GI exam 3 Pathology questions
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Cirrhosis
A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency room in a disoriented state. Physical examination reveals signs of poor hygiene and an odor of alcohol, as well as jaundice, splenomegaly, and ascites. The patient has a coarse fl apping tremor of the hands, palmar erythema, and diffuse spider angiomata. The abdomen displays dilated paraumbilical veins. Serum levels of ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin are all mildly elevated. Soon after admission, the patient vomits a large amount of blood. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of hematemesis in this patient?
(A) Acute alcoholic hepatitis
(B) Acute gastritis
(C) Cirrhosis
(D) Hepatic steatosis
(E) Mallory-Weiss tear
Increased portal hydrostatic pressure
For the patient described in Question 1, which of the following pathophysiologic mechanisms is most directly associated with the development of ascites?
(A) Decreased aldosterone secretion
(B) Decreased intravascular volume
(C) Hyperalbuminemia
(D) Increased intravascular oncotic pressure
(E) Increased portal hydrostatic pressure
Gilbert syndrome
An 18-year-old man presents with a 2-week history of yellow skin and sclerae but is otherwise asymptomatic. He recalls a similar episode 2 years previously. His brother also has recurrent jaundice. The serum bilirubin is 5.2 mg/dL, mostly in the unconjugated form. Serum AST and ALT levels are normal, as is the urinalysis. Two weeks later, the jaundice resolves spontaneously. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
(B) Dubin-Johnson syndrome
(C) Gilbert syndrome
(D) Hereditary hemochromatosis
(E) Wilson disease
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
A 48 years old woman has a 3 week history of fatigue and yellow skin and sclerae. Physical examination is unremarkable except for mild jaundice. The serum bilirubin level is 3.7 mg/dL, mostly in the unconjugated form. Liver function tests including serum AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase are normal. The hemoglobin level is 6.0 g/dL. After corticosteroids are administered, the jaundice resolves. Which of the following diseases is the most likely cause of hyperbilirubinemia in this patient
(A) Acute hepatitis B infection
(B) Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
(C) Gallstone in the common bile duct
(D) Primary biliary cirrhosis
(E) Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Acute viral hepatitis A
A 20-year-old woman presents with a 2-week history of fever, malaise, and brown-colored urine. She recently visited Mexico. Physical examination reveals jaundice, mild hepatomegaly, and tenderness in the right upper quadrant. The serum bilirubin is 7.8 mg/dL, with 60% in the conjugated form. Serum levels of AST and ALT are markedly elevated (400 and 392 U/L, respectively). Serum albumin and immunoglobulin levels are normal. Serum IgM anti-hepatitis A virus (anti-HAV) is positive. IgG anti-hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBsAg) antibodies are positive. Anti-hepatitis C virus antibodies are negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Acute viral hepatitis A
(B) Acute viral hepatitis B
(C) Acute viral hepatitis C
(D) Autoimmune hepatitis
(E) Chronic viral hepatitis B
Unconjugated bilirubin
A 3-day-old neonate born after a 32-week gestation develops yellow skin. Physical examination of the infant is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely to be increased in this neonate's serum?
(A) Alanine aminotransferase
(B) Carotene
(C) Conjugated bilirubin
(D) Galactosyltransferase
(E) Unconjugated bilirubin
Acute viral hepatitis
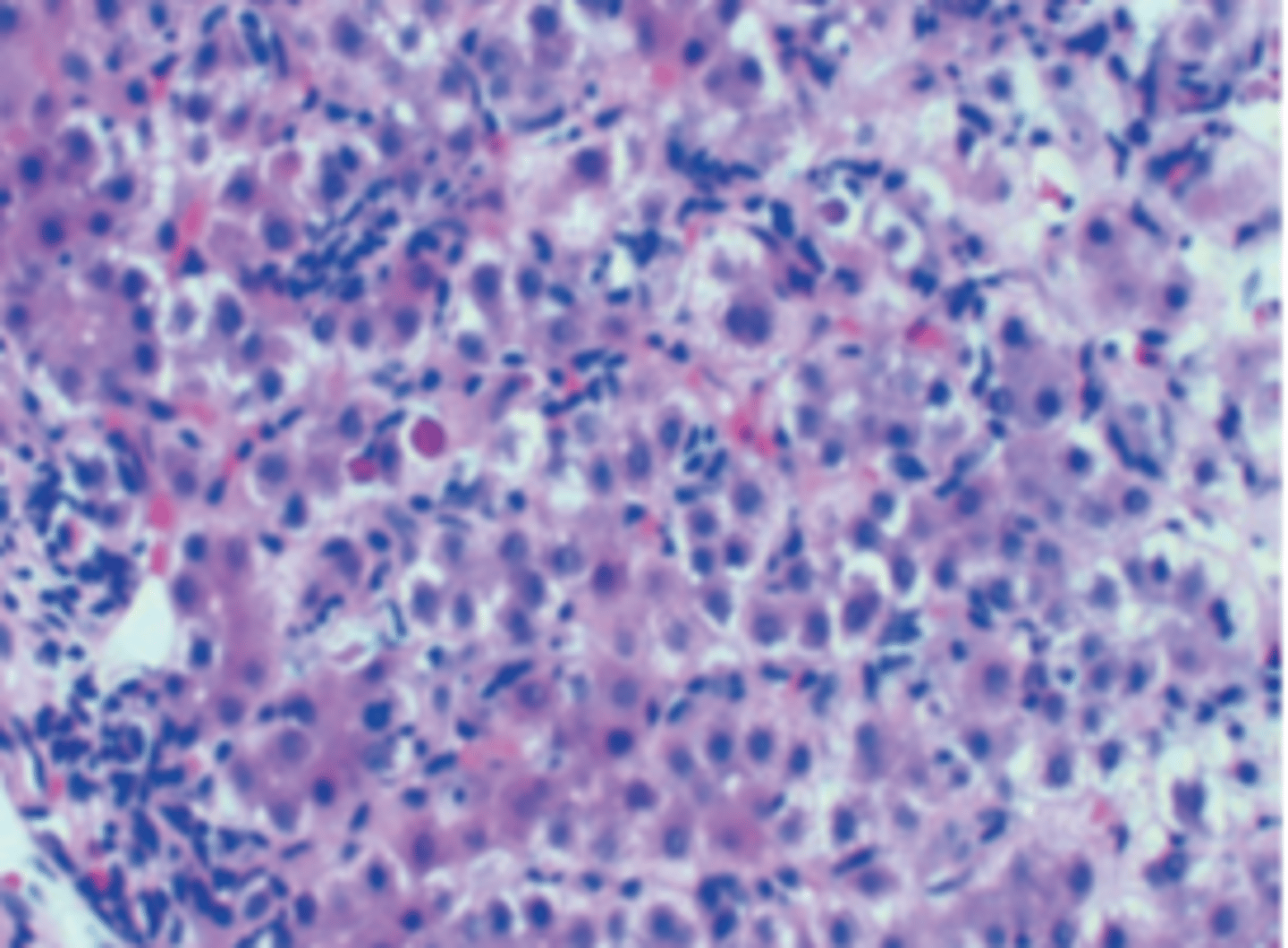
A previously healthy 38-year-old man complains of yellow discoloration of his eyes, abdominal pain, and low-grade fever of 1-month duration. Physical examination demonstrates a distended abdomen, right upper quadrant tenderness, and a palpable liver edge 2 cm below the right costal margin. Total serum bilirubin is 7.4 mg/dL. Serum levels of AST and ALT are elevated (229 and 495 U/L, respectively). The prothrombin time is prolonged (18 seconds). A liver biopsy is shown in the image. The arrows point to Councilman bodies. The pathologic findings are indicative of which of the following liver diseases?
(A) Acute viral hepatitis
(B) Alcoholic cirrhosis
(C) Cardiac cirrhosis
(D) Hemochromatosis
(E) Primary biliary cirrhosis
Chronic Hepatitis B
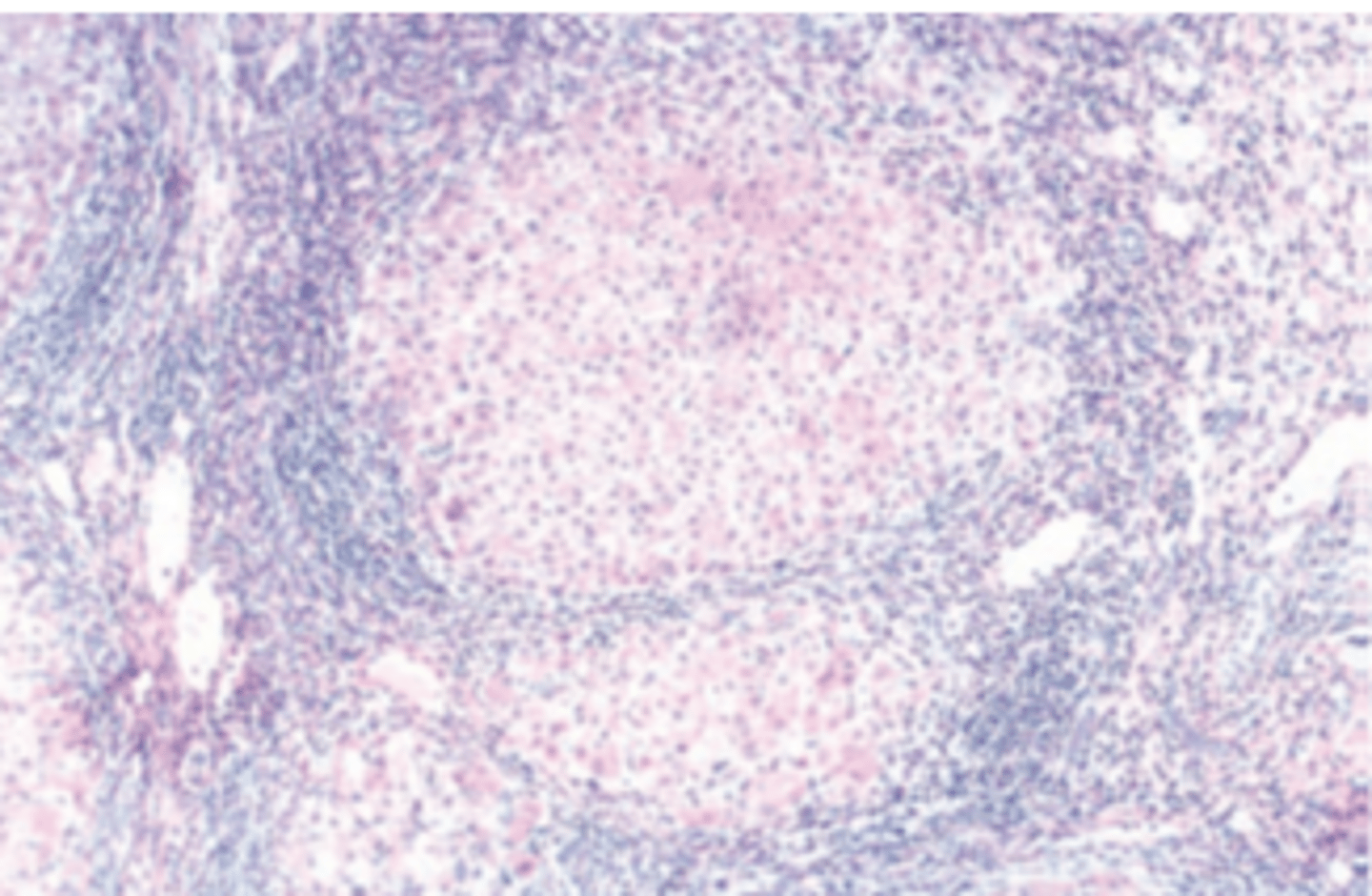
A 30-year-old man presents with a 9-month history of fatigue and recurrent fever. He also complains of yellow skin and sclerae, abdominal tenderness, and dark urine. Physical examination reveals jaundice and mild hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies demonstrate elevated serum bilirubin (3.1 mg/ dL), decreased serum albumin (2.5 g/dL), and prolonged prothrombin time (17 seconds). Serologic tests reveal antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen (IgG anti-HBcAg). The serum is positive for HBsAg and HbeAg. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Acute hepatitis B
(B) Alcoholic hepatitis
(C) Chronic hepatitis B
(D) Delta virus infection
(E) Subacute hepatic necrosis secondary to hepatitis B infection
Polyarthritis nodosa (PAN)
The patient described in the previous Question is most likely to develop which of the following vascular inflammatory diseases?
