1. polymers
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
dental applications for polymers
Adhesive system
Direct restorative material
Indirect restorative material
Temporary restorative material
Resin cement
Core and fiber post
Pit and fissure sealant
Cavity liner
bonding
Cavity varnish
Pigment and stain
Custom tray
Impression material
Denture base
Denture teeth
Soft resin
Orthodontic device
Bite registration
Occlusal device
Endodontic filling
Rubber dam
Dental instrument
3D printing
Monomer
Chemical compound that is capable of reacting to form a polymer
-mers suffix meaning
The term used to designate the repeating unit or units in a polymer chain
thus, mers are the “links” in the chain
poly- prefix meaning
Chemical compound consisting of a large molecule formed by the union of many smaller repeating units (mers)
Poly(methylmethacrylate)
acrylic resin
a commonly used acrylic thermoplastic dental material
derived by polymerization of the monomer, methylmethacrylate (MMA)
curing
the process of hardening or setting a material, typically a resin or a composite, into its final form
a chemical reaction in which low-molecular-weight monomers (or small
polymers) are converted into higher-molecular-weight materials to attain
desired properties
Polymerization
Chemical reaction in which monomers of a low molecular weight are converted into chains of polymers with a high molecular weight
Free-radical
An atom or group of atoms (R) with an unpaired electron (•).
R• produces reactions that initiate and propagate polymerization and eventually lead to a final set
steps of polymerization: Induction
Activation of free radicals, which in turn initiates growing polymer chains.
steps of polymerization: Propagation
Stage of polymerization during which polymer chains continue to grow to high-molecular weights.
steps of polymerization: Termination
Stage of polymerization during which polymer chains no longer grow
Degree of conversion/ degree of cure/ degree of monomer-to-polymer conversion
Percentage of carbon-carbon double bonds (-C=C) converted to single bonds (-C-C-) during curing to form a polymeric resin.
Polymerization shrinkage
Arises as the monomer is converted to polymer and the free space it occupies reduces.
Polymerization stress that is resulted from volumetric shrinkage can be affected by:
[1] total volume of material
[2] monomeric composition
[3] filler particle amount
[4] polymerization speed
[5] c-factor
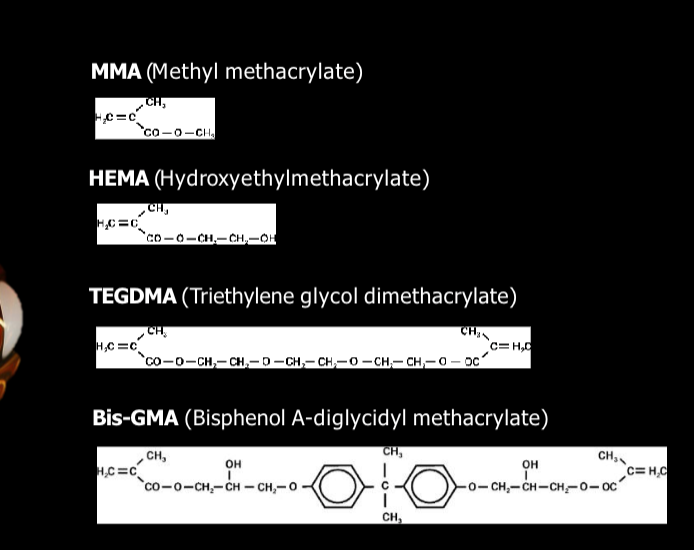
trends for these molecules
size increases going down
molecular weight increases going down = less shrink with packable bc more viscous + bigger molecules
viscosity increases going down
flowable will shrink more bc its lighter
Activation
Process by which sufficient energy is provided to induce an initiator to
generate free radicals and cause polymerization to begin
Activator
Source of energy used to activate an initiator and produce free radicals.
