ANAT 3001 nervous tissue
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
function of nervous system
gather information from stimuli by sensory receptors
process the information
produce a response by activating effector organs (muscles or glands)
structural parts of the nervous system
CNS
brain
spinal cord
integrating and command center of NS
PNS
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
ganglia
mostly nerves that carry signals to and from CNS
systems of the nervous system
sensory: receives sensory information
motor: carries signals to muscles and glands
sensory system
somatic
sensations on the skin of the body wall (touch pain, pressure, pulled muscle)
proprioception (position of body in space)
special senses (hearing, vision, taste)
visceral (automatic)
sense stimuli from viscera (internal organs) such as stretch, pain, temperature, blood concentrations
motor system
somatic
generally voluntary
stimulates contraction of skeletal muscles
visceral
generally voluntary
stimulates contraction smooth and cardiac muscles, secretion by glands
nervous tissue cells
neurons
glial cells
neurons
excitable cells, transmit signal
glial cells
non excitable, support neurons
characteristics of neurons
conduct electrical signals along plasma membrane
extreme longevity
do not divide
high metabolic rate
neuron = nerve cell = nerve fiber
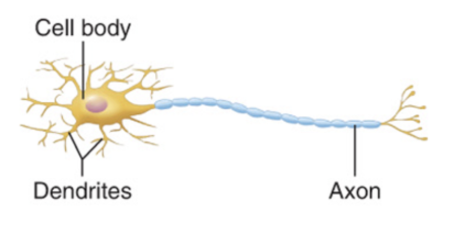
basic features of a neuron
dendrites
processes that receive impulses and send it towards cell body
cell body
contains nucleus and cytoplasm
axon
process that carries impulse away from cell body
neuron communication
neurons communicate through a synapse - pass information
presynaptic neuron
release neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) from axon
postsynaptic neuron
neurotransmitters bind to postsynaptic membrane
structural classifications of neurons
multipolar
unipolar
bipolar
multipolar
many processes extend from cell body
many dendrites, one axon
most abundant (99% of neurons)
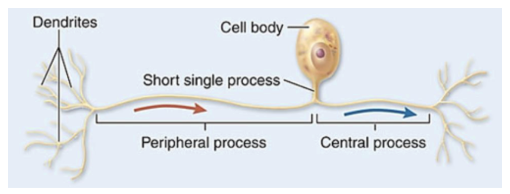
unipolar
one process from cell body that divides into 2 processes