(A) Allergic angiitis
(B) Buerger disease
(C) Giant cell arteritis
(D) Polyarteritis nodosa
(E) Wegener granulomatosis
Carcinoma of the gallbladder
A 40-year-old woman presents with a long history of vague upper abdominal pain and frequent indigestion. Physical examination reveals an obese woman with jaundice and abdominal tenderness. Serum bilirubin is elevated (4.2 mg/dL). There is a mild increase in serum AST and ALT (62 and 57 U/L, respectively) and a moderate increase in alkaline phosphatase (325 U/L). Markers for viral hepatitis are negative. Abdominal ultrasound examination shows echogenic stone-like material within the gallbladder and thickening of the gallbladder wall. An intrahepatic mass is also visualized adjacent to the gallbladder. A cholecystectomy is performed. Histologic examination shows dense fibrosis and glandular structures in the wall of the gallbladder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Carcinoma of the gallbladder
(B) Hemangiosarcoma
(C) Hepatic adenoma
(D) Hepatocellular carcinoma
(E) Metastatic carcinoma of the stomach
Ammonia
A 60-year-old man is found in a state of disorientation and is brought to the emergency room in a comatose state. He lived alone, ate poorly, and drank large amounts of hard liquor. Physical examination reveals an emaciated man with a distended abdomen, jaundice, ascites, and a slightly enlarged liver and spleen. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. What blood test would confirm a diagnosis of hepatic coma?
(A) Alanine aminotransferase
(B) Alkaline phosphatase
(C) Ammonia
(D) Bilirubin
(E) Urea nitrogen
Autoimmune hepatitis
A 20-year-old woman presents with a 4-week history of dry mouth, fatigue, fever, and yellow sclerae. Physical examination shows mild jaundice and hepatomegaly. Serum total bilirubin is 3.3 mg/dL. Serologic markers for viral hepatitis are negative. The anti-mitochondrial antibody test is negative. A liver biopsy discloses parenchymal and periportal inflammatory cell infiltrates composed primarily of lymphocytes and plasma cells. The patient's signs and symptoms abate following 2 months of treatment with steroids. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Autoimmune hepatitis
(B) Extrahepatic jaundice
(C) Primary biliary cirrhosis
(D) Primary sclerosing cholangitis
(E) Wilson disease
Cholangiocarcioma
A 52-year-old recent immigrant from Vietnam complains of abdominal swelling, weight loss, and upper abdominal pain of 3 weeks in duration. His past medical history includes malaria and infection with the liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis. The liver is hard to palpation. An abdominal CT scan shows a hypoattenuated mass with lobulated margins in the liver. A biopsy discloses well-differentiated neoplastic glands embedded in a dense fi brous stroma. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Carcinoma of the gallbladder
(B) Cholangiocarcinoma
(C) Hemangiosarcoma
(D) Hepatocellular carcinoma
(E) Metastatic colon adenocarcinoma
No histologic changes
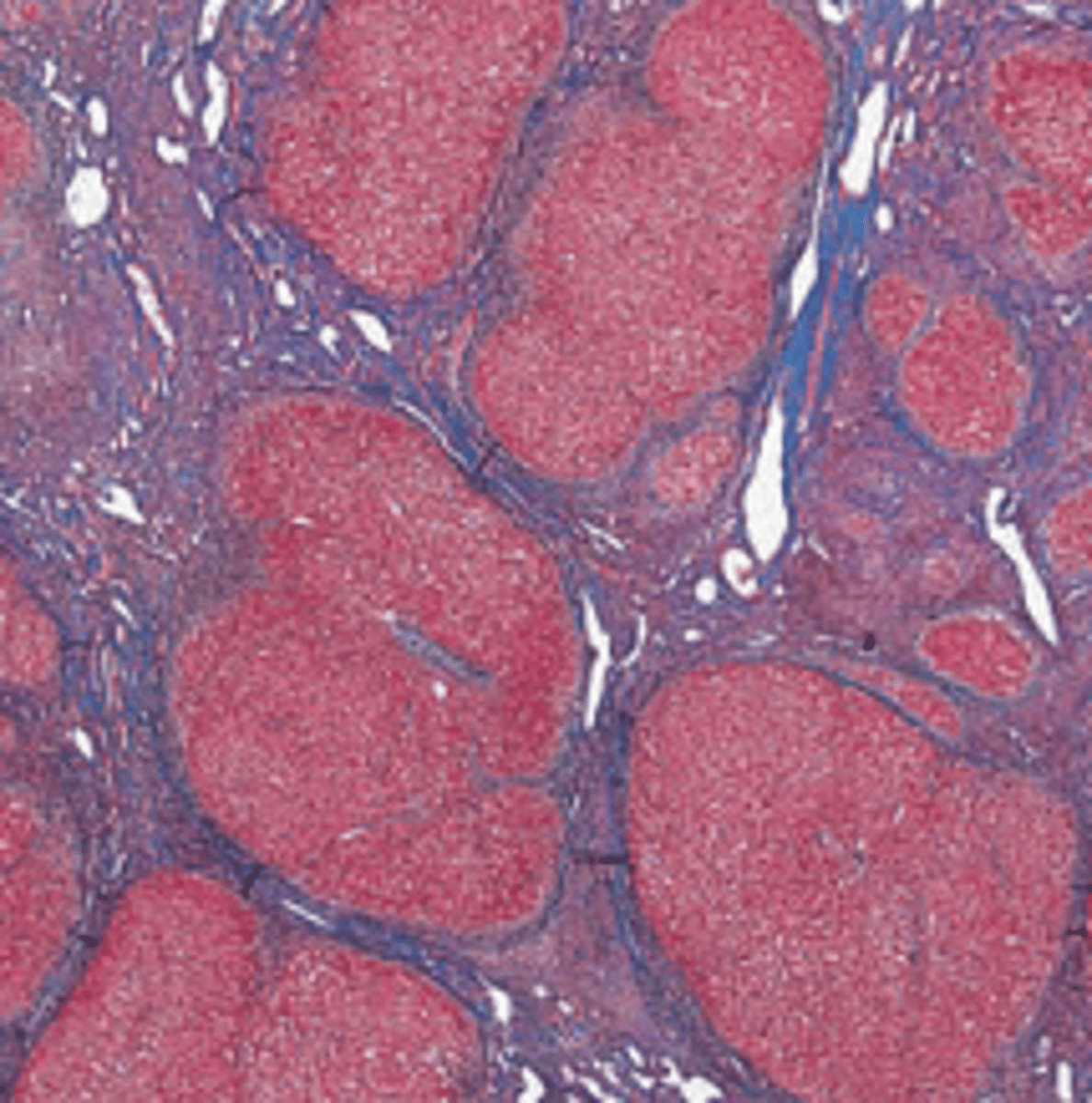
A 58-year-old man with longstanding alcoholic cirrhosis presents with abdominal pain, fever, and an episode of hematemesis. Physical examination reveals jaundice and a markedly distended abdomen. The patient is disoriented and has a coarse fl apping tremor of the hands. Laboratory studies reveal modestly elevated serum levels of AST and ALT (96 and 92 U/L, respectively) and a high serum level of alkaline phosphatase (320 U/L). Prothrombin time is prolonged (20 seconds). The WBC count is 18,000/μL. Shortly after admission, the patient develops coma, adult respiratory distress syndrome, and renal failure (oliguria and elevated serum levels of BUN and creatinine), leading to death within 3 days. Histologic examination of the patient's kidney at autopsy would most likely show which of the following?
(A) Interstitial nephritis
(B) Membranous nephropathy
(C) No histologic changes
(D) Proliferative glomerulonephritis
(E) Pyelonephritis
Nodular regeneration and scarring
A liver biopsy in the patient described in the previous Question would definitely show which of the following pathologic changes?
(A) Dilated bile ducts and portal inflammation (B) Fatty liver
(C) Nodular regeneration and scarring
(D) Periportal necrosis and peripheral cholestasis
(E) Scattered single cell necrosis and acidophilic bodies
Sickle cell disease
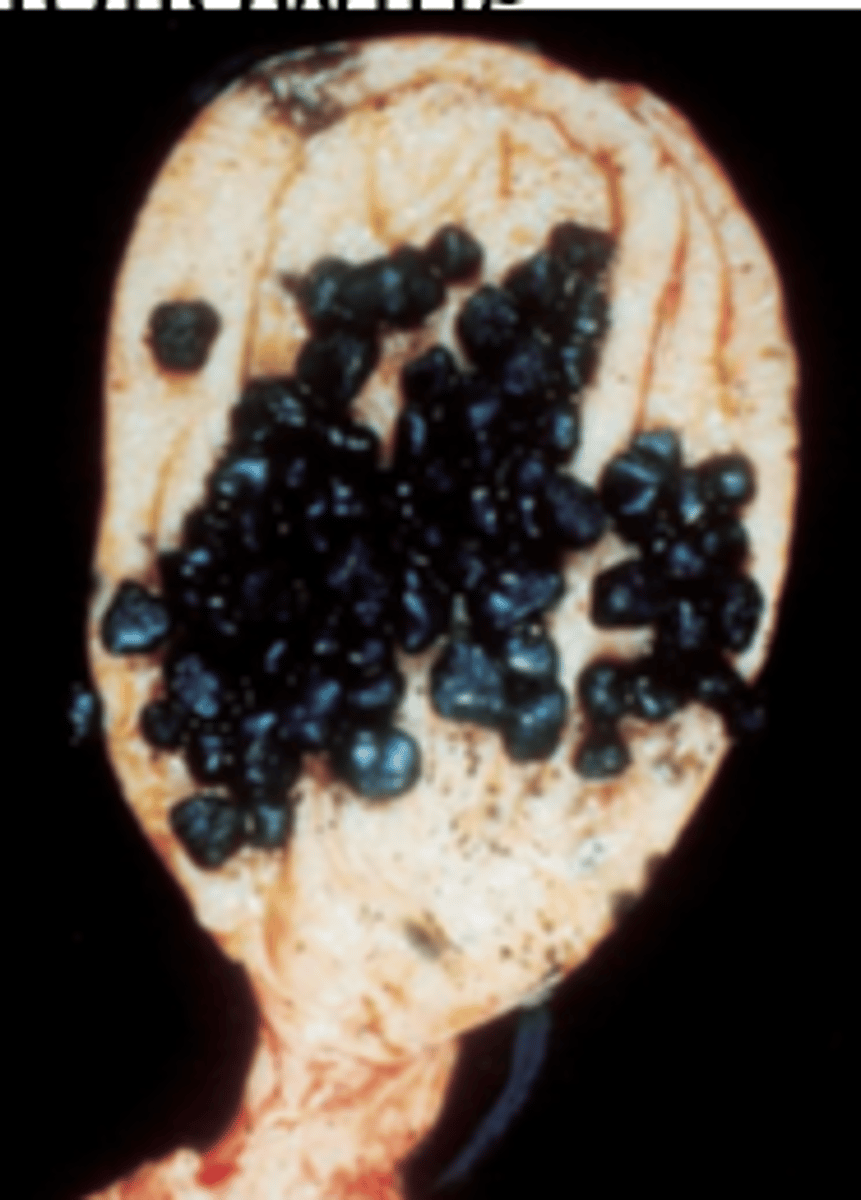
A 40-year-old black woman has frequent indigestion after meals and abdominal pain. Physical examination demonstrates a moderately obese woman in no acute distress. An ultrasound examination demonstrates numerous echogenic objects within the gallbladder. A cholecystectomy is performed, and the surgical specimen is shown in the image. The gallstones seen in this patient are typically associated with which of the following diseases?
