dental embry, histo, and anatomy ch 3-4 quiz
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
embryology
the study of prenatal development
prenatal development
begins with the start of pregnancy and continues until the birth of the child
9 month gestation period divided into 3 trimesters
primordium
the earliest indication of a tissue type or an organ during prenatal development
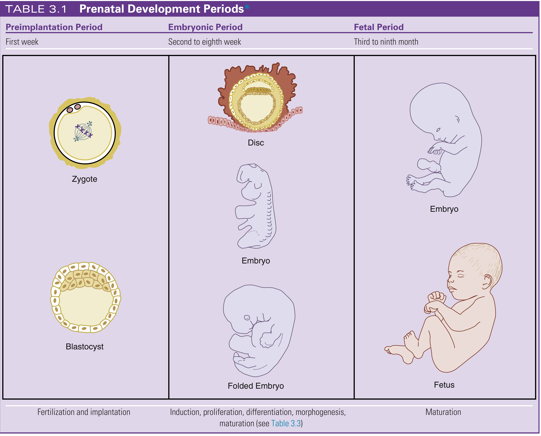
preimplantation period
begins during first week after conception
most congenital malformations (birth defects) occur during both the preimplantation and embryonic period
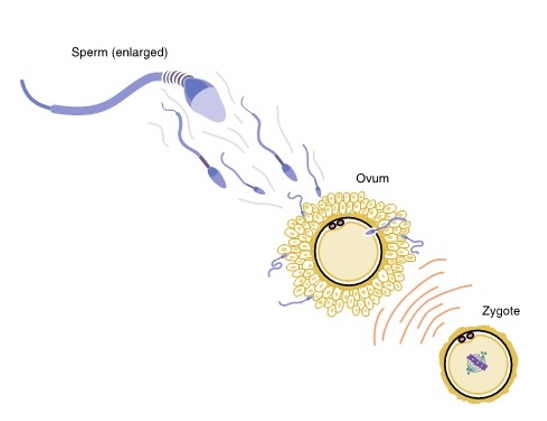
a woman’s ovum is penetrated by sperm during fertilization and final stage of meiosis occurs in ovum
zygote (fertilized egg) forms
undergoes mitosis to form cleavage
becomes morula
becomes vesicle known as blastocyst
end of first week blastocyst implants into endometrium
congenital malformations
birth defects
evident at birth
most occur during both the preimplantation period and the embryonic period
amniocentesis
amniotic fluid test (AFT)
is a prenatal diagnostic procedure to detect chromosomal abnormalities where the amniotic fluid is removed and its fetal cells are grown for microscopic study of the chromosomes and sampled for other fetal complications
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT)
new type of prenatal genetic test that does not pose any risk
a cell free fetal DNA testing that involves a simple blood draw from the pregnant women
teratogens
environmental agents and factors that include infections, drugs, and radiation that are considered __

chemical teratogens
methylmercury
polychlorinated biphenyls

drug teratogens
ethanol
tetracycline
phenytoin sodium
lithium
methotrexate
aminopterin
diethylstilbestrol
warfarin
thalidomide
isotretinoin (retinoic acid)
androgens
progesterone

infectious teratogens
rubella virus
syphilis spirochete
herpes simplex virus
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)

radiation teratogen
high levels of ionizing radiation
depends on the dose and severity
can cause cleft lip or cleft palate
may injure embryonic cells, resulting in cell death, chromosomal injurt, and delay of intellectual and physical growth

zygote
fertilized egg
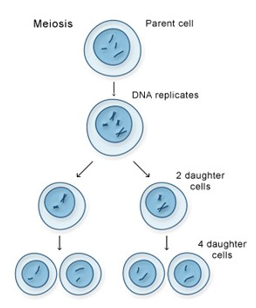
meiosis
joining of chromosomes from both biologic parents forms a new individual with “shuffled” chromosomes
joining of sperm and ovum creates a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes (23 from dad, 23 from mom)
this diploid cell goes through meiosis to shuffle genetic material and form 4 haploid daughter cells with 23 chromosomes
cleavage
After implantation, the zygote undergoes mitosis (individual cell divison) that splits it into more and more cells
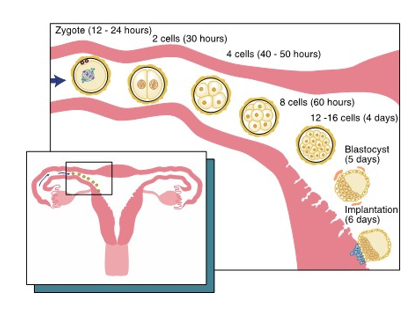
morula
after initial cleavage
the solid ball of cells
gets its name for having the appearance of a mulberrry
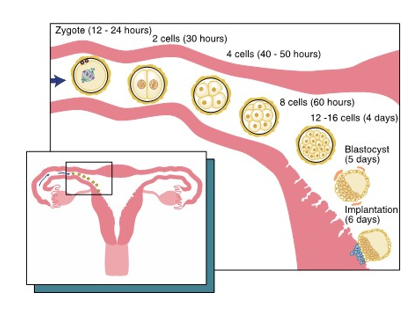
blastocyst
Due to the ongoing process of mitosis and secretion of fluid by the cells within the morula, the zygote becomes a vesicle known as a blastocyst
also known as blastula
travels down the fallopian tube then undergoes implantation in the endometrium lining of the uterus
