Anatomy & Physiology - Muscular System Vocabulary (copy)
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
A Band
Situated on either side of the H zone of a muscle sarcomere, that is the area where contraction and relaxation of the muscle occurs, where sarcomeres overlap during muscle movements
Involuntary Muscle
a muscle that contracts without conscious control. Examples include the smooth and cardiac muscles.
Transverse (T) Tubule
Extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells.
Fascicle
a group of muscle fibers is “bundled” as a unit within the whole muscle.
Tropomyosin-troponin Complex
regulates skeletal muscle by blocking the myosin binding site of actin in the absence of Ca2+.
Acetylcholine
the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system. This can stimulate a response or block a response and thus can have excitatory or inhibitory effects.
Isometric Contraction
a muscle contraction without motion. They are used to stabilize a joint, such as when a weight is held at waist level neither raising nor lowering it.
Sarcolemma
the fine transparent tubular sheath which envelops the fibers of skeletal muscles. It acts as a barrier between the extracellular and intracellular compartments, defining the individual muscle fiber from its surroundings.
Acetylcholine Receptor
an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
Isotonic Contraction
maintain constant tension in the muscle as the muscle changes length.
Sarcomere
the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber. Each one is composed of two main protein filaments—actin and myosin—which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction.
Acetylcholinesterace
an enzyme found in the synapse between nerve cells and muscle cells. It springs into action soon after a signal is passed, breaking down the acetylcholine. This effectively stops the signal, allowing the pieces to be recycled and rebuilt into new neurotransmitters for the next message.
Latent Period
a short delay (1-2 msec) from the time when the action potential reaches the muscle until tension can be observed in the muscle.
Sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells.
Actin
protein that is an important contributor to the contractile property of muscle and other cells.
Length-tension relationship
In general, as muscles shorten, they are able to generate greater amounts of tension. However, shortening a muscle beyond a certain point will not longer generate any increases in tension.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum that is important in transmitting the electrical impulse as well as in the storage of calcium ions.
Aerobic Metabolism
occurs when the body produces energy (in the form of ATP) using oxygen. Fats and carbohydrates are the main fuels in this.
Motor end plate
a chemical synapse between the terminal part of the motor neuron and the target muscle.
Sliding Filament Theory
the explanation for how muscles contract to produce force. The actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres of muscle fibers bind to create cross-bridges and slide past one another, creating a contraction.
Anaerobic Metabolism
ATP production without oxygen (or in the absence of oxygen), occurs by direct phosphate transfer from molecules such as glycolytic intermediates or creatine phosphate (CrP), to ADP forming ATP. Glucose is the only fuel for anaerobic metabolism.
Motor Neuron
a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to control muscles and glands.
Skeletal Muscle
The functions of this muscle include producing movement, maintaining body posture, controlling body temperature, and stabilizing joints.
Aponeurosis
a thin sheath of connective tissue that helps connect your muscles to your bones. Aponeuroses are similar to tendons, but is a thin sheet of connective tissue.
Motor Unit
The combination of an individual motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers that it innervates.
Spatial Summation
signals coming from multiple simultaneous inputs.
Asynchronous Firing of Motor Units
one contracts and then a fraction of a second later another contracts before the first has time to relax and then another fires and so on.This allows for smooth muscle contraction.
Multiunit Smooth Muscle
differs from single-unit in that each smooth-muscle cell receives its synaptic input. This gives multi-unit smooth muscle much finer control. It is found in the airways of the lungs, large arteries, and ciliary muscles of the eye.
Striations
repeating A and I bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of myofibrils.
Muscle Fiber
Each skeletal muscle fiber is a single cylindrical muscle cell. An individual skeletal muscle may be made up of hundreds, or even thousands, of these bundled together and wrapped in a connective tissue covering.
Synaptic Cleft
a small gap between the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
Cardiac Muscle
makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. It is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle.
Muscle Tone (Tonus)
the natural and continuous slight contraction of a muscle that gives resistance to passive stretching during relaxation.
Synaptic Knob
Also called a bouton, is a relay point at the tip of a transmitting neuron in the brain.
Glycogen
the stored form of glucose that's made up of many connected glucose molecules.
Twitch Contraction
the contractile response of a single muscle fiber to a single stimulus from a motor neuron.