(A) Chronic pancreatitis
(B) Diabetes mellitus
(C) Familial hypercholesterolemia
(D) Hyperparathyroidism
(E) Sickle cell disease
Hepatitis B virus
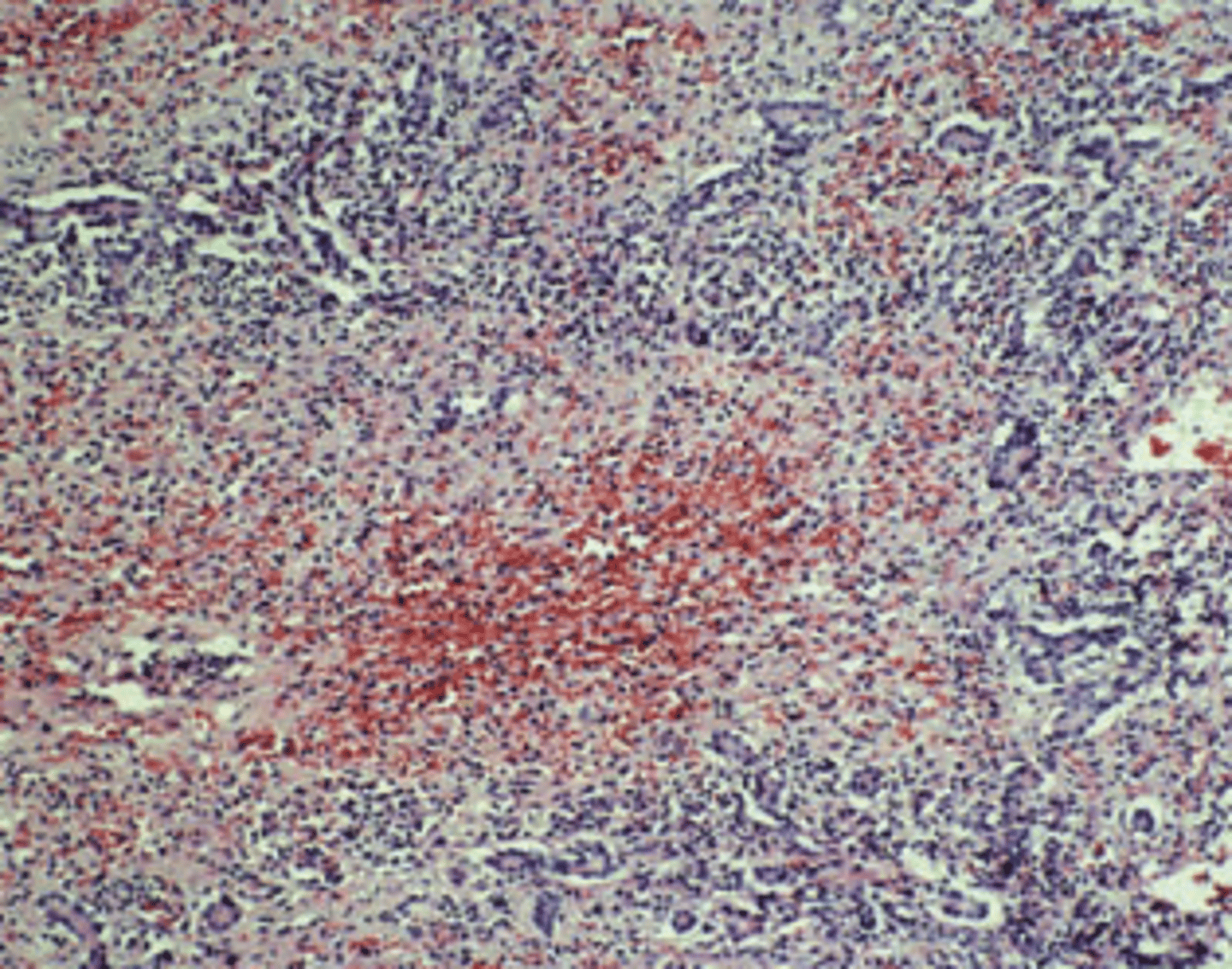
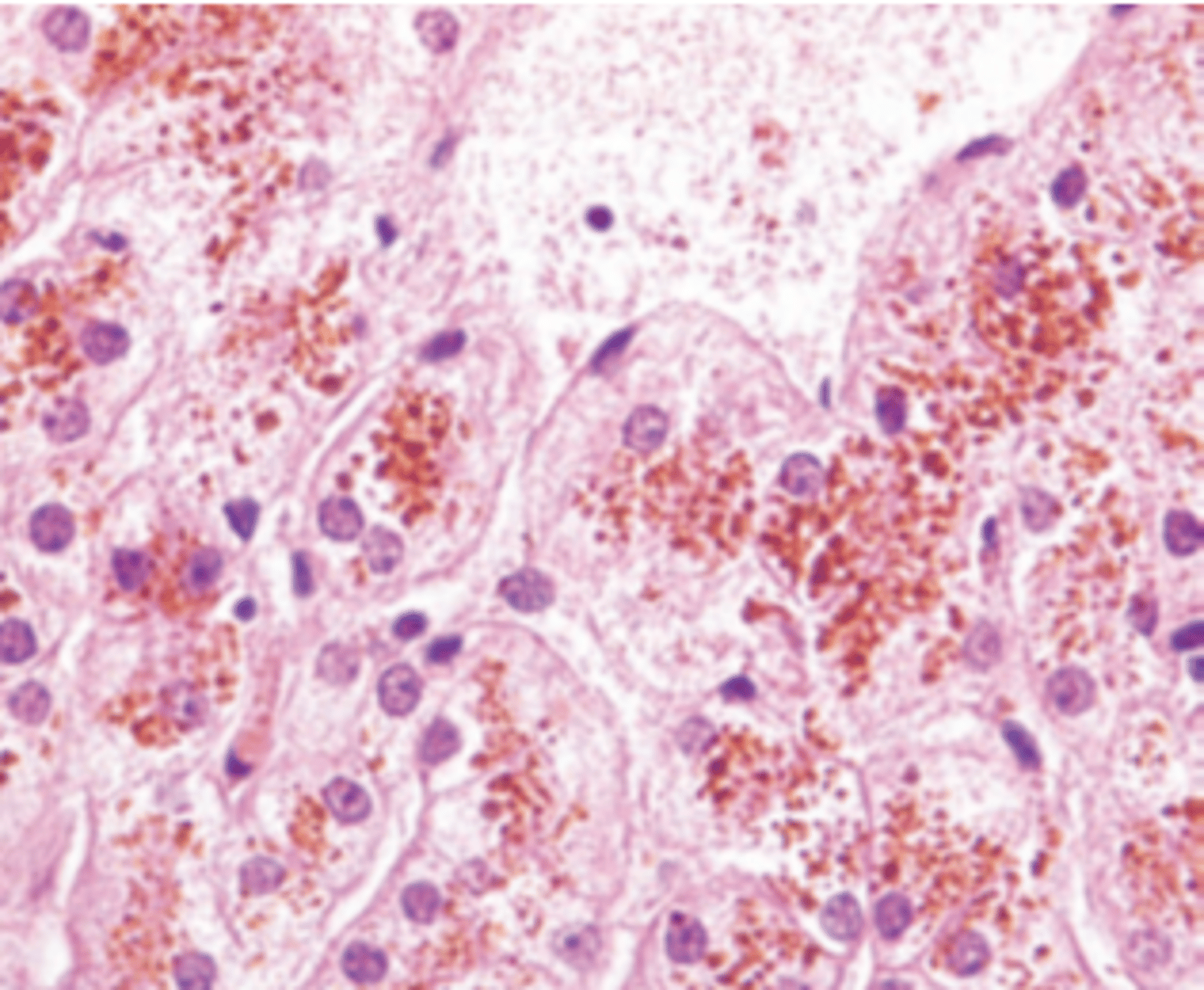
A 25-year-old heroin addict presents in a disoriented state with a 5-day history of fatigue, malaise, and dark-colored urine. Physical examination reveals jaundice and multiple petechial hemorrhages on the upper extremities. Laboratory studies show serum bilirubin of 15.6 mg/dL, mostly in the conjugated form, 10-fold elevations of serum AST and ALT, high levels of blood ammonia, and increased prothrombin time (15 seconds). The patient's condition deteriorates and he develops stage 4 hepatic encephalopathy. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following viruses is most likely responsible for the clinical and pathologic findings in this patient?
(A) Cytomegalovirus
(B) Hepatitis A virus
(C) Hepatitis B virus
(D) Hepatitis C virus
(E) Hepatitis E virus
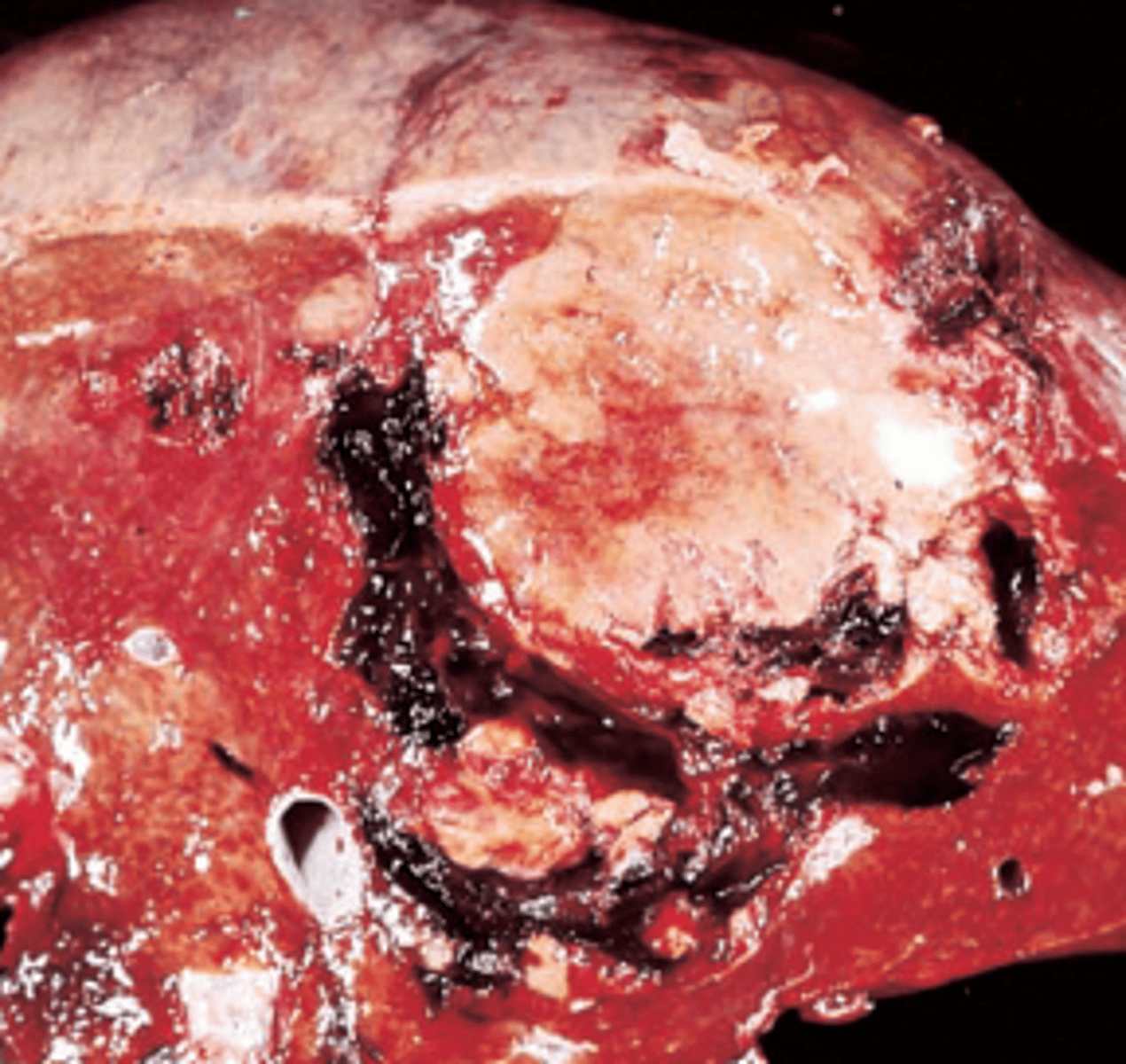
Oral contraceptives
A 25-year-old woman complains of sudden onset of acute abdominal pain. Physical examination shows abdominal distention. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), respirations 22 per minute, heart rate 110 per minute, and blood pressure 70/50 mm Hg. A tap of the abdomen returns blood. A CT scan reveals a solitary 20-cm mass of the liver. A surgically resected portion of the liver is shown in the image. This patient's tumor was most likely associated with chronic exposure to which of the following?
