CA Neurology
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
What are the 3 primary sections of the brain?
Cerebrum (cerebral cortex)
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Is the ascending spinal cord tract sensory or motor? Are the nuclei located anterior or posterior?
Sensory; Posterior
Is the descending spinal cord tract sensory or motor? Are the nuclei located anterior or posterior?
Motor; Anterior
How many cranial nerve pairs compose the peripheral nervous system?
12 pairs
How many spinal nerve pairs compose the peripheral nervous system?
31 pairs
What is the function of the Corticospinal (Pyramidal) Tract?
Mediates voluntary movement and inhibits muscle tone
What disease commonly impacts the Corticospinal (Pyramidal) Tract?
ALS
What is the function of the Basal Ganglia System?
Maintains muscle tone and controls body movements
What diseases commonly impact the Basal Ganglia System?
Parkinson's Disease, Huntington's Diseases, Tourette Syndrome
What is the function of the Cerebellar System?
Coordinates motor activity, balance, and posture
What diseases commonly impact the Cerebellar System?
Multiple Sclerosis, Ataxia, Astrocytomas
When upper motor neurons are damaged above the crossover in the medulla, motor impairment develops on the _____________ side of the body
Contralateral
When upper motor neurons are damaged below the crossover in the medulla, motor impairment develops on the _____________ side of the body
Ipsilateral
What are the 3 principle motor pathways?
Corticospinal (Pyramidal) Tract
Basal Ganglia System
Cerebellar System
What are the 2 principle sensory pathways?
Spinothalamic Tract
Posterior Columns
What is the function of the Spinothalamic Tract?
Transmits sensations of pain, temperature, and crude touch
What is the function of the Posterior Columns?
Transmit sensations of proprioception, vibratory sense, and fine touch
True or False: In the corticospinal tract, damage or deficit occurs below the level of injury or lesion
True
Hyperreflexia and increased muscle tone is due to a lesion on an ____________ neuron
Upper Motor Neuron
Hyporeflexia, absent reflexes, weakness, paralysis, and decreased muscle tone are due to a lesion on an ____________ neuron
Lower Motor Neuron
What is a dermatome?
A band of skin innervated by the sensory root of a single spinal nerve; Help to localize lesions to a specific spinal cord segment
______ are the most basic unit of sensory and motor function to determine a neurological response
Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTRs)
Deep Tendon Reflexes: Biceps
C5
Deep Tendon Reflexes: Triceps
C7
Deep Tendon Reflexes: Brachioradialis
C6
Deep Tendon Reflexes: Knee
L4
Deep Tendon Reflexes: Ankle
S1
Superficial (Skin) Reflexes: Upper Abdomen
T8
T9
T10
Superficial (Skin) Reflexes: Lower Abdomen
T10
T11
T12
Superficial (Skin) Reflexes: Plantar
L5
S1
Superficial (Skin) Reflexes: Anal
S2
S3
S4

____________ lie in the motor strip of the cerebral cortex. Their axons synapse with motor nuclei in the brainstem and spinal cord
Upper Motor Neurons
____________ have cell bodies in the spinal cord. Their axons transmit impulses through anterior spinal root and spinal nerves into the periphery
Lower Motor Neurons

In UMN lesions, muscle tone ____________ and deep tendon reflexes ____________
Increase; Increase
In LMN lesions, muscle tone ____________ and deep tendon reflexes ____________
Decrease--> leads to weakness/paralysis; Decrease
True or False: Diseases of the basal ganglia and cerebellar system cause paralysis
False
____________ refers to a patient's capacity for arousal or wakefulness. It is determined by the level that patient can be aroused to perform in response to stimuli from the examiner
Level of Consciousness

____________: using normal tone of voice, patient's arousal intact; responds fully & appropriately
Alert
____________: using loud tone of voice, patient appears drowsy but opens eyes and responds then falls asleep
Lethargic

____________: shake patient gently; patient opens eyes but responds slowly, somewhat confused
Obtunded

____________: apply painful stimulus to arouse patient from sleep, verbal responses slow/absent, unresponsive when stimulus ceases
Stuporous
____________: unarousable with eyes closed after repeated painful stimuli, no response to environment
Comatose
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
Personality characteristics
Decision-making
Movement
Recognition of smell
Speech ability-> Broca's area
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
Identify objects
Spatial awareness
Interpretation of pain/touch
Understanding language-> Wernicke's area
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Visual processing
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
Short-term memory
Speech
Musical rhythm
What is Broca's area?