peripheral process carries sensory info from skin to cell body
central process travels to the CNS
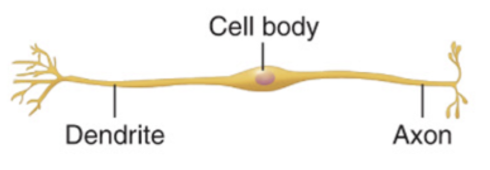
bipolar
2 processes extend from cell body
very rare
some special sensory organs (inner ear, olfactory, retina)
functional classifications of neurons
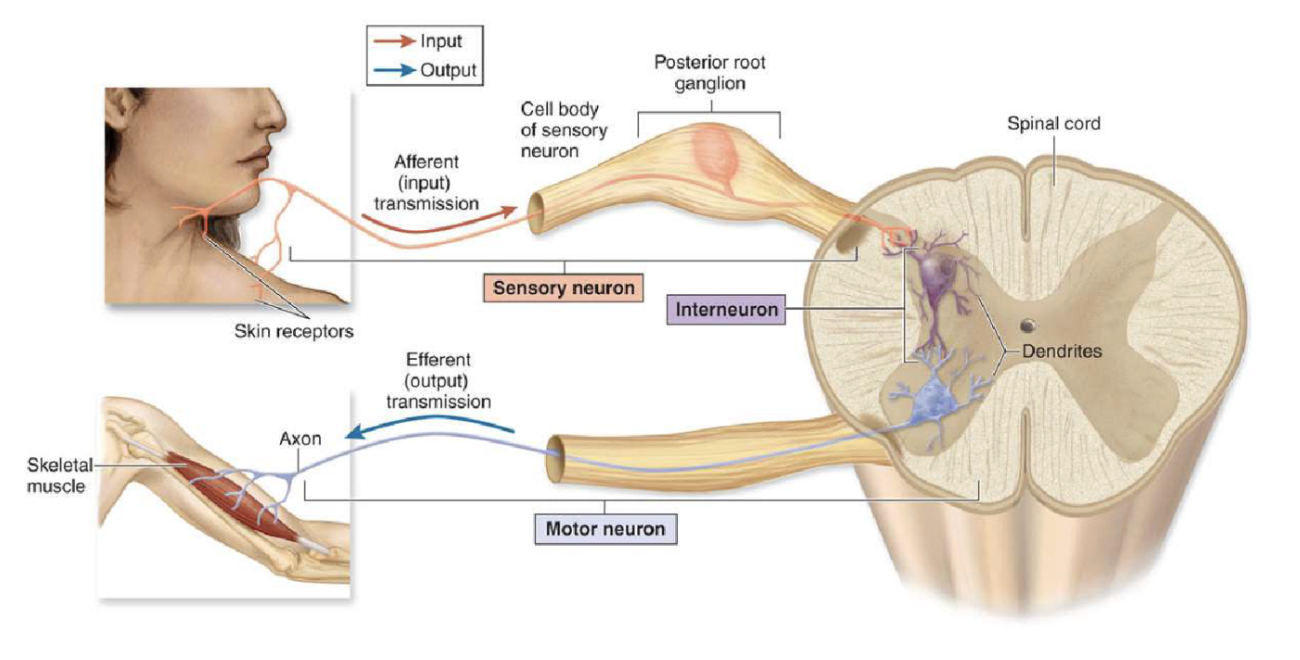
sensory neurons (afferent)
interneuron
motor neurons (efferent)
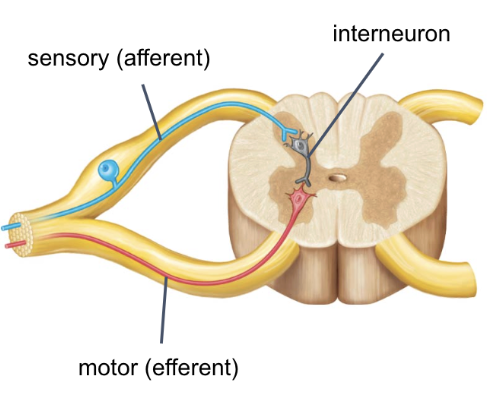
sensory neurons (afferent)
transmit impulse toward CNS from receptors in PNS
most are unipolar with ganglia outside CNS
central process terminates in CNS
interneuron
between sensory and motor neurons
multipolar neurons within the CNS
99.98% of all neurons
motor neurons (efferent)
transmit impulse away from CNS
multipolar
cell body in CNS with axon synapsing on target organ
gray and white matter in CNS
brain and spinal cord have distinct gray and white matter that vary by contents
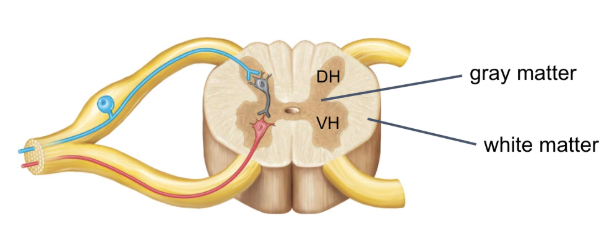
gray matter
butterfly shaped central region
posterior wing is dorsal horn, anterior wing is ventral horn
contains cell bodies, dendrites, and nonmyelinated axons
white matter
surround the gray matter
contains myelinated axons (myelin sheaths give white color)
axons ascent or descent spinal cord to carry impulses to different parts of CNS
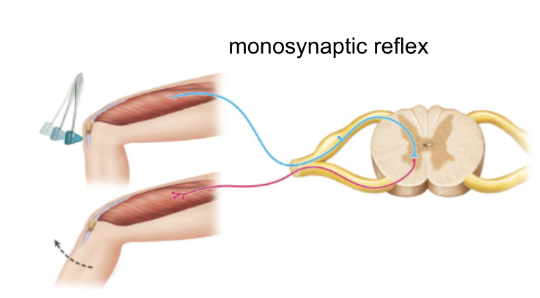
basic spinal cord circuit
reflexes
reflex arc
monosynaptic reflex
polysynaptic reflex
reflex arc
simple chain of neurons that causes simplest reflexive behaviors
information is not processes by brain before response
monosynaptic reflex
simplest reflex
sensory neuron synapses with motor neuron (no interneuron)
ex: knee jerk flex
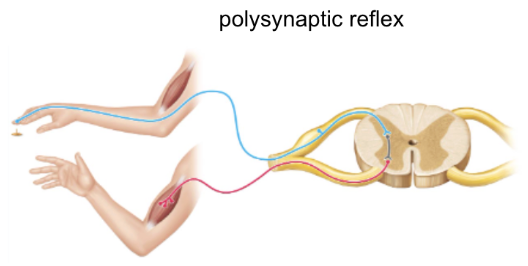
polysynaptic reflex
more common
one or more interneurons
ex: withdrawal reflex
nerve
rope like organ of PNS
neuron
single impulse conducting cell
nerve vs neuron
a nerve consists of many axons or neurons
a nerve can carry axons of
motor neurons only
sensory neurons only
both sensory and motor neurons
many axons are bundles together as fascicles, many fascicles make up a nerve (remember muscle tissue!!)