(A) Carbon tetrachloride
(B) Halothane
(C) L-thyroxine
(D) Oral contraceptives
(E) Vinyl chloride
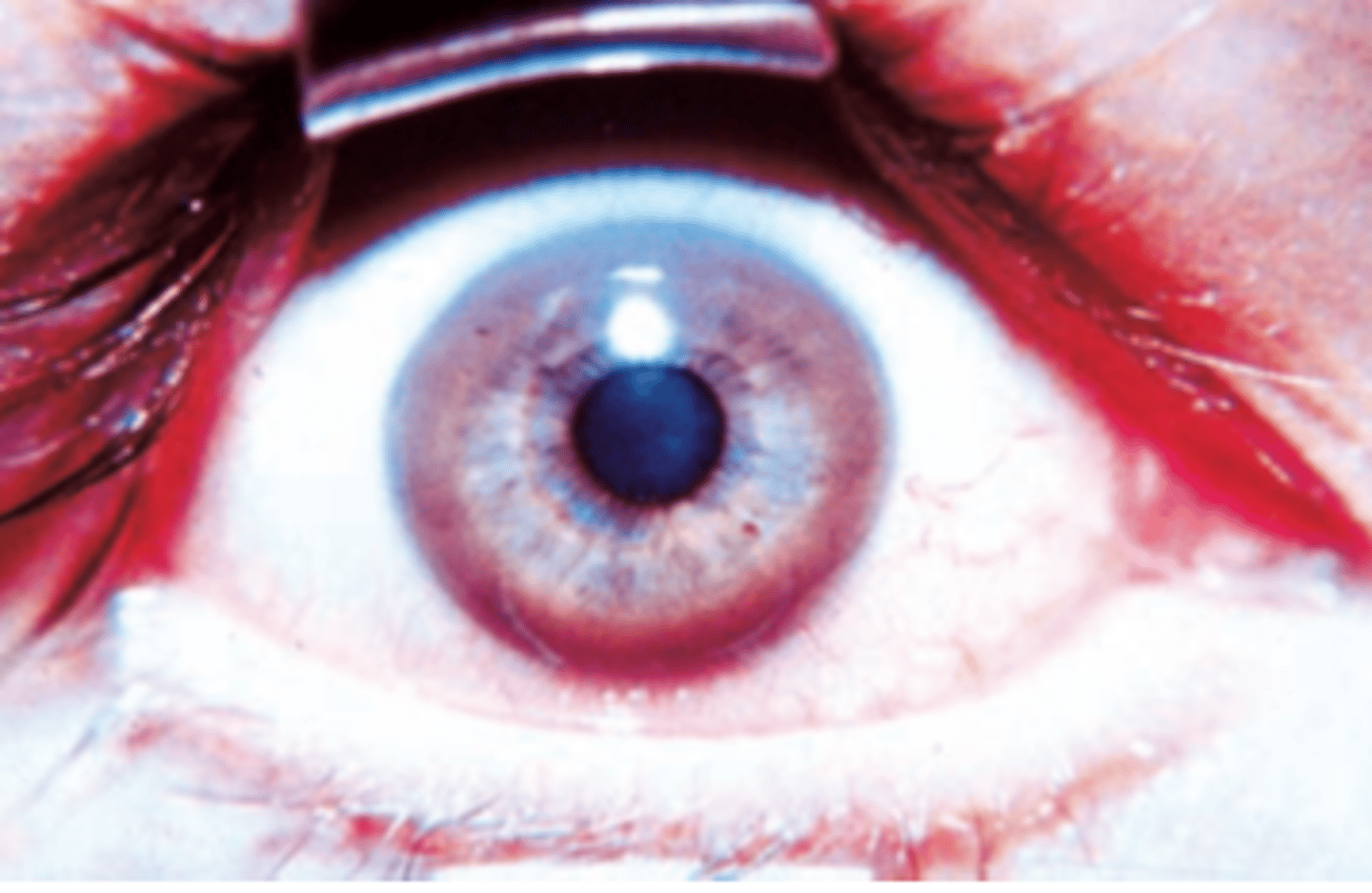
Copper
A 15-year-old boy complains of a 2-month history of fatigue, abdominal pain, and yellow eyes and skin. Physical examination shows tremor of his hands, lack of coordination, and mild jaundice. The results of an ophthalmic examination are shown in the image. This patient most likely has an inborn error of metabolism associated with tissue overload of which of the following elements?
(A) Copper
(B) Iron
(C) Lead
(D) Magnesium
(E) Mercury
Alcoholic hepatitis
A 49-year-old woman presents with a 1-month history of yellow discoloration of her eyes, abdominal pain, malaise, weight loss, and low-grade fever (38.4°C, 101°F). Physical examination shows a distended abdomen with right upper quadrant tenderness and a palpable liver 2 cm below the right costal margin. Laboratory studies reveal decreased serum albumin (2.6 g/dL), elevated serum AST (225 U/L) and ALT (150 U/L), and increased alkaline phosphatase (210 U/L). The prothrombin time is prolonged (15 seconds). A moderate leukocytosis (13,500/μL, 80% neutrophils) is observed. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. These pathologic findings are most commonly associated with which of the following liver diseases?
(A) Alcoholic hepatitis
(B) Chronic hepatitis B
(C) Chronic hepatitis C
(D) Hemochromatosis
(E) Primary biliary cirrhosis
Xanthoma
A 36-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of progressive generalized itching, weight loss, fatigue, and yellow sclerae. She denies use of oral contraceptives or any other medication. Physical examination reveals mild jaundice and steatorrhea. Blood studies show a high cholesterol level of 350 mg/ dL, elevated serum alkaline phosphatase (240 U/L), and normal levels of AST and ALT. An intravenous cholangiogram shows no evidence of obstruction. An antimitochondrial antibody test is positive; antinuclear antibodies are not present. Which of the following skin manifestations is expected in this patient?
(A) Acanthosis nigricans
(B) Hyperpigmentation
(C) Keratoacanthoma
(D) Seborrheic keratosis
(E) Xanthoma
Intrahepatic bile duct damage
For the patient described in the previous Question, a liver biopsy would most likely show which of the following pathologic findings?
(A) Central hyaline sclerosis
(B) Cholangiocarcinoma
(C) Hemosiderosis
(D) Intrahepatic bile duct damage
(E) Macrovesicular steatosis
Revert to normal
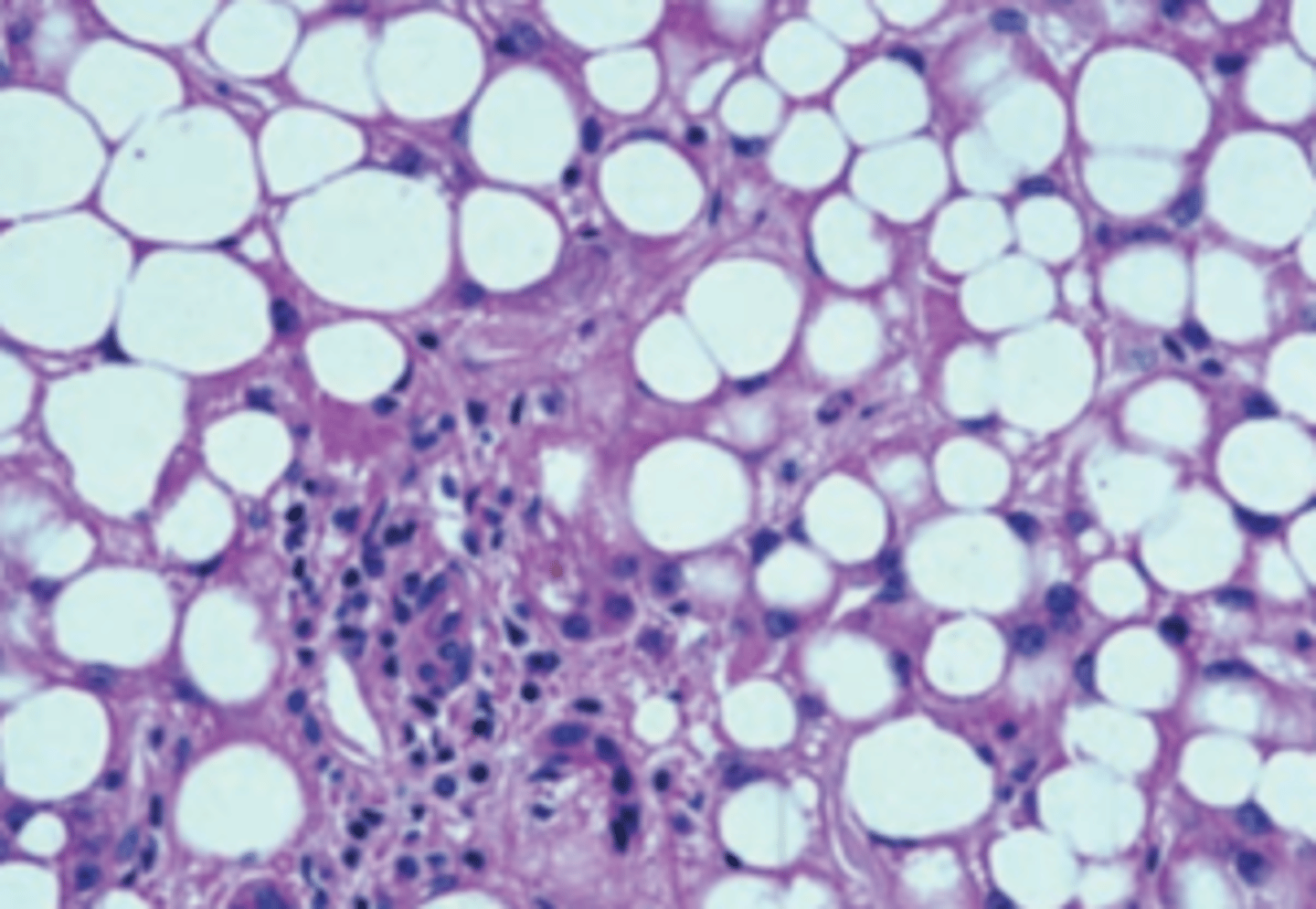
A 60-year-old man has a 6-month history of abdominal swelling. On a daily basis, he smokes two packs of cigarettes, drinks five cups of coffee, and reports that he consumes 2 sixpacks of beer. Physical examination shows a distended abdomen with a palpable liver 2 cm below the costal margin. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. If this patient becomes abstinent, his liver will most likely do which of the following?
(A) Develop hepatocellular carcinoma
(B) Progress to cirrhosis
(C) Progress to inflammatory hepatitis
(D) Remain unchanged
(E) Revert to normal
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
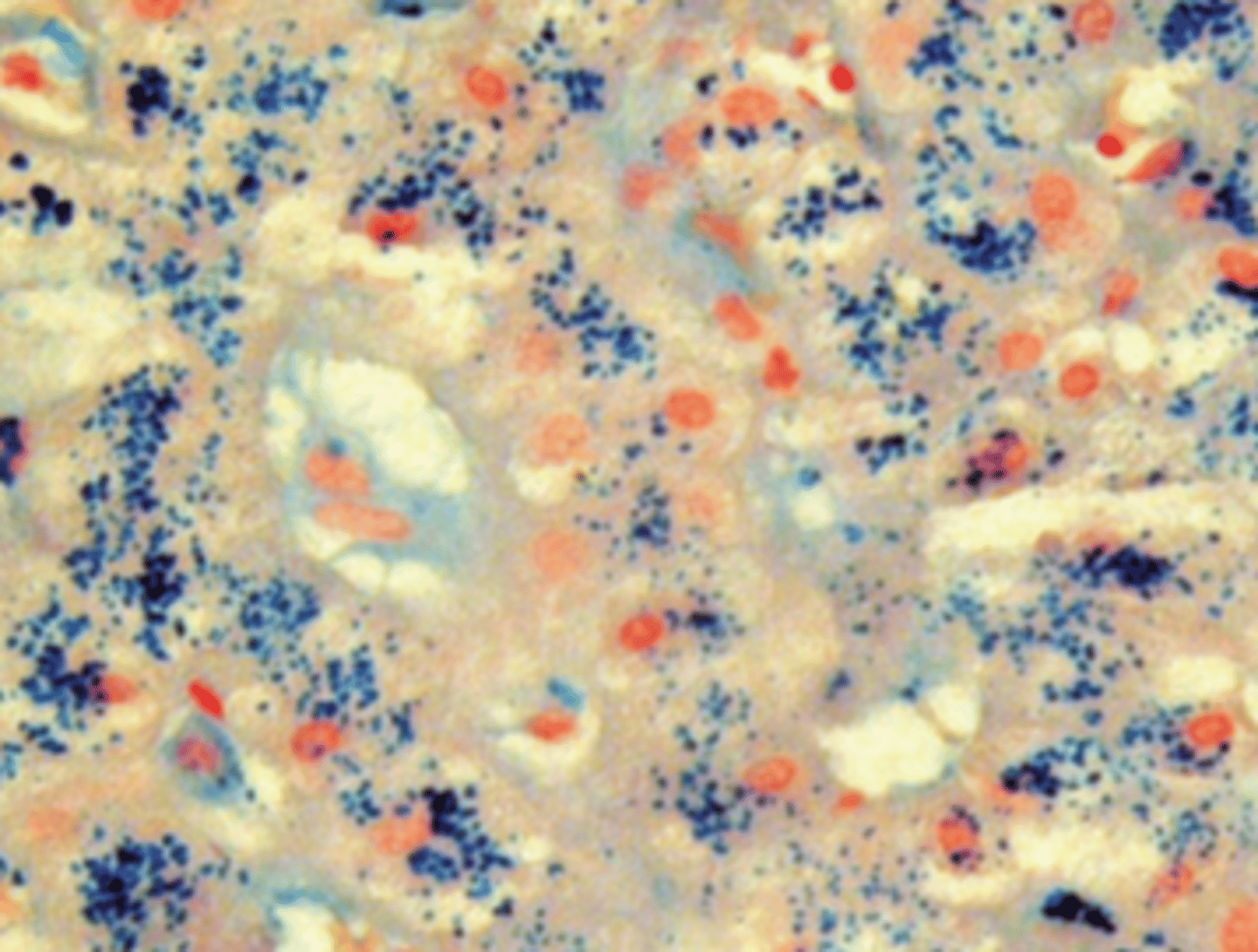
A 54-year-old man presents with a 9-month history of progressive skin pigmentation. He passes large amounts of urine and is always thirsty. His father died of liver cancer. Physical examination reveals a dark skin color and an enlarged liver. Laboratory studies show normal serum levels of corticotropin. A glucose tolerance test indicates chemical diabetes. A liver biopsy stained with Prussian blue is shown in the image. If untreated, which of the following conditions is most likely to develop in this patient?
