Ch 20 Pregnancy, Development, and Lactation
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
erection results from a ___ reflex triggered by sexual stimuli
parasympathetic
erection occurs when more blood enters the penis via the ___ than leaves it via the ___
enters via arteries
leaves via veins
hydraulic pressure
more blood enters the penis than leaves it
What is copulation?
act of breeding
What is ejaculation?
Reflex expulsion of sperm from male reproductive tract
What is the 1st stage of ejaculation?
emission - movement of sperm from epididymis & fluid from accessory repro glands into urethra
What is the 2nd stages of ejaculation?
expulsion - rhythmic contractions around urethra that pump semen
Where in the female reproductive tract does sperm deposit from ejaculation?
- typically upper portion of the vagina
- pigs and horses - directly into the uterus
How does spermatozoa get transported to oviducts?
mainly by contractions of the uterus and oviducts, action of cilia in oviducts, and oxytocin
What is capacitation?
process sperm undergo in the female reproductive tract that increases their fertility before contact w/ ovum
What changes occur during capacitation?
ion and metabolic rates changes in cells, exposure of digestive enzymes on acrosome
acrosome
digestive enzyme containing caplike structure that covers head of spermatozoa
What is fertilization?
physical entry of the head of a spermatozoa into an ovum
corona radiata
layers of cumulus cells from the follicle
zona pellucida
thick, gel-like membrane that surrounds the ovum’s cell membrane
What is a zygote?
fertilized ovum
What is the male pronucleus?
sperm nucleus, after fertilization, but before ovum & sperm nuclei come together
What is the female pronucleus?
nucleus of a fertilized ovum, before ovum & sperm nuclei come together
What is cleavage?
process of very rapid cell division after an ovum has been fertilized, rapid increase of cells, but cell stays same size
How does the zygote move into uterus?
delicate muscle contraction and cilia movements slowly and gently propel zygote down oviduct and toward uterus
What happens during morula stage of zygote development?
solid mass of cells, few days after fertilization, resembles a raspberry
What happens during blastocyst stage of zygote development?
ready for implantation in uterus, shaped like tiny hollow ball of cells with a "bump" on the side
What is implantation?
means by which the blastocyst makes itself a home by embedding itself in the endometrium of the uterus
multiparous species implantation
multiple blastocsyts randomly space themselves along the horns & body of the uterus as they implant
What is an embryo?
developing offspring during first trimester
Described the structure of placenta
multilayered, fluid filled, membranous sac that develops around embryo and is connected by the umbilical cord
Name the fluid filled sacs of placenta
amniotic sac
allantoic sac
What is the amniotic sac?
the fluid-filled sac that contains and protects a developing fetus
What is the allantoic sac?
fluid filled sac formed by the allantois that surrounds the amniotic sac
What is charion?
outer most layer of placenta, attaches to the uterine lining, linked to fetus by umbilical cord
What do the umbilical arteries do?
carry waste filled, deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta
What does the umbilical vein do?
carries nutrient rich, oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
What is the urachus?
tube in umbilical cord that drains urine from the fetus's urinary bladder into the allantioic sac of the placenta
Where do the fetal and maternal blood vessels intertwine?
where the chorion attaches to the lining of the uterus
What are the four types of placental attachment?
diffuse
cotyledonary
zonary
discoid
Describe diffuse placental attachment
attachment sites are spread diffusely over surface of placenta
detaches easily
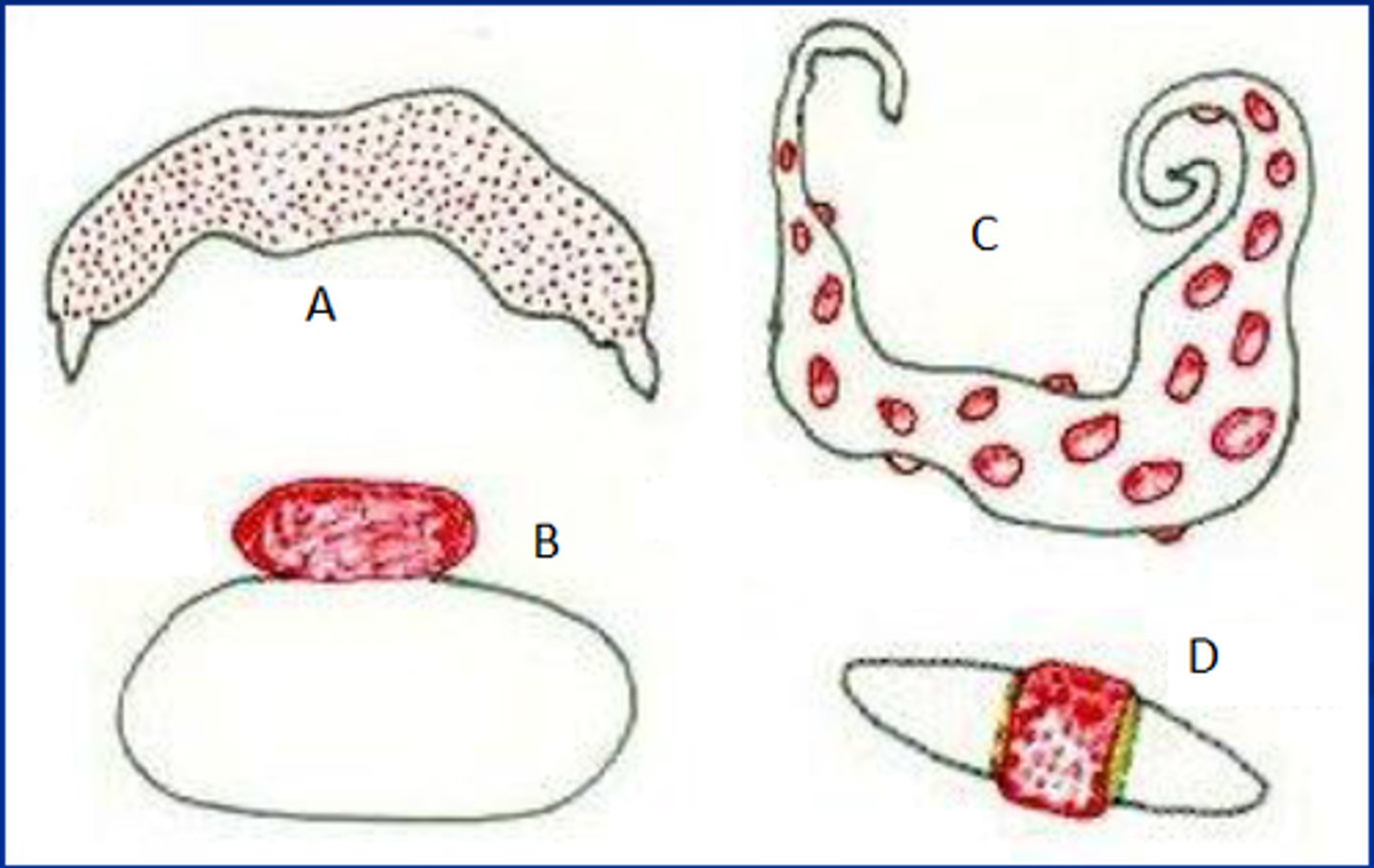
diffuse placental attachment animals
horses, pigs, camelids
Describe a cotyledonary placental attachment
most complicated
attachment site are small, discrete and numerous (placentome)
sometimes doesn't detach completely
cotyledonary placental attachment animals
ruminants (cattle, sheep, goats)
Describe zonary placental attachment.
placenta attaches to uterus in a belt shaped zone that encircles the placenta
detaches easily
zonary placental attachment. animals
dogs
cats
Describe discoid placental attachment
single, discrete, disc shaped area of attachment
Describe discoid placental attachment animals
humans
primates
rabbits
many rodents
What is gestation period?
the time from fertilization of the ovum to delivery of the newborn
trimesters
gestation divided into 3 often unequal segments
What is the first trimester?
period of embryo - organizing and developing of placenta
What is the second trimester?
fetal development period, when fetus starts taking shape - body tissues, organs and systems develop during this period
What is the third trimester?
period of fetal growth, fetus grows dramatically preparing to transition from a parasitic to a free living existence
What is parturition?
the birth process
How does the blood flow change after birth?
foramen ovale and ductus arterious must close fairly quickly
What is relaxin?
hormone released by placenta late in pregnancy
what does relaxin do
helps relax ligaments in bones around the birth canal to ease the passage of the newborn
What are the 3 stage of labor?
uterine contractions
delivery of newborn
delivery of placenta
uterine contractions
myometrium (muscle layer of uterus) contracts as cervix relaxes & dilates
delivery of newborn
combo of strong uterine & abdominal muscle contractions
rupture of amniotic & allantoic sacs of placenta
delivery of placenta
placenta separates from the wall of the uterus
expelled by weaker uterine contractions
What is involution of the uterus?
process of reduction in size of uterus and return to non-pregnant state
mammary glands
specialized skin glands
produce colostrum & milk
Where are the mammary glands located in dog, cat, swine?
inguinal, abdominal & thoracic region
Where are the mammary glands located in cattle, horse?
inguinal region
Number of mammary glands in goats, horses, sheep
2
Number of mammary glands in cattle
4
Number of mammary glands in cats & dogs
10
4 quarters in cow udder
each quarter is different than the other 3
have their own milk-secreting systems & ducts leading down to their own teats
mastitis
infection of mammary gland
What is mammary alveoli?
milk secreting units of mammary gland, arranged like clusters of grapes around alveolar duct
What is the mammary gland sinus?
located just dorsal to the teat, large space in mammary gland, large milk ducts empty into it
What is the teat sinus?
large space within the teat of the cow that fills with milk when milk let down occurs, looks like upside down pear
What is the streak canal?
passageway at the tip of the teat of the cow that carries milk from the teat sinus outside the body
What hormones promote mammary development?
prolactin
growth hormone
estrogen
progesterone
thyroid-stimulating hormone
adrenocorticotropic hormone
directly encourage mammary gland development
prolactin
growth hormone
stimulate ovaries to produce estrogen & progesterone during each heat cycle
follicle stimulating hormone FSH
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
encourage alveoli & duct systems of mammary glands to develop
estrogen
progesterone
influence process indirectly thru target organs (thyroid gland & adrenal cortex)
thyroid-stimulating hormone
adrenocorticotropic hormone
What is colostrum?
initial secretion of the mammary gland before milk is produced
What is colostrum made of?
rich in nutrients, has a laxative effect, contain antibodies
What is meconium?
dark, tarry material in intestine of newborn animal, first feces passed
What is the most critical role of colostrum?
passive immunity
What is lactation?
process of milk production
What is the key to continuation of lactation?
physical stimulation of the teat or nipple, combined with regular removal of milk
What is involution of mammary gland?
"drying up" of the mammary glands
What is milk let-down?
The sudden expulsion of milk after proper stimulation