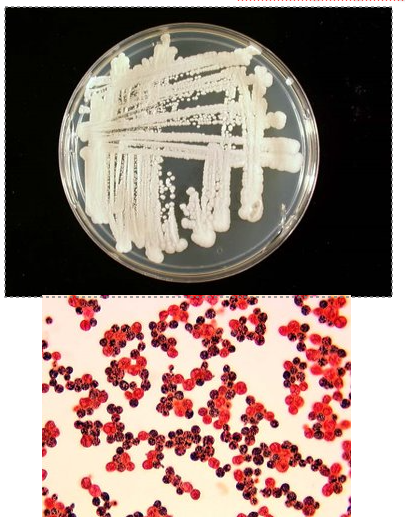
Intro to Mycology, Yeasts
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
fungi vs bacteria
fungi:
eukaryote, uni/multicellular heterotrophic, cell wall (chitin, glucan, mannans), asexual/sexual reproduction
bacteria:
prokaryote, unicellular, heterotrophic/autotrophic, cell wall (peptidoglycans), asexual repro
fungal cell wall
cell wall = mannoprotein, glucan, chitin
cell membrane = ergosterol
fungal forms: yeast
unicellular
asexual repro via budding
colony: creamy, dry, mucoid
fungal forms: mold
multicellular hyphae
asexual/sexual repro by spores
colony: fuzzy or powdery
fungi names
anamorph? telemorph?
anamorph = asexual (often observed in med mycology)
telemorph = sexual
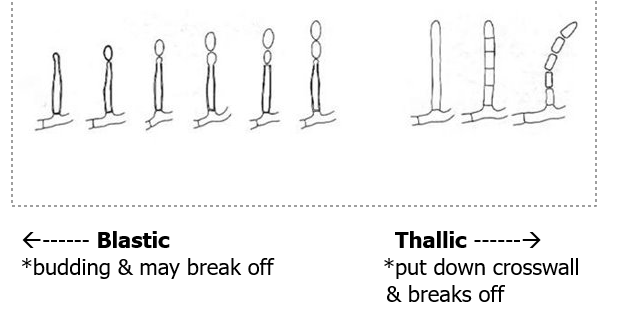
conidiogenesis
blastic
thallic
blastic = produces spores from conidiogenous cell (holoblastic, enteroblastic)
thallic = “ “ from existing hyphal structure (arthoconidia, aleurioconidia)
dimorphic fungi
thermodimorphic - exist as 2 forms:
30C: mold/free living form in nature or lab temp
37C: changes to yeast/parasitic form in tissue or lab
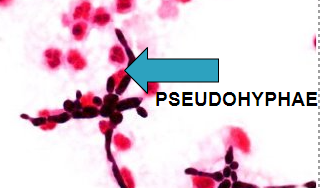
pseudohyphae
tubular str that result from incomplete budding of yeast cells
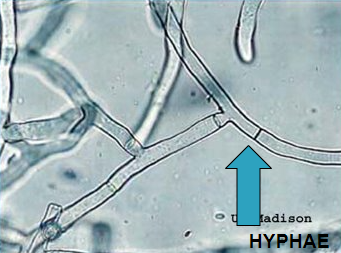
hyphae types
most common in mold
septate: cross wall
non-septate: no cross wall
pauciseptate: rare cross walls (zygomyces)
blastoconidia (yeast)
repro yeast str, forms along pseudohyphae, hyphae, or singly
conidia types (mold)