1.Chemical;
2.Physical (light or heat)
Activation Mode: light cured
Best control over setting time
Higher color stability over time
Pre-heated composite*
Cure depends exclusively on the light
Does not require mixing
Basically, a flowable composite
Pre-heated composite
Activation Mode: self cured
Cure depends exclusively on a chemical reaction
Requires mixing
No control over setting time
Lower color stability over time
Activation Mode: dual cured
Cure depends on chemical reaction AND light-curing (light is required*
Requires mixing
Medium control over setting time
Lower color stability over time
Best of “both worlds”
Initiator
A free radical-forming chemical used to start the polymerization reaction.
inhibitor
A chemical added to resin systems to provide increased working time and
extended storage life by minimizing spontaneous polymerization
acrylic resin composition liquid
Methyl Methacrylate (MMA)
Tertiary amine
Inhibitor
Dimethacrylate (cross linking agent)
acrylic resin composition powder
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)
Benzoyl peroxide
Pigments and opacifiers
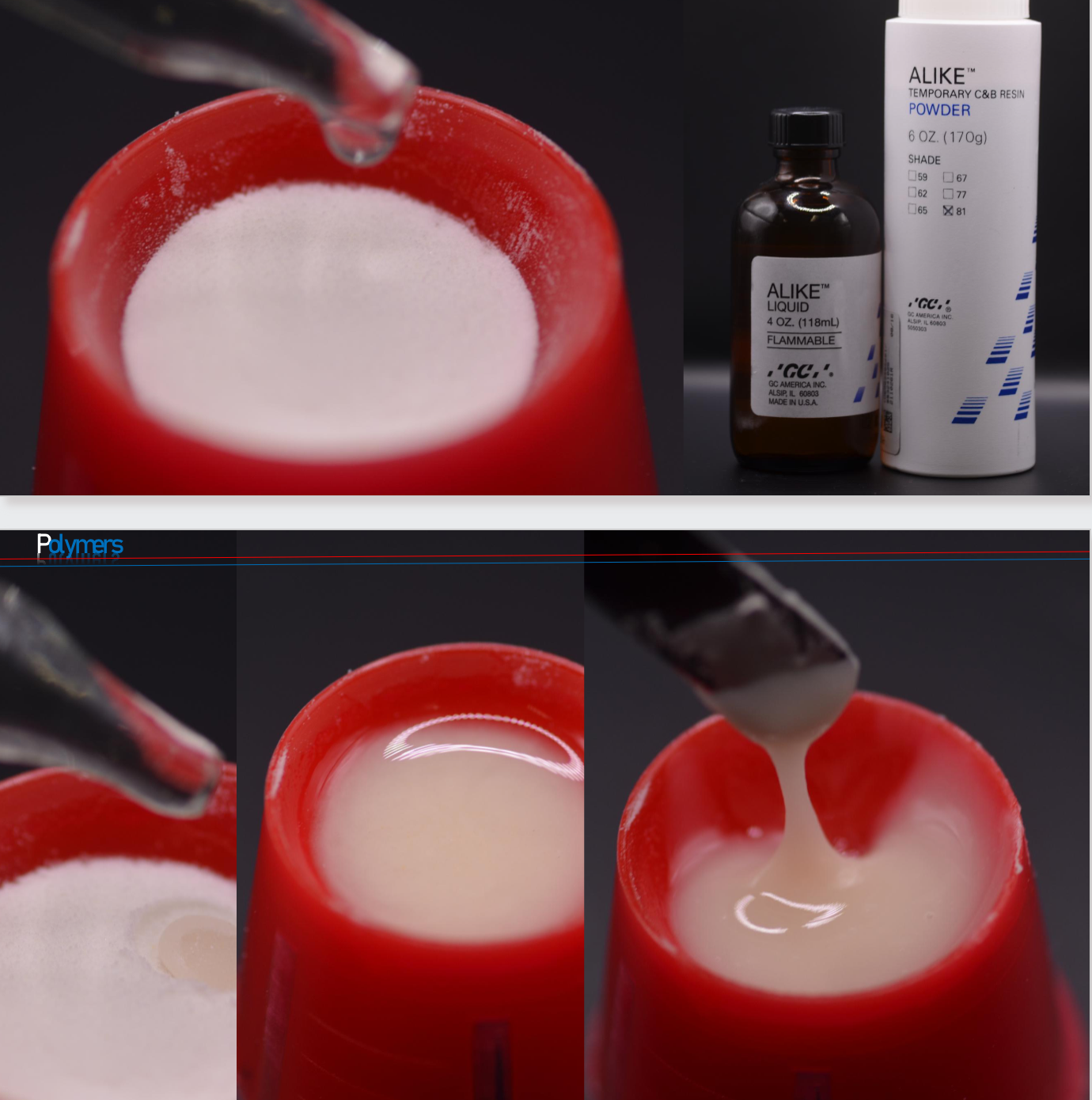
Stages of polymerization
When monomer and polymer are mixed in the proper proportions, a workable mass is produced.
