PAS 407 Heart Conduction
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
P wave
- SA node depolarization
- atrial contraction
PR segment
- delay at AV node
QRS complex
- ventrical depolarization
- atrial repolarization
ST segment
- plateau phase between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
T wave
- ventricle repolarization
first phase of cardiac cycle
Passive/Ventricular filling
- heart is in diastole and at "relaxation"
- 80% of blood freely pools into the ventricles
second phase of cardiac cycle
atrial contraction
- remaining 20% of blood contracted into the ventricles by the atria
third phase of cardiac cycle
isovolumetric ventricular contraction
- pressure slowly begins to rise in the ventricles and they start to contract
- the cuspid valves close causing the first heart sound "lub"
fourth phase of the cardiac cycle
ventricular ejection
- pressure is at its highest in the ventricles and blood is ejected into the major vessels the aorta and pulmonary trunk
final phase of the cardiac cycle
ventricular relaxation
- ventricles relax and the semilunar valves close causing the second heart sound "dub"
abnormalities in the ST segment can suggest a ____________
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
inverted T waves is correlated with..
an area of ischemia
peaking T waves
hyperkalemia, early myocardial infarction
ventrilcular fibrillation (V fib)
- random patterns of depolarization/repolarization across different aspects of the ventricular wall
- blood cannot properly be delivered to the major vessels
- In an EKG, no QRS complex can be seen or a wormy or squiggly appearance
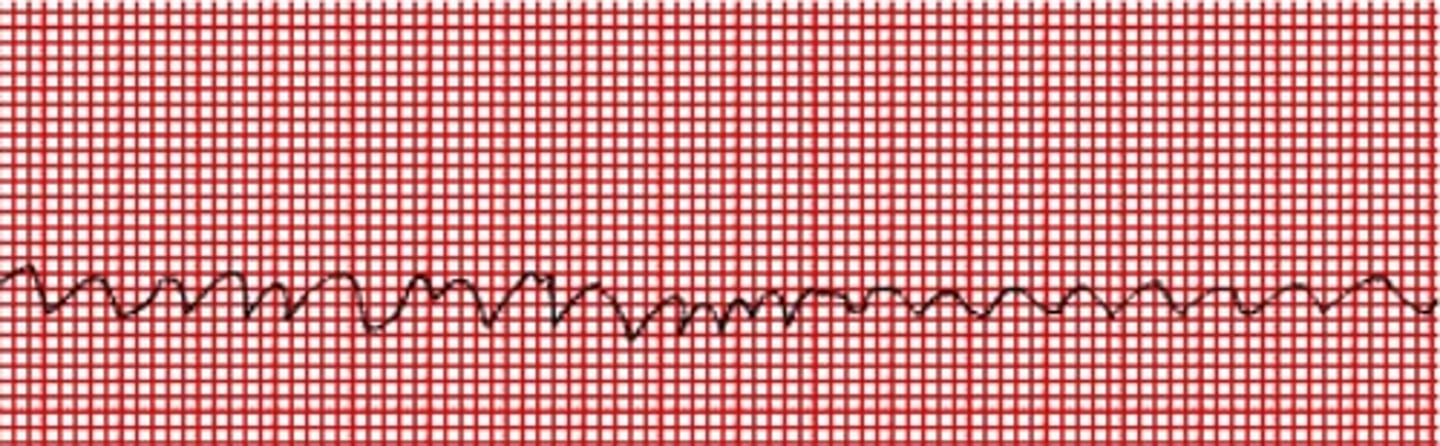
ectopic pacemaker
- areas of excitability that depolarize rapidly other than the SA node
- this can start in the ventricles causing a PVC "premature ventricular contraction"
- EKG, typically no P wave or PR segment