trophoblast and embryoblast layers
after a week of cleavage, the blastocysts consists of a layer of peripheral cells and a small inner mass of embryonic cells
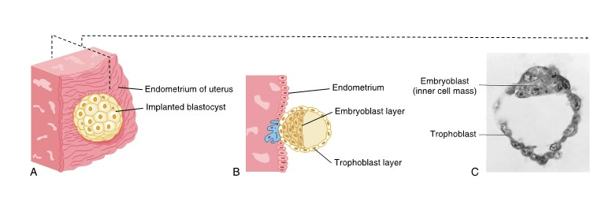
trophoblast layer
layer of peripheral cells located on the top of the blastocyst
will give rise to important prenatal tissues
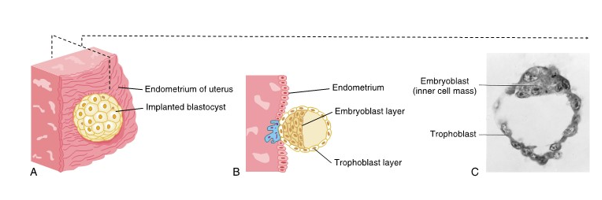
embryoblast layer
layer of peripheral cells found as the inner cell mass of the blastocyst
what will later become an embryo
syndrome
a group of specific signs and symptoms
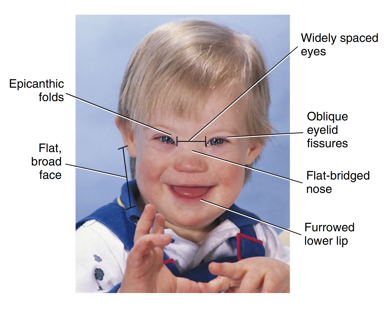
down syndrome
also known as trisomy 21
An extra chromosome number 21 is present after meiotic division
characterized by epicanthic folds, oblique eyelid fissures, flat-bridged nose, furrowed lower lip, widely-spaced eyes, and a flat broad face
increased levels of periodontal disease, delayed tooth eruption, fewer teeth present, microdontia, and increased risk of alzheimer’s disease
ectopic pregnancy
when implantation may occur outside the uterus, involving the condition
most occur within fallopian tube
associated with factors that delay or prevent transport of the dividing zygote to the uterus
embryonic period
the second period of prenatal development
extends from the beginning of the second week to the twelfth week
induction
developmental process
action of one group of cells on another that leads to establishment of developmental pathway in responding tissue
first step, planning stage
signals are sent and cells communicate in order to guide what each part will develop into
proliferation
controlled cellular growth and accumulation of byproducts
massive cell growth to have enough “materials” for plans
growth may be appositional or interstitial
differentiation
change in identical embryonic cells to become distinct structurally and functionally
cells become specialized to do unique jobs
occurs at various rates
morphogenesis
development of specific tissue structure or differing form due to embryonic cell migration or proliferation and inductive interactions
development of specific tissue structure or shape
body starts taking and forming physical shape
maturation
final stage, finishing touch
attainment of adult function and size due to proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis
cells and organs complete development and start working properly
appositional growth
tissue enlarges its size by the addition of layers on the outside of a structure
interstitial growth
occurs from deep within a tissue or organ
inter = inside
cytodifferentiation
is the development of different cell types
histodifferentiation
is the development of different histologic tissue types within a structure
morphodifferentiation
is the development of the differing morphology, which makes up its structure or shape, for each organ or system
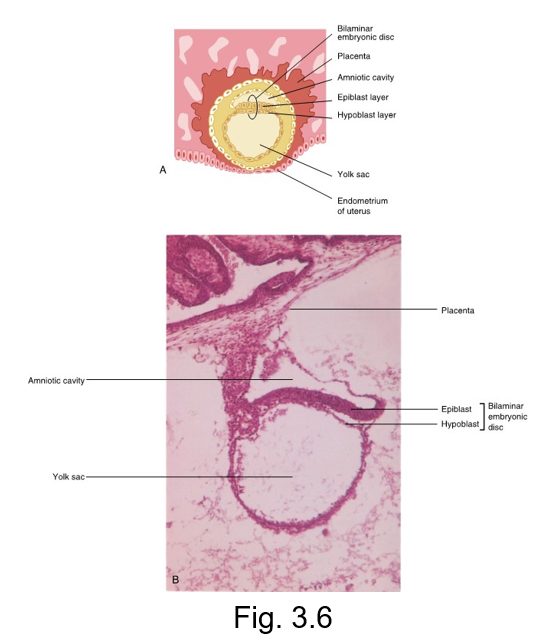
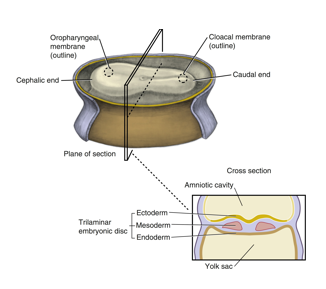
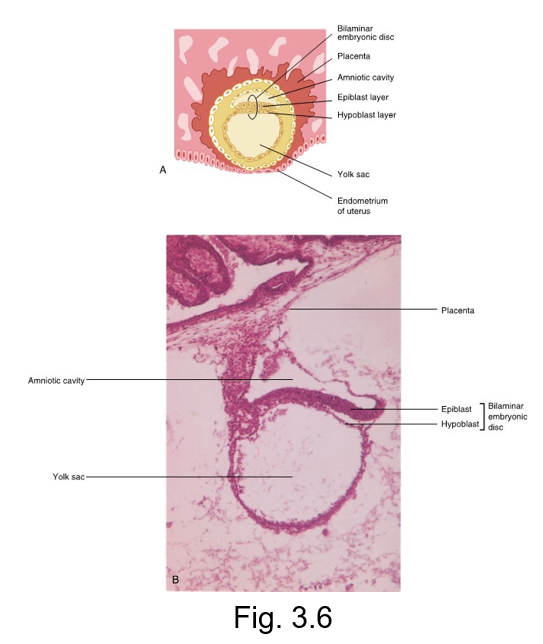
second week of prenatal development
implanted blastocyst grows
Increased number of embryonic cells creates the embryonic cell layers (germ layers) within the blastocyst
A bilaminar embryonic disc is eventually developed