(A) Acute hepatitis
(B) Addison disease
(C) Cholangiocarcinoma
(D) Cholelithiasis
(E) Hepatocellular carcinoma
Budd-Chiari syndrome
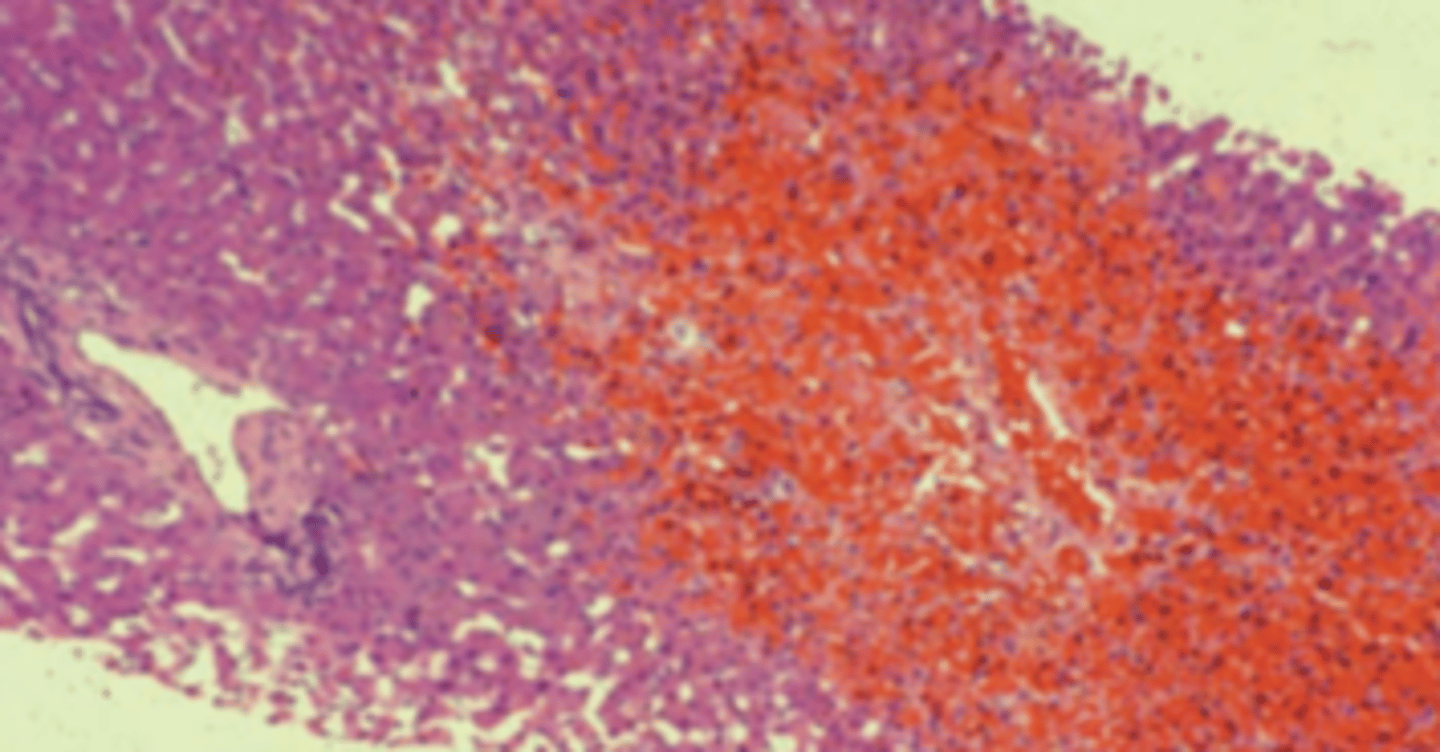
A 28-year-old woman presents with a 4-day history of abdominal pain and increasing abdominal girth. She does not drink alcoholic beverages but smokes a pack of cigarettes a day. Except for oral contraceptives, she takes no medications. Physical examination shows hepatomegaly, ascites, and mild jaundice. A liver biopsy is obtained (shown in the image). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Budd-Chiari syndrome
(B) Chronic hepatitis B
(C) Extrahepatic cholestasis
(D) Primary biliary cirrhosis
(E) Secondary biliary cirrhosis
Increased hepatic cholesterol secretion
A 47-year-old woman presents with a 3-month history of vague upper abdominal pain after fatty meals, some abdominal distension, and frequent indigestion. Physical examination shows an obese woman (BMI = 30 kg/m2) with right upper quadrant tenderness. An ultrasound examination discloses multiple echogenic objects in the gallbladder. The opened gallbladder is shown in the image. Which of the following metabolic changes is most likely associated with the formation of gallstones in this patient?
(A) Decreased hepatic bilirubin conjugation
(B) Decreased serum albumin
(C) Increased bilirubin uptake by the liver
(D) Increased hepatic calcium secretion
(E) Increased hepatic cholesterol secretion
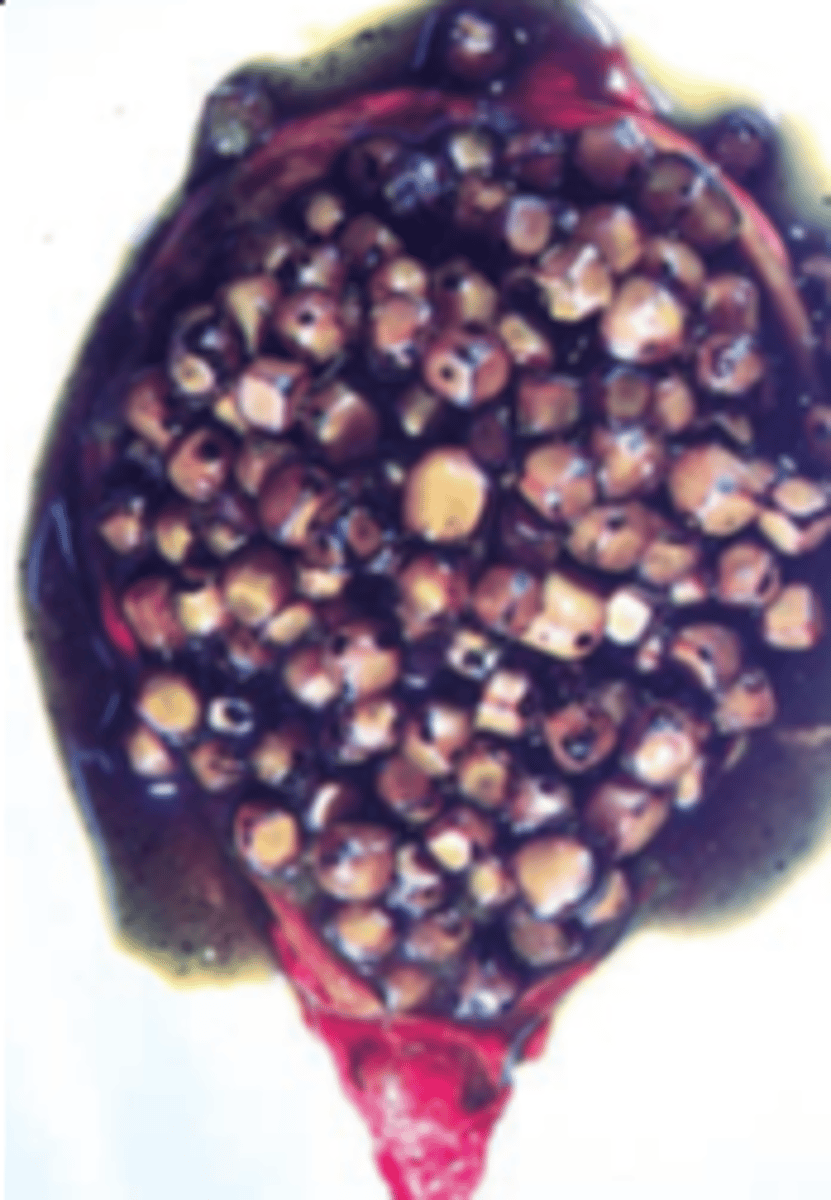

Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
For the patient described in the previous Question, which of the following is a common complication?
(A) Bile peritonitis
(B) Chronic passive congestion of the liver
(C) Confluent hepatic necrosis
(D) Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
(E) Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Alpha-fetoprotein
A 68-year-old man complains of vague abdominal pain, intermittent fever, and a 20-lb (9-kg) weight loss over the past 6 months. For the past 12 years, he has suffered from chronic hepatitis B. On physical examination, the patient shows diffuse abdominal tenderness, hepatomegaly, and mild jaundice. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a diffusely nodular liver, with a dominant mass measuring 3 cm in diameter. A needle biopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following serum markers is useful for monitoring the progression of disease in this patient?
(A) Alkaline phosphatase
(B) Alpha-fetoprotein
(C) Anti-HBc antibody
(D) Carcinoembryonic antigen
(E) Human chorionic gonadotropin
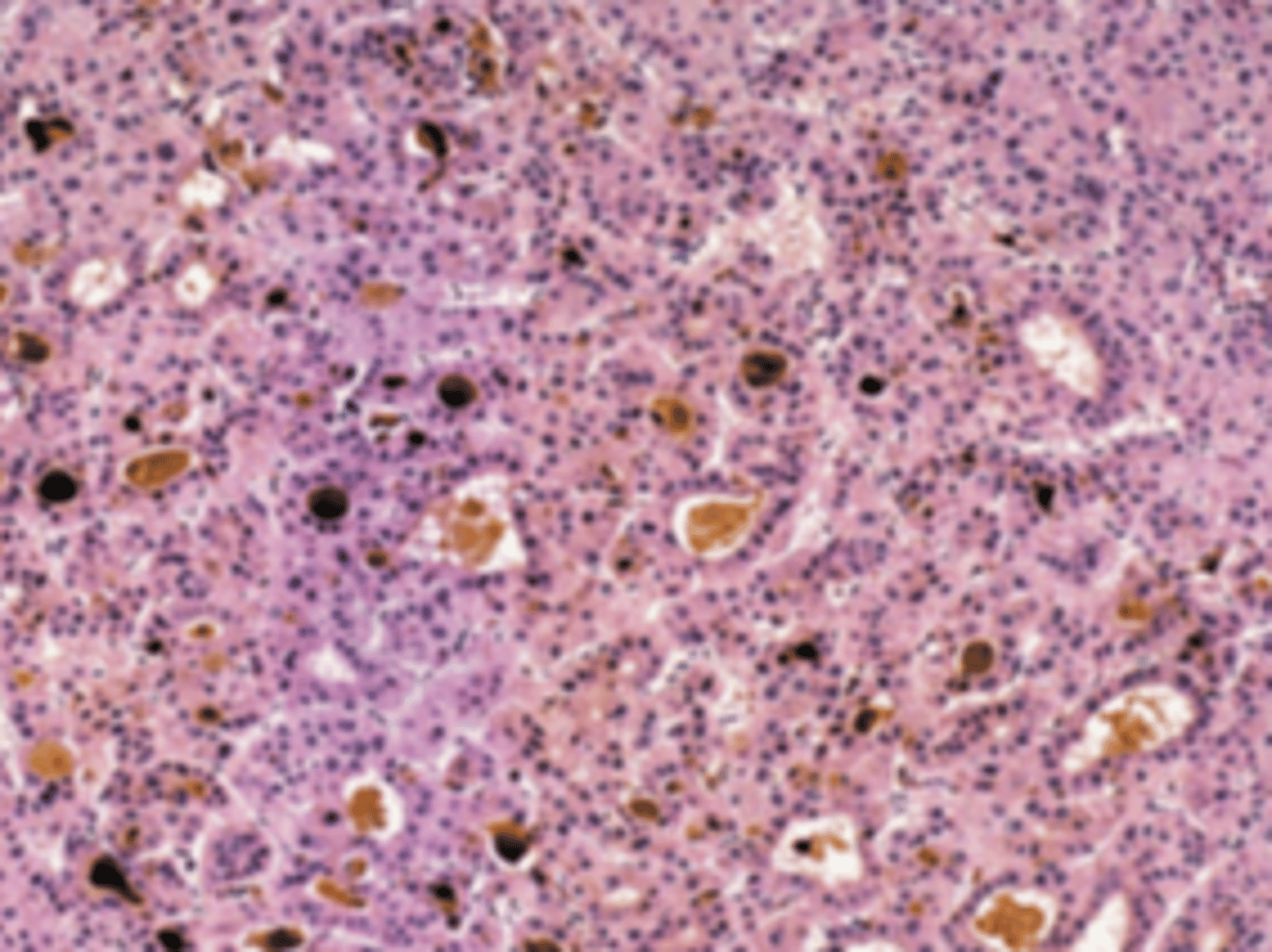
Liver biopsy
A 30-year-old man presents with a 3-week history of fatigue, occasional fever, yellow skin and sclerae, tenderness below the right costal margin, and dark urine. Physical examination reveals jaundice and mild hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies show elevated serum levels of bilirubin, decreased albumin, and prolonged prothrombin time. Serologic tests disclose antibodies to hepatitis C virus. Which of the following tests is the most accurate method for assessing the extent of liver disease in this patient?
