BIO224: Chapter 16, Endocrine System (Day 1, NO DIAGRAMS)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Endocrine system
synthesize and secrete chemical messengers
hormones
chemical messengers that interact with specific target cells to influence their function
Endocrine functions
1.) MAINTAIN fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base homeostasis
2.) GROWTH
3.) REGULATE metabolic reactions
4.) EFFECT FUNCTION of cell immediately to several days
Three types of signaling pathways
Endocrine, paracrine, autocrine
Endocrine
secrete into blood; DISTANT targets
Paracrine
chemicals secreted by cells into extracellular space; near by but different types of cells
Autocrine
chemicals secreted by cells into interstitial fluid; elicit effects from same cell or cell type
Ductless glandular epithelial cells
secrete hormones into extracellular fluid for transport by bloodstream
Three groups of endocrine organs
primary organs, secondary organs, neuroendocrine
primary organs
organs only have endocrine functions
secondary organs
endocrine functions and many other non-endocrine functions
neuroendocrine
nervous tissue chemicals that have hormonal function, in the brain
Primary endocrine organs
1.) Hypothalamus
2.) Pituitary gland
3.) Pineal gland
4.) Thyroid gland
5.) Parathyroid gland
6.) Thymus
7.) Adrenal gland
8.) Pancreas
Secondary endocrine organs
1.) heart
2.) kidneys
3.) small intestines
4.) gonads
Classes of hormones by structure
Amino-acid hormones, steroid hormones
Amino-acid hormones
Hydrophilic hormones binding to plasma membrane receptors, DO NOT ENTER.
- free, travels independently through blood
- breakdown quickly, quick response; seconds to minutes
Steroid hormones
derived from cholesterol; hydrophobic hormones that bind to receptors in cytosol or nucleus
- usually bound to protein
- can survive for weeks
Paraneoplastic Syndrome
Hormones produced by lung and intestinal cancel cells cause imbalance of electrolyte and fluid; most common inappropriate ADH secretion
How can Paraneoplastic Syndrome lead to early cancer diagnosis?
Cancer cells secrete hormone that mimic ADH
Hormone transport through blood classification
physiological classification; free hormones, bound hormones
free hormones
hydrophilic, quick breakdown for use
Does hydrophilic hormones always make them free?
No, some are protein bound, such as growth hormone
Bound hormones
hydrophobic, bound to plasma proteins and released when needed; extends lifespan of hormone in blood
Hydrophilic hormones
cannot readily cross plasma membrane; interact with receptors in target cell's plasma membrane
Hydrophobic hormones
can cross through plasma membrane; interact with receptors in cytosol or nucleus
Second messenger
relays a signal from a hormone (the first messenger) that cannot enter the cell directly to target molecules inside the cell
g-protein
molecular switch inside cells that transmits signals from outside the cell to its interior
adenylate cyclase
enzyme activated by g-protein that uses ATP to make cAMP
cAMP function
second messenger; carries the signal inside the cell
- activates PKA (protein kinase A)
Phosphorylation
when PKA adds phosphate groups to specific proteins in the cell
Function of phosphorylated proteins
trigger the actual cellular response
- speeding up a reaction, changing gene activity, or controlling cell functions
7 Effects of hormone actions
1.) stimulate secretion
2.) activate/inhibit enzymes
3.) stimulate/inhibit mitosis/meiosis
4.) ion channels
5.) transcription; gene expression
6.) fluid electrolyte balance
7.) homeostasis
Hormone interactions
maintenance of homeostasis, needs synergist and antagonist
Antagonist
act on same target cells for opposite effects
Synergist
act on same target cells for same STRONGER effect with interaction of multiple hormones instead of just one
Humoral stimulation origin
non-neurological
Neural stimulation origin
neuron causes epinephrine and norepinephrine
Hypothalamus
Vital to many homeostatic functions; direct and indirect
Direct
hormone controls certain body functions
Tropic
control secretion of hormones from other endocrine glands
Hormones of hypothalamus
ADH and oxytocin
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone; increases water reabsorption (intake)
Oxytocin function
uterine contractions and milk ejection
Hormones of Anterior Pituitary
1.) Tropic Hormones
2.) Somatotropin or growth hormone
3.) Adrenocorticotropic hormone
4.) Thyroid stimulating hormone
5.) Follicle stimulating hormone
5.) Luteinizing hormone
Hypothalamus controls many functions of ____. Such as....
