Transcriptomics and Single Cell RNA-Sequencing II
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2-5-25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
why use single cell RNA-seq?
subsets of cells may experience dramatic changes that are averaged out or diluted by the presence of a large number of nonresponsive cells
are there rare species? Are they important?
define heterogeneity
identify rare cell populations
cell population dynamics
detection of rare, functional cell types
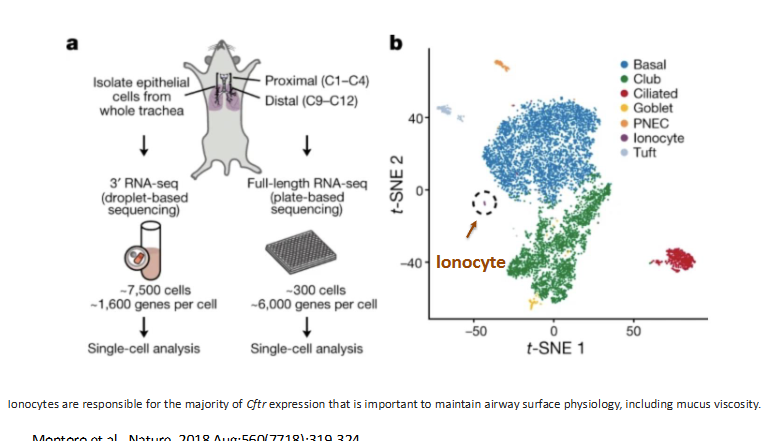
ionocyte is rare but its expression is linked to cystic fibrosis
reveal cellular identity of cancers
decision of treatment
see where tumors originate
broad applications in immunology
differentiate antibodies (healthy vs disease)
antigen specificity (do different binding and then RNA seq)
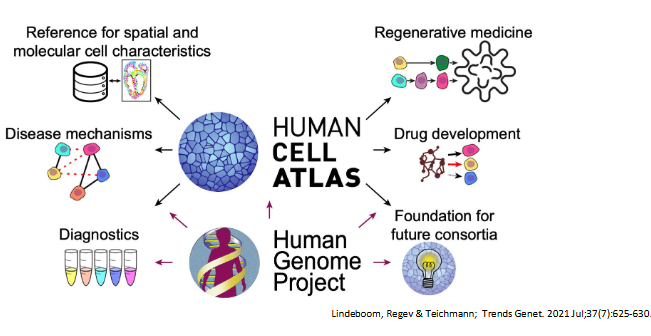
the human cell atlas consortium
aiming to map every cell type in the human body
the NIH brain initiative
the first scientific goal is “discovering diversity: identify ad provide experimental access to the different brain cell types to determine their roles in health and disease”
get function info from scRNA-seq
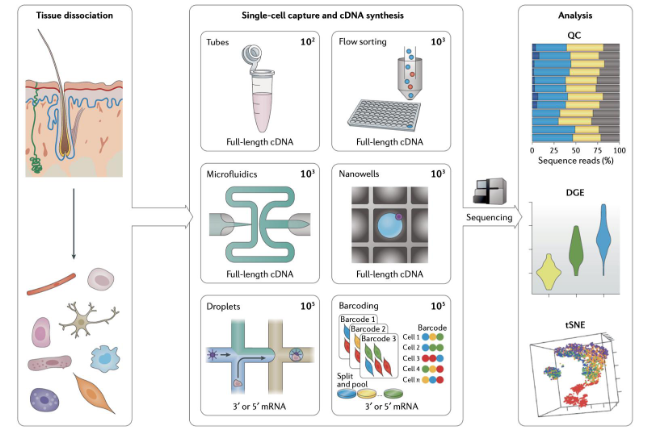
scRNA-seq workflow
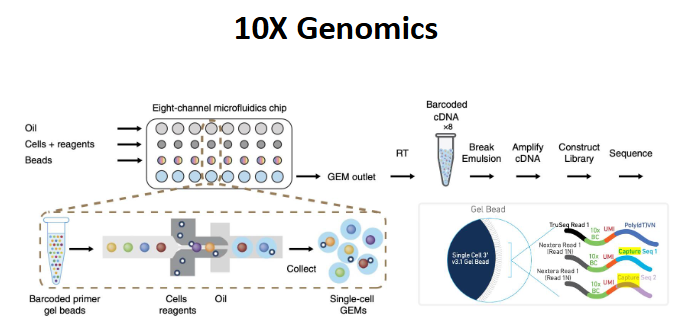
10x genomics (droplet approach)
oil + cells + beads (barcodes and primers)
GEM: gel beads in emulsion, an emulsion that contains a mixture of biochem reagents (unqiuely barcoded gel beads) and zero, one, or more suspended cells/nuclei
