Zoo-Lec (Sem-1) Integumentary System
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
integument
external covering of an animal; shows adaptations for the animal’s environment
integumentum
Latin word of origin for integument; meaning cover
protection; support; movement
the three main functions of the integumentary system
surface of exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes
function of integument; some organisms (amphibians especially) use the skin as a respiratory organ
protection from injury and invasions of microorganisms
function of integument; forms a physical barrier between the external environment (bacteria, chemicals, and temperature) and the internal environment
regulation of body temperature
function of integument; keeping body temperature within limits even when environmental temperature varies (thermoregulation)
reception of environmental stimuli
function of integument; presence of sensory nerve endings that receive and interpret stimuli
prevention of desiccation
function of integument; presence of thick layers and outer lubrication film to avoid extreme moisture loss
desiccation
the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying
invertebrate
an umbrella term describing animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a spine or backbone)
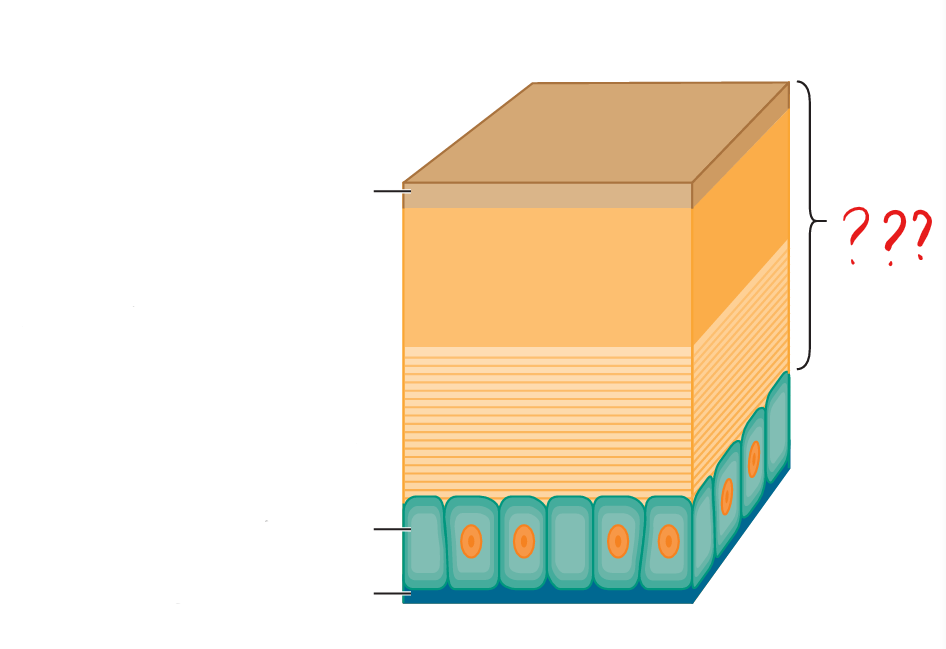
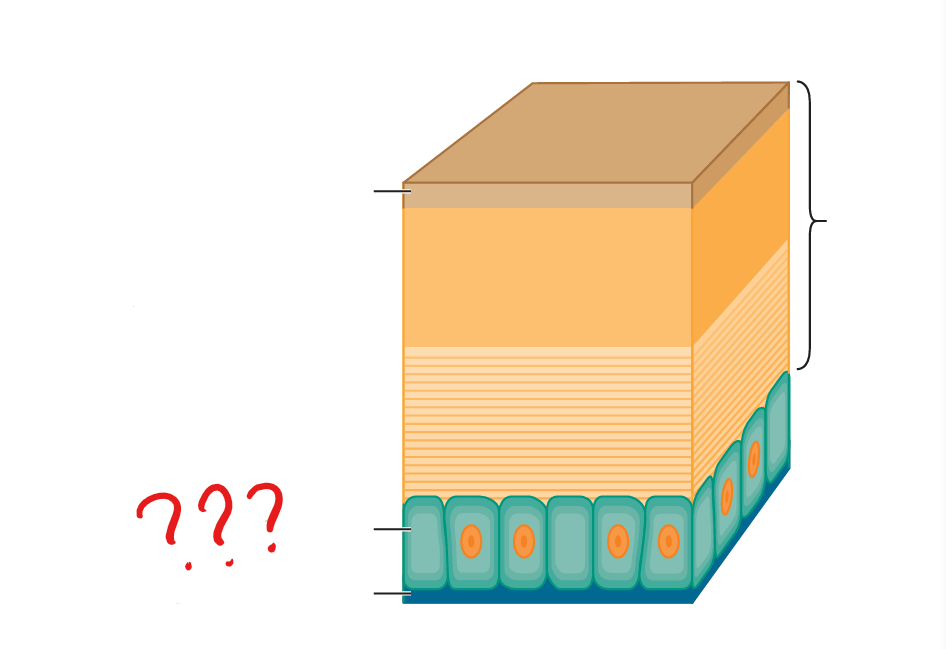
invertebrate integument
the outer covering of animals that lack a vertebral column; consists of a single layer of columnar epithelial cells (epidermis)
invertebrate epidermis
a single layer of epithelial cells; rests on a thin extracellular layer of collagenous fibers
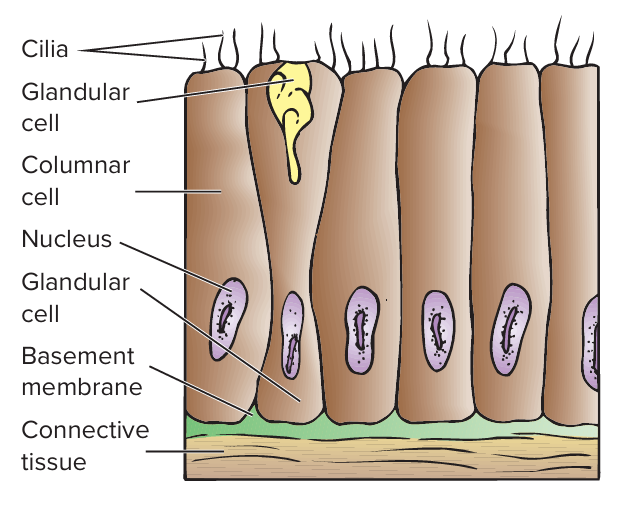
basement membrane
a thin extracellular layer of collagenous fibers; separates the epidermis from underlying muscles or other tissues
cilia
modified outer layer; present in the epidermis of free-living flatworms (e.g. Platyhelminthes, Turbellaria) that move by ciliary locomotion
epidermal glands
may secrete mucus and noxious chemicals that protect the animal (e.g. Mollusca, Gastropoda) and secrete skeletal materials like calcium carbonate (e.g. Cnidaria, anthozoan hard corals)
syncytial tegument
the epidermis of parasitic flatworms (Cestoidea and Trematoda) that protects against host defenses and aids cestodes (e.g. tapeworms, Cestoda) in the absorption of nutrients from the host digestive tract
cuticle