The disc is suspended in the endometrium lining the uterus between two fluid-filled cavities, the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac
These layers are the ectoderm and endoderm
The placenta develops from interactions of the trophoblast layer and the endometrial tissue
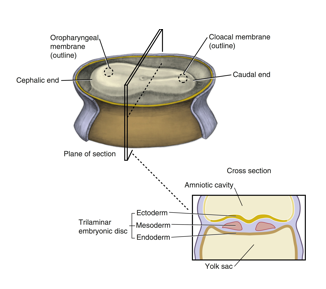
bilaminar embryonic disc
developed from the blastocyst and appears as a three dimensional but flattened, essentially circular plate of bi layer cells
consists of ectoderm (top layer)
and endoderm (bottom layer)
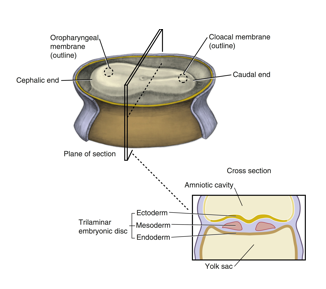
ectoderm
origin: epiblast layer
histologic features: columnar
future structures: epidermis; sensory epithelium of eyes, ears, nose, nervous system, neural crest cells; mammary and cutaneous glands
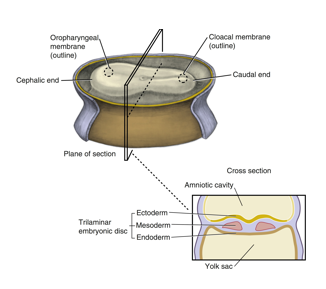
mesoderm
origin: migrating cells from epiblast layer (primitive streak)
Histologic features: varies
future structures: dermis, muscle, bone, lymphatics, blood cells and bone marrow, cartilage, reproductive and excretory organs
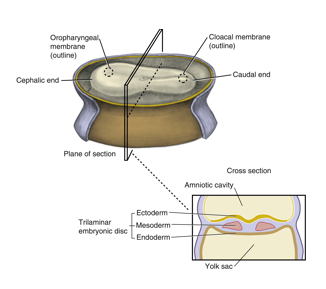
endoderm
origin: migrating cells from epiblast layer
histologic features: cuboidal
future structures: respiratory and digestive system linings, liver, pancreatic cells
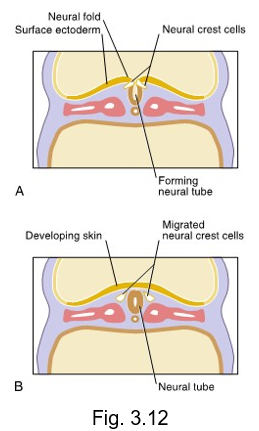
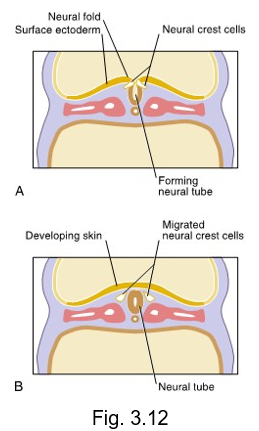
neural crest cells
origin: migrating neuroectoderm
histologic features: varies
future structures: components of nervous system pigment cells, connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, certain dental tissue
migrate from the crests of the neural folds and disperse within mesenchyme
essential in formation of most oral and dental tissue except for the enamel and certain types of cementum as well as the development of the face and neck
placenta
a prenatal organ that joins the pregnant female and the developing embryo
develops from interactions of the trophoblast layer and endometrial tissue
permit selective exchange of soluble bloodborne substances between them (O, CO2, and nutritional/ hormonal substances)
third week
The primitive streak forms within the bilaminar embryonic disc
primitive streak causes bilateral symmetry
Cells from the primitive streak migrate and move down, eventually becoming the mesoderm, causing the bilaminar disc to be trilamniar
cephalic end forms along with the oropharyngeal membrane
oropharyngeal membrane includes ectoderm and endoderm but NO MESODERM
This membrane is the location of the primitive mouth (stomodeum) of the embryo and the beginning of the digestive tract
trilaminar disc also has a caudal end
CNS begins to develop
formation of the neuroectoderm from the ectoderm within the neural plate that thickens to form the neural groove
neural groove deepens to become surrounded by the neural folds
neural folds meet and fuse, forming the neural tube
neural crest cells develop from neuroectoderm and migrate from the crests of neural folds and disperse within the mesenchyme
vital in the formation of most oral and dental tissue, except for the enamel and certain types of cementum, as well as the development of the face and neck
By the end of the third week, the mesoderm differentiates and divides on each side of the neural tube to form somites