Glycogen-Lactic Acid System
uses glucose stored in the muscles as glycogen during anaerobic metabolism to produce energy quickly. Lactic acid is produced as an end product.
Visceral(Single Unit) Smooth Muscle
produces slow, steady contractions that allow substances, such as food in the digestive tract, to move through the body.
I Band
it is called the light band that contains only the thin filament (actin).
Recruitment
a measure of how many motor neurons are activated in a particular muscle.
Voluntary Muscle
skeletal muscles of the body that attach to bones and control movement of the limbs, head, neck, and body under conscious control.
Incomplete Tetany
when the muscle fibers do not completely relax before the next stimulus because they are being stimulated at a fast rate; however there is a partial relaxation of the muscle fibers between the twitches.
Innervation
The distribution or supply of nerves to a part.
Refractory Period
a state of recovery that occurs after a neuron has fired an action potential. During this period, another action potential cannot be easily produced.
Wave Summation
occurs when stimulations are delivered to a muscle fiber faster than it is able to completely relax.
Intercalated Disks
gap junctions that link adjacent cardiac muscles so that electrical impulses can travel between cells and causes to contract almost simultaneously.
Relaxation Phase Z Line
The Z-lines are closer during contraction because actin and myosin interaction generates cross-bridges, which slide the myofilaments over each other. During relaxation, myosin and actin detach and the Z-lines slide back apart.
Agonist (Prime Mover)
These muscles cause the movement to occur. They are also referred to as prime movers since they are the muscles that are primarily responsible for generating the movement.
Gracilis
a slender superficial muscle of the inner thigh
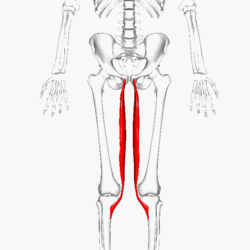
Semimembranosus
a muscle within the posterior compartment of the thigh.
Antagonist
These muscles act in opposition to the movement generated by the agonists and are responsible for returning a limb to its initial position.
Hamstrings
any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in between the hip and the knee (from medial to lateral: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris).
Semitendinosus
One of the three muscles that make up the h muscle group, and it is located at the posterior and medial aspect of the thigh. This is so named due to it having a long tendon of insertion.
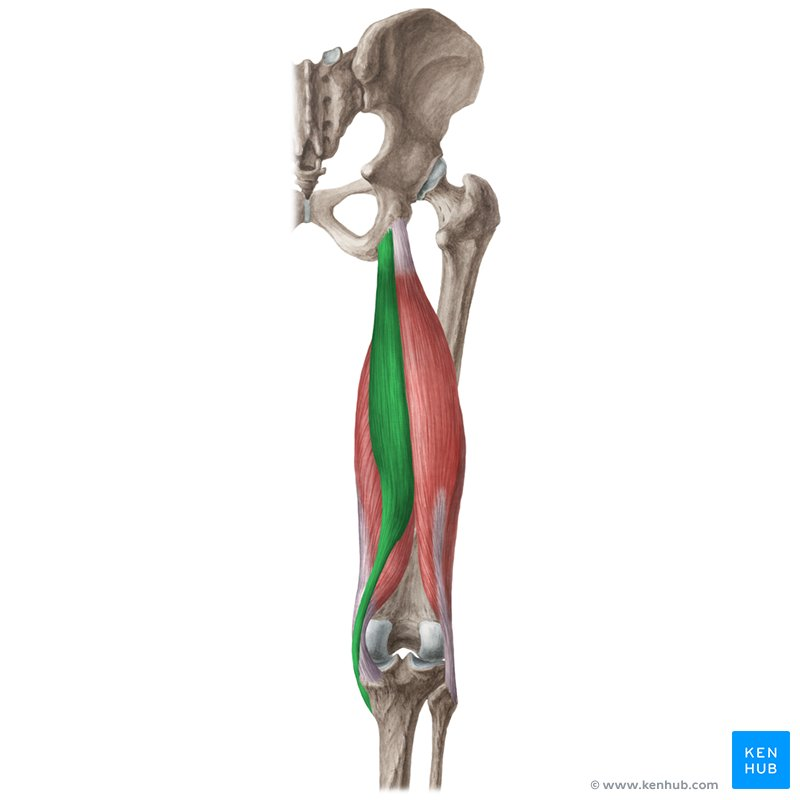
Belly
The widest part of a muscle
Insertion
the place where one end of a muscle is attached to the freely moving bone of its joint.