non-living; possessed by all ecdysozoans; secreted by the epidermis; either collagenous or chitinous; hardened in arthropods; provide protection but restricts growth; is shed periodically
restrict growth
the cuticle provides protection, but they also…
sclerotization
biological processes that cause tissues to become hard and stiff
invertebrate hypodermis
the epidermis when it is overlain by a cuticle; secretes the cuticle
invertebrate dermis
a connective tissue layer below the basement membrane; secretes calcium ossicles that comprise endoskeletal elements in the Echinodermata
proglottid
each segment in the strobila of a tapeworm, containing a complete sexually mature reproductive system
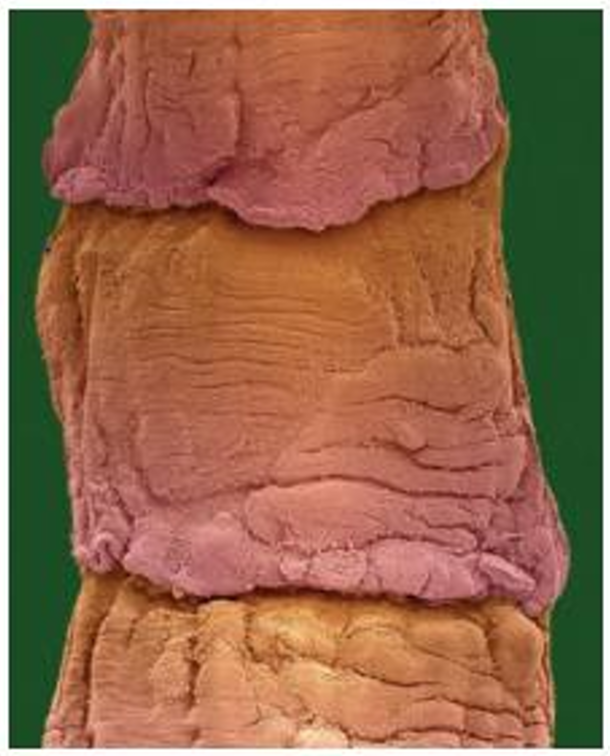
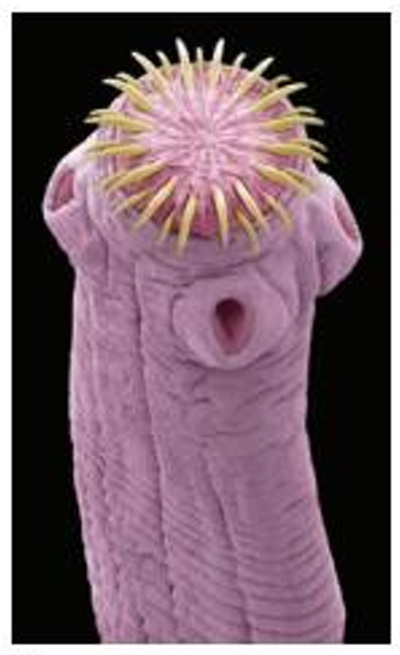
scolex
the head of a tapeworm either in the larva or adult stage from which the proglottids are produced by budding
vertebrate
animals that possess a vertebral column and/or notochord at any point in their lives
vertebrate integument
often simply called skin; with multi-cell layered epidermis
vertebrate epidermis
often comprised of multiple cell layers and is underlain by a basement membrane
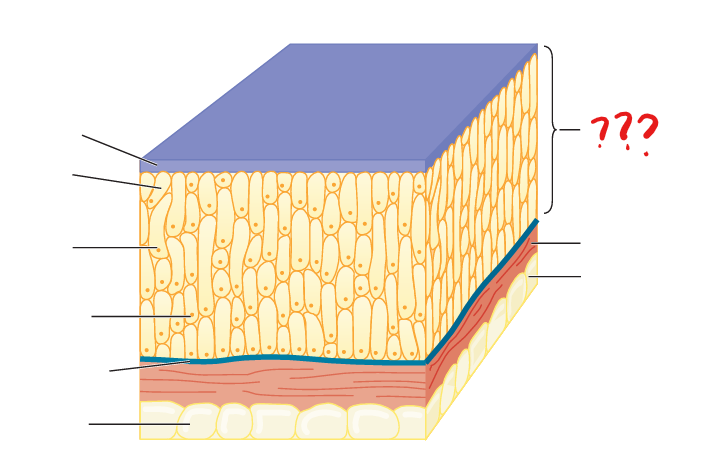
vertebrate dermis
comprised of collagenous and other connective tissue fibers and cells
