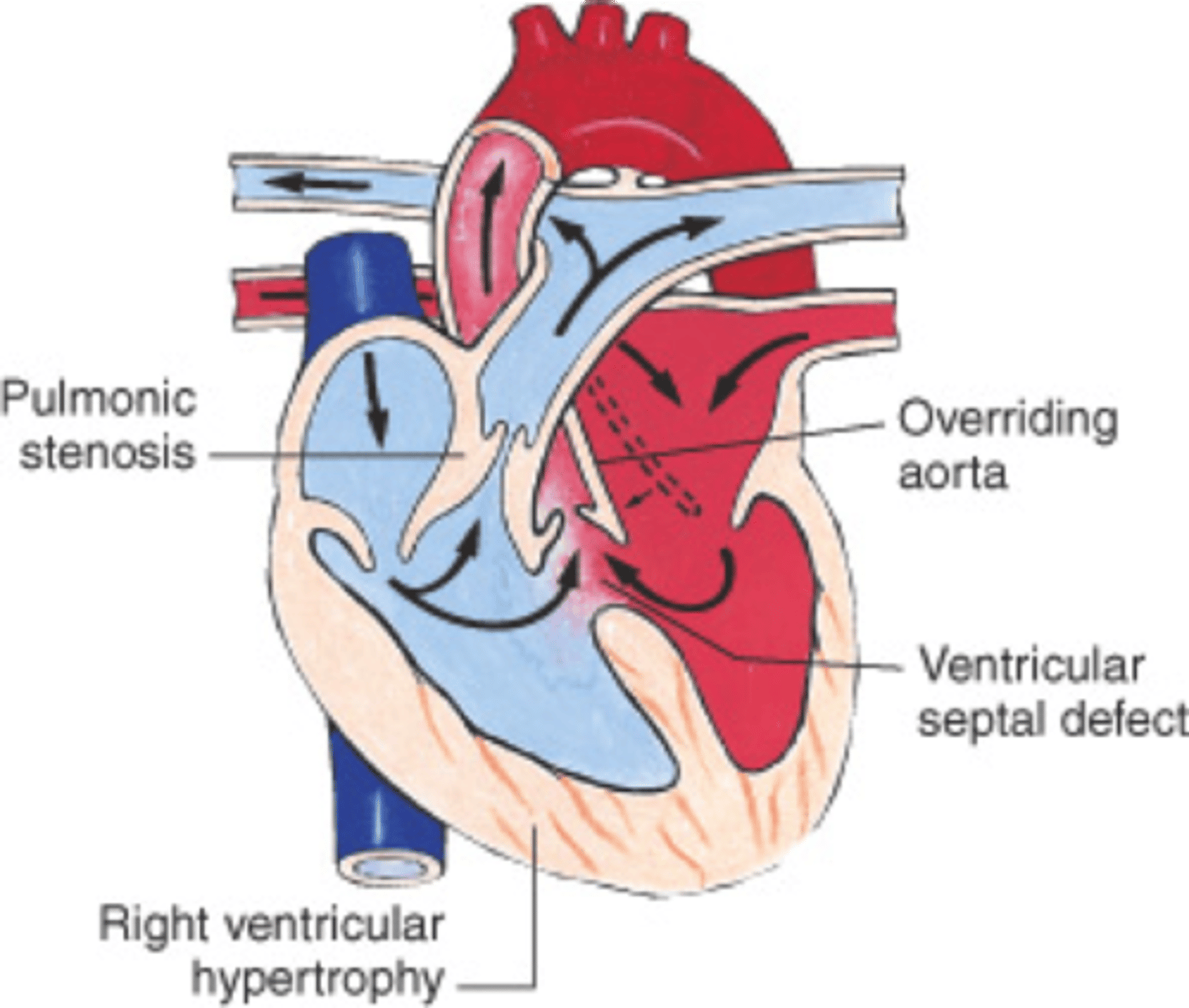
What are the 4 defects with TOF?
- VSD
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Reight ventricular hypertrophy
- Overriding Aorta
Symptoms of TOF?
- Cyanosis at birth
- Loud murmur
- SOB and rapid RR
- Poor weight gain
- Tiring easily
- Trouble feeding
- Hypercyanotic spells
- Irritability
- Clubbing
- Polycythemia
Hypercyanotic/tet spells
Often seen with TOF
- dyspnea
- bradycardia
- fainting
- seizures
- Cyanosis
- straining
- infection
- fever
Treatment of TOF
Multiple surgeries to increase pulmonary blood flow during infancy
- repair of VSD
- pulmonary stenosis repair
Medications for TOF
- Prostaglandin infusion (if critically low sats)
- ABX prophylaxis
- Furosemide/lasix
- Morphine during tet spells
What is HLHS?