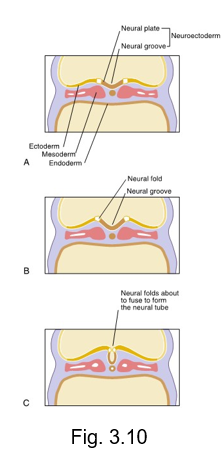
neural plate
central band of cells that extends the length of the embryo from the cephalic end to caudal end
undergoes further growth and thickening
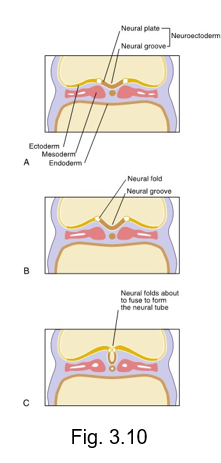
neural groove
after the neural plate undergoes further growth and thickening, it deepens and invaginates inward forming the __ __
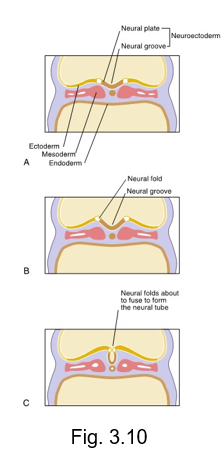
neural folds
near the end of the third week, the neural groove deepens further and is surrounded by the __ __
neural tube
is formed during the fourth week by the neural folds undergoing fusion at the most superior part
somites
38-paired cuboidal segments of mesoderm
located on both sides of the developing nervous system
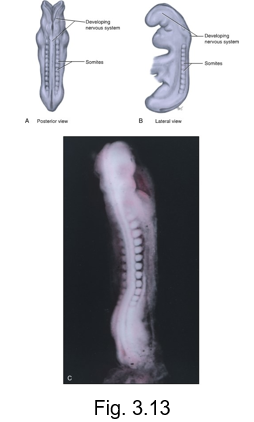
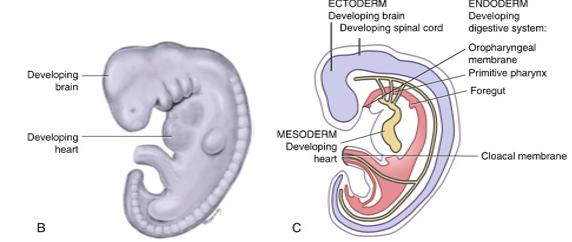
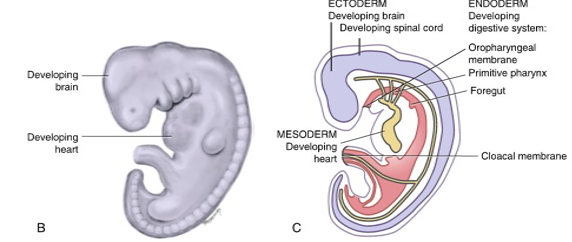
fourth week
disc undergoes embryonic folding as a result of extensive growth of ectoderm and there is development of the brain and spinal cord, heart, and digestive tract
movement of embryonic cell layers form long and hollow tube lined by endoderm from oropharyngeal membrane to cloacal membrane
anterior part of this tube is the foregut
two posterior parts are midgut and hindgut
face and neck begin to develop, with the primitive eyes, ears, nose, oral cavity, and jaw areas
foregut
forms the primitive pharynx or primitive throat and includes a part of the primitive yolk sac as it becomes enclosed with folding
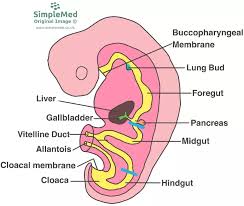
midgut
forms the rest of the mature pharynx
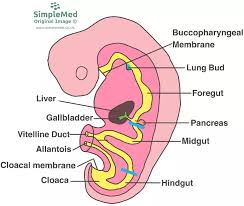
hindgut
behind (hiny)
forms the remainder of digestive tract
ectodermal dysplasia
abnormal development of one or more structures of ectoderm
partial or incomplete anodontia of some or all teeth in each dentition
teeth present frequently have developmental distubances
anodontia
no
absence of some or all teeth in each dentition
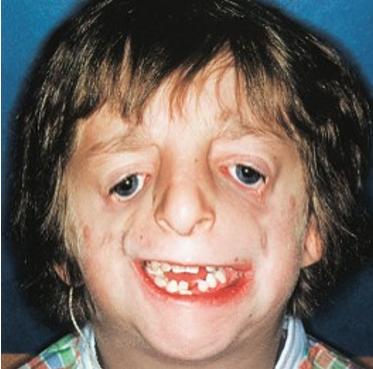
treacher collins syndrome (TCS)
if there is a failure of migration of the neural crest cells to the facial region, TCS or mandibulofacial dysostosis develops in the embryo
failure of specific orofacial development
downward slanting eyes
underdeveloped zygomatic bone
drooping lateral lower eyelids
Conductive hearing loss with malformed or absent ears
dental developmental disturbances such as adontia, enamel dysplasia with abnormal mineralization, and micrognathia
micrognathia
small lower jaw
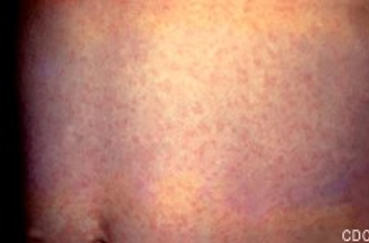
rubella
an example of an infective teratogen
results in cataracts, cardiac defects, and deafness
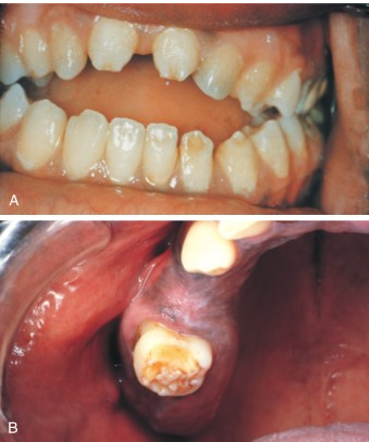
syphilis
another infective teratogen
bacterial spirochete causing treponema pallidum
produces defects in incisors (hutchinson incisor) and molars (mulberry molar) as well as blindness, deafness, and possible paralysis if not treated
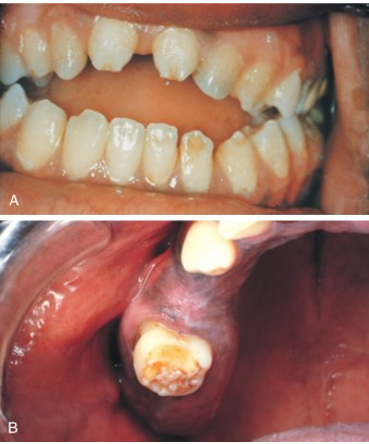
hutchinson incisor
a dental anomaly associated with congenital syphilis.
They are characterized by peg-shaped, notched, and widely spaced upper central incisors.
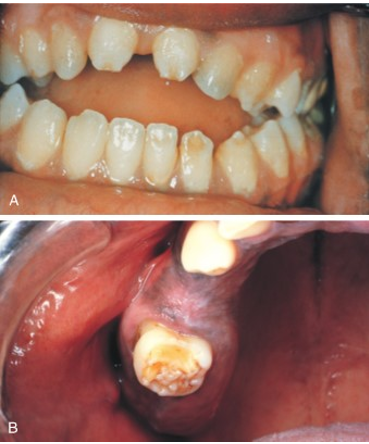
mulberry molar
a dental anomaly associated with congenital syphilis.
