BCFP S01 + S02
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
S01: DNA Structure and Replication; S02: Chromatin
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
List the pyrimidines vs purines
What is the main difference between the 2?
Pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine
Purine: adenine, guanine
Pyrimidines have 1 ring, purines have 2 rings
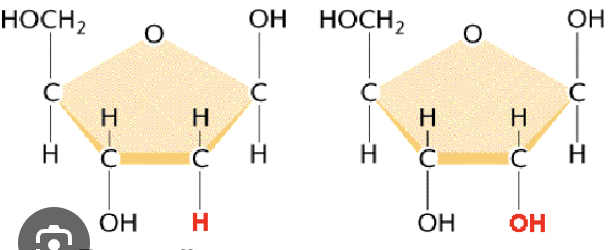
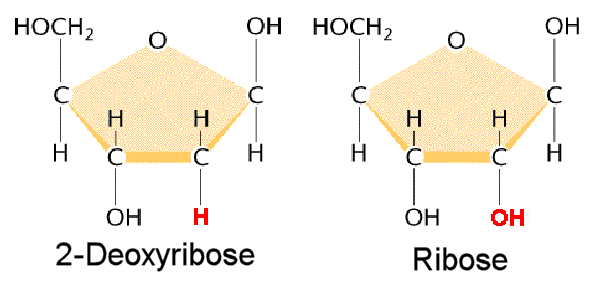
Identify the ribose vs deoxyribose:
Which group on a nucleotide is key for polymerization?
The 3’ OH group
The following are names of _______:
adenosine
guanosine
cytidine
uridine
thymidine
nucleosides
Nucleotide vs nucleoside
Nucleotide: base + sugar + phosphate
Nucleoside: base + sugar
Which bond links the backbone of nucleotides together? What type of bond is it?
Phosphodiester bond - covalent bond
C-G bonds contain ___ H bonds and are (more/less) stable.
A-T bonds contain ___ H bonds and are (more/less) stable.
C-G: 3 bonds; more stable
A-T: 2 bonds; less stable
Which bonds links bases together (A-T and C-G)?
Hydrogen bonds
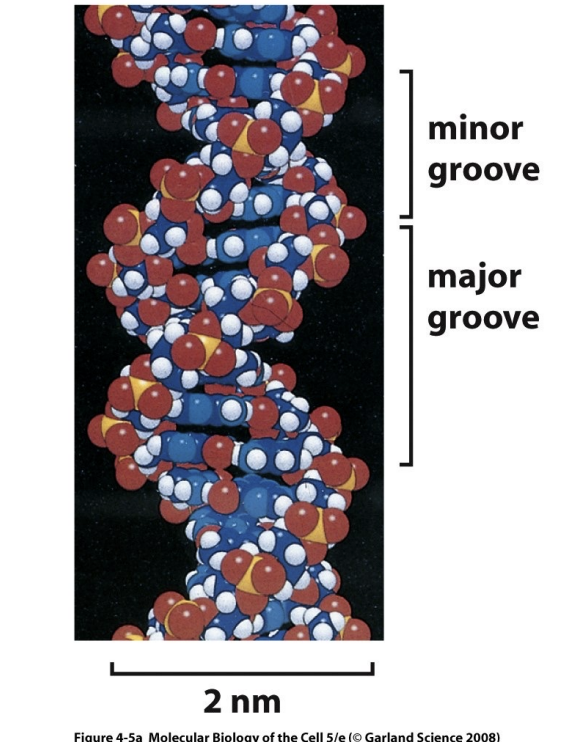
Function of the major groove
Where transcription factors interact with DNA
In phosphodiester bonds, the ___ -OH of one nucleotide attacks the ____ -PO4 group of the next.
3’ OH group
5’ PO4 group
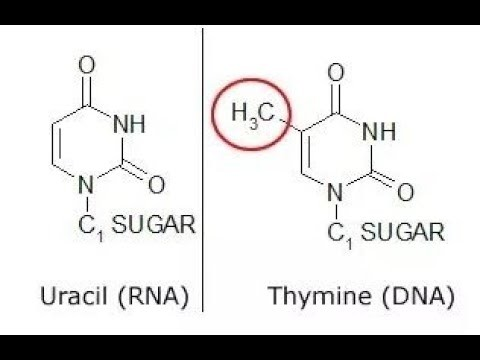
Structural difference between thymine and uracil
Thymine has a methyl group on its 5’ C
RNA is typically found as (shorter/longer), (ss/ds) strands.
shorter
ss
T/F: DNA replication is bidirectional with 1 origin of replication
F: bidirectional with multiple origins of replication
DNA pol II reads in the ______ direction and synthesizes in the ____ direction.