1 bead per cell is best
10x genomics3’
3’ more common to capture (poly A)
need to add adapter to other end of cDNA o(only one adapter on5’ mRNA) (use reverse transcriptate to add template switching oligion) TSO known PCR amplifier then ligate adapter
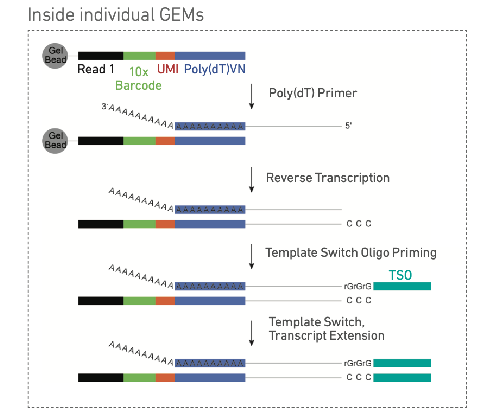
10× genomics 3’ capture continued
after last step amplify then pool (image)
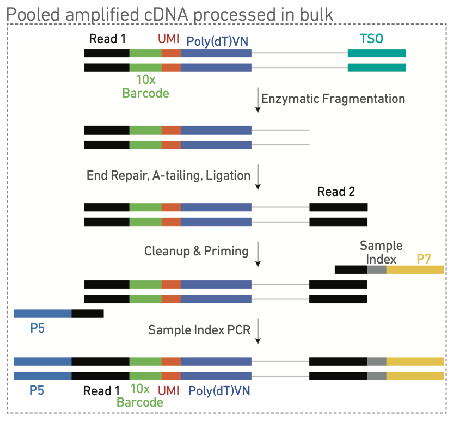
10x genomics 5’ capture
template switch oligo just in different spot (in middle)
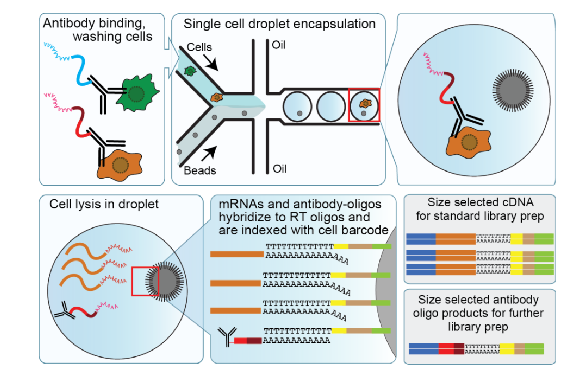
CITE-seq (cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitomes
simultaneously quantifies cell surface protein and transcriptomic data within a single cell readout
DNA oligo tagged antibodies are used to capture cell surface proteins
expands number of proteins that can be measured complied to cytometry (has to do with number of bar codes)
single cell 5’ CRISPR screening
cas9 nuclease from the microbial CRISPR adaptive immune system is localized to specific DNA sequences via the guide sequnce on its guide RNA
simultaneously detects gene expression oligo dt primer
Combines CRISPR perturbation with single-cell RNA-seq to link genotype (sgRNA) to phenotype (gene expression changes).
🧬 Workflow:
1⃣ CRISPR perturbation (KO, CRISPRi, CRISPRa).
2⃣ Single-cell capture (10x Chromium, 5' barcoding of mRNA + sgRNA).
3⃣ Library prep & sequencing (separate gene expression & guide RNA libraries).