the permanent first molars have a characteristic rounded, bumpy surface, resembling a mulberry
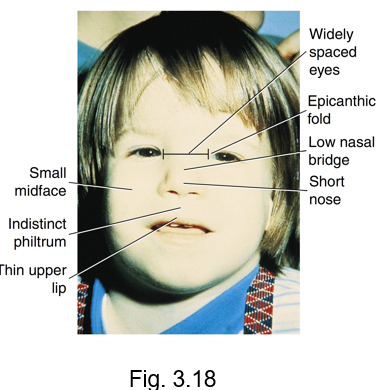
fetal alcohol syndrome
presents with noted orofacial features and various levels of intellectual disability
cause by the pregnant woman’s excessive use of ethanol during the embryonic period
characterized by
small midface
indistinct philtrum
thin upper lip
widely spaced eyes
epicanthic fold
low nasal bridge
short nose
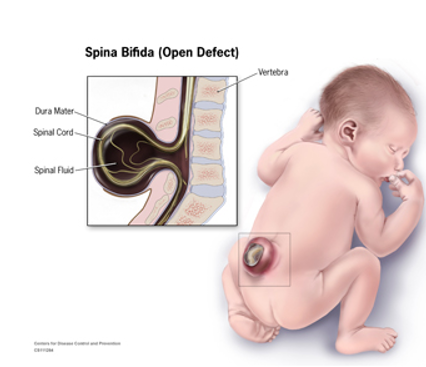
spinal bifida
failure of fusion of neural tube results in neural tube defects of the tissue overlying the spinal cord
characterized by defects in vertebral arches and various degrees of disability
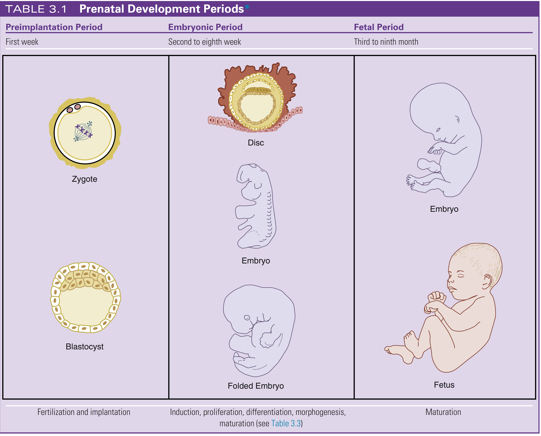
fetal period
follows the embryonic period and begins from the twelfth week (third month) aka begins during the second trimester
maturation of existing structures occurring as the embryo enlarges to become a fetus
includes further proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis
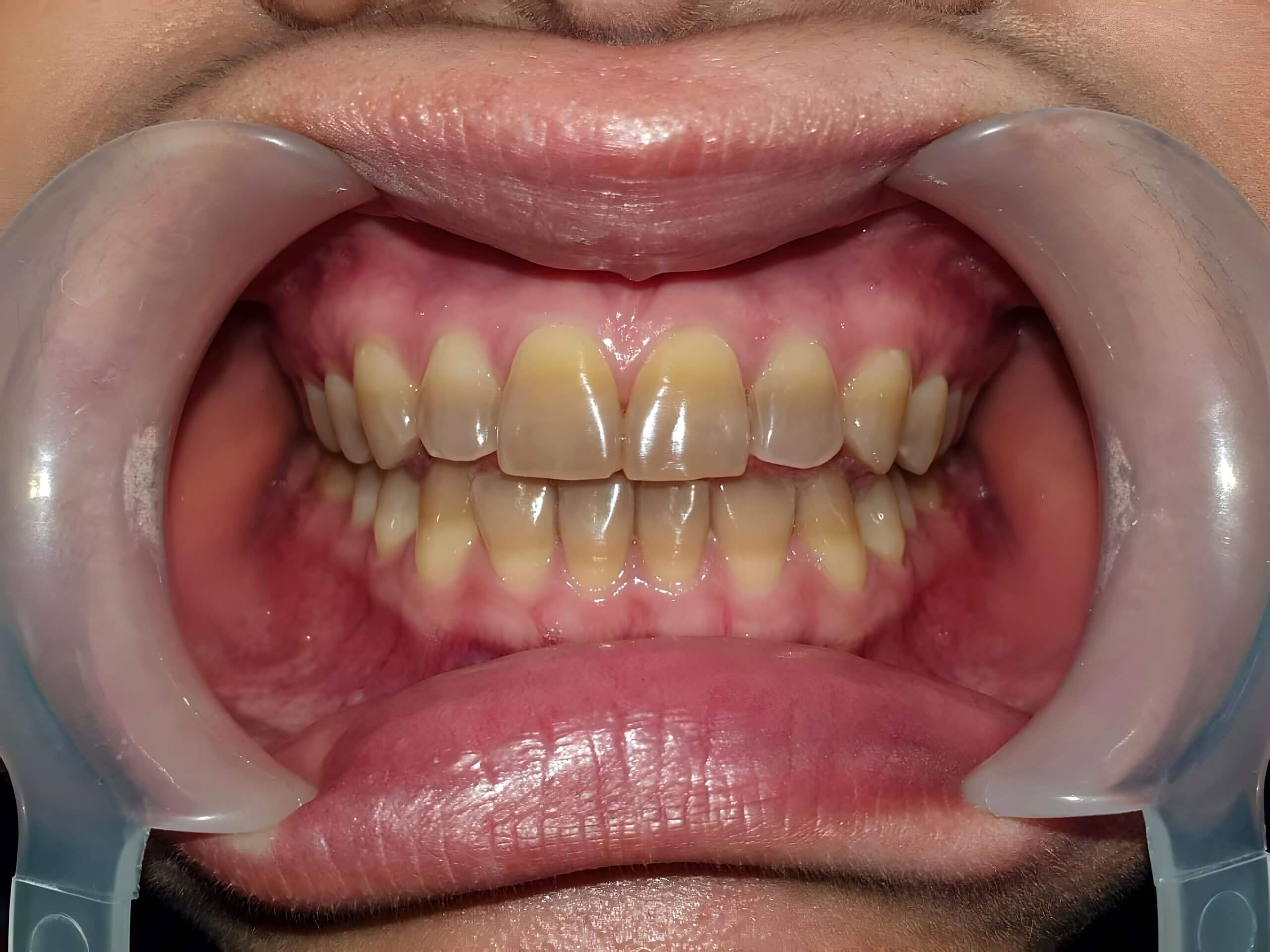
tetracycline stain
systemic tetracycline antibiotic therapy of the pregnant woman can act as a teratogenic drug during fetal period
intrinsic yellow to yellow-brown discoloration within teeth can occur in slight, moderate, or severe degrees as antibiotic becomes chemically bound to tooth
easily visible
permanent teeth may be effected
may require full cover crowns or veneers to improve appearance or even whitening
the face and its associated tissue begin to form during the __ week of prenatal development within the embryonic period
fourth week
the fourth to twelfth week are the most important for DHCP to know because most orofacial structures are formed
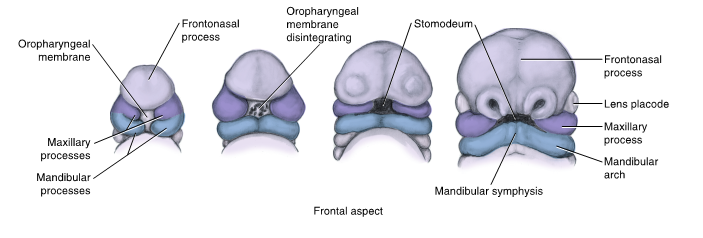
facial development within the fourth week of prenatal development
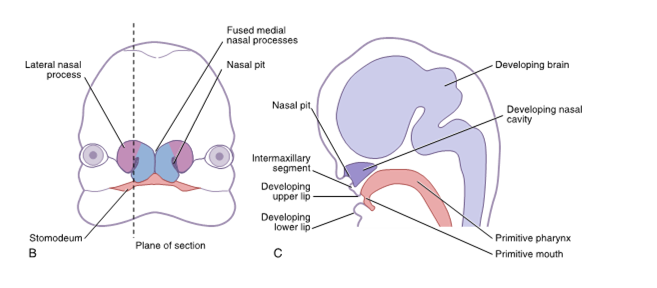
disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane of stomodeum enlarges primitive mouth, allowing access to the primitive pharynx and further growth
mandibular processes fuse to form the mandibular arch that then fuses to form the mandible and lower lip
frontonasal process forms and gives rise to the nasal placodes, nasal pits, medial and lateral nasal processes, and intermaxillary segment to form the nose and primary palate
intermaxillary segment forms four front teeth
maxillary process forms from the mandibular arch on each side of the stomodeum
maxillary processes fuse with each medial nasal process to form upper lip and with each mandibular arch to form the labial commissures
in the fourth week, organs begin to form developing stages in the embryo, this process is known as
organogenesis
brain, face, and heart are now noted as developing organs
embryonic layers involved in facial development
all three embryonic layers are involved in facial development
this includes the ectoderm
the mesoderm
and the endoderm
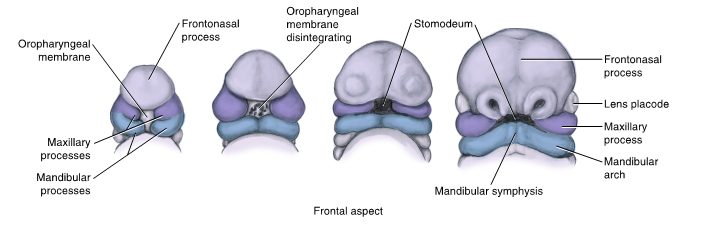
early development of the face is due to ___ and __ of the ectomesenchhyme that is derived from neural crest cells
proliferation and migration
how to facial structures become smooth?
