Transport in animals
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Bohr effect
Oxygen dissociation curve will form a sigmoid shape shifting to the right
Haemoglobin affinity for oxygen high co2
Oxyhaemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen in area of High CO2
Haemoglobin affinity for oxygen low co2
Oxyhaemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen in area of Low CO2
Respiring tissues
When haemoglobin has a low affinity for oxygen
It can release oxygen more readily
This is released in respiring cells - more CO2
Need oxygen for respiration
Lungs
Higher affinity for the oxygen
Will want to bind to the oxygen more readily
Binds to oxygen to be transported around the body
How does fetal Hb differ
Fetal Hb has a higher affinity curve shifts to the left
Fetal Hb has a higher affinity for O2
Fetal Hb can get oxygen from mothers blood in placenta
Fetus cannot respire for themselves needs O2 for growth
Hb structure
Haemoglobin as a quaternary structure
Made of 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits
Haem group in the center were oxygen binds
Each haemoglobin molecule can bind to 4 oxygen molecules
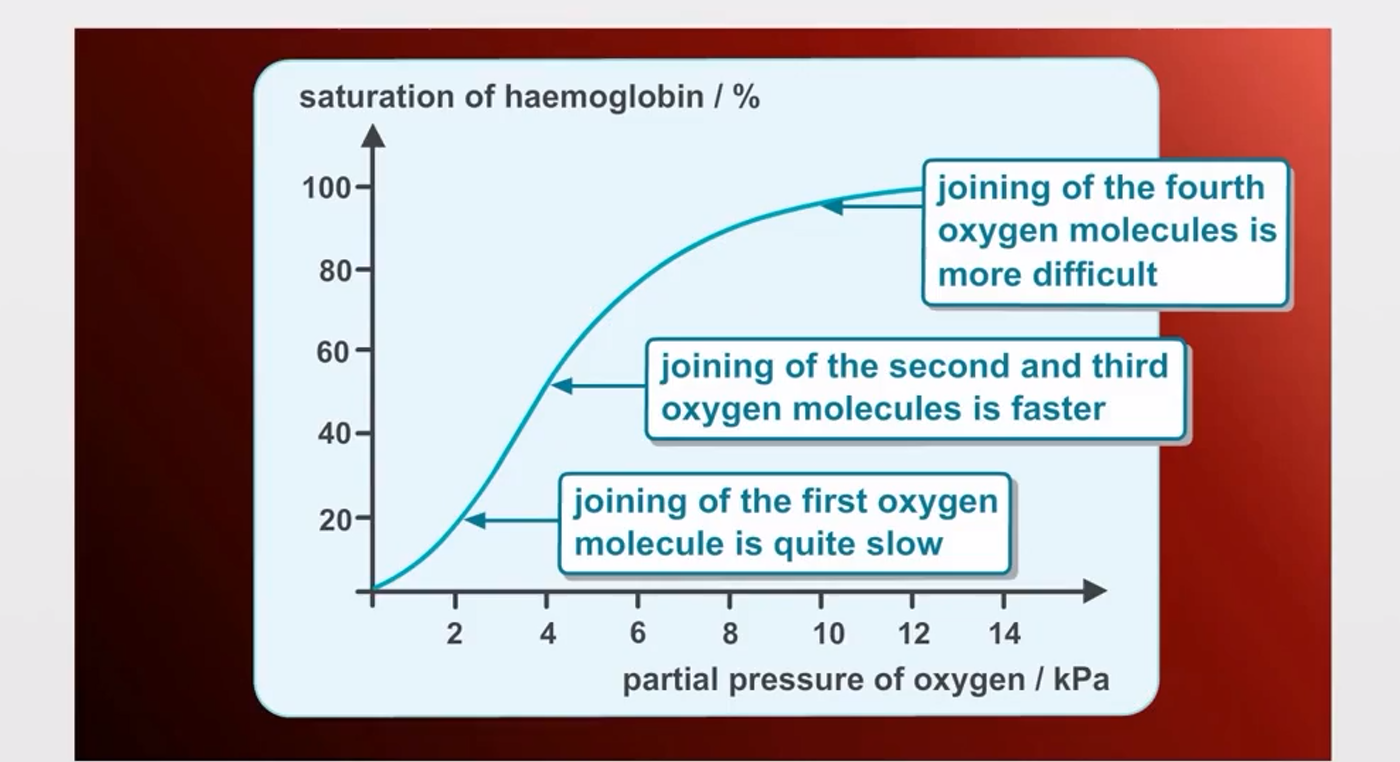
How does it become easier for O2 to bind to haemoglobin
Once one oxygen molecule has binded to the haem group
There is a conformational change making it easier for more O2 to bind
Increasing haemoglobin affinity for O2
O2 dissociation curve
As partial pressure of O2 increases so does the saturation of haemoglobin
Why is O2 affinity low in high CO2 conc
CO2 is acidic changing the structure of haemoglobin
Lowering its affinity for O2
A small decrease in pH will result in a large decrease in percentage saturation of O2
Ways Co2 can be transported
5% Dissolves directly into blood plasma
20% Forms carbaminohemoglobin with amino group
75% Hydrogencarbonate ions
CO2 + H20 —→ Carbonic acid
Sped up by catalyst by carbonic anhydrase in -rbc
Low CO2 in rbc
Forms a steep concentration gradient - high rate of CO2 diffusing into rbc’s
Carbonic acid splits into H+ and HCO3-
HCO3- diffuses to blood plasma
Charge imbalance - Cl - diffuses in (chloride shift)
Haemoglobin binds to H+ —→ Haemoglononic acid