Reads 3’ to 5’
Synthesizes 5’ to 3’
Explain how DNA replication occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction on both strands using Okazaki fragments.
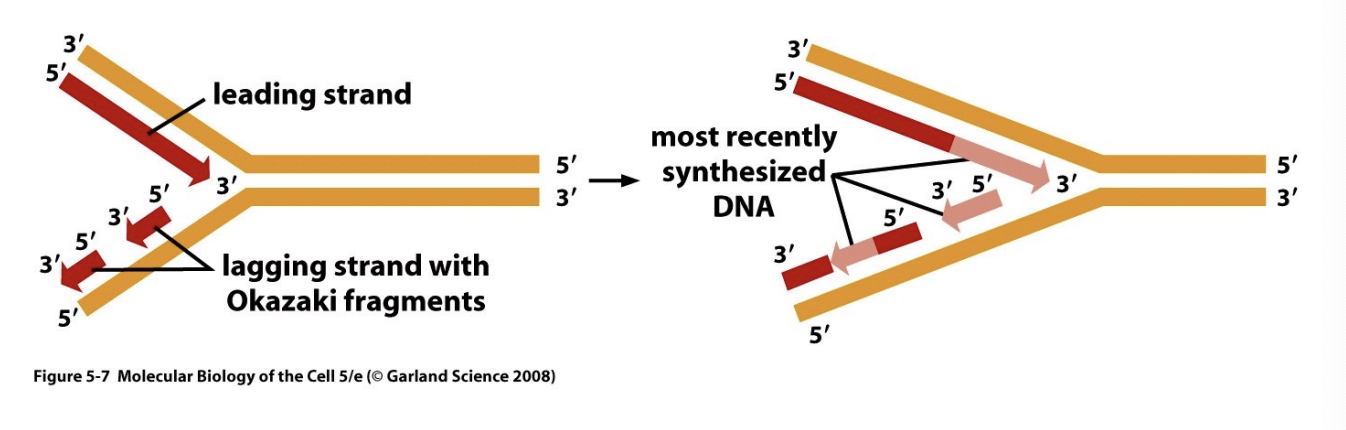
DNA primase:
Function
Directionality
DNA primase lays down an RNA primer in the 5’ to 3’ direction to the newly synthesized strand, since DNA pol needs an free 3’ OH group to build off from
DNA polymerase function
Synthesizes complementary strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction
DNA polymerase 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity
Proofreads and fixes strands in the opposite direction of synthesis
DNA helicase
Motor proteins that hydrolyze ATP to unwind DNA
Replication fork
Which enzyme creates it?
Y shaped region in DNA where it is being unwound
DNA helicase
ss DNA binding proteins
Stabilize the unwound DNA to prevent re-annealing
DNA ligase
Seals “nicks” in DNA after DNA polymerase fills the gaps left by RNA primers
Supercoiling
+ vs - supercoiling
Extra twists on the DNA strand
+ supercoiling: when DNA is overwound, making DNA strands harder to separate
- supercoiling: when DNA is underwound, allowing the helix to open up
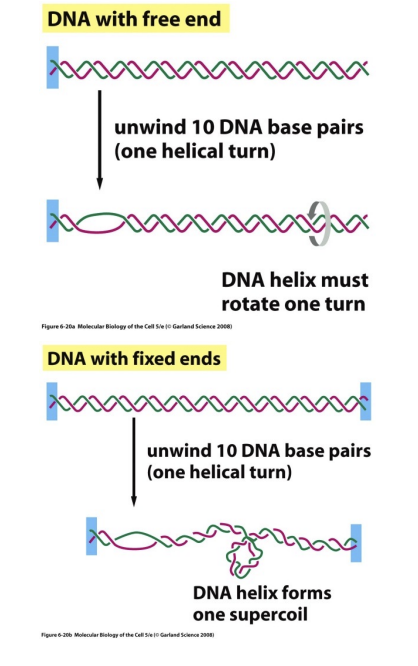
In DNA with free ends, we need to unwind ___ DNA base pairs (aka __ helical turn) to rotate and alleviate the stress.