with most facial fusion, furrow are eliminated as underlying mesenchyme migrates into the furrow
this migration takes place because adjacent mesenchyme grows and merges beneath external ectoderm during the maturation of the structure
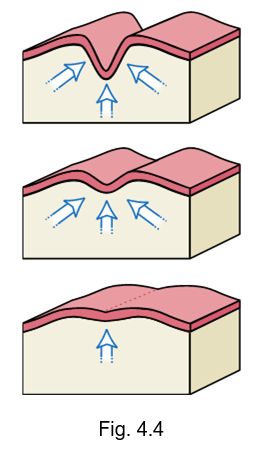
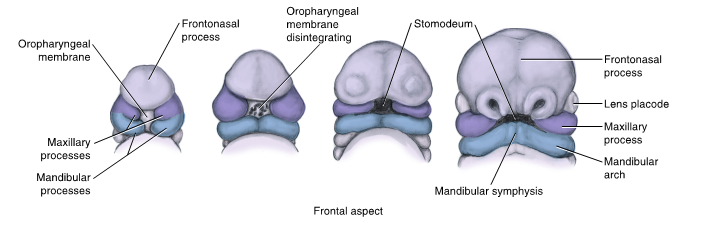
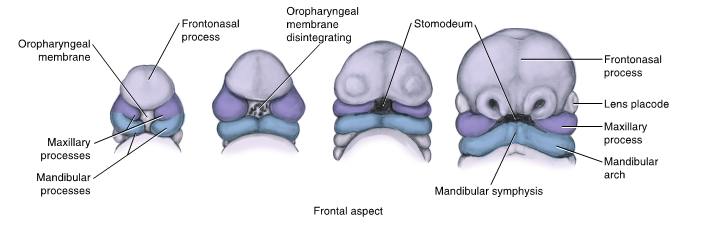
also known as primitive mouth
stomodeum
is limited in depth by the oropharyngeal membrane which eventually disintegrates, allowing the cavity to connect to the developing digestive tract
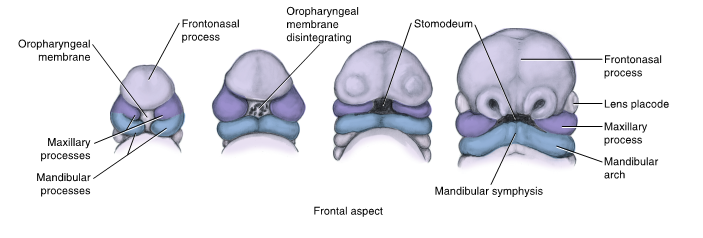
mesenchyme
a loosely organized, mainly mesodermal embryonic connective tissue which develops into connective and skeletal tissues, including blood and lymph
ectomesenchyme
a type of mesenchyme derived from the neural crest, specifically in the cranial region during vertebrate development
mesoderm taken over by neural crest cells
oropharyngeal membrane
separates the stomodeum from the primitive pharynx
the first event in development of the face during the latter part of the fourth week of prenatal development is disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane
mandibular processes
two bulges that appear inferior to primitive mouth
consist of a core of mesenchyme formed in part by NCCs that migrated to the facial region
fuse to form mandibular arch
developing mandibular arch
gives rise to the lower face, the lower lip, mandibular teeth, and associated tissue