(A) Liver biopsy
(B) Serum alkaline phosphatase
(C) Serum ammonia
(D) Serum immunoglobulins
(E) Serum transaminases
Predictable toxic liver injury
A 38-year-old man is brought to the emergency room with clouded sensorium and lethargy. He had been degreasing the engine parts of an old car the previous day, using industrial solvents. Later that evening he felt ill, and by morning, he was difficult to rouse. Serum ALT is extremely high (2,400 U/L). He dies 2 days later in hepatic coma. Which of the following liver injuries is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Alcoholic hepatitis
(B) Allergic reaction
(C) Budd-Chiari syndrome
(D) Idiosyncratic reaction
(E) Predictable toxic liver injury
Chronic Hepatitis B
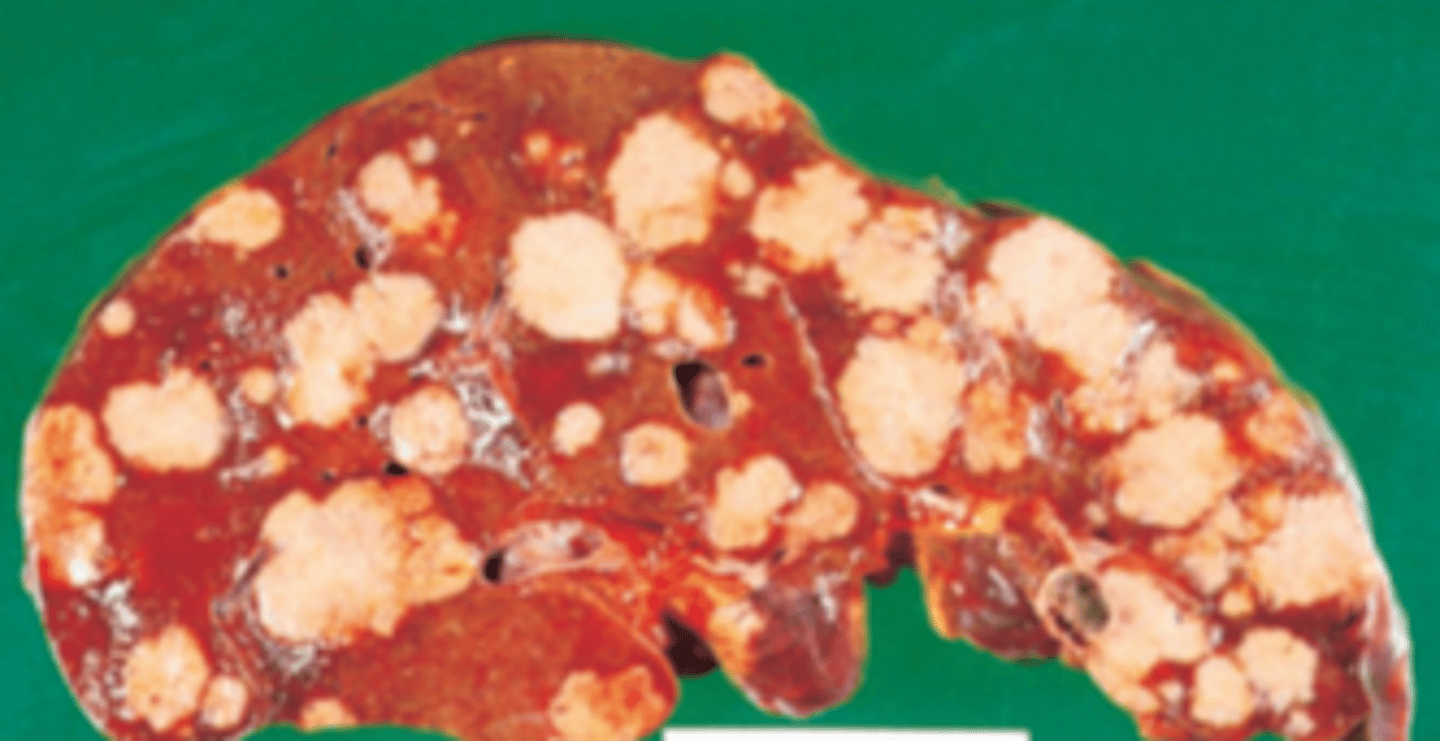
A 66-year-old man presents with a 2-week history of abdominal bloating, weight loss, and pain in the right upper quadrant. The patient had a serious motor vehicle accident 16 years ago, in which he required transfusion of 10 U of whole blood. On physical examination, he exhibits massive distension of the abdomen. The liver is hard on palpation and occupies the entire right side of the abdomen. Laboratory studies show a low serum albumin (2.2 g/dL) and a markedly elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein. An abdominal ultrasound examination reveals ascites. The patient expires 6 months later. The liver at autopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most common cause of this disease worldwide?
(A) Alcoholic hepatitis
(B) Autoimmune hepatitis
(C) Chronic hepatitis B
(D) Chronic hepatitis C
(E) Hepatitis E
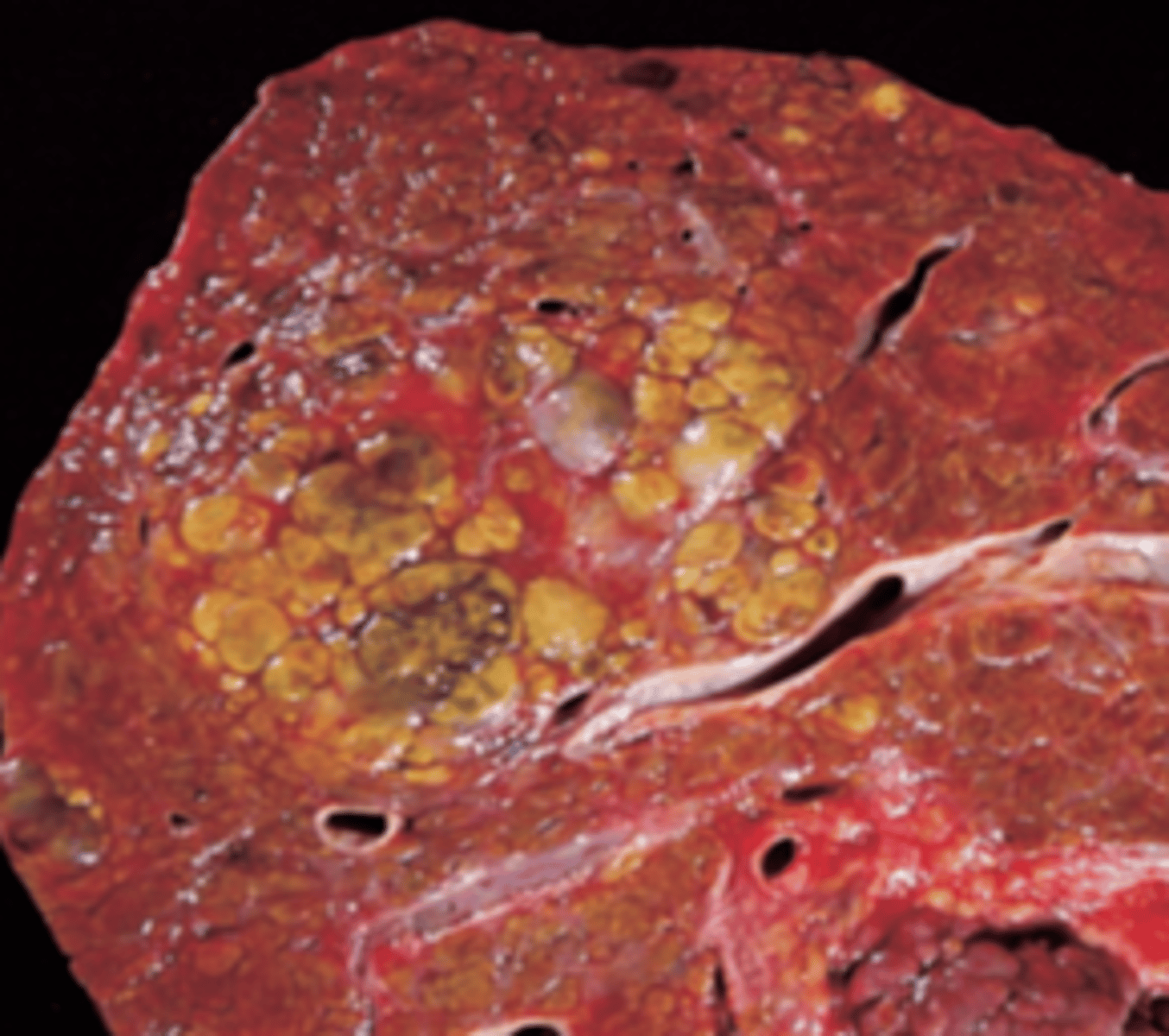
Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
A 60-year-old woman presents with several years of abdominal pain radiating to her back and a 5-day history of yellow skin and sclerae. She has lost 15 lb during the past several months, and her stools have become lighter in color. On physical examination, the patient is cachectic and jaundiced. The liver edge descends 1 cm below the right costal margin and is nontender. Her right calf is tender and erythematous. Serum AST and ALT are at the upper limits of normal, but alkaline phosphatase is increased to 430 U/L. A CT scan shows a mass in the head of the pancreas. What is the most likely cause of jaundice in this patient?
(A) Acute viral hepatitis
(B) Alcoholic hepatitis
(C) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
(D) Drug-induced hepatitis
(E) Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
Cholangiocarcinoma
A 40-year-old woman complains of having severe back pain for about 3 months and recurrent fever. Her past medical history is significant for ulcerative colitis. On physical examination, the patient is thin and jaundiced. The liver edge descends 1 cm below the right costal margin and is nontender. Laboratory studies show normal serum levels of AST and ALT but elevated serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (420 U/L). Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography demonstrates a beaded appearance of the extrahepatic biliary tree. Which of the following diseases is a late complication of this patient's condition?
(A) Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder
(B) Cholangiocarcinoma
(C) Hepatic adenoma
(D) Hepatic angiosarcoma
(E) Hepatocellular carcinoma
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
A 32-year-old man presents with a 6-month history of yellow skin and sclerae. Physical examination shows mild jaundice, pitting edema, and ascites. Laboratory studies reveal decreased serum albumin (2.6 g/dL) and increased serum AST and ALT (120 and 140 U/L, respectively). A liver biopsy stained with period acid-Schiff (PAS) reagent and diastase digestion is shown in the image. This patient has which of the following genetic diseases?