In DNA with fixed ends (like in our bodies), we need to unwind ___ DNA base pairs to form one ______.
In DNA with free ends, we need to unwind 10 DNA base pairs (aka 1 helical turn) to rotate and alleviate the stress.
In DNA with fixed ends (like in our bodies), we need to unwind 10 DNA base pairs to form one supercoil.
Topoisomerase
Relieves torsional stress (aka supercoiling) in DNA by cleaving bonds
Topoisomerase I vs II
I: breaks one strand and then seals
II: breaks both strands and then seals
______ DNA replication enzymes are clinical targets for anti-bacterials by (enhancing/inhibiting) strand cutting.
topoisomerase
inhibiting
______ DNA replication enzymes are clinical targets for anti-cancer by (enhancing/inhibiting) strand cutting.
Topoisomerase
enhancing
Telomerase is a (DNA/RNA) dependent (DNA/RNA) polymerase that extends _______ repeats to the _____ strand.
Telomerase is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase that extends telomere repeats to the parental strand.
Telomere
Protective repetitive stretches of DNA at the tips
What type of enzyme is telomerase? Explain how it functions.
Reverse transcriptase: contains RNA templates and synthesizes DNA complementary to its own RNA. This gets added to the 3’ of the parental strand so the ends of DNA can be replicated.
End-replication problem
On the end of lagging strand, there is no free 3’ OH group for DNA polymerase to build off of. This would cause the chromosome to shorten a little bit during every replication.
Chromatin = ____ + _____ proteins + _____ proteins
DNA + histone + non histone proteins
List if the following events require mostly euchromatin or heterochromatin:
Transcription
Mitosis
G1/S/G2
Transcription: euchromatin
Mitosis: heterochromatin
G1/S/G2: euchromatin
Nucleosome structure
2 copies of each of the 4 core histone proteins with DNA wrapped around it. Beads are separated via linker DNA.
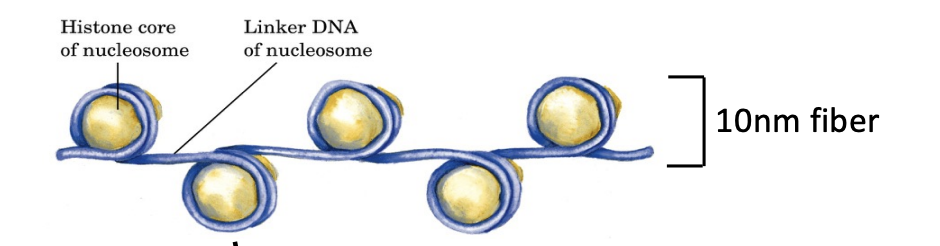
What are the 4 core histones found in nucleosomes?
H2A, H2B, H3, H4
H1 linker histone
Promotes more compact chromatin folding (10 nm → 30 nm fiber)
What are the 2 parts of a histone protein?
The histone fold and the N-terminal tail
The histone fold consists of ___ alpha helices and ___ loops that dimerize with another histone protein. These combine to form a ___mer that forms the bead of the nucleosome.
3 alpha helices and 2 loops
octomer
The N-terminal tail of core histones contain (acidic/basic) proteins that contain AAs like ____ and _____.
basic
lysine, ariginine
The ______ of core histones are the targets of post-translational modifications
N-terminal tails
_____ catalyze acetylation of lysines on core histones.
_____ catalyze deacetylations of lysines on core histones.
HATs (histone acetyltransferases) catalyze acetylation of lysines on core histones.
HDACs (histone deacetylases) catalyze deacetylations of lysines on core histones.
Generally, (acetylation/deacetylation) and (methylation/demethylation) are associated with euchromatin and increased transcriptional activity.
acetylation and demethylation
Acetylation of core histones works by ____ positively charged lysines, which ___ histone interactions with negatively charged DNA and loosens the chromatin.
neutralizing
weakens
_____ catalyze methylation of lysines on core histones.
_____ catalyze demethylations of lysines on core histones.
Histone methyltransferases (HMTs) catalyze methylation of lysines on core histones.