After fusion of the left and right mandibular processes, the mandibular arch extends as a band of tissue inferior to the stomodeum and between the developing brain and heart
Meckel cartilage
forms within each mandibular arch during growth
most disappears as the bony mandible forms by intramembranous ossification lateral to and in close association with cartilage
frontonasal process
begins to develop during the fourth week as a bulge of tissue at the most cephalic end of the embryo
origin: ectodermal tissue and neural crest cells
future structures: medial and lateral nasal processes
placodes
rounded areas of specialized thickened ectoderm found at the location of developing special sense organs
lens, otic, nasal
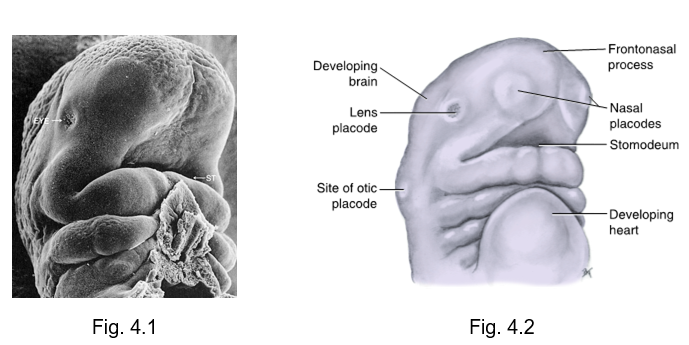
oronasal membrane
originally separates stomodeum and nasal sacs
the face develops __ and __
medially and inferiorly
everything growing joins and meets at nasal (coming up and down, and from side to side to meet in the middle)
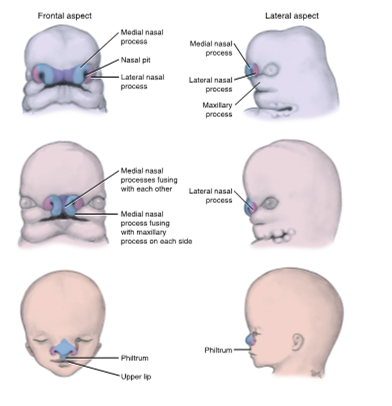
intermaxillary segment
the paired medial nasal processes also fuse internally and grow inferiorly on the inside of the stomodeum, forming the __ ___ by the end of seventh week
upper and lower lip formation
the maxillary processes contribute to the sides of the upper lip and the two medial nasal process contribute to the midline philtrum
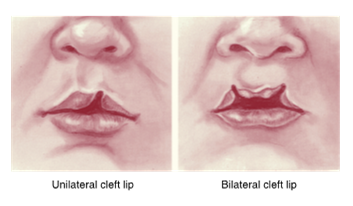
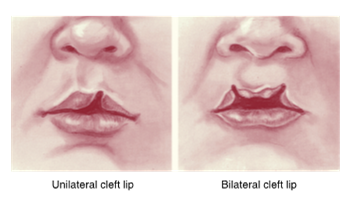
cleft lip
results from failure of fusion of the maxillary process with the medial nasal process
varying degrees of disfigurement