(A) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
(B) Glycogen storage disease
(C) Hereditary hemochromatosis
(D) Hurler syndrome
(E) Pompe syndrome
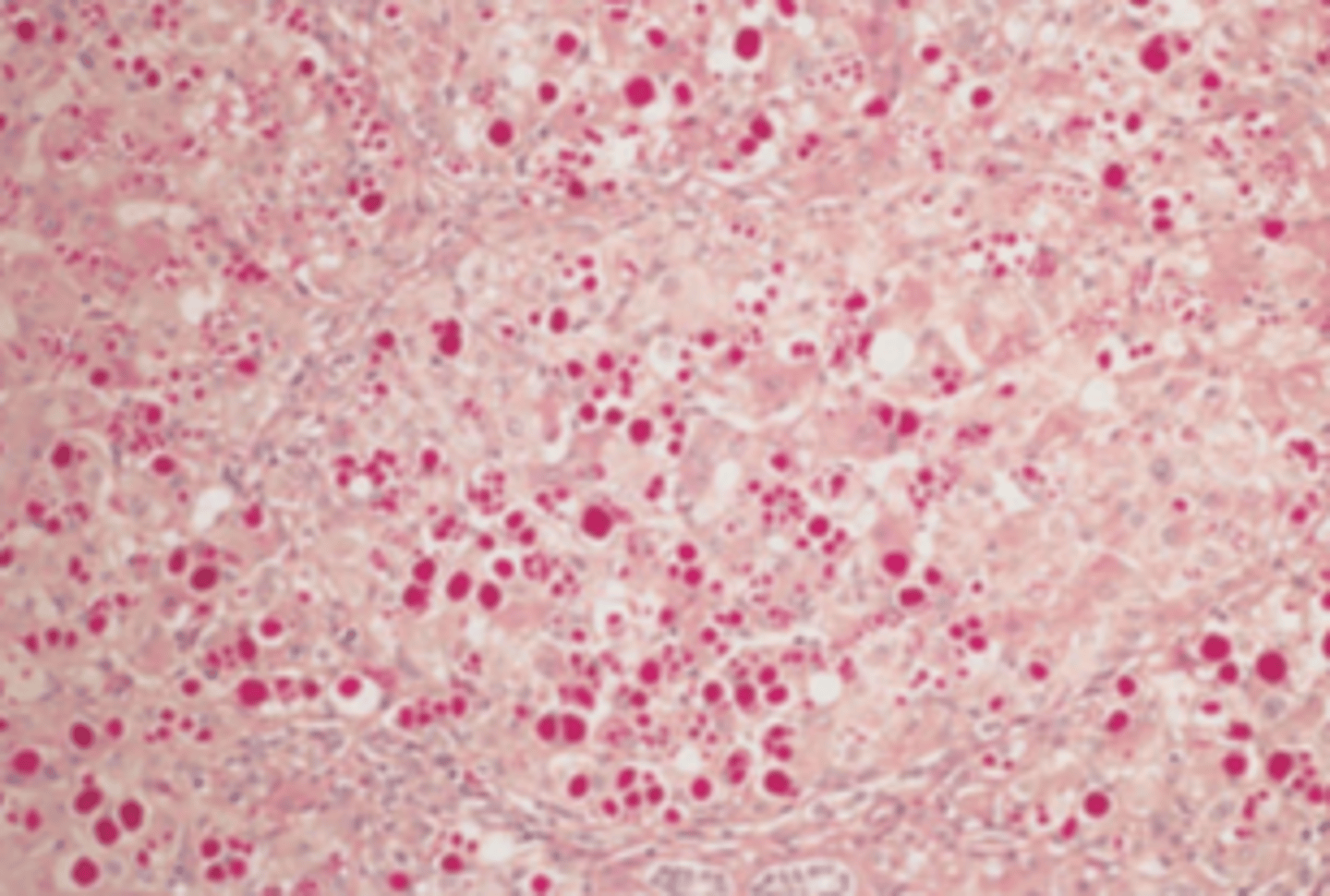
Pyogenic liver abscess
A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency room with right upper quadrant pain, shaking chills, and a fever of 38.7°C (103°F). His past medical history is signifi cant for an appendectomy 2 weeks previously. Physical examination reveals hepatomegaly and tenderness in the right upper quadrant. Laboratory studies show normal levels of serum albumin, ALT, and bilirubin, as well as increased alkaline phosphatase of 240 U/L. The WBC count is 28,000/μL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Acute cholecystitis
(B) Acute hepatitis
(C) Diffuse peritonitis
(D) Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
(E) Pyogenic liver abscess
Massive hepatic necrosis
A previously healthy, 24-year-old woman presents with a 1-week history of intermittent fever, lethargy, and yellow skin and sclerae. Physical examination shows jaundice. Laboratory studies reveal decreased serum albumin (2.2 g/dL), extremely high levels of AST and ALT (1,200 and 1,800 U/L, respectively), and elevated alkaline phosphatase (300 U/L). Her ceruloplasmin level is normal. She is admitted to the hospital. Her condition progressively deteriorates, and she develops hepatic encephalopathy and hepatorenal syndrome. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
(B) Hereditary hemochromatosis
(C) Massive hepatic necrosis
(D) Primary biliary cirrhosis
(E) Sclerosing cholangitis
Acetaminophen toxicity
A 36-year-old, alcoholic woman presents with a 1-week history of yellow skin and sclerae. She has suffered persistent headaches. Her vital signs are normal. Physical examination reveals jaundice. Laboratory studies disclose markedly elevated levels of AST and ALT (956 and 1,400 U/L, respectively). A few days later, she develops hepatic encephalopathy and renal failure. A liver biopsy shows prominent centrilobular necrosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Acetaminophen toxicity
(B) Fatty liver of pregnancy
(C) Metastatic carcinoma
(D) Reye syndrome
(E) Wilson disease
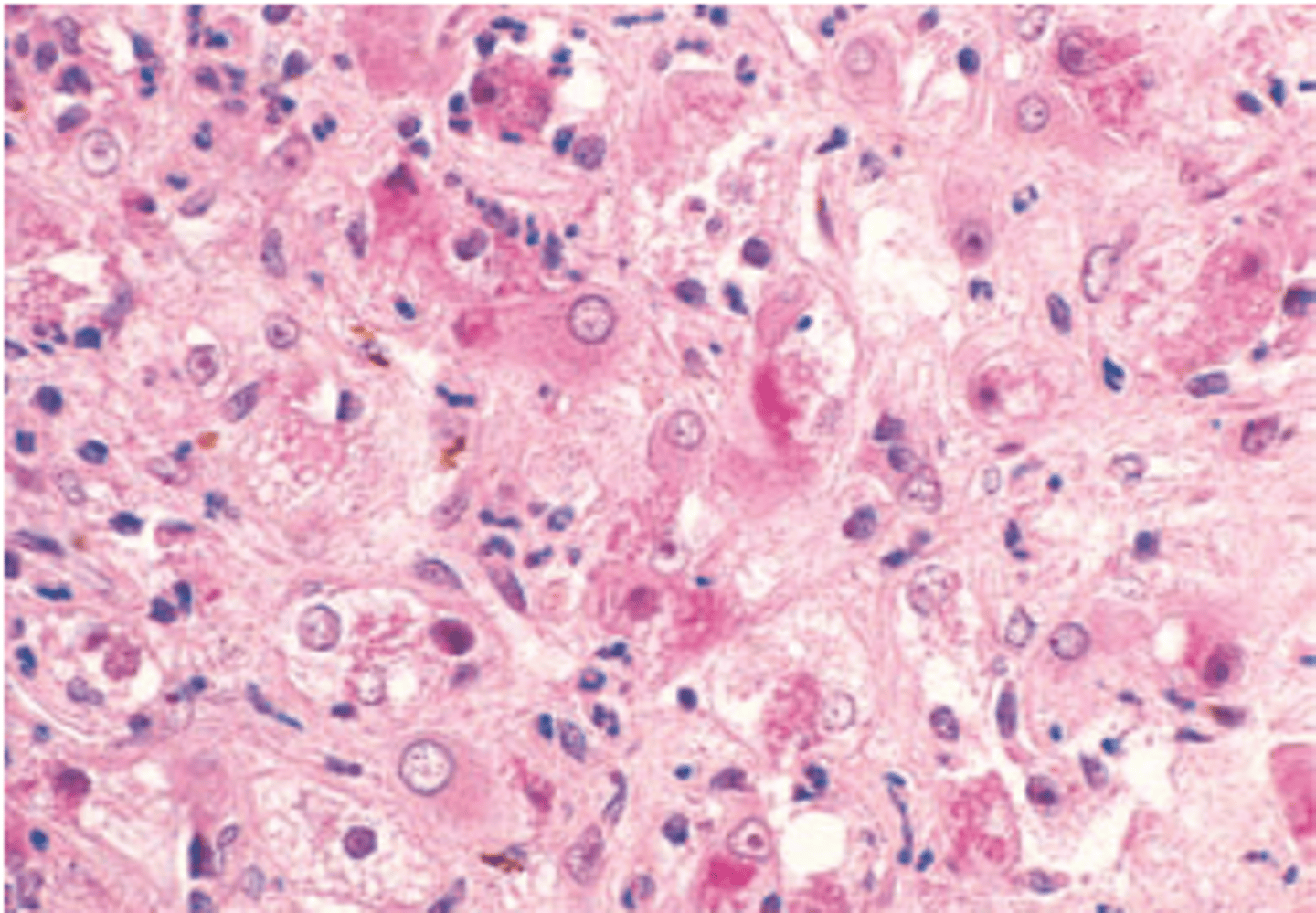
Amebic liver abscess
A 30-year-old man from Mexico presents with a 3-week history of constant pain in his upper right quadrant and epigastrium and persistent cough. The patient also reports a recent history of nausea, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea. Physical examination shows hepatomegaly and tenderness over the right upper quadrant. A liver biopsy displays fibroblastic proliferation and trophozoites (shown in the image). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Amebic liver abscess
(B) Cystic hydatid disease
(C) Hepatic malaria
(D) Pyogenic liver abscess
(E) Weil disease
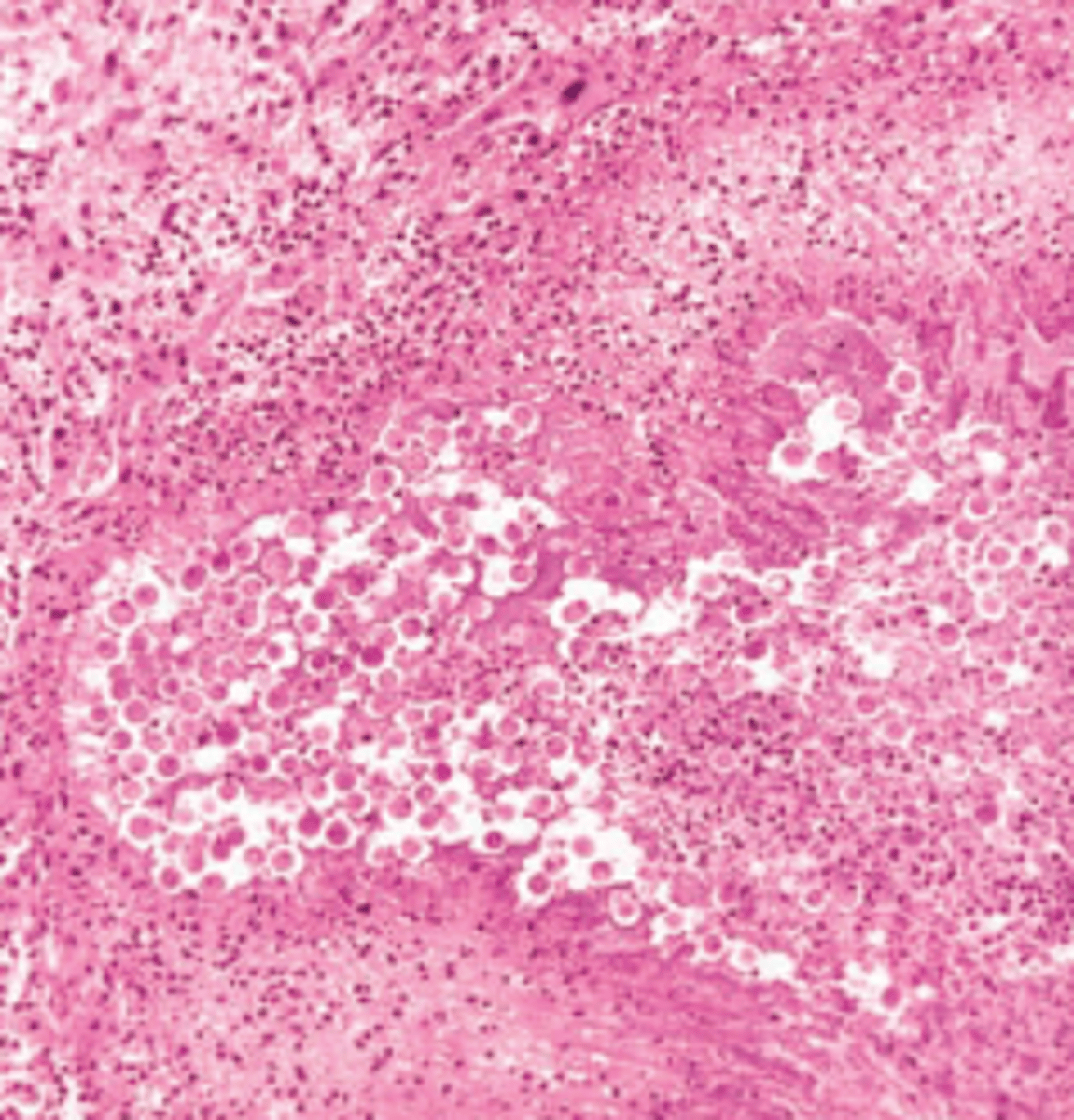
Metastatic carcinoma of the liver
A 69-year-old woman arrives in the emergency room complaining of weakness, abdominal pain, and a 9 kg (20 lb) weight loss during the past month. Physical examination reveals jaundice, conspicuous hepatomegaly, and ascites. The patient expires, and a section of liver is examined at autopsy (shown in the image). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Hemangiosarcoma of the liver
(B) Metastatic carcinoma of the liver
(C) Miliary tuberculosis
(D) Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
(E) Sarcoidosis
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
A 22-year-old man presents with a 3-week history of yellow skin and sclerae but is otherwise asymptomatic. He recalls a similar episode 2 years previously. Occasionally, he has noticed dark-colored urine. The serum bilirubin is 4.4 mg/dL, mostly in the conjugated form. Serum AST and ALT levels are normal. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
(B) Crigler-Najjar syndrome
(C) Dubin-Johnson syndrome
(D) Gilbert syndrome
(E) Wilson disease
Fulminant liver failure
A 22-year-old woman from India presents with a 1-week history of fever, malaise, and nausea. The patient is 6 months pregnant. Physical examination reveals jaundice and right upper quadrant pain. Results of laboratory studies include serum bilirubin of 5.2 mg/dL (60% conjugated), AST of 400 U/L, ALT of 392 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 70 U/L, anti-HAV antibodies negative, HBsAg negative, and IgM anti- hepatitis E virus (anti-HEV) antibodies positive. The patient is at high risk for which of the following?