Resultant mass passes through five distinct stages:
sandy
stringy
dough-like
rubber
stiff
Sandy phase
Little or no interaction occurs on a molecular level.
Polymer beads remain unaltered, and the consistency of the mixture an be
described as “grainy”

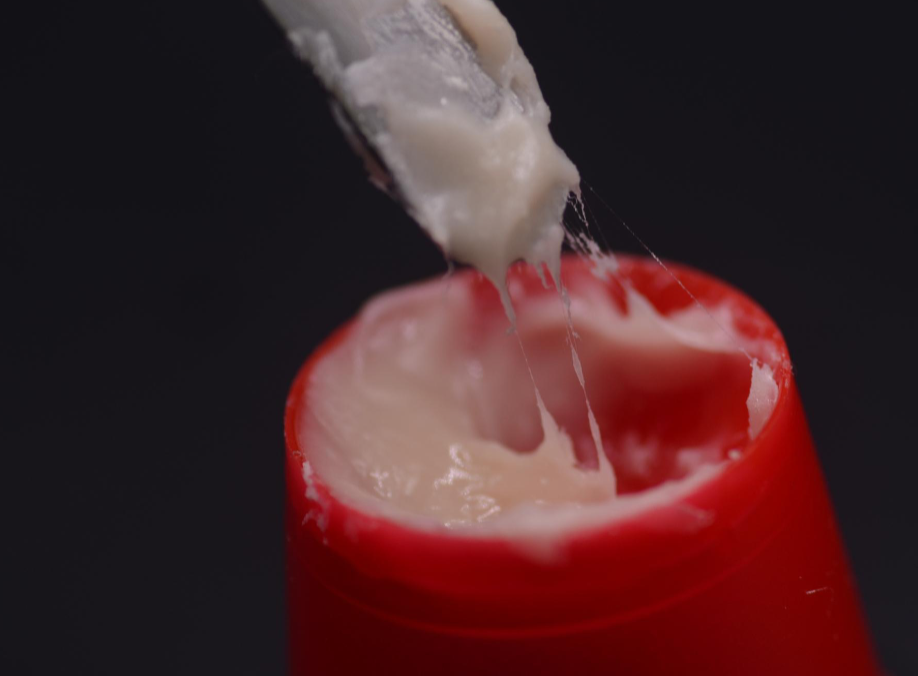
Stringy (fibrilar) phase
Monomer attacks the surfaces of individual polymer beads and is absorbed
into the beads.
Some polymer chains are formed, increasing the viscosity of the mixture

Doughlike (plastic) phase
An increased number of polymer chains enter the solution.