An area in the posterior left frontal lobe-> critical for speech production
What is Wernicke's area?
An area in the posterior left temporal lobe-> critical for understanding speech
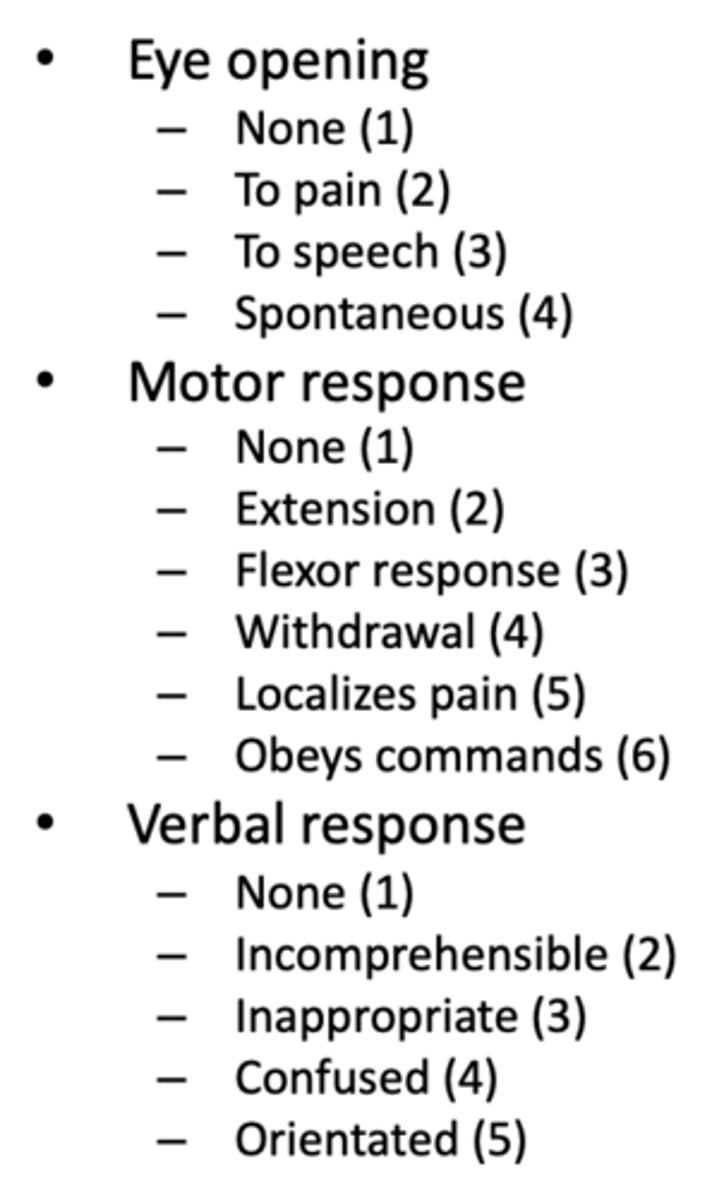
What are the points of the Glasgow Coma Scale?
What is decerebrate posturing?
Extensor response: Hands pushed to sides and body hyper-extended. Arms are stiffly extended, adducted & hyperpronated. Hyperextension of the legs with plantar flexion of the feet.
"extensor = All E's"
What is decorticate posturing?
Flexion response: Hands pulled to chest. Internal rotation and adduction of the arms with flexion of the elbows, wrists & fingers.
"flexor - toward the cord"
What can small or pinpoint pupils indicate?
Response to morphine, heroin, or other narcotics; Pontine lesion
What can fixed, midposition pupils indicate?
Structural damage in the midbrain
What can large pupils indicate?
Response to cocaine, amphetamine, LSD, or other sympathetic nervous system antagonists
What can a unilateral, large pupil indicate?
Herniation of the temporal lobe or CN III infarction
What is Brudzinski sign?
