Important Terms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Long-run Economic Growth
the process by which rising productivity increases the average standard of living.
real GDP per capita
the amount of production in the economy, per person, adjusted for changes in the price level
Formula for current real GDP
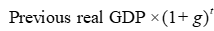
Rule of 70
determine how long it will take for an economic variable to double
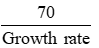
Labor Productivity
the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work
Potential GDP
the level of real GDP attained when all firms are operating at capacity
Capacity
refers to “normal” hours and a “normal” sized workforce.
Financial System
the system of financial markets and financial intermediaries through which firms acquire funds from households
Financial Markets
markets where financial securities, such as stocks and bonds, are bought and sold
Financial Security
a document (sometimes electronic) stating the terms under which funds pass from the buyer of the security to the seller.
Stock
financial security representing partial ownership of a firm
Bond
financial security promising to repay a fixed amount of funds. Essentially a loan from a household to a firm
Financial Intermediaries
firms, such as banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and insurance companies, that borrow funds from savers and lend them to borrowers.
3 key services of the financial system
Risk Sharing
Liquidity
Information
Risk Sharing
By allowing investors to spread their money over many different assets, investors can reduce their risk while maintaining a high expected return on their investment
Liquidity
The financial system allows savers to quickly convert their investments into cash
Information
The prices of financial securities represent the beliefs of other investors and financial intermediaries about the future revenue stream from holding those securities.
Private Savings
household income that is not spent
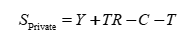
Public saving
The government “saves” whatever it brings in but does not spend
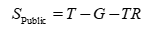
Balanced Budget (Spublic=0)
the government spends as much as it brings in
Budget Deficits (Spublic = –)
when money going out (spending ) exceeds money coming in (revenue)
Budget Surplus (Spublic = +)
when money going in (revenue) exceeds money coming out (spending)
Market for Loanable Funds
a (conceptual) interaction of borrowers and lenders that determines the market interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds exchanged
Crowding Out
a decline in private expenditure as a result of increases in government purchases
Great Recession
The period of recession starting in late 2007 and ending in mid 2009 was the longest and most severe since the Great Depression of the 1930s
Great Moderation
Business cycles have been particularly mild since the mid-1980s