glial cells or neuroglia
support cells in nervous tissue
glial cells in CNS
astrocytes
microglial cells
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
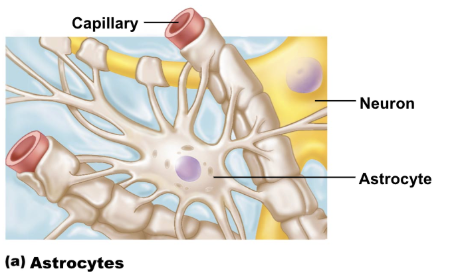
astrocytes
star shapes, most abundant cell
radiating ends attach to axons and capillaries
regulate blood flow in active brain regions
regulate neurotransmitter levels
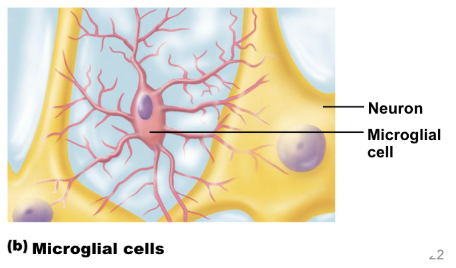
microglial cells
smallest, least abundant cell
macrophages of CNS
engulf invading microorganisms and dead neurons
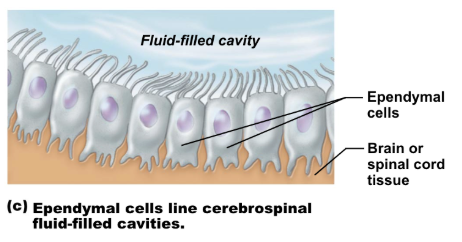
ependymal cells
form epithelium that lines central cavity of spinal cord and brain (ventricles)
produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
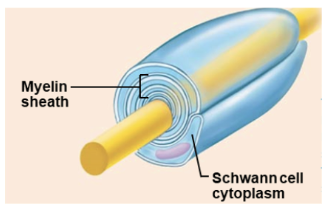
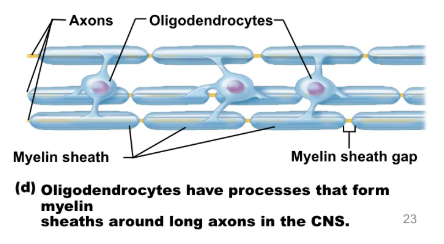
oligodendrocytes
processes wrap around axons in CNS
create an insulating cover (myelin sheath)
myelin sheaths - increase speed of impulse conduction along axon, more energy efficient
glial cells in PNS
satellite cells
schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
satellite cells
surround neuron cell bodies within ganglia
regulate delivery of nutrients and removal of waste from neurons
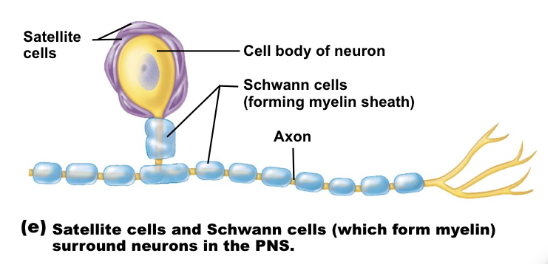
schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
myelinate axons in PNS
each neurolemmocyte is a single myelin sheath on an axon