Environmental Physiology of Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
how is gonadal sex determined by reptiles and some fish?
by the temperature that the embryo experienced during a critical period in development
what is the critical period in development when sex is determined called?
the temperature-sensitive period
what are the three patterns of TSD
type Ia, type Ib, type II
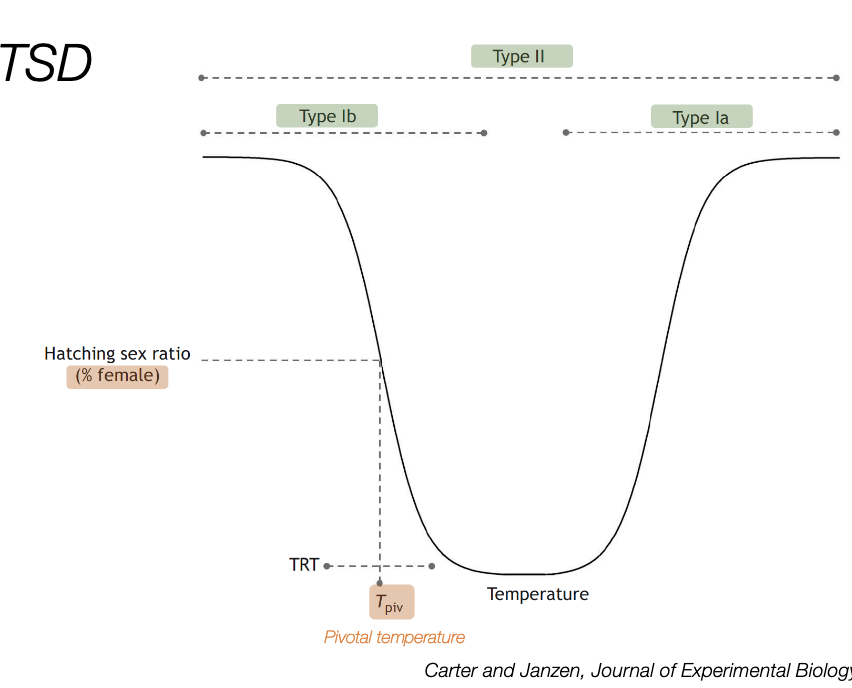
type Ia
only males at low temperatures, only female at high temperatures, mixed sex ratios in betweenw
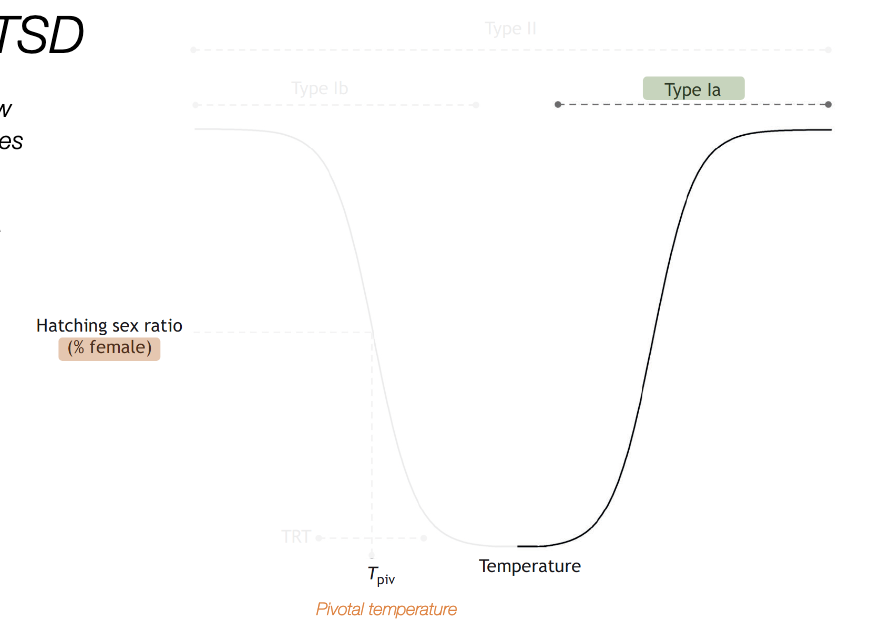
what is the pivotal temperature?
the temperature at which sex ratios are 50:50
type Ib
only females at low temperatures, only males at high temperatures, mixed sex ratios in between
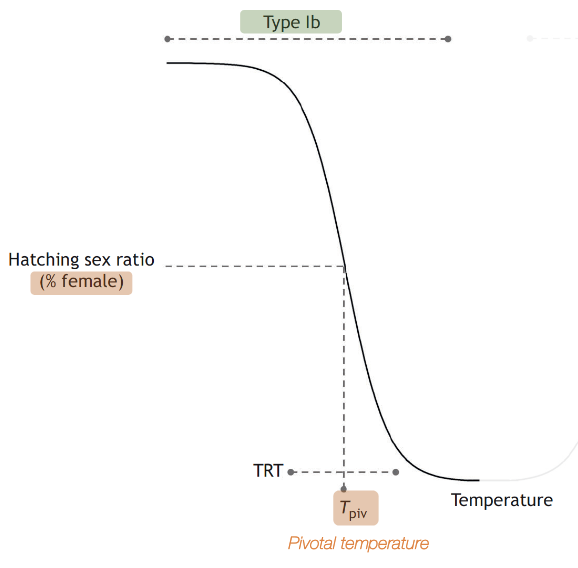
is the range of temperatures that produce mixed sex ratios always the same
no it varies between species
type II
only females at low and high temperatures, mixed sex ratios at intermediate temperatures
what determines the sex in species that have genetic sex determination?
