Animal Diversity I
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Animals are ____trophic
heterotrophic
cell structure of animals
eukaryotic, no cell wall
animals shared derived character
extracellular matrix
extracellular matrix functions
collagen;
connection & support
All animals are ____cellular.
multicellular
All animals have specialized ____.
cells
Most animals have specialized ____.
tissues
Higher forms of animals have specialized ____.
organs
draw embryonic development in animals
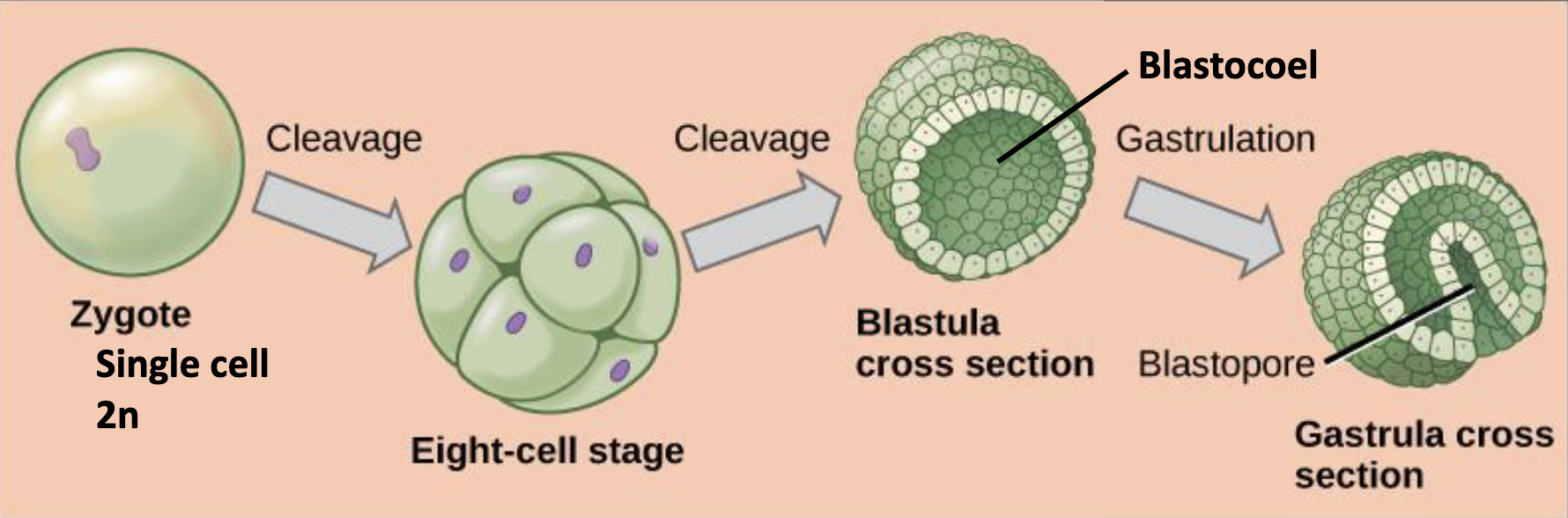
sequence embryonic development in animals
zygote
cleavage
blastulation
gastrulation
cleavage
mitotic divisions without cell growth
blastulation
more cleavage and ball becomes hollow, forming a blastula
gastrulation
folds inward and expands into blastocoel, forming a gastrula
homeobox genes
code for proteins that regulate development → morphology
body plan
set of morphological and developmental characters that represent key steps in evolution
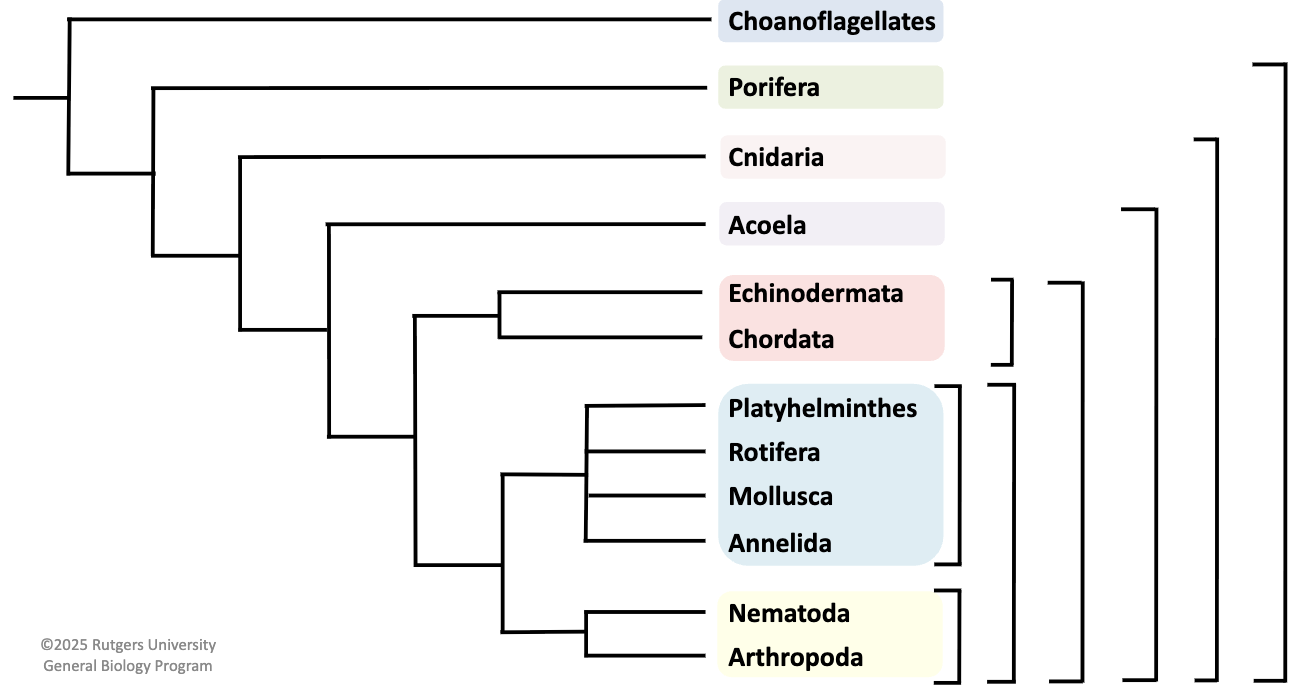
draw the metazoa (kingdom animalia) phylogeny
symmetry
arrangement of body structures in relation to an axis of the body
asymmetry
no line produces mirror images
two types of symmetry
radial
bilateral
radial symmetry
multiple planes produce mirror images;
no right and left sides;
sessile and planktonic animals
bilateral symmetry
only one plane through midline produces mirror images;
right and left halves;
cephalization
cephalization
concentration of nerve tissues at the anterior end of the individual;
CNS;
coordinate complex movements
What is the basal metazoan that does not have specialized tissues?
porifera (sponges)
Which clade has specialized tissues?
eumetazoa
draw embryonic tissue development
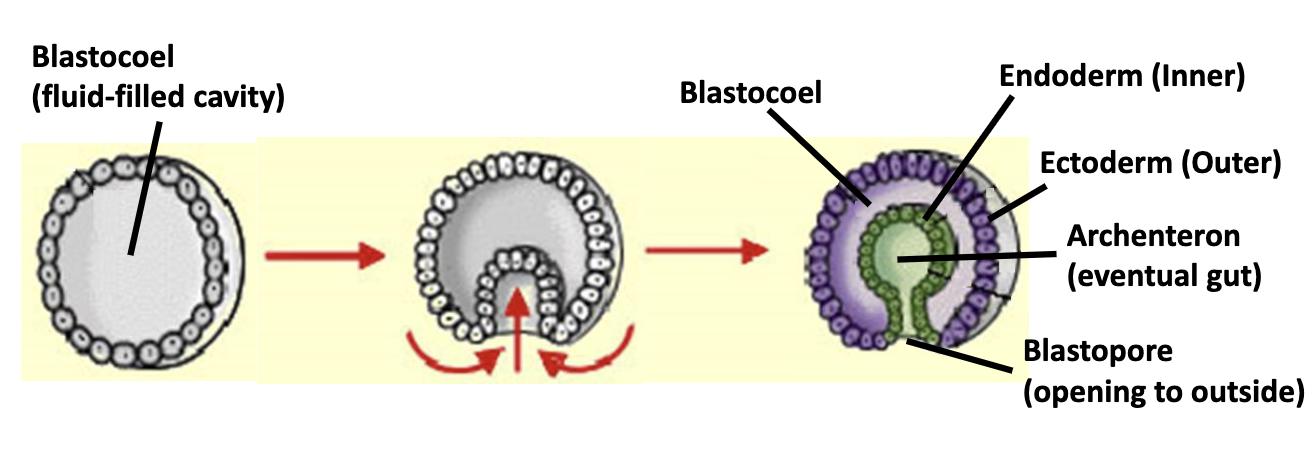
What are the 3 germ layers of embryonic tissue development?
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
ectoderm
outer covering and nervous system;
all eumetazoans
endoderm
lines archenteron;
lining of digestive tube and organs;
all eumetazoans
mesoderm
layer between the ectoderm and endoderm;
most other body structures;
not all eumetazoans
diploblastic
develop only ectoderm and endoderm layers
triploblastic
develop all 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
coelom
fluid-filled space between the body wall and digestive tube
The coelom is only in…
triploblasts
3 types of body cavities
acoelomate
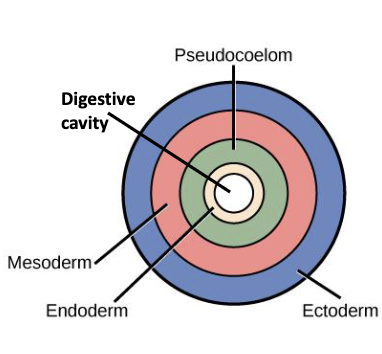
pseudocoelomate
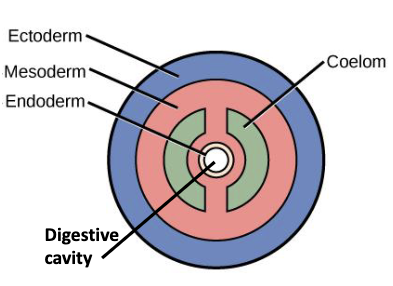
eucoelomate
acoelomate
ancestor had coelom, but it was lost
