Ch 3 : Audit Planning, Types of Audit Tests, and Materality
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
steps in a audit
client acceptance and continuance —> preliminary engagement activities —>
what must a firm do before accepting a client
1. Has the capabilities to perform the engagement
2. Complies with legal and relevant ethical requirements
3. Has considered the integrity of the client
slides 4 5 6

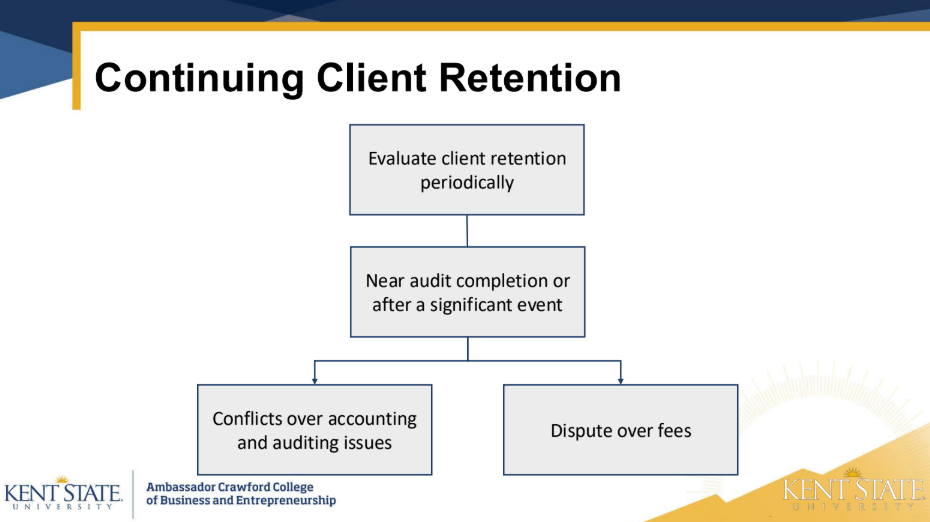
discussion - A switch in auditors sometimes occurs. What are
possible reasons for a switch in auditors?
financial struggles
disagreements
grew too big
discussion - Why do financial statements users want to know the
true reason for the switch in auditors? (public
entities)
can be used to hide fraud
what is a engagement letter
formalized agreement between auditor and client
who signs the engagement letter?
the partner



Factors for Evaluating the Reliability of the Internal Audit Function
objectivity
competence
systematic and disciplined approach

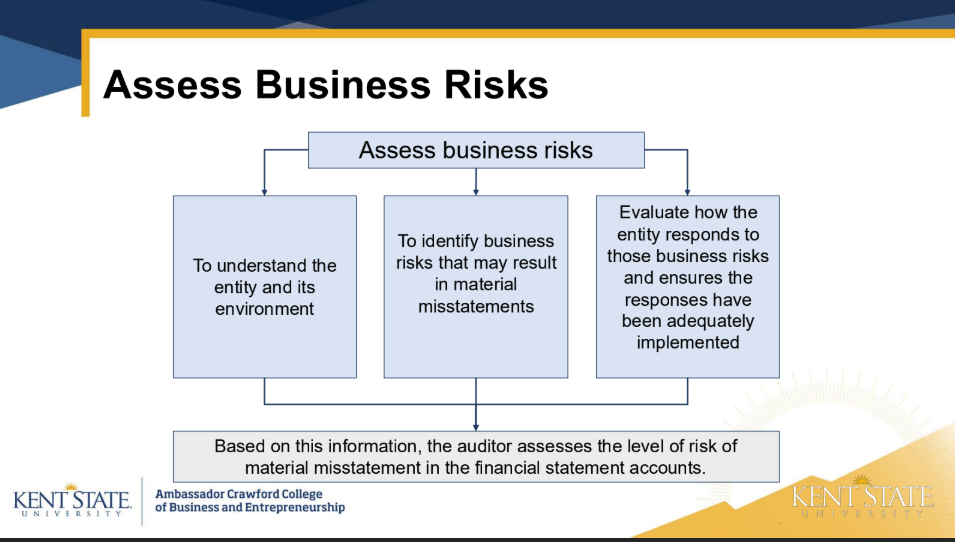
steps to establish materiality
determine overall materiality —>determine tolerable misstatement —> evaluate aduit findings
slides 20 21 22
Which of the following would an auditor most likely use in
determining overall materiality when planning an audit?
A.The anticipated sample size of the planned substantive tests
B.The entity’s income before taxes for the period-to-date (e.g., 6
months)
C.The results of tests of controls
D.The contents of the engagement letter
B
Suppose that you are the auditor of a major retail client and your firm sets materiality at 5% of income before taxes (IBT).
Your client reported the following IBT for the first two quarters of the year: 1st quarter = $1,200,000 and 2nd quarter = $1,500,000. You are in the process of establishing overall materiality for the client. Based on prior years, the client has a 10% decline in IBT from the 2nd quarter to the 3rd quarter. You also know that IBT in the 4th quarter increases by 25% over the 3rd quarter.
Required: Determine the amount of overall materiality for the audit based on these preliminary accounts.


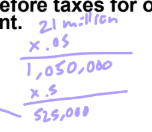
mulit location businesses
how do auditor determine how much attention to each location
level of risk
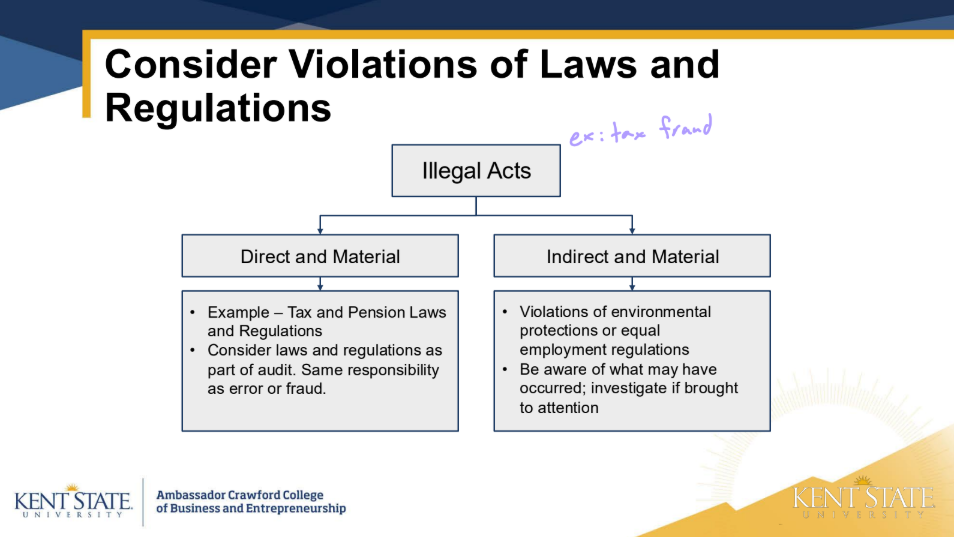
Which of these statements concerning illegal acts by clients is correct?
A. An auditor’s responsibility to detect illegal acts that have a direct and material
effect on the financial statements is the same as that for errors and fraud
B.An audit in accordance with auditing standards normally includes audit
procedures specifically designed to detect illegal acts that have an indirect but
material effect on the financial statements
C. An auditor considers illegal acts from the perspective of the reliability of
management’s representations rather than their relation to audit objectives
derived from financial statement assertions
D. An auditor has no responsibility to detect illegal acts by clients that have an
indirect effect on the financial statements
A