Astrophysics
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the main difference between a scalar and a vector quantity?
A scalar has only magnitude, while a vector has both magnitude and direction.
Classify the following as scalar or vector: speed, distance, velocity, displacement, acceleration.
Speed - scalar, distance - scalar, velocity - vector, displacement - vector, acceleration - vector.
An athlete runs two full laps around a 400 m track. What is their displacement at the end?
0 m
A hiker walks 3 km north, then 2 km south. What is their total distance? What is their displacement?
Distance = 5 km, Displacement = 1 km north
A tourist explores 10 km around a city and finishes at their hotel. What is their displacement?
0 km
A dog runs 60 m in 12 s. What is its average speed?
5 m/s
Convert 54 km/h into m/s.
15 m/s
A train travels 150 km in 2.5 h. What is its average speed in km/h?
60 km/h
On a road trip, the car drives 90 km in 1.5 h, then waits 30 minutes before continuing another 30 km in 0.5 h. What is the average speed of the entire trip?
48 km/h
What is the difference between instantaneous and average speed?
Instantaneous is the speed at an exact moment of time, while the average is the entire journey.
If a runner covers 100 m in 20 s, what is their average speed?
5 m/s
A car travels 500 m east in 20 seconds. What is its velocity?
25 m/s east
Two cyclists ride at 10 km/h, one north and one south. Do they have the same velocity? Why or why not?
No, because their directions are different.
A runner speeds up from 5 m/s to 9 m/s in 2 s. What is their acceleration?
2 m/s²
A skateboarder slows from 10 m/s to 4 m/s over 3 s. What is their acceleration?
-2 m/s²
A motorbike accelerates uniformly from rest to 28 m/s in 7 s. Find its acceleration.
4 m/s²
What is the acceleration due to gravity on Earth?
9.81 m/s²
After falling freely for 3 seconds, how fast is an object moving?
About 29.4 m/s downward
Why does a parachute increase air resistance?
A larger surface area increases drag, reducing acceleration until terminal velocity is reached.
On a distance-time graph, what does a flat line mean?
The object has stopped
On a distance-time graph, what does a steeper gradient mean?
A higher speed
On a speed-time graph, what does the gradient represent?
Acceleration
On a speed-time graph, what does the area under the curve represent?
Distance travelled
On a displacement-time graph, how would you show that an object has returned to its starting position?
The line ends back at zero displacement
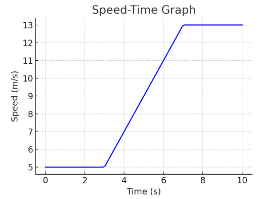
What is the speed at 2 seconds?
5m/s
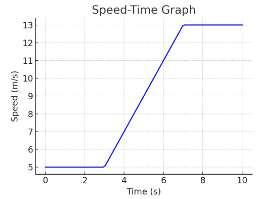
Calculate the acceleration during the increasing section
(13-5)(7-3) = 2m/s²
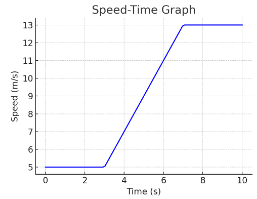
What is the total distance travelled after 10 s?
0–3 s: 5×3=15
3-7 s ((5+13)/2)×4 = 37
7–10 s: 13×3=39
Total = 15 + 36 + 39 = 90 m
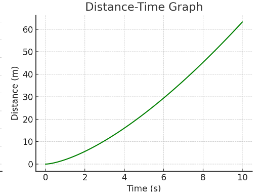
Is the object moving at constant speed?
No — the graph is curved, not straight.
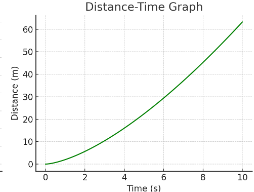
How can you tell the speed is changing?
The slope (speed) increases as time increases.
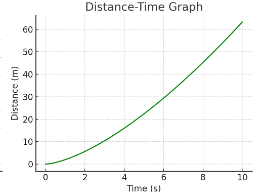
What does the curve’s steepness represent?
The gradient of the line = speed.
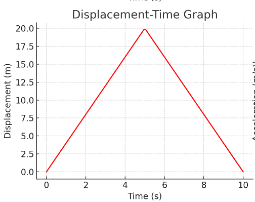
What happens between 0–5 s?
It moves away from the start at a constant speed (slope = 4 m/s).
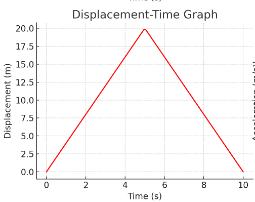
What happens between 5–10 s?
It moves away from the start at a constant speed (slope = -4 m/s).
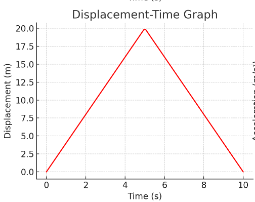
Did the object return to its starting position?
Yes, because final displacement = 0.
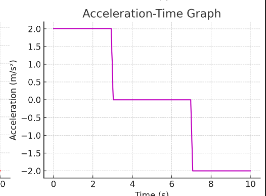
What is the acceleration at t=2 st = 2\text{ s}t=2 s?
+2 m/s²
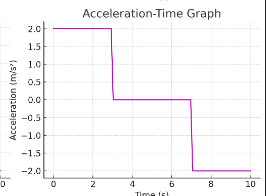
When is the object moving with uniform velocity?
Between 3–7 s(acceleration = 0).
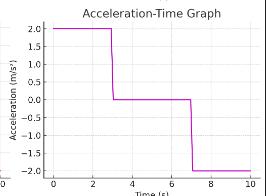
Calculate the change in velocity between 0–3 s
Δv = a × t = 2 × 3 = 6m/s
What is terminal velocity?
The constant speed a falling object reaches when air resistance balances gravity.
State Newton’s First Law of Motion
An object at rest or in motion remains at rest or in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
What is the difference between inertia and momentum?
Inertia is an object's resistance to changes in its motion, while momentum is the quantity of motion an object has due to its mass and velocity.
State Newton’s Second Law of Motion
F = ma
Explain the relationship between mass or acceleration and force.
The greater the mass or acceleration, the greater the force needed.
Explain the relationship between mass and acceleration
With the same amount of force is applied to two different objects, the one with the greater mass has lower acceleration.
State Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
What is the difference between weight and mass.
Mass is the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location, while weight is the force exerted on that mass by gravity and varies with the strength of the gravitational field.
Name three contact forces
Push (compression)
Pull (tension)
Friction (acts in the opposite direction of motion)
Name three non-contact forces
Gravitational
Electromagnetic
Strong and weak nuclear force
Static friction
Friction which is experienced when an object is placed on a surface
Kinetic friction
Due to the movement of an object on a surface
State Kepler’s First Law
Each planet's orbit is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci
State Kepler’s Second Law
The area from one time to another time is equal to another area with the same time interval
State Kepler’s Third Law
“The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major of its axis” (T² = a3)
Geostationary orbit
Satellites travel in the same direction and at the same rate as Earth is spinning. Therefore they are always above the same place on Earth.
Geostationary satellite examples
Communications, GPS, TV.
Polar orbit
Satellites travel north to south, crossing over both poles. Their orbit is fixed in space as they travel, the Earth rotates inside their orbit.
Polar satellite examples
Weather forecasting, military observations.