Histone demethylases (HDMs) catalyze demethylations of lysines of core histones.
Lysine acetylation vs methylation net charge changes
Acetylation: lysine + → neutral
Methylation: no net charge change
The histone code explains how _____ proteins are recruited to chromatin when they recognize ________ modifications such as ___ and ____.
The histone code explains how reader proteins are recruited to chromatin when they recognize post-translational modifications such as acetylation and methylation.
______ proteins are responsible for altering local chromatin structure after recruitment.
Reader
T/F: reader proteins recruitment leads to heterochromatin formation
F: depends, can lead to heterochromatin or euchromatin depending on the histone post-translational modification
(Bromodomains/chromo (PHD) domains) recognize acetylated histones.
(Bromodomains/chromo (PHD) domains) recognize methylated histones.
These are both examples of ______.
Bromodomains recognize acetylated histones.
(Chromo (PHD)) domains recognize methylated histones.
reader proteins
Constitutive heterochromatin are found in _______.
centromeric DNA
What are the 3 ways to alter chromatin structure?
Histone post-translational modifications
Chromatin remodeling complexes
Histone variants
Chromatin remodeling complexes
ATPases that disrupt histone-DNA contacts within nucleosomes
2 ways that chromatin remodeling complexes alter histone-DNA contacts
Nucleosome sliding: sliding nucleosomes to expose underlying DNA
Altering DNA-histone interactions (ex: to loosen and expose DNA)
Histone variants
Variants of histones that have specialized effects
Telomeres are (ss/ds) DNA that form a __-loop to _________.
Telomeres are ss DNA that form a t-loop to protect the chromosomes from being mistaken for a ds break that needs to be repaired.
Centromere
Region of chromosomal DNA where sister chromatids connect and kinetochores assemble.
Kinetochore
Protein complex that binds centromeres and acts as an attachment site for microtubules and chromosomal separation in mitosis/meiosis.
Giemsa staining (G-banding) is a (high/low) resolution method of visualizing chromosomes. It can detect (large/small) scale chromosomal features like the ____ of chromosomes.
low resolution
large scale
number
Giemsa staining (G-banding) source material AND staining method
WBCs arrested in metaphase
Stains regions with a higher AT base composition
Metacentric
Submetacentric
Acrocentric
Metacentric: centromere in middle
Submetacentric: centromere slightly closer to one end
Acrocentric: centromere significantly closer to one end
Primary constriction of chromosomes
The centromere, where the sister chromatids are most tightly connected
T/F: sister chromatids are connected along the whole length of a chromosome
T
p vs q arm of chromosome
p: short arm
q: long arm
The human genome is made up of roughly ___% single copy genes and ___% repetitive DNA sequences.
5% single copy genes
95% repetitive DNA sequences
Within the 95% repetitive DNA of a human genome, it can be divided into which 2 categories?
Tandem: arrays of repeated DNA sequences
Dispersed: DNA repeats occuring throughout the genome
Minisatellites vs microsatellite array and repeat lengths
Minisatellite: arrays of 0.1-20 kb, with repeat units of 10-70 bp
Microsatellite: arrays <100 bp long, with repeat units of < 10 bp
Minisatellites are also called ______.
Microsatellites are also called _____.
Mini: VNTRs
Micro: STRPs
Expansion of trinucleotide repeats, present in Huntington’s, myotonic dystrophy, and Fragile X syndrome
Trinucleotide repeat syndromes
Mini/microsatellites are examples of (tandem/dispersed) repeats.
tandem
LINES and SINES are examples of (tandem/dispersed) repeats.
dispersed
Explain what it means that LINES/SINES are retrotransposons.
They can copy and paste themselves elsewhere into DNA.
Explain how LINES are autonomous.
LINE is transcribed into RNA
This RNA encodes a reverse transcriptase that allows them to synthesize their own DNA and insert it elsewhere.
SINES are (autonomous/non-autonomous), which means ______.
non-autonomous
they use LINE elements to form a reverse transcriptase
SINES are ______ bp in length.
LINES are ______ bp in length.
SINES: 80-400 bps
LINES: several kilobases
Much of the human genome variation occurs in the sequence and repeat numbers of _____.
VNTRs (minisatellites) and STRPs (microsatellites)