Severe neck stiffness causes a patient's hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed
*Sign of meningitis
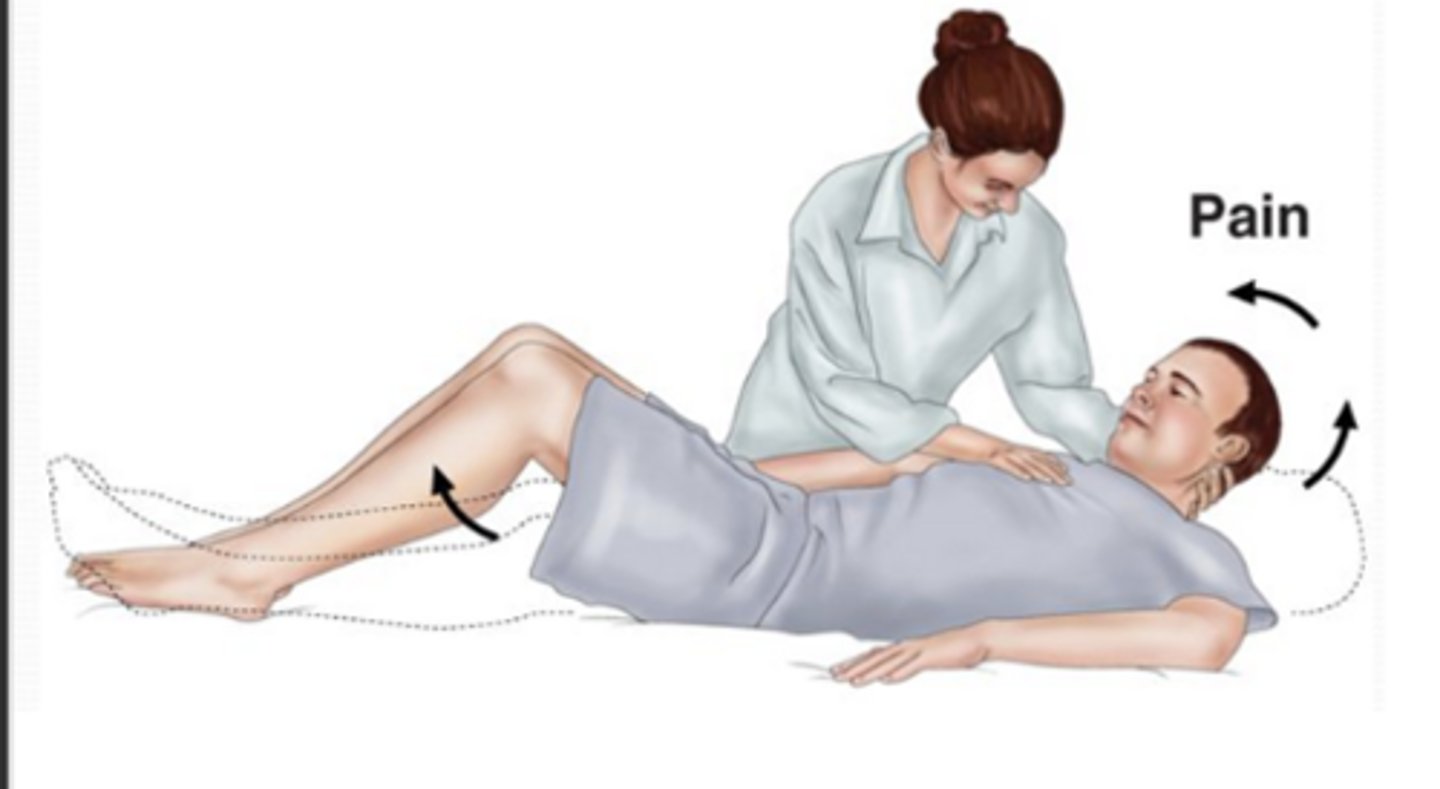
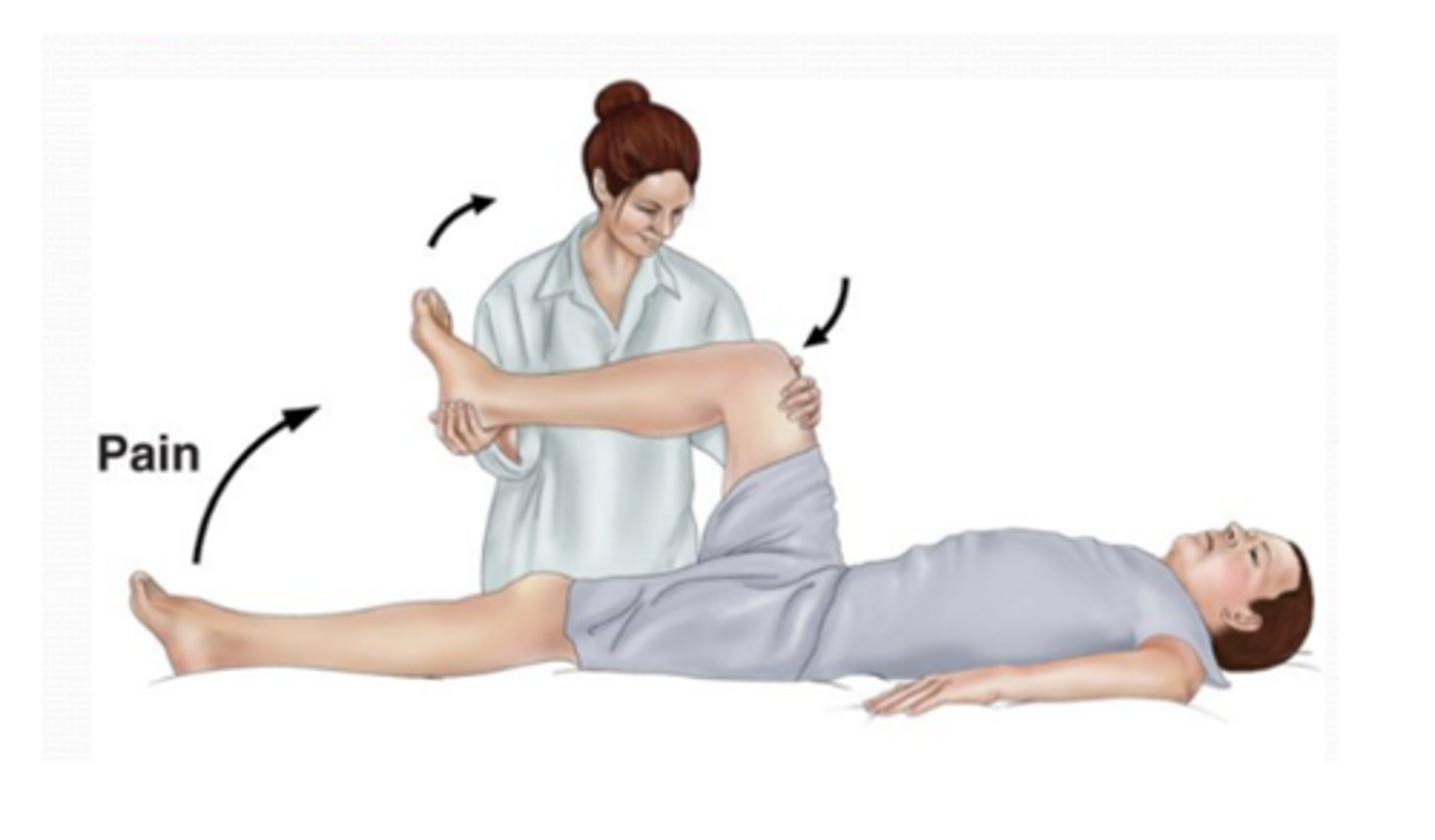
What is Kernig sign?