anterior pituitary
- stimulating or inhibiting release of hormones from anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus produces and releases ___ hormones.
trophic
First tier
RELEASE: neuroendocrine cells of hypothalamus secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones in response to change
Second tier
tropic hormones' effect on anterior pituitary; stimulates or inhibits
Third tier
actions of anterior pituitary hormones at target tissues; target tissue glands secrete hormones that can affect various homeostatic variables
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol and aldosterone
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulates milk production in mammary glands
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
stimulate sex hormones; not direct, increase levels
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
secreted by the pituitary gland to stimulate maturation of the egg and sperm
Growth Hormone (GH)
regulates the growth of the body; usually direct
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources
Main function of growth hormone
regulation of growth of various tissues such as skeletal, cardiac muscle, adipose, liver, cartilage, and bone
Growth hormone disorders
imbalances in GH secretion resulting in disruptions in growth
Gigantism
hypersecretion of GH BEFORE epiphyseal plate closure; results in extremely height and size of other tissues (heart)
Acromegaly
hypersecretion of GH AFTER epiphyseal plate closure; tissues of head, face, hands, and feet affected, results in distortion and possible heart failure
pituitary dwarfism
GH hyposecretion; short, but proportional limbs and trunk
Does GH promote fat breakdown and protein synthesis? What problems arise?
Yes, but excessive GH can lead to hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) and growth of tissues (tongue and bones)
How do you effectively administer GH protein hormone drugs?
injection; oral is ineffective
GH protein hormone
destroyed by acid and enzymatic reactions in stomach
Thyroid gland
secretes thyroid hormone and calcitonin
What is the shape of the thyroid gland?
butterfly
What is the thyroid gland made of on a microscopic level?