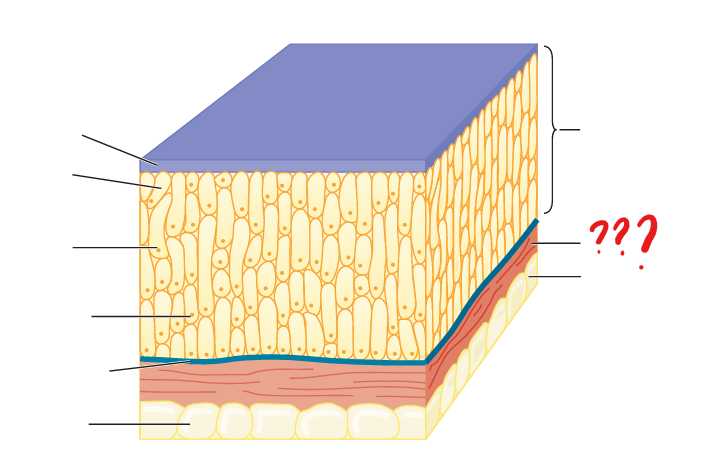
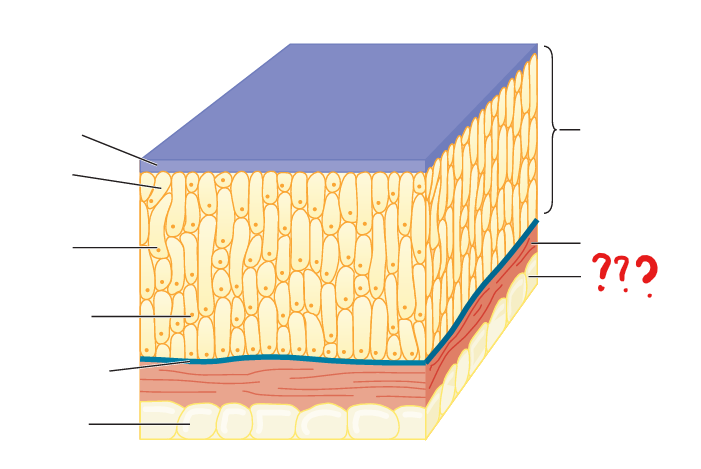
vertebrate hypodermis
in contrast to that described for ecdysozoans, consists of connective tissues (including adipose), nerve endings, and blood vessels; separates the integument from deeper tissues, such as muscle tissue
Petromyzon
adult lamprey
fish epidermis
outer layer that is multilayered and richly supplied with glandular cells
hagfish (class Myxini); lampreys (class Petromyzontida)
fishes with a scaleless integument with mucous-secreting cells
granular cells
contribute to a mucous coat that reduces friction between the water and the surface of the animal
mucous coat
protects against bacteria and other infections
thread cells
found in hagfishes; produce cords of mucus that are secreted through multicellular slime glands
slime
secreted when the hagfish is irritated and discourages predators whose gills may be clogged by copious slime discharge
pheromones
secreted by epidermal cells; communicate danger or other chemical messages to members of the same species
dermally derived scales
absent in hagfishes and lampreys; protect a fish and are oriented in a fashion that reduces friction as the fish swims; present in Chondrichthyes and bony fishes