repro mold str
form at ends of conidiogenesis cell
→ micro- & macroconidia
direct fungal exam (DFE)
calcofluor white stain → binds to chitin & cellulose
histological stains for fungi
Gomori Methenamine silver stain = gray/black (easiest histo stain)
…
non-blood fungi cultures set up (primary media)
IMA - chloramphenicol
BHI
BHI/SB - non-inhibitory
BHI G&C - gentamicin, chlora
BHI CC&G - ““ cycloheximide
Mycosel - cycloheximide & chloramphenicol (for dermatophytes)
CHROMagar Candida - for mixed Candida infns
blood fungi cultures
only upon special request, otherwise, routine blood culture bottles used
secondary fungi media
sabouraud dextrose agar - non-inhib
PDA: potato dextrose - induce sporulation (molds)
PFA: potato flake
yeast extract
BHI
corn meal agar (CMA) - to ID common yeast
fungi culture incubation
37C: BHI, CHROM
30C: BHI CC&G, IMA, Mycosel
fungal bloods: 42 days
regular: 2x/wk for 4 weeks
tools to ID fungi (macroscopic)
growth rate, colonial morph, texture, pigment (front & back)
tools to ID fungi (microscopic)
lactophenol aniline blue slide: scotch tape method
tease mount
slide culture
fungi culture workup
mold isolated: ID to genus level for all sources
yeast isolated:
resp source: r/o Cryptococcus, ID upon request
nonresp: if Candida, ID to sp level; if non-Candida, ID to genus level
Antifungal Susceptibility testing
mold: upon request, long TAT
yeast:
done for all BLOOD cultures for Candidas p
sterile body fluids, and SIS cultures