(A) Diabetes mellitus
(B) Fulminant liver failure
(C) Pulmonary thromboembolism
(D) Renal failure
(E) Sclerosing cholangitis
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
A 55-year-old, obese man (BMI = 34 kg/m2) comes to the physician for a routine physical examination. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus that is controlled by medication and diet. The patient neither drinks nor smokes. Physical examination shows mild hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies reveal normal serum levels of albumin and bilirubin and mildly elevated serum levels of AST and ALT (80 and 100 U/L, respectively). The serum level of alkaline phosphatase is normal (70 U/L), and total serum cholesterol is elevated to 290 mg/dL. The CBC is normal. Abdominal ultrasound reveals diffuse fatty infiltration of the liver. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Autoimmune hepatitis
(B) Cirrhosis of the liver
(C) Diabetic ketoacidosis
(D) Glycogen storage disease
(E) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Andersen disease
A 6-month-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents, who noticed gradual enlargement of the child's abdomen. Physical examination reveals massive hepatomegaly. Laboratory studies show normal serum levels of albumin, bilirubin, and hepatic enzymes. Liver biopsy discloses enlarged hepatocytes with PAS-positive inclusions. Laboratory studies reveal the presence of amylopectin. Deposits of this abnormal glycogen are also found in a biopsy of skeletal muscle. Which of the following is the appropriate diagnosis?
(A) Andersen disease
(B) Fabry disease
(C) Gaucher disease
(D) Krabbe disease
(E) Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Porphobilinogen deaminase
A 20-year-old woman complains of intermittent, colicky abdominal pain, fi ne tremors of her hands, excess sweating, and a general feeling of restlessness. Laboratory studies reveal an inherited defect in the biosynthesis of heme. This patient's genetic disease is most likely caused by deficiency of which of the following liver enzymes?
(A) Alanine aminotransferase
(B) Alkaline phosphatase
(C) Porphobilinogen deaminase
(D) Uridine diphosphate glucuronyl transferase
(E) Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
Neonatal hepatitis
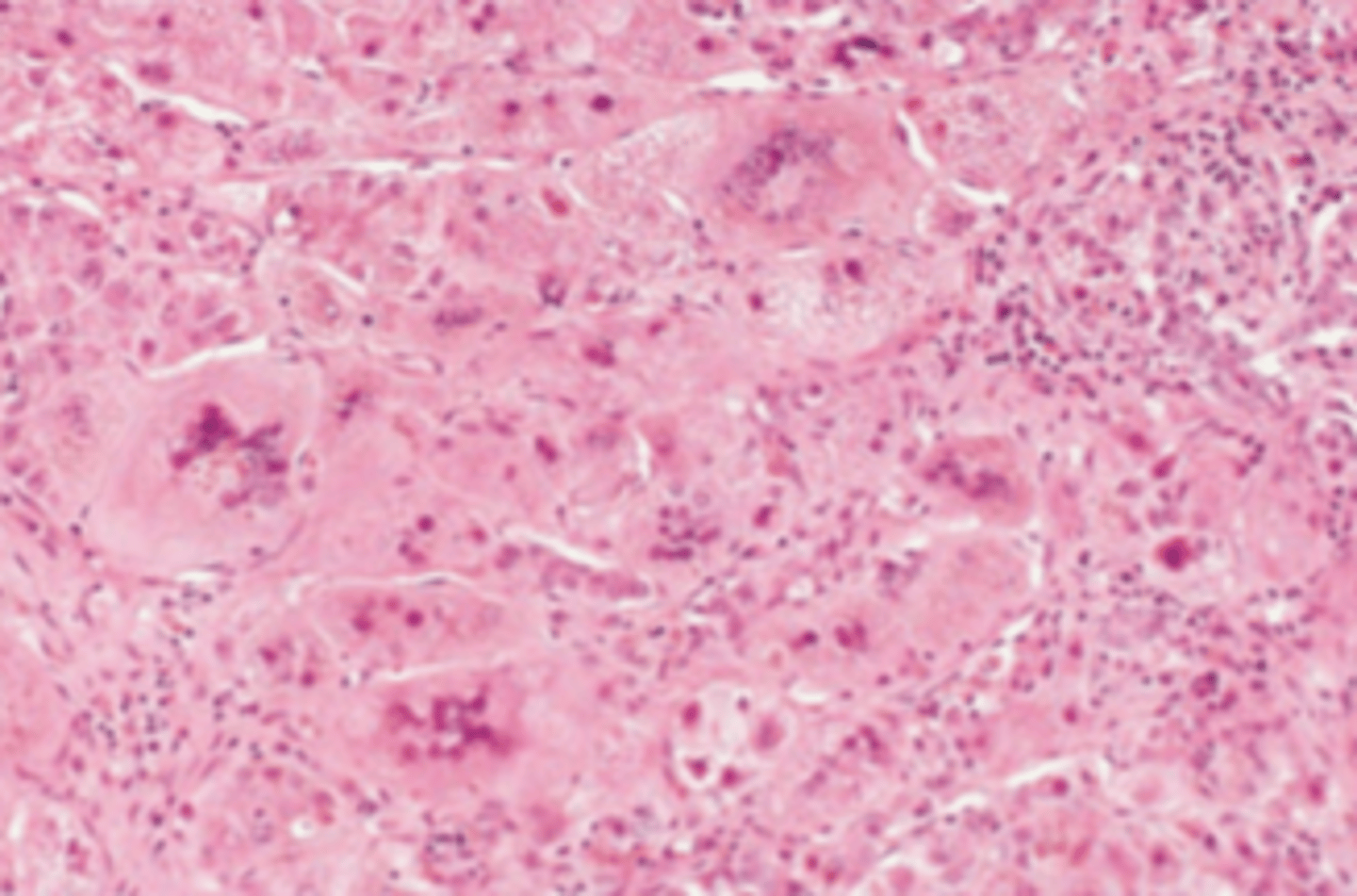
A 4-week-old infant has been evaluated for jaundice and hepatomegaly since birth. Laboratory studies reveal markedly elevated serum levels of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase and high serum levels of AST and ALT. A liver biopsy is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Autoimmune hepatitis
(B) Dubin-Johnson syndrome
(C) Neonatal hepatitis
(D) Reye syndrome
(E) Sclerosing cholangitis
Biliary atresia
Which of the following is a possible cause of liver disease in the patient described in the previous Question?
(A) Acute hepatitis A
(B) Annular pancreas
(C) Biliary atresia
(D) Cholelithiasis
(E) Cystic fibrosis
acute cholecystitis
A 45-year-old, mildly obese woman presents with a 1-week history of upper abdominal pain, fever, shaking chills, and occasional vomiting. Physical examination shows severe right upper quadrant tenderness. Laboratory studies include serum bilirubin of 1.0 mg/dL, AST of 25 U/L, ALT of 35 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 220 U/L (high), WBC of 14,000/μL, and amylase of 95 U/L (normal). An ultrasound examination of the abdomen reveals a normal-appearing liver and bile duct and thickening of the wall of the gallbladder. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
(A) Acute cholecystitis
(B) Acute pancreatitis
(C) Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder
(D) Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
(E) Primary biliary cirrhosis
Hepatitis C virus
A 59-year-old man complains of vague abdominal pain, intermittent fever, and a 9-kg (20-lb) weight loss over the past 8 months. His past medical history is significant for drug abuse, although he claims to be drug free for the past 10 years. On physical examination, the patient shows diffuse abdominal tenderness, hepatomegaly, and mild jaundice. Serologic tests for antibodies to the hepatitis B core antigen (IgG anti-HBcAg) and surface antigen (HBsAg) were negative elsewhere. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a diffusely nodular liver, with a dominant mass measuring 5 cm in diameter. A liver biopsy shows neoplastic hepatocytes. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's neoplasm?
(A) α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
(B) Autoimmune hepatitis
(C) Hemochromatosis
(D) Hepatitis C virus
(E) Primary biliary cirrhosis
Adrenals
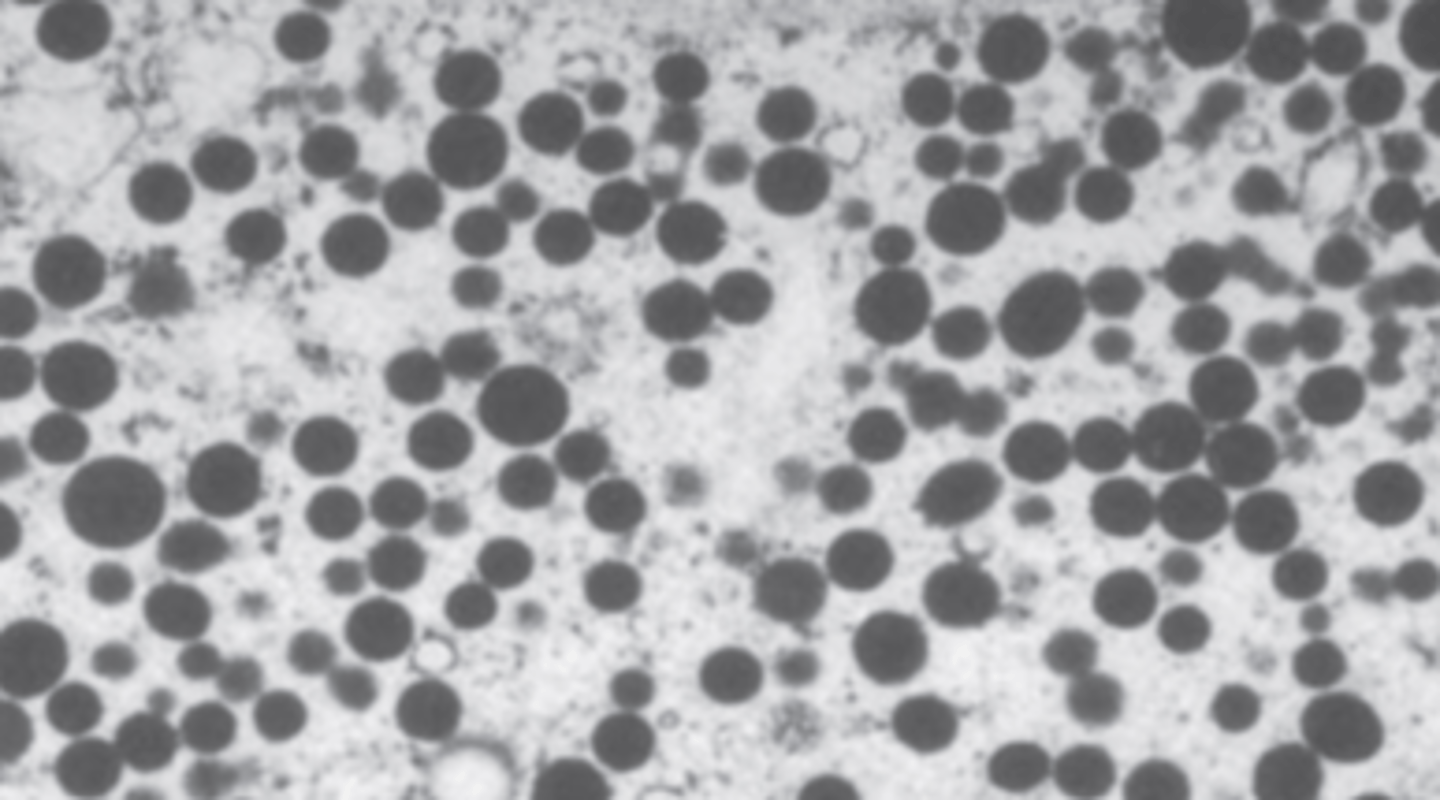
A 59-year-old man complains of weakness and 5 kg (11 lb) weight loss during the past month. An abdominal CT scan suggests metastatic cancer involving the liver and the retroperitoneum. A CT-guided biopsy displays a poorly- differentiated neoplasm. Electron microscopy of the biopsy is shown. Which of the following organs is the most likely primary site for this patient's malignant neoplasm?
(A) Adrenals
(B) Kidneys
(C) Prostate
(D) Testes
(E) Thyroid
Hyperestrogenism
A 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency room in a disoriented state. The patient has an odor of alcohol on his breath. Physical examination reveals palmar erythema, diffuse spider angiomata on the upper trunk and face, and gynecomastia. A liver biopsy shows micronodular cirrhosis, massive steatosis, and Mallory hyaline. Serum levels of ammonia are elevated. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of gynecomastia in this patient?
(A) Hyperbilirubinemia
(B) Hyperestrogenism
(C) Hypersensitivity vasculitis
(D) Hypoalbuminemia
(E) Ketoacidosis