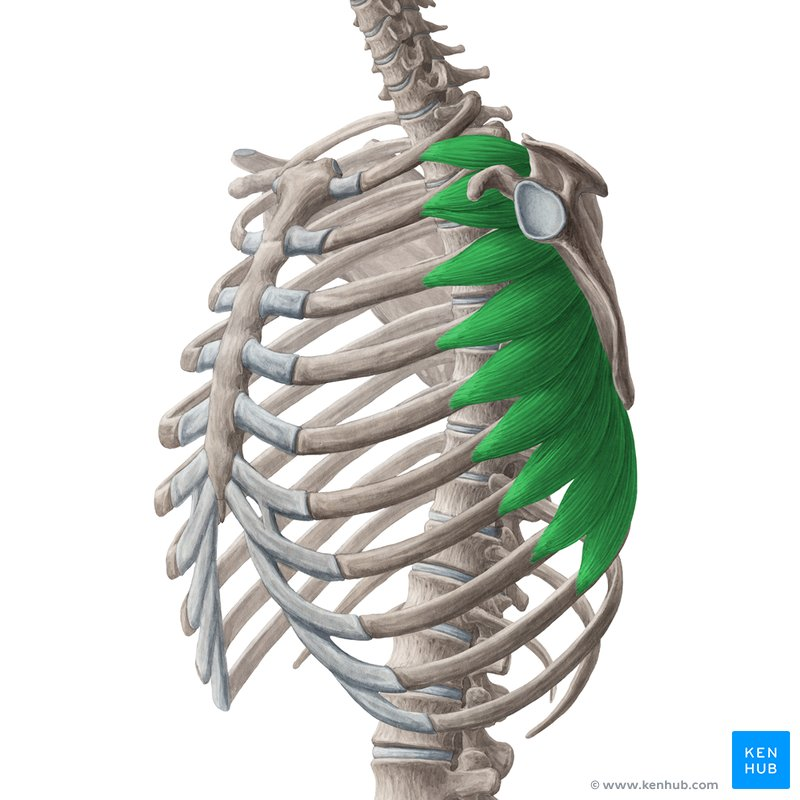
Serratus Anterior
very thin and covers the side of the ribcage. Also called the “boxer” muscle.
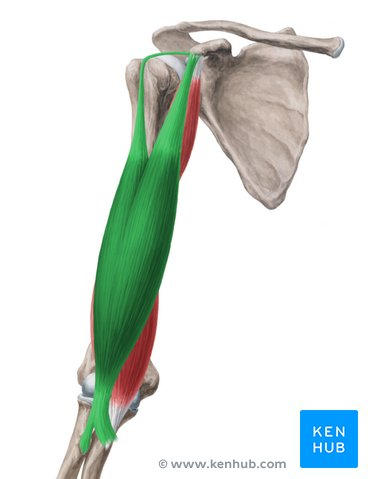
Biceps Brachii
commonly known as the biceps, is a large, thick muscle on the ventral portion of the upper arm.
Latissimus Dorsi
a broad, flat muscle occupying most of the lower posterior thorax. The muscle's primary function is to move the upper extremity, but it is also considered an accessory muscle of respiration.
Sternocleidomastoids
Each of a pair of long muscles that connect the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process of the temporal bone and serve to turn and nod the head.
Biceps Femoris
a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh, and lies in the posterolateral aspect.
Complete Tetany
the stimulus frequency is so high that the relaxation phase disappears completely, contractions become continuous.
Myocyte
A muscle cell
Synaptic Vesicle
small, electron-lucent vesicles that are clustered at presynaptic terminals. They store neurotransmitters and release them by calcium-triggered exocytosis.
Conductivity
Ability to cross space in between neurons.
Myofibril
a cylindrical bundle of contractile filaments within the skeletal muscle cell. These are composed of individual contractile proteins called myofilaments.
Temporal Summation
the effects of impulses received at the same place can add up if the impulses are received in close temporal succession.
Contractility
the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten
Myofilament
threadlike structures that comprise the myofibril inside the muscle cell. There are two main types of myofilaments: thin filaments and thick filaments. In skeletal muscle, these are arranged in a repeating pattern of light and dark bands.