only in house for Candida
non-invasive Candidiasis
mucocutaneous: oral cavity (thrush), trachea, bronchi, gastric
cutaneous: moist skin areas (armpit, groin), diaper rash in neonates
invasive Candidiasis
enters bloodstream → disseminates
catheter related (m/c)
acute disseminated
chronic disseminated Candidaisis - immunocompromised
deep organ
DFE note:
pseudohyphae
true hyphae & arthroconidia
number of buds & attachment
CHROM vs corn meal agar
CHROM - good for mixed Candida infns
CMA - see microscopic morph of yeast
Candida albicans
chrom: green
CMA: clusters of blastoconidia & single terminal chlamydospores
feet on SBA! (not always)
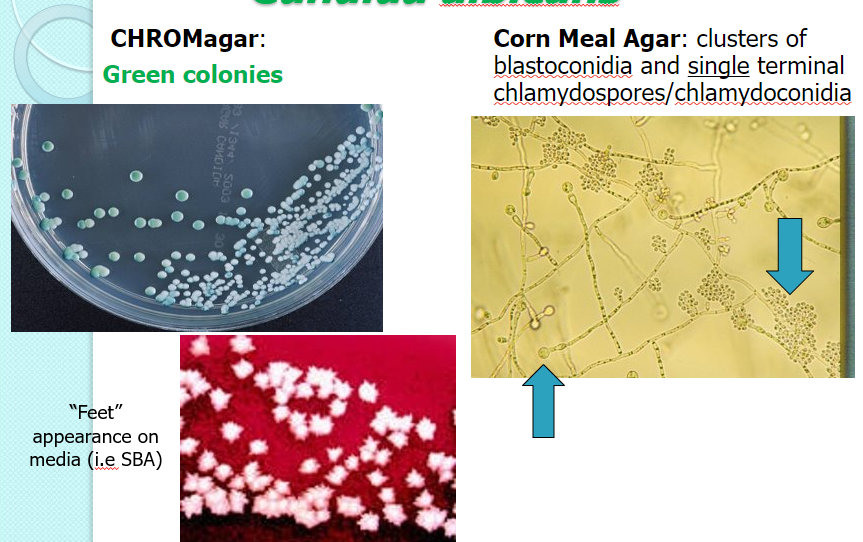
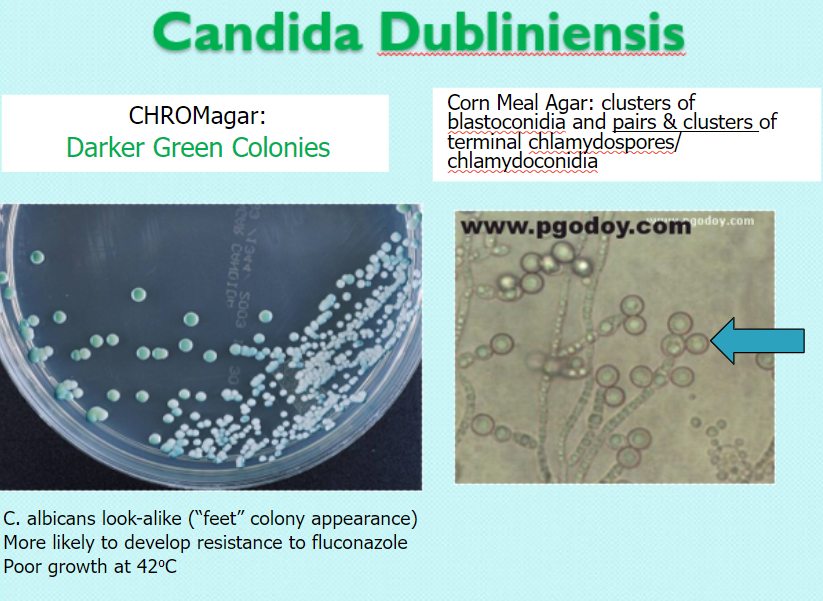
Candida dubliniensis
chrom: darker green
CMA: clusters of blastoconidia & pairs/clusters of terminal chlamydospores
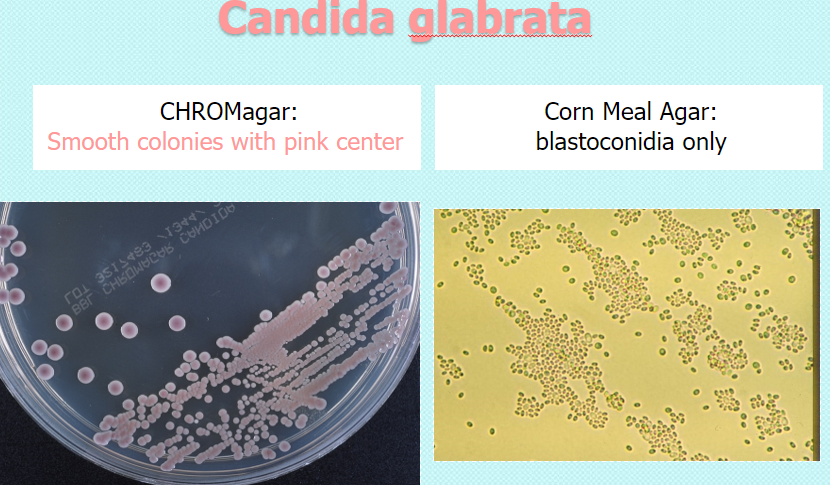
Candida glabrata
chrom: smooth w mauve center
CMA: blastoconidia only, no pseudohyphae
rapid trehalose +
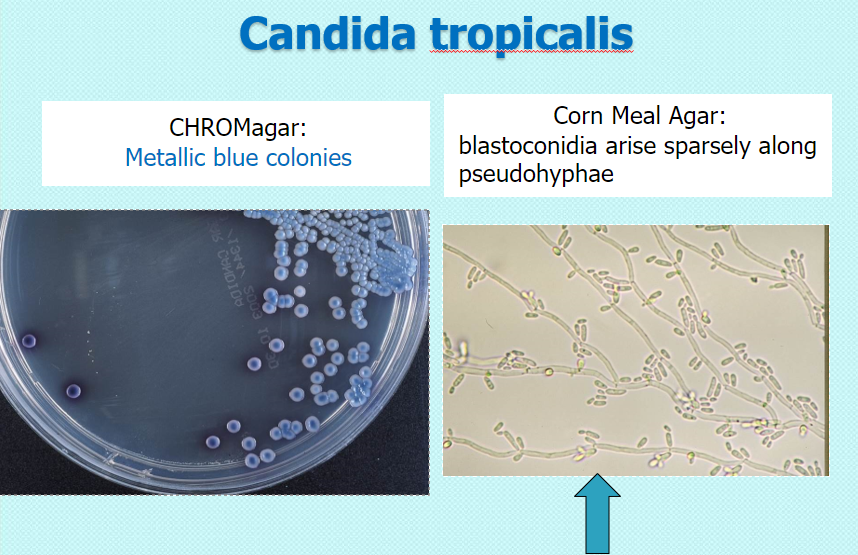
Candida tropicalis
chrom: metallic blue
CMA: blastoconidia arise sparsely along pseudohyphae (no chlamydospores)
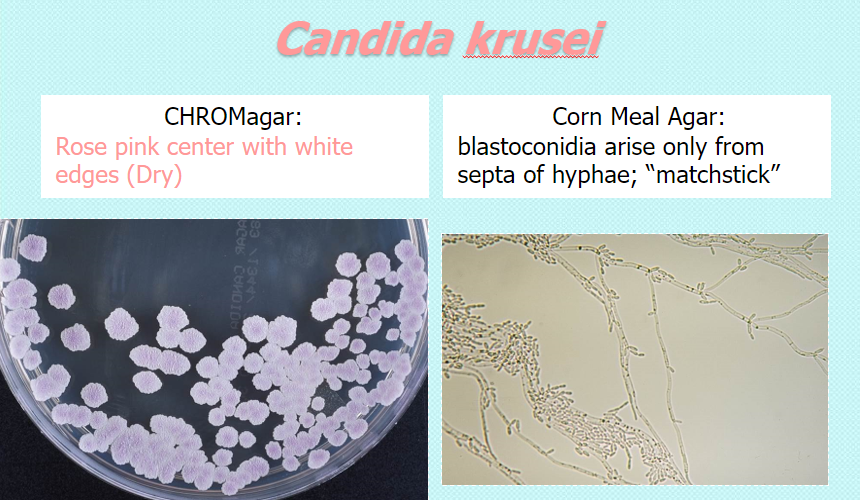
Candida krusei
chrom: rose pink center w white edges, dry
CMA: blastoconidia arise only from septa of hyphae, matchstick (septate or pseudoseptate)
**intrinsically fluconazole-R
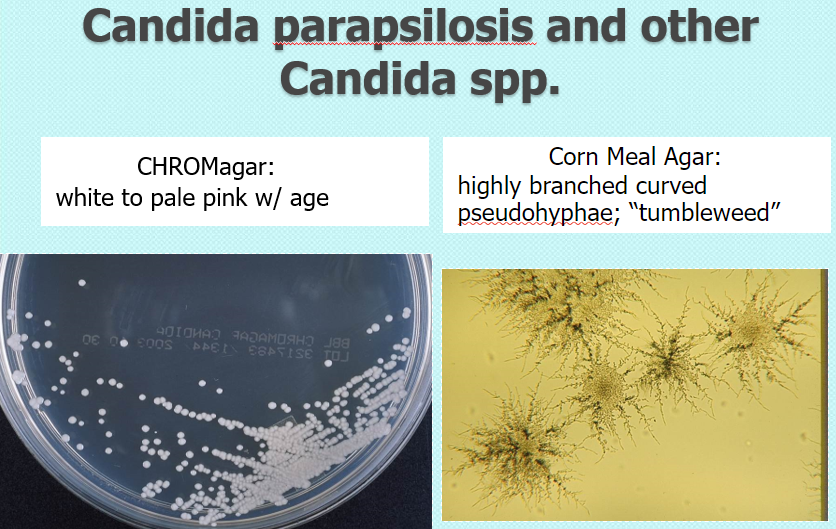
Candida parapsilosis & other spp
chrom: white to pink w age
CMA: highly branched curved pseudohyphae; “tumbleweed”