Chondrichthyes
sharks and their relatives
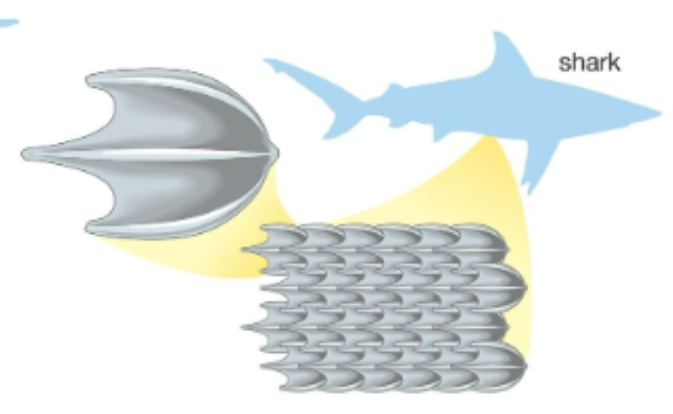
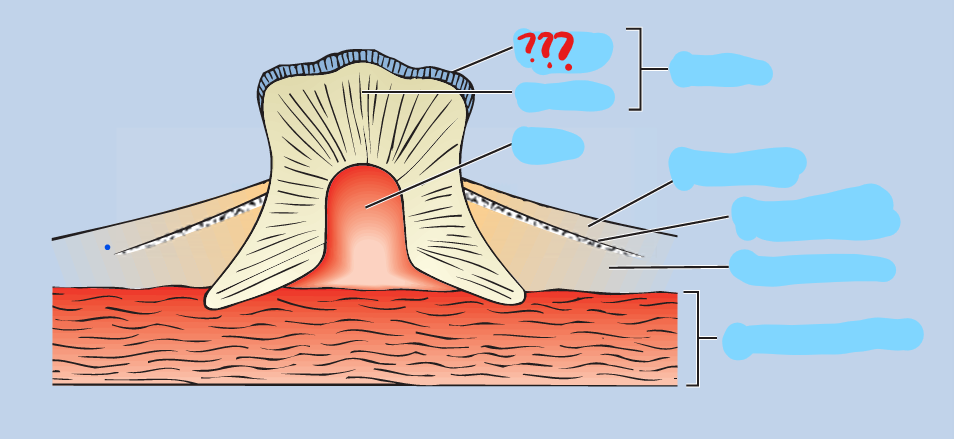
denticles
present in most Chondrichthyes; small placoid scales arising from and seated in the dermis; comprised of a bone-like calcified matrix called dentine, and each scale projects through the epidermis; wear and are replaced through the life of the fish
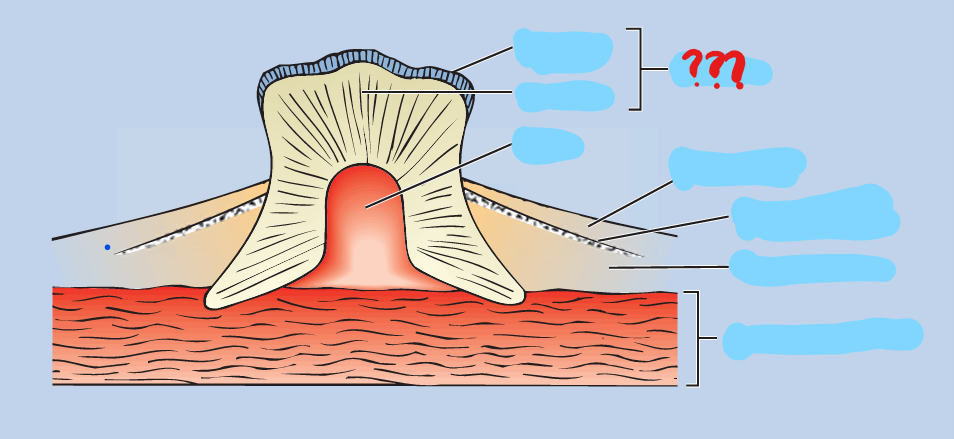
placoid
toothlike, being made of dentin with a pointed backward projection of enamel, as in sharks and rays
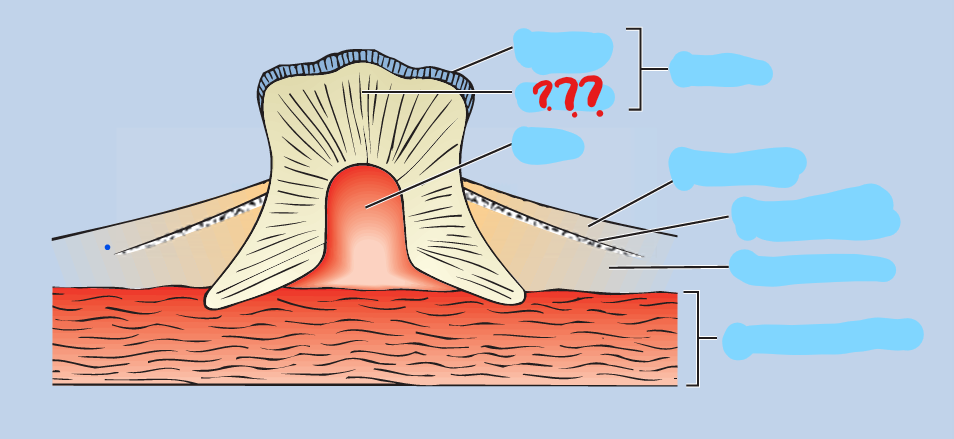
dentine
a bone-like calcified matrix
enamel
secreted by the epidermis; covers the dentine core
true
true or false: the scales of bony fishes do not lose their covering of epidermal cells
scales
are classified based on structure, but they are all comprised of a layering of dermal bone, dentine, and an epidermally derived layer of enamel
dermal bone; dentine; epidermal-derived layer of enamel
layers within a scale
dermal blood capillaries
associated with the scales of bony fishes; grow throughout the life of a fish; growth patterns produce the rings that are useful in determining the age of a fish