Patient lies supine, thigh is flexed at right angle, and it hurts to extend leg
*Sign of meningitis
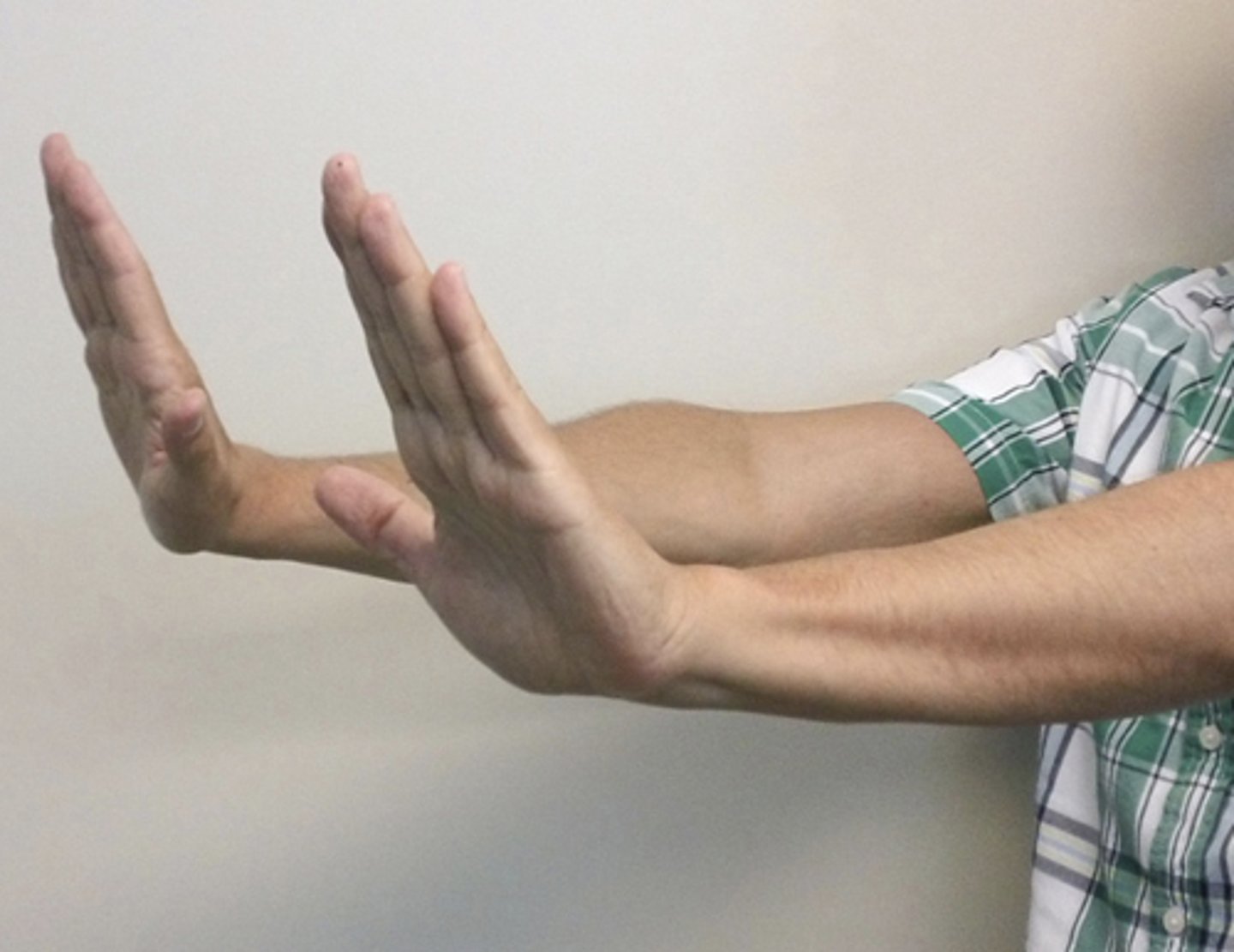
What is asterixis and what does it indicate?
Sudden, brief, nonrhythmic flexion of hands and fingers after asking patient to "stop traffic"
Can indicate hepatic failure encephalopathy, uremic syndrome, or barbiturate overdose

What is Broca's aphasia?
Damage to left frontal lobe; speech is nonfluent but meaningful, patient aware of their difficulty
What is Wernicke's aphasia?
Damage to left temporal lobe; speech is fluent but words are jumbled, obscuring all meaning; patient unaware of their deficit
What is dysarthria?
Difficulty speaking due to weakened or paralyzed muscles of speech
What is aphonia?
Loss of voice
What is dysdiadochokinesis and how is it tested?
Inability to arrest one motion and initiate the opposite
Tested by rapid alternating movements (flip flopping hands against thigh or tapping foot quickly)
What is dysmetria and how is it tested?
The inability to control the distance, speed, and range of motion necessary to perform smoothly coordinated movements
Tested by point-to-point movements (finger to nose or heel to shin)
What is ataxia and how is it tested?
Loss of coordination
Tested with gait assessments
What is the Romberg Test?
Patient stands with feet together and their eyes open, then closes their eyes for 30-60 seconds
What is Pronator Drift?
Patient stands or sits for 30 seconds with arms straight forward, palms up, and eyes closed. Their arms are then tapped briskly downward

In ataxia from ____________ and loss of position sense, vision compensates for sensory loss. During the Romberg test, patients will stand okay with theirs eyes open but will lose balance with eyes closed
Posterior (Dorsal) Column Disease
In ____________ ataxia, patients will have difficulty standing whether eyes are open or closed during the Romberg test
Cerebellar

In ____________, patient will pronate the contralateral forearm and have downward drift with flexion of fingers
Corticospinal Tract (UMN) Lesion

In ____________, patient will have upward drift and overshoots and bounces to correct it (d/t loss of position sense)
Cerebellar Disease
What is spastic hemiparesis?
Flexed arm held close to body while client drags toe of leg or circles it stiffly outward and forward
Due to corticospinal tract lesion in stroke
What causes a scissor gait?
Spinal cord disease causing bilateral lower extremity spasticity (eg, cerebral palsy)
What is a Parkinsonian (propulsive) gait?
Stooped, shuffled, involuntary hastening (festination), arm swing decreased
Seen in basal ganglia defects of Parkinson disease
What is a Steppage gait?
The hip and knee are elevated excessively high to lift the plantar flexed foot off the ground
Seen in foot drop, usually secondary to a LMN lesion causing anterior tibialis weakness
What gait occurs with Cerebellar Ataxia?
Staggering, unsteady, wide based gait
What gait occurs with Sensory Ataxia?
Unsteady, wide based gait with double tapping sound (throwing heels then toes forward)
Seen in loss of position sense in legs (w/ polyneuropathy or posterior column disease)
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve I?
Sinusitis, smoking, aging, cocaine use, Parkinson disease
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve II?
Papilloedema, glaucoma, stroke, retinal emboli, optic neuritis, pituitary tumor
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve II + III?
Anisocoria (unequal pupils) d/t intracranial hemorrhage, transtentorial herniation (if comatose), Horner syndrome
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve III, IV, + VI?
Nystagmus, ptosis (drooping of upper eyelids), diplopia, astigmatism, myasthenia gravis, graves disease, Horner syndrome, cerebellar disease
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve V?
Stroke, CNS lesions, trigeminal neuralgia, acoustic neuroma
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve VII?
Stroke, bells palsy
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve VIII?
Cerumen impaction, otitis media, Meniere's disease, aging
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve IX + X?
Pharyngeal weakness
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve V, VII, X, + XII?
Aphonia (loss of voice) d/t vocal cord paralysis, dysarthria (poor articulation) d/t cerebellar disease, aphasia
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve XI?
Trapezius atrophy d/t peripheral nerve disorder, bilateral weakness of sternocleidomastoids
What may cause abnormal function of Cranial Nerve XII?
Cortical lesion, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), polio
What is a nystagmus?
Involuntary eye movement that may be horizontal, vertical (midbrain), rotary, or mixed
Can be a sign of CNS disease such as MS, encephalitis, head trauma, brain tumor, or cerebellar disease
True or False: Nystagmus usually occurs in the direction of the diseases side
True
What are the 3 types of tremors and what causes them?
Resting (eg, pill-rolling tremor of parkinson disease)
Postural (eg, benign essential/familial tremor)
Intention (eg, cerebellar disease, multiple sclerosis)
What 5 involuntary movements might occur with neurological disease?
Oral-facial dyskinesias (eg, tardive dyskinesia)
Tics (eg, tourette syndrome)
Dystonia (eg, torticollis)
Athetosis (eg, cerebral palsy)
Chorea (eg, huntington disease)
What is atrophy?
Loss of muscle bulk or wasting; results from disease of PNS (eg, DM neuropathy) or diseases of muscles themselves
Fasciculation with atrophy results from a ___________
LMN lesion
What is Pseudohypertrophy?
Increased bulk with diminished strength (eg, Duchenne muscular dystrophy)
What is spasticity? What is it caused by?
Increased tone--> rate-dependent, greater with rapid movement
Caused by UMN lesion or corticospinal tract lesion
What is rigidity? What is it caused by?
Increased resistance--> not rate-dependent
Caused by lesion in the basal ganglia
What is flaccidity? What is it caused by?
Marked floppiness
Caused by LMN lesion
What is paratonia? What is it caused by?
Sudden changes in tone with passive ROM
Caused by lesion in both hemispheres, usually frontal lobes
What is the scale for grading muscle strength?
0 = No contraction noted
1 = Barely detectable contraction
2 = Active movement w/ gravity eliminated
3 = Active movement against gravity
4 = Active mvmt against gravity & some resistance
5 = Active movement against full resistance w/o evident fatigue - This is NORMAL strength