Candida auris
MDR, high mortality rate
90% fluconazole R
30% amphotericin R
some found to be R to all classes: azoles, polyene, echinocandins
persist on human skin, environment due to biofilm & resist standard cleaning procedures
C. auris protocol
report to CDC
ID w MALDI; Vitek can misID
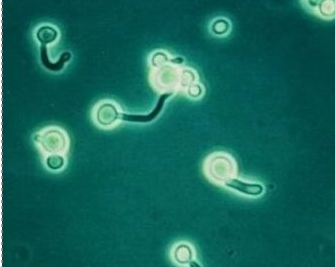
germ tube test
germ tube = non-constricting tube str from yeast after 2-4 hrs of incubation in fetal bovine serum
C. albicans + in 37C & 42C
C. dubliensis + in 37C, but - in 42C
if + → presumptive ID for either C. albicans or C. dubliensis
rapid trehalose
pos rxn = yellow color after 3 hr at 42C
pos for C. glabrata

API20C
based on carb assimilation
48-72h → pos = turbidity
backup if no MALDI ID
Vitek II YST card
same as API20C but automated
MALDI-TOF
matrix assisted laser deabsorption / ionization time of flight (rapid ID)
sample plus matrix → submitted to laser → convert to heat energy → vaporizes into ions
electrical field guides ions into vacuum tube → sep it by weight & flight time → displays into peaks/spectrum → compared to database, given confidence level
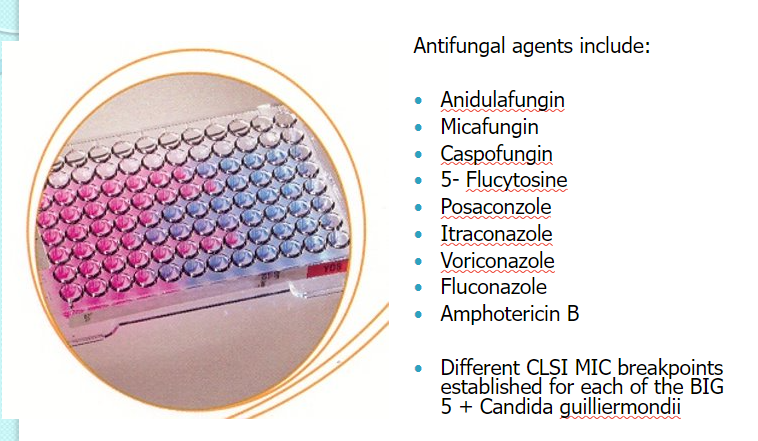
AST for yeast
agar: KB, etest
broth
sensititre yeastone (Trek Dx)
for Candida spp
MIC = 50% of growth reduction, 1st blue well
pink = pos/growth
blue = neg/NG
left to right one Afx (low to high conc)
amphotericin B is vertical
intrinsic Afx resistance
amphotericin B
fluconazole
caspofungi/micafungin
amp B-R → C. lusitaniae, Malassezia furfur