multiple follicle cells
Function of follicle cells
follicles cells at the edge of the cell produce and secrete thyroglobulin
Colloid
protein rich gel-like material; has precursor for thyroid hormone and high concentration of iodine- need for thyroid hormone synthesis
Parafollicular cells
large cells in spaces between adjacent thyroid follicles that produce calcitonin
Thyroid hormone is derived from...
amino acid TYROSINE bound to IODINE; hydrophobic qualities
T3
"triiodothyronine"; functional form
T4
"thyroxine"; storage
What cell contains thyroid hormone receptors?
almost every cell
Effects of thyroid hormone
1.) regulation of metabolic rate and thermoregulation
2.) promotion of growth and development
3.) synergism with sympathetic nervous system
"Regulation of metabolic rate and thermoregulation" meaning
set metabolic rate
"promote growth and development" meaning
thyroid hormones needed for normal bone growth, muscle growth, and nervous system development
"Synergism with sympathetic nervous system" meaning
increase thyroid hormone levels, act on target cells of sympathetic nervous system
Hyperthyroidism
T3 and T4 extremely elevated, but hypothalamus does not detect increase; leads to decreased TSH and elevated T3 and T4
Hyperthyroidism symptoms
heat intolerance, weight loss, BP and HR disruptions, goiter, and exophthalmos
goiter
enlargement of the thyroid gland
Exophthalmos
bulging eyes
Graves' disease
common hyperthyroidism; immune produces abnormal proteins that MIMIC TSH actions on thyroid glands
Hypothyroidism
thyroid gland cannot produce more T3 and T4; receptors sense levels are low so cells secrete more TRH and TSH in attempt to stimulate thyroid; results in elevated TSH and decreased T3 and T4
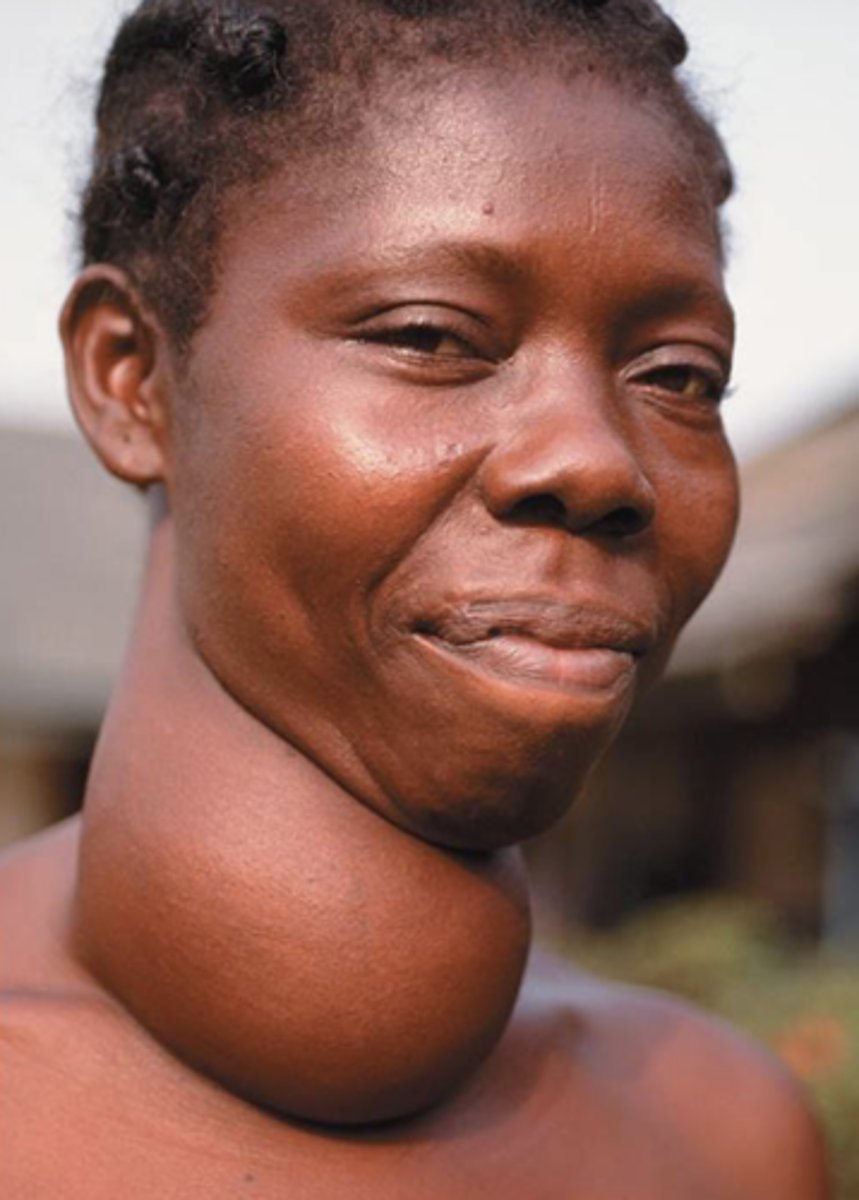
Why do the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary not stimulate the thyroid gland during hypothyroidism?
hypothalamus and anterior pituitary don't know thyroid is not functioning
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
weigh gain, fatigue, slow heart rate and respiration rate, cold intolerance
What are some potential causes of hypothyroidism?