4⃣ Data analysis (assign sgRNAs to cells, identify expression changes).
combinatorial indexing (doesn’t rely on machine)
split -seq
advantages: compatible with fixed cells or nuclei, allows efficient sample mutliplexing, requires no customized equipment
reverse transcription adds barcodes (new one after each split, different barcodes allow for cell differentiation, rare cells will share exact 4 barcodes)
can’t do on fresh cells
very pure! (even for fresh samples like they show)
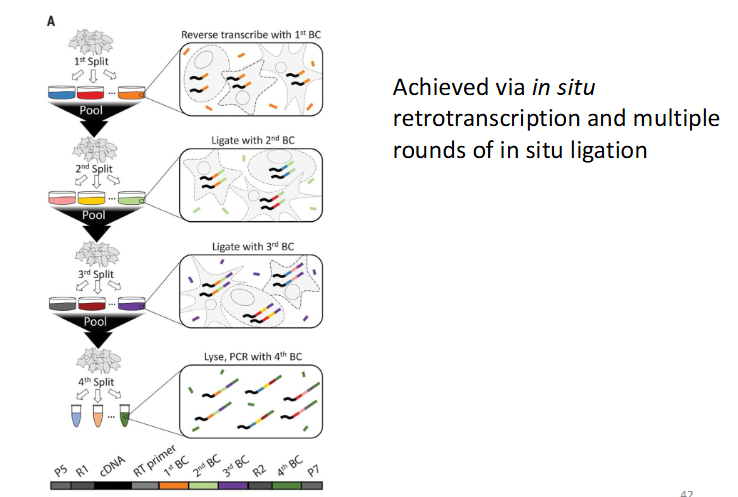
Plate-based approaches
single cell separation via fluorescence activated cell sorting
Single-Cell Separation via FACS isolates individual cells based on fluorescence. Cells are labeled with fluorescent markers, passed through a flow cytometer, and sorted using electrostatic charges based on their fluorescence signals. This method provides high purity and specificity but requires fluorescent labeling and may induce cell stress.
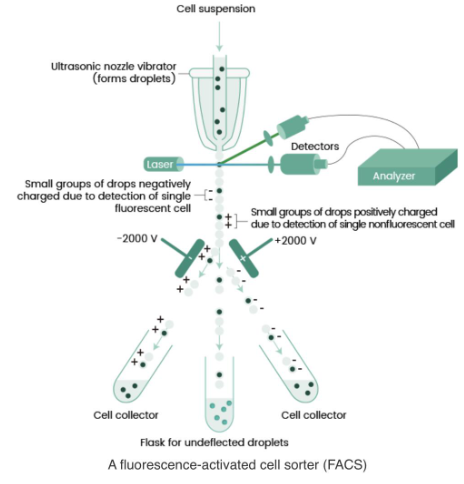
plate approaches (SMART)
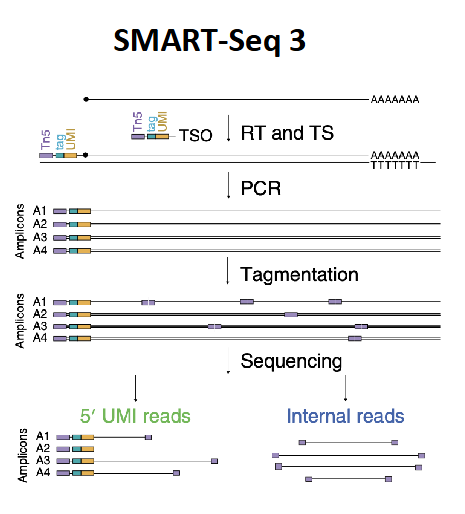
SMART-seq 3
5 UMI reads and internal reads
major factors to be considered when choosing a scRNA-seq method
trade offs between profiling more cells (breadth) or more transcripts per cell (depth)
typically, plate based often capture the fewest cells but detect more genes per cell whereas droplet based systems can be used to profile the greatest number of cells and have been used to generate individual data sets from more than one million cells
the need of sequencing full length of transcripts
full length scRNA seq requires each cell to be processed independently to the final scRNA seq library, allow investigation of alternative splicing and allele specific expression
experimental cost