fluconazole-R → C. krusei
Casp/Mica-R → Cryptococcus neoformans / gattii
Cryptococcus neoformans
#1 clin significant
found in bird poop (pigeons) & contaminated soil; infn via aerosols
immunocompromised, infants, young children, HIV
Cryptococcus gattii
#2 clin significant
found in Pacific NW, eucalyptus tree, soil in tropical/subtropical areas
causes disease in immuno- competent & compromised
pneumonia, meningitis
cryptococcoma: infectious granules/lesions in brain, lungs, eyes
aggressive treatment req’d!
Crypto virulence factors
capsules
proteinase
mannoproteins
superoxide dismutase
melanin pigment
polyol metabolites
Cryptococcosis forms
CNS: MG, 100% fatal if untreated
pulmonary: pneumonia, pulmonary lesions
cutaneous: manifestation of systemic infn
disseminated
lab ID of Crypto
DFE: india ink (can be false neg due to non-capsule strains)
urease +
NO3 reduction -
phenoloxidase (L-DOPA ferric citrate test)
niger seed agar test: maroon red-brown black pigment
Crypto Ag lateral flow assay (CSF, for both sp)
why is india ink not reliable?
false neg from non-encapsulated Crypto
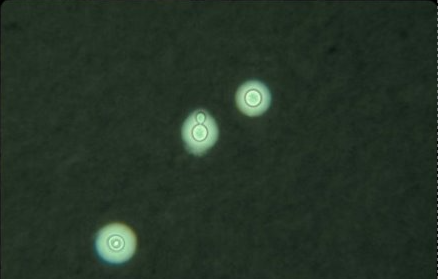
caffeic acid agar/niger seed
cornmeal agar morph: Crypto
no pseudohyphae
round yeast
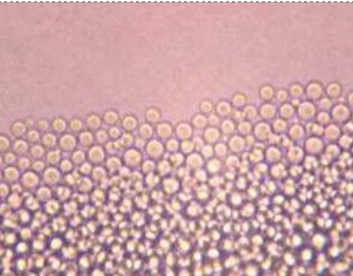
how to distinguish Crypto neoformans from C. gattii?
canavinine-glycine-bromthymol blue agar:
pos rxn: blue color → C. gattii
MADLI TOF
DNA detection by PCR
impt to do bc treatment is more aggressive for C. gattii!