branchial apparatus or pharyngeal apparatus
consists of the arches, grooves, and membranes, as well as pouches
Arches are made from mesoderm
clefts formed from ectoderm
pouch formed from endoderm
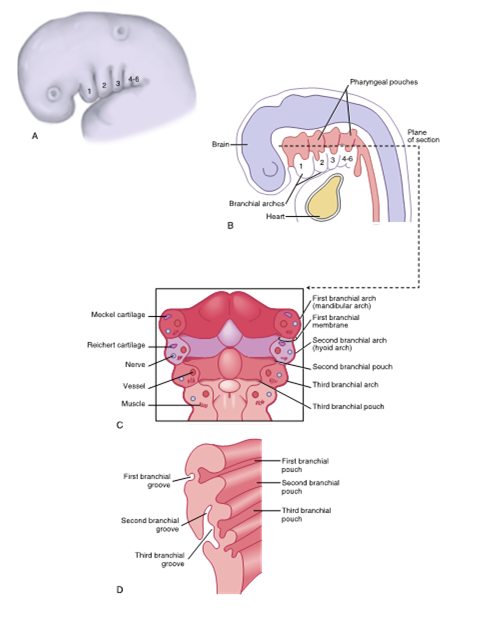
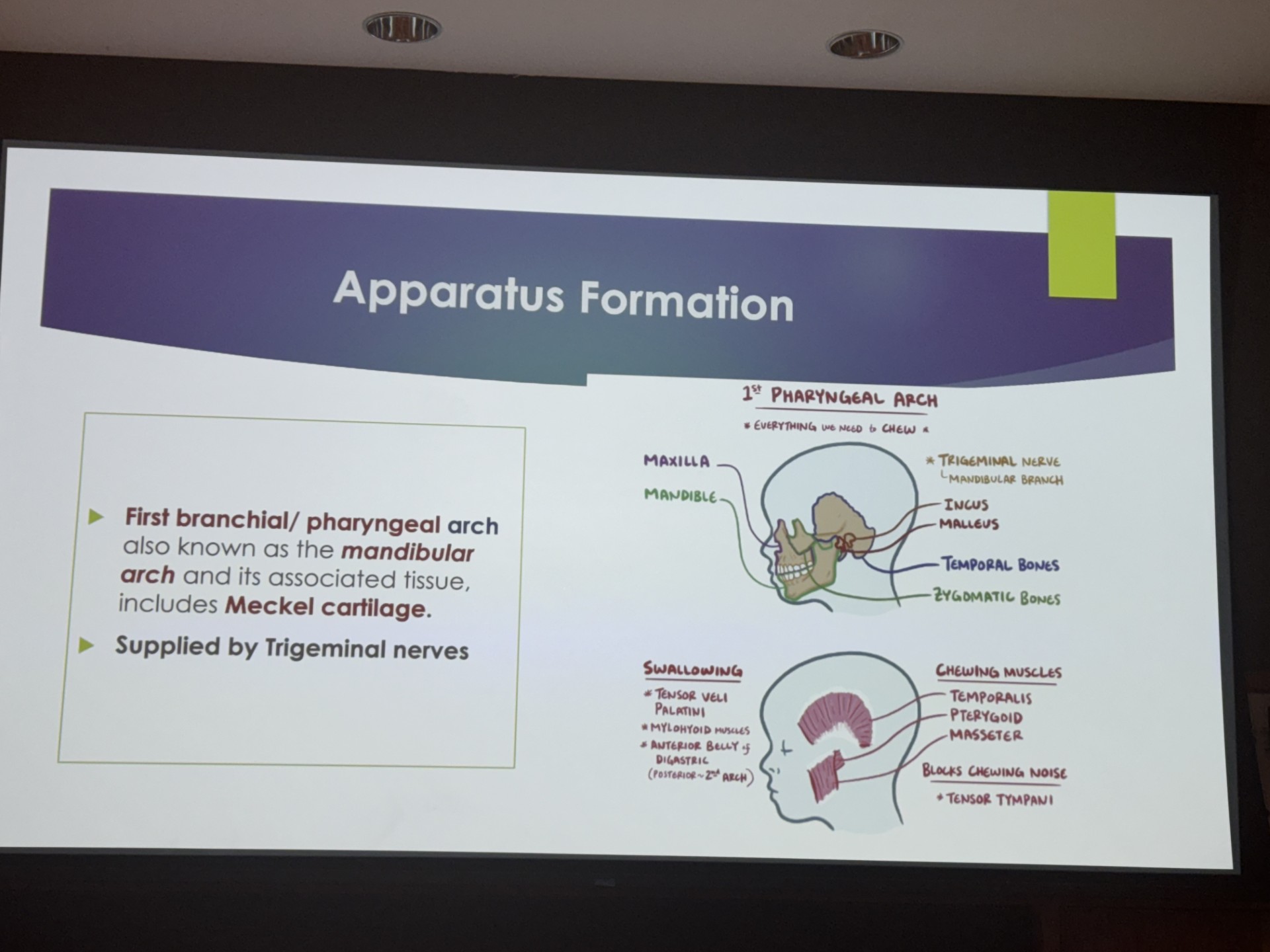
first pharyngeal arch
mandibular arch
contain meckel cartilage
everything we need to chew
forms the trigeminal nerve
maxilla
mandible
incus
malleus
temporal bone
zygomatic bone
muscles of mastication (temporalis, pterygoid, masseter)
the neck develops from the primitive __ and the __apparatus
primitive pharynx
the brachial (pharyngeal) apparatus
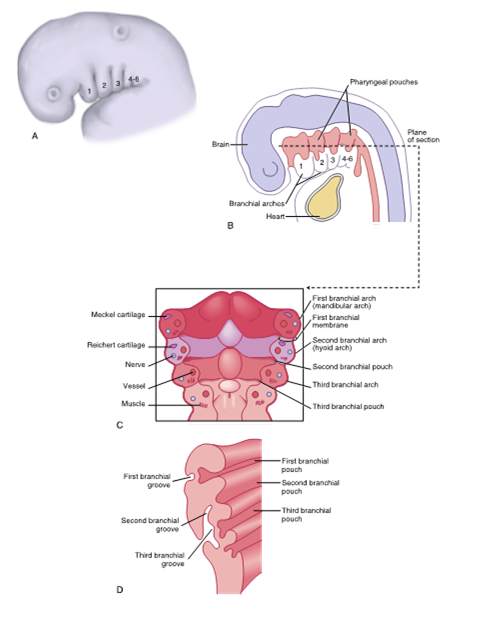
the pharyngeal apparatus consists of arches, __ ,membranes, and __
grooves
pouches
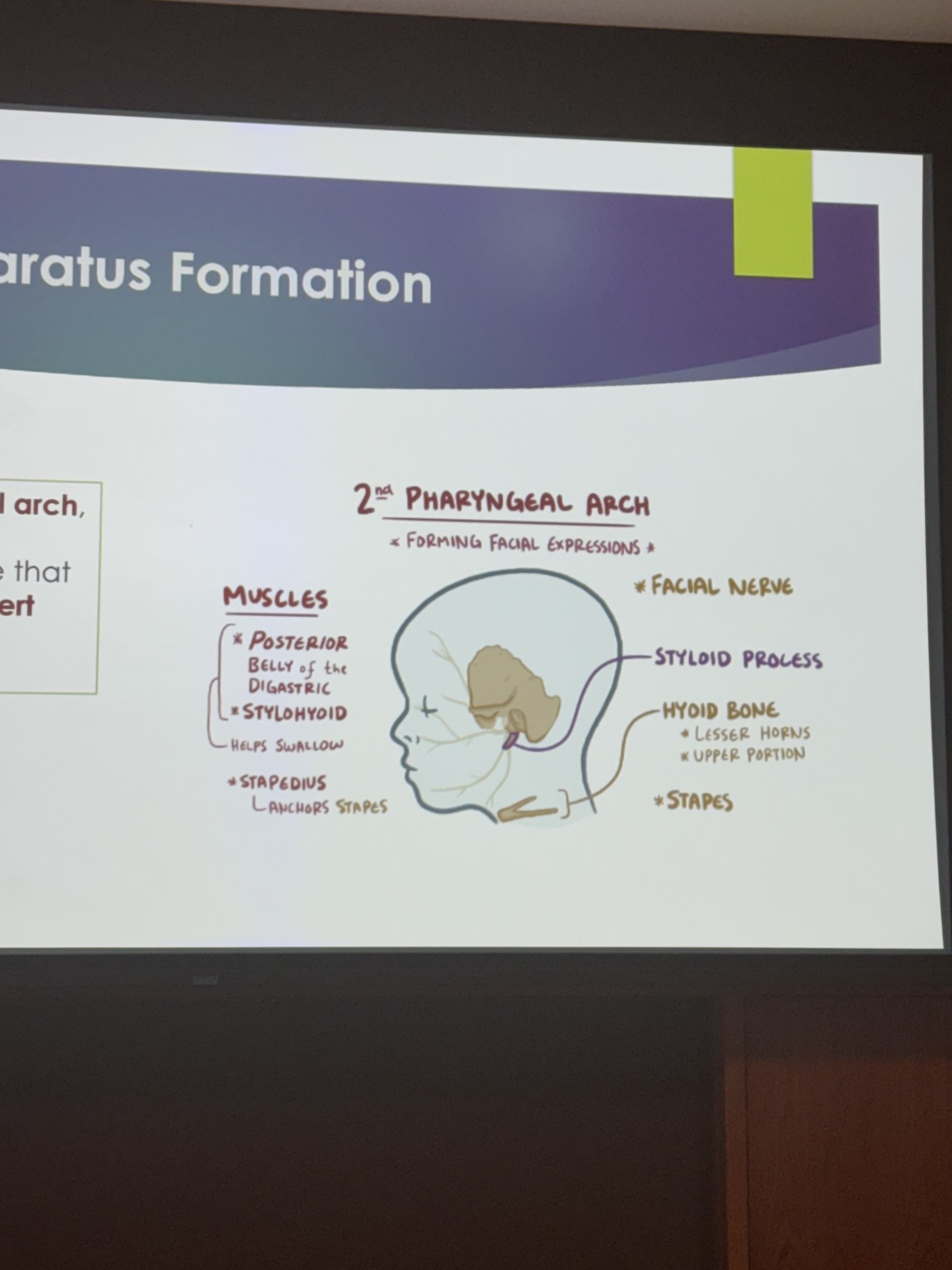
second pharyngeal arch
known as the hyoid arch
consists of cartilage similar to first pharyngeal arch call Reichert cartilage
forming facial expressions
forms the facial nerve
styloid process
hyoid bone
stapes
posterior belly of the digastric muscle
stylohyoid
stapedius
third pharyngeal arch
helps swallow
unnamed cartilage
forms glossopharyngeal nerve
forms stylopharyngeus
fourth and sixth pharyngeal arch
laryngeal cartilages
forms the vagus nerve
does not form bones
forms superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves
a condition that may occur if the second pharyngeal groove does not obliterate is a __ cyst
brachial cleft cyst
failure of fusion processes can result in__ lip or _ palate
cleft lip or cleft palate