immune system disorder or lack of available iodine
congenital hypothyroidism
occurs when infant is born with INADEQUATE thyroid function; can lead to delayed physical and nervous system development- potential mental retardation if left untreated
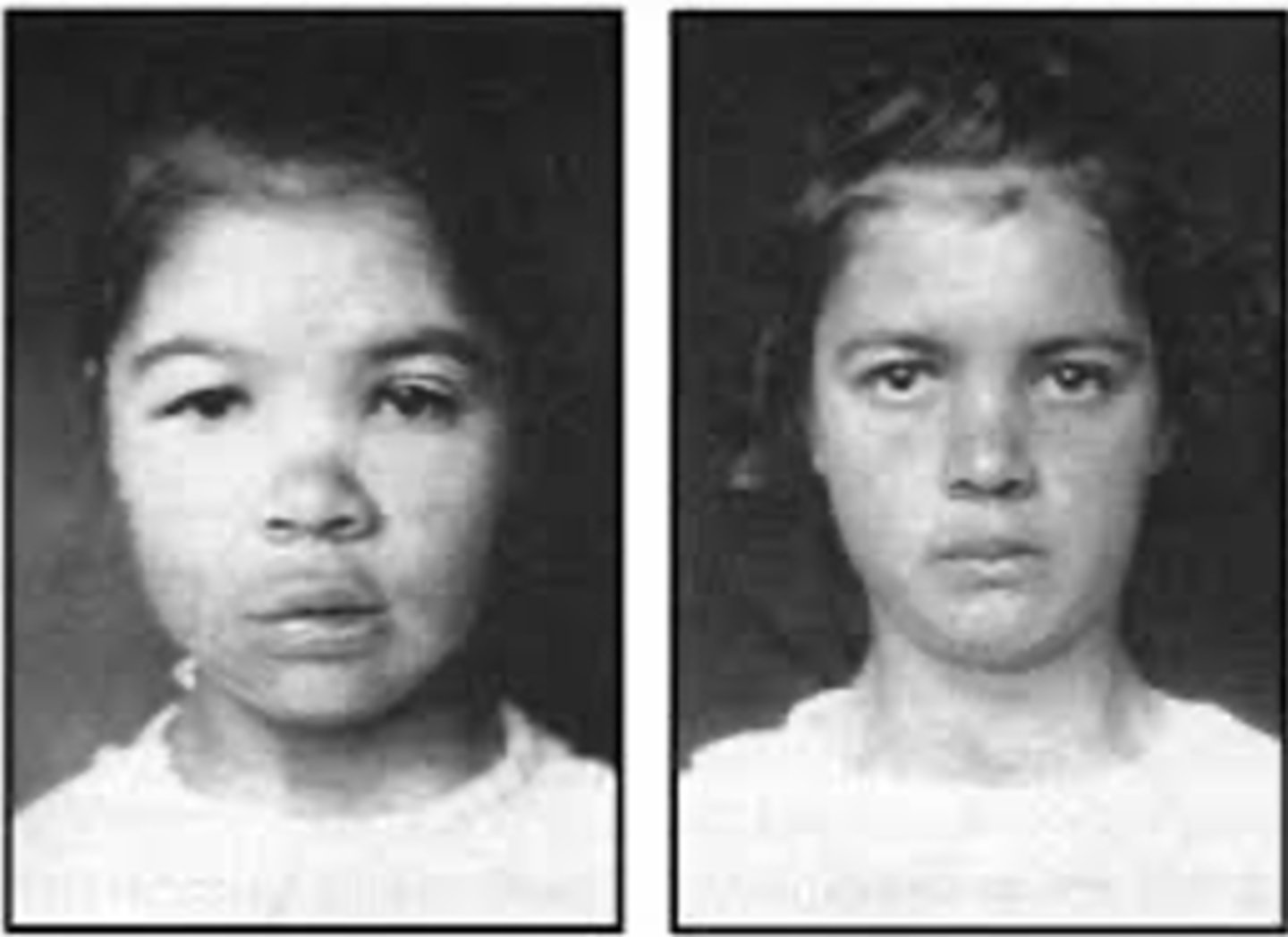
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
autoimmune disorder; immune system attacks thyroid tissue
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis symptoms
Dry skin
tiredness
weight gain,
puffy face
intolerance to cold
mild depression
memory lapses
joint pain and stiffness
hair loss