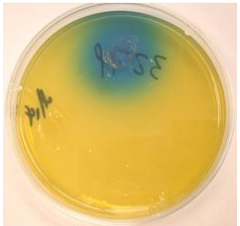
Malassezia furfur complex (lipophilic)
normal skin flora, lipophilic, can cause disease
disease: Tinea versicolor
may infect pt due to lipid rich catheter infusions, ie neonates receiving parenteral nutrition w lipids
non-lipophilic yeast Malassezia pachydermatis
dogs = host
occasionally iso from humans
doesn’t need oil
Lipophilic yeast ID
Malassezia furfur req lipids → olive oil
fungal BC (pt <1yr) → add olive oil
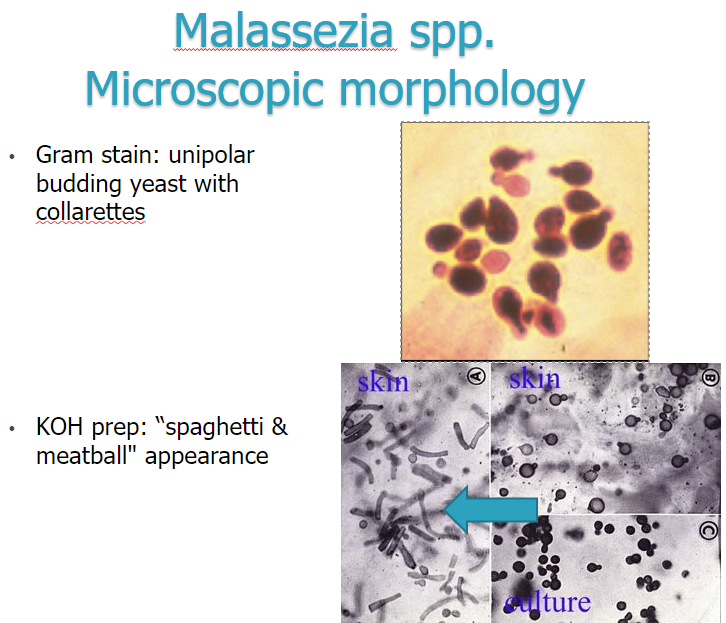
GST: unipolar budding yeast w collarettes, bowling pins or russian dolls
KOH prep: spaghetti & meatballs
other yeast:
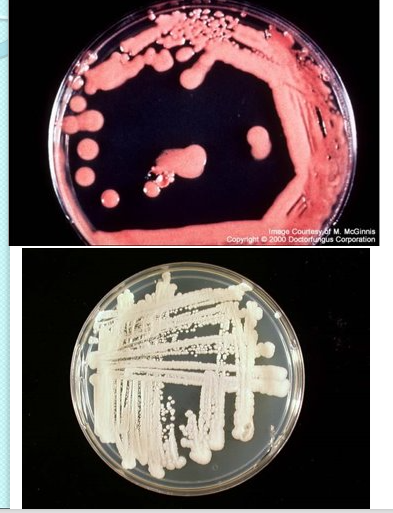
Rhodotorula spp.
Saccharomyces spp.
col: smooth, mucoid, salmon color
col: moist, white
yeast-like fungi
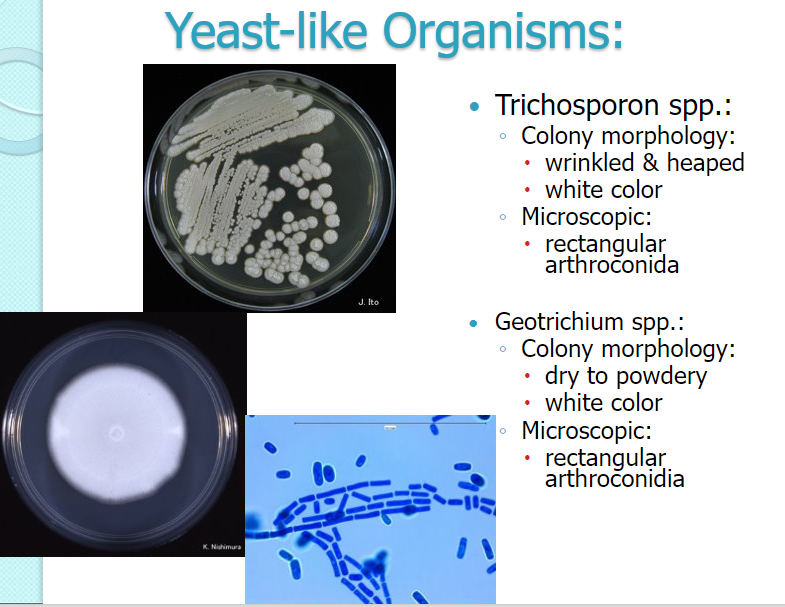
Trichosporon spp: wrinkled, heaped, white; rectangular arthroconidia
Geotrichium spp.: dry to powdery, white, rectangular arthroconidia
Prototheca spp.
green algae that lacks chlorophyll
resembles yeast
round cells (sporangia) containing sporangiospores (endospores) no true budding
stains blotchy