Clinically, mass behaves as a pliable dough (no longer sticks to the surface of
instruments)
Ideal stage for compression molding
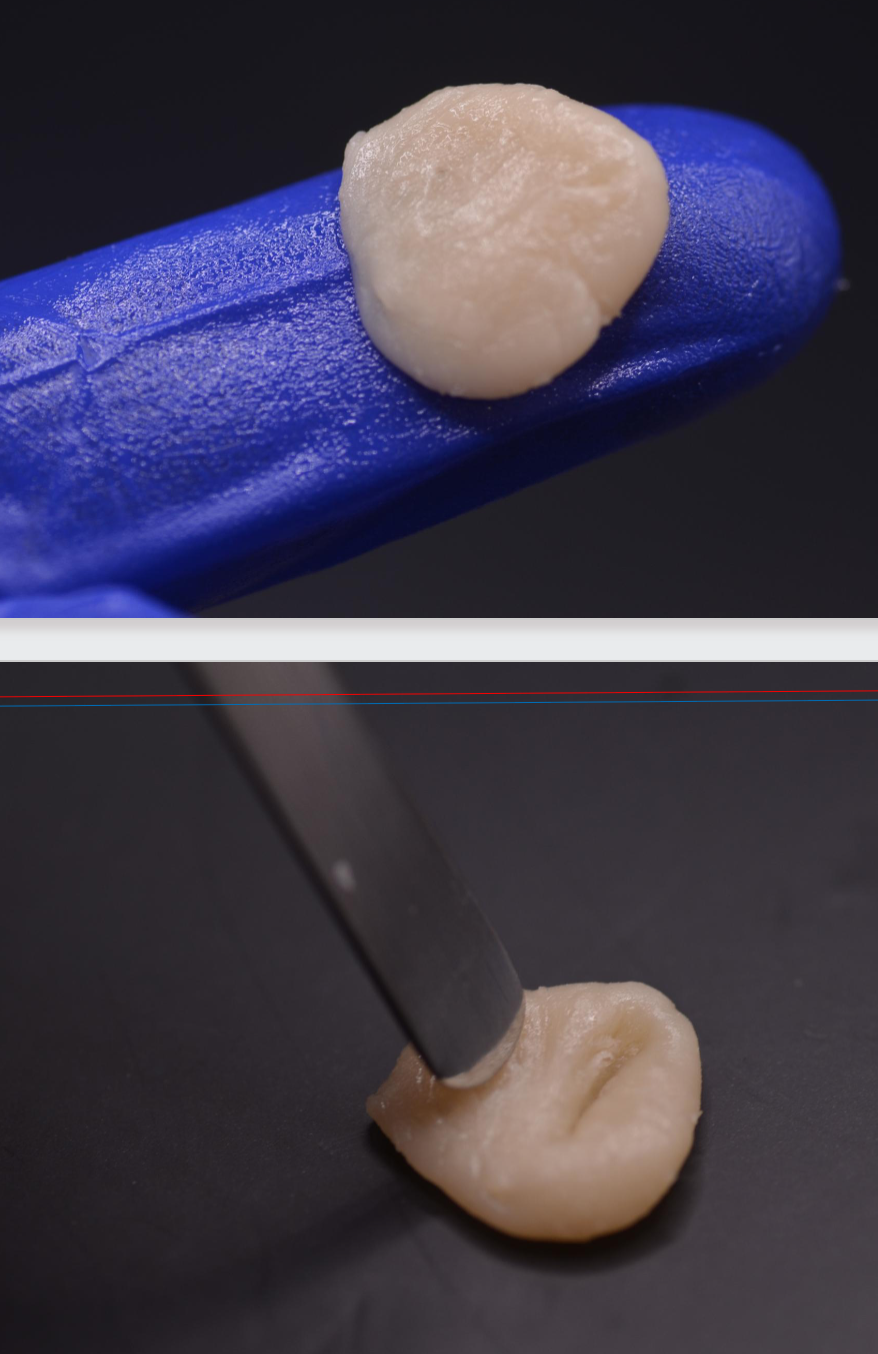
rubbery phase
Monomer is dissipated by evaporation and by further penetration into remaining polymer beads.
Mass rebounds when compressed or stretched (elastic), it cannot be used to copy structures
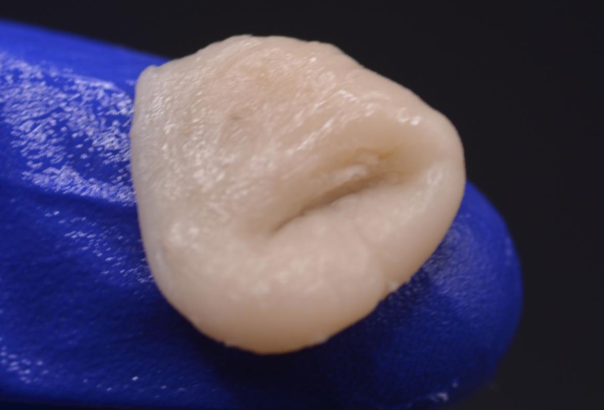
stiff (dense) phase
Continued evaporation of unreacted monomers, mixture becomes stiff.
Clinically, mixture appears dry and resistant to mechanical deformation

Denture base
The part of the denture that rests on the soft tissues overlying the maxillary and mandibular jawbone and that anchors the artificial teeth.’
Heat-cured.
Elastomers
In general, polymers are hydrophobic.