the expression of specific genes (ex :SRY for Y chromosome) determines the expression of a cascade of genes, that will develop into an ovary or testis
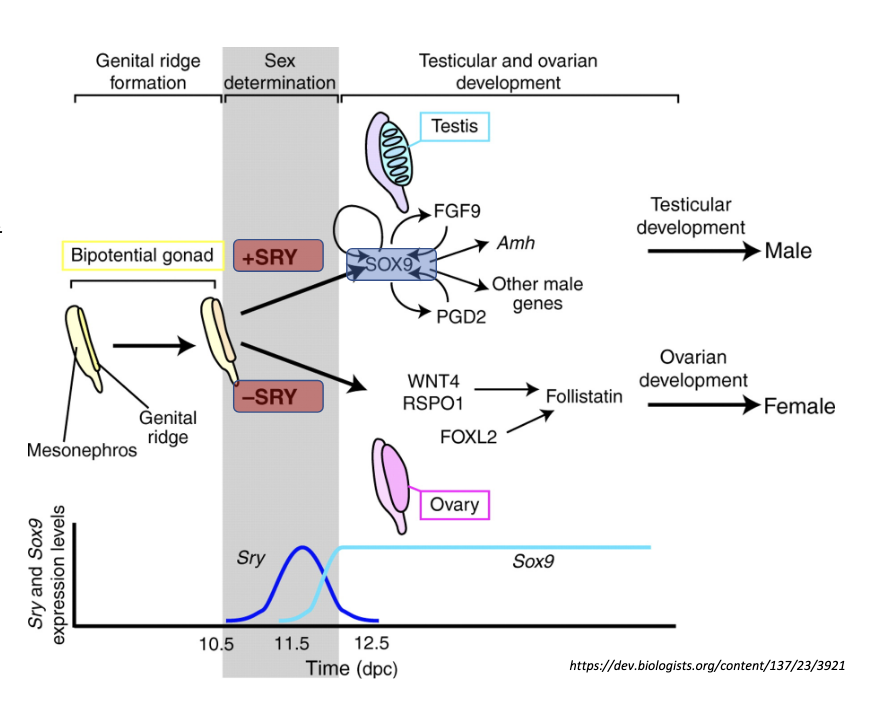
what are androgens used for?
masculinization of sex ratios (offspring more likely to develop into a male)
what enzyme converts androgens to estrogens?
aromatase
what are estrogens used for?
feminization of sex ratios (more likely to develop into a female)
how does temperature affect various aspects of biosynthesis pathway?
1b: during temperature-sensitive period, temperature increases can inhibit aromatase, leading to a higher ratio of males
1a: during temperature-sensitive period, temperature increases can increase the expression of aromatase
which androgen cannot be converted to an estrogen via aromatase?
dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and it binds very well to androgen receptors
aromatase levels at temperatures that produce females
higher aromatase expression
what kind of experiment can you conduct to determine the role of aromatase or estrogen in sex-determination in type Ia, type Ib, and type II species?
if estrogens promote the development of females:
analyze expression of aromatase as well as estrogen receptors at various temperatures
try to increase estrogen levels or estrogen receptor expression in eggs incubated at male-biased temperatures
try to inhibit estrogen synthesis/reception in eggs incubated at female-biased temperatures
what happens if you inhibit aromatase during development?
there is a decrease the proportion of females (increases the proportion of embryos that develops into males), especially at temperatures that promote female development
what is 5-alpha reductase?
an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of DHT (which cannot be converted into estrogens)
what happens when 5-alpha reductase is inhibited?
there is an increase the proportion of females (decreases the proportion of embryos that develops into males), especially at temperatures that promote male development
what are the evolutionary impacts of skewed sex ratios?
raising global temperatures can lead to changes in sex ratios, more of one sex than the other. This results in less reproduction and more competition for mates
what sort of behavioural adaptations could animals with TSD engage in to mitigate the effects of climate change (raise in temperature)? What sorts of constraints could there be on the evolution of these behaviours?
For sea turtles:
Bury nests deeper (cooler eggs)
limb morphology and ability for hatchlings to climb out of the nests as constraints
Build nests in cooler, less exposed to sunlight areas
nest site availability and general range of temperatures at nesting areas could be limited, as well as rising sea levels
Find nest sites that are cooler (different geographical area)
nest philopatry (stay in same area they’re born in)
species distributions could shift
start reproducing sooner
what sort of physiological or genetic features affecting TSD might be selected for as a result of rising global temperatures?
Reproduce earlier and lay eggs at a cooler time of year
but might be difficult due to environmental cues that control this
Selection for individuals with different temperature-dependent sex ratio curves (variation in the temperature-dependence of enzymes/receptors)
Selection for genetic sex determination
evolutionary transitions between TSD and GSD can happen rapidly
what else can disrupt the sex ratios of TSD species?
endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), by mimicking the effects of sex steroid hormones