Underdeveloped left heart
- aorta and left ventricle are underdeveloped
Symptoms of HLHS?
- Cyanosis
- Weak of absent pulses
- s/sx of HF
- progressive deterioration if closure of PDA occurs
HLHS treatment?
- 3 stage repair
- Prostaglandin to keep PDA open
- Cardiac transplant in future
HLHS medications
- Digoxin
- Diuretics
- O2
- Prostagnlandins to keep PDA open
HLHS education
- Fatal if no surgical repair
- avoid supplemental oxygen
- heart transplantation may be necessary
- lifelong arrhythmias following repair
CHD signs and symptoms
- Tachycardia (most common) >160 bpmü - Difficulty feeding (most common parental complaints)
- Wake to feed, weak suck, cyanosis with feeds, long feeds, sleeping during feeds (freq stim)
- Tachypnea >60 bpm
- Cyanosis (C vs. A)
- FTT
- Developmental delays
- Possible BP changes
- CHF (no distended neck veins)
Interventions for CHD
- meds
- frequent weights
- activity as tolerated
- rest periods
- cluster care
Nutrition with CHD
- high calorie meals and formula
- NG remainder of feeds
- Special nipple to decrease energy expendeture
- BMI / growth trends
Pre op considerations
- VS
- Weight
- Perfusion
- Auscultation
- NPO
- meds
Post op considerations
same as preop but add:
- possible mechanical ventilation
- chest tube care
- neuro checks
- dosage changes
- I/O
- Pulmonary toilet
- Pain assessment
- Mobility asap
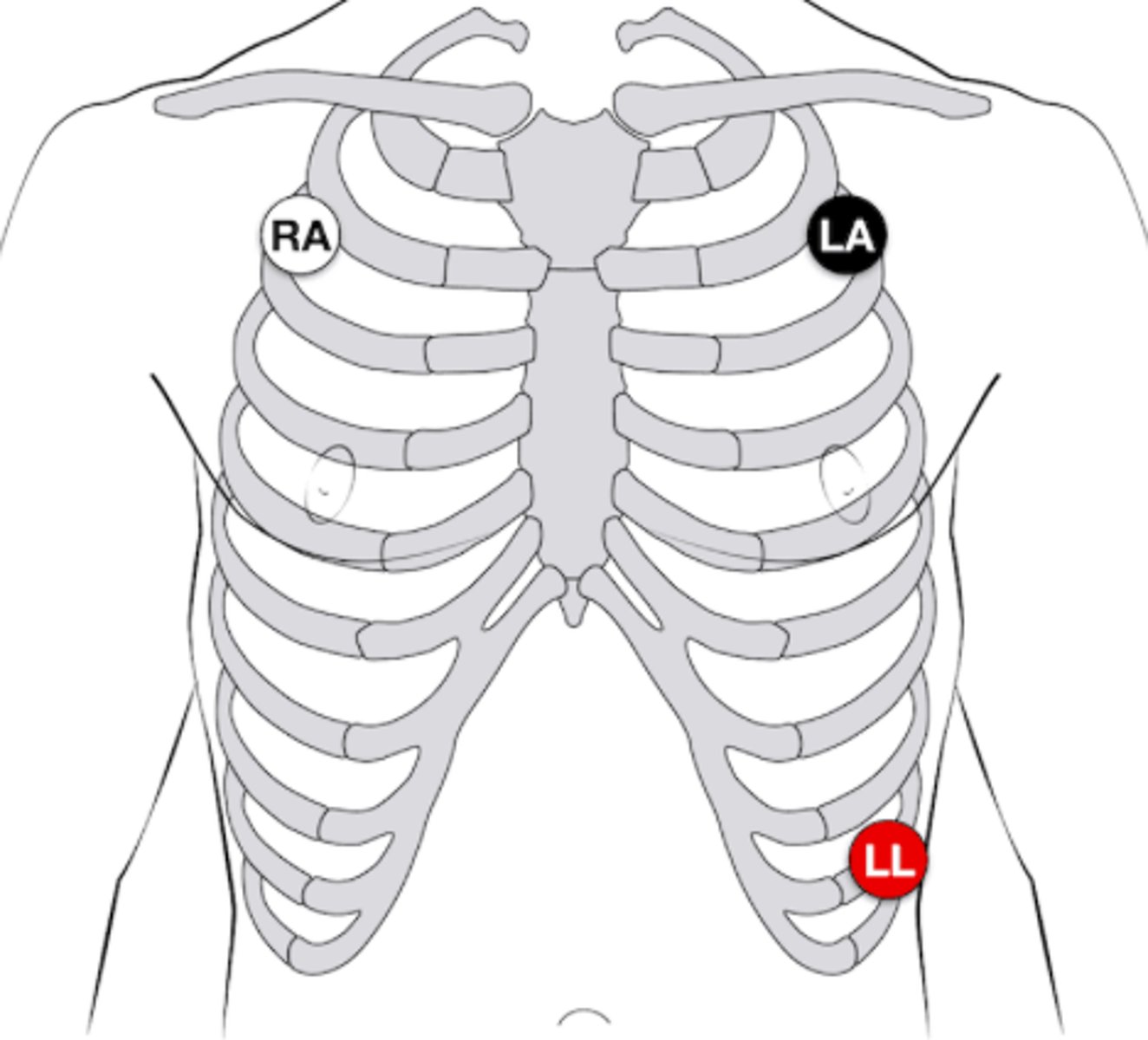
3 lead Electrode Placement
Where to put pressure if cardiac cath sit is bleeding?
1" above site
What defects increase pulmonary blood flow?
- ASD
- VSD
- PDA
FEAR cues
F - feeding poorly
E - energy is low
A - always fussy
R - rapid respirations
patent ductus arteriosus
should close within 72 hours of birth
PDA surgery
ligation
- if indomethacin and ibuprofen do not work to close
Which way does blood flow with cyanotic defects?
Right to left side of heart
Clinical presentation of cyanotic defects?
- Tet spells
- Polycythemia
- Clubbing
treatment for tet spells
- Put children in knee chest position to increase systemic pressure → push blood into pulmonary vasculature
- Give oxygen
- Give morphine → smooth muscle relaxant
- Give IVF → prevent dehydration (can lead to TET spell)
tetralogy of fallot
Coarctation of aorta
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- ASD
- Want to keep PDA open
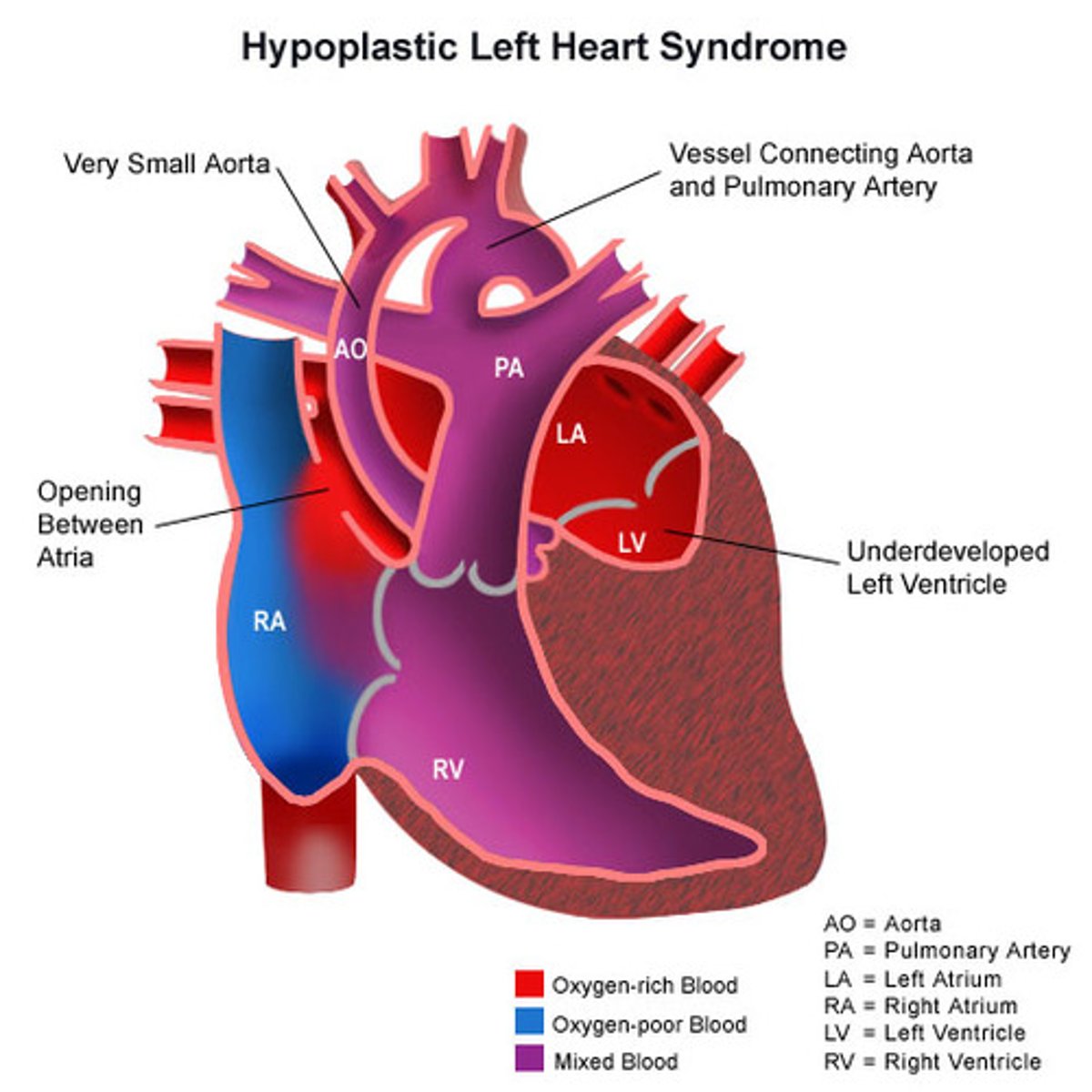
Symptoms of HLHS
- cyanosis
- hypoperfused
- blood flow to body severely impacted
Symptoms of impaired myocardial function
tachycardia, fatigue, weakness, restless, pale, cool extremities, decrease BP, decreased urine output (<1 mL/kg/hr)
Symptoms of Pulmonary congestion
tachypnea, dyspnea, respiratory distress, exercise intolerance, cyanosis, difficulty feeding
symptoms of systemic venous congestion
peripheral and periorbital edema, weight gain, ascites, hepatomegaly, neck vein decisions
Digoxin therapeutic level
0.8-2.0 ng/mL
Signs of digoxin toxicity
- bradycardia
- halo in vision
- lethargy
- vomiting
Contraindications to digoxin
Bradycardia
- Adolescents: above 60
- School aged: above 70
- Infants: above 90
Digoxin dosage timing
Given 1-2 hours before or after meals
- q 12 hours
- if miss dose give as soon as possible (if more than 4 hr after skip)
Hyperkalemia cause
potassium sparing diuretics and increased potassium in diet
Hyperkalemia symptoms
- muscle twitches, cramps
- irritability
- decreased BP
- EKG changes
- Dysrhythmias
- Abdominal cramping
- Diarrhea
Hypokalemia causes
loop or thiazide diuretics
Hypokalemia symptoms
- Alkalosis
- Shallow respiration
- Irritability
- Confusion, drowsiness
- Weakness, fatigue
- Arrhythmias
- Lethargy
- Thready pulse
- Decreased intestinal mobility (N/V and ileus can occur)
When does rheumatic fever occur?
2-6 weeks after an untreated or partially treated group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection of the upper respiratory tract.
Principle manifestation of rheumatic fever involve...
- Heart
- Joints
- Skin
- CNS
Treatment of rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever with carditis and residual heat disease (with valvular disease) → Antibiotic prophylaxis for 10 years or until age 40
Rheumatic fever with carditis but no residual heat disease (no valvular disease) → antibitioic prophylaxis for 10 years or until age 25
Rheumatic fever without carditis → antibiotic prophylaxis for 5 years or until age 21
JONES CAFE PAL
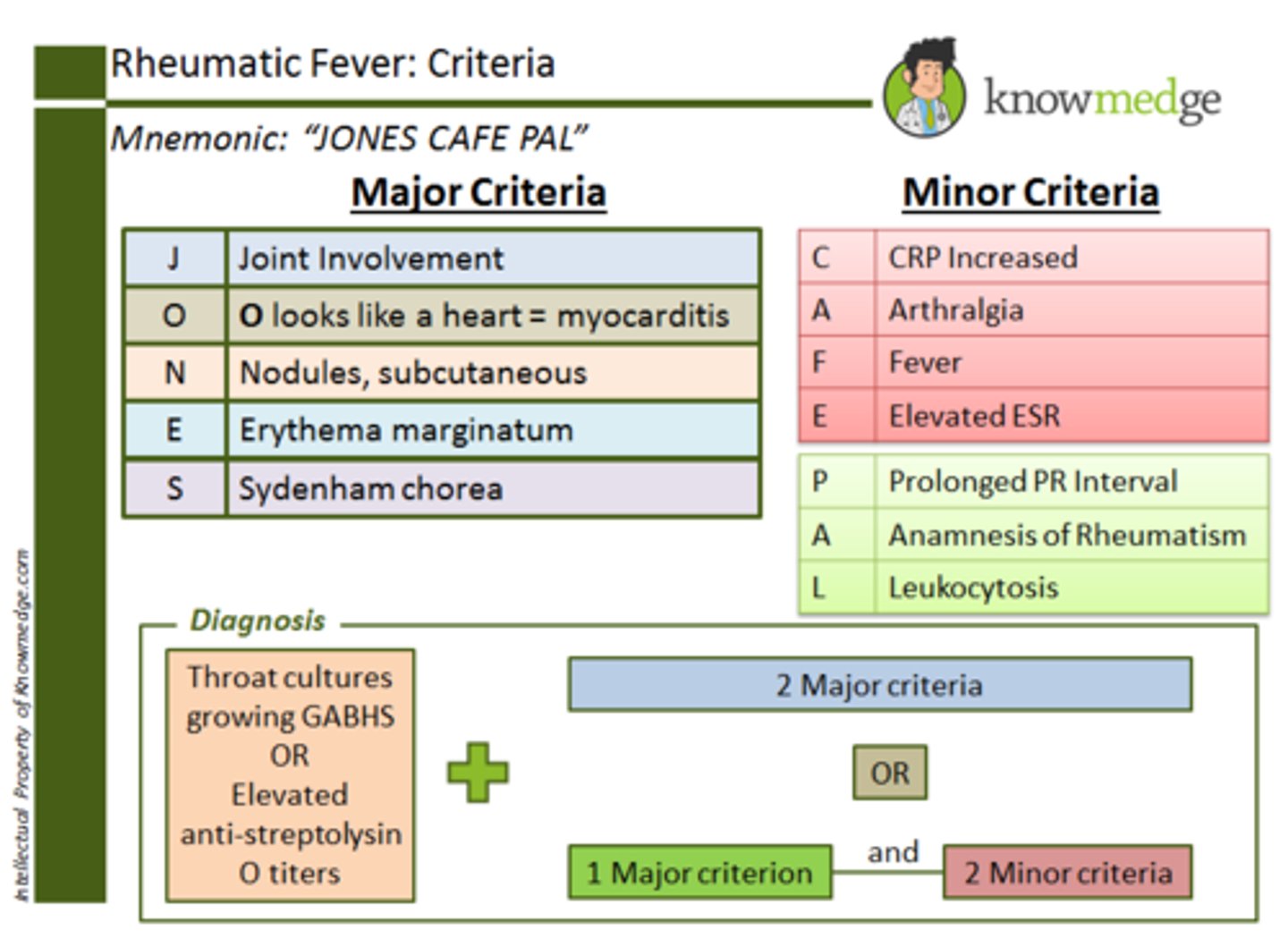
Diagnosis of Rheumatic fever
2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor
Jones Criteria
Polyarthritis (joints)
Carditis (<3)
Nodules subcutaneous
Erythema marginatum
Sydenham chorea
Kawasaki disease
Red Disease
- red sclera
- dry cracked lips
- red tongue
- red palms and soles (sloughing of skin)
- red conjunctiva
high fever for 5 days will not be touches by anything
Treatment of Kawasaki Disease
IVIG → Intravenous immunoglobulin in acute phase
- Help with inflammation
- Typically give once and fever will stop
ASA 80-100 mg/kg/day for fever
- High doses of aspirin when have fever
- Once fever resolves → 3-5 mg/kg/day as an antiplatelet
What labs with kawasaki
ESR and CRP will be elevated
- ECHO to monitor vessels in heart
IVIG and live vaccines
no live vaccines for 1 year following IVIG
Kawasaki disease etiolgoy
Acute systemic vasculitis
- can lead to MI and aneurysms if untreated
Heart Rates
80-150 Infant
70-110 Toddler
65-110 Preschool
60-95 School age
55-85 adolescents
BP
Systolic BP Diastolic BP
(mm Hg) (mmHg)
65-100 45-65
90-105 55-70
95-110 60-75
100-120 60-75
110-125 65-85
Where is apex located
4th ICS under 7
5th ICS after 7
What allergies to assess for prior to cardiac cath
- shellfish
- iodine
Family education with Kawasaki
- S/S of aspirin toxicity → HA, confusion, dizziness, tinnitus
- No NSAIDs when on aspirin therapy
- No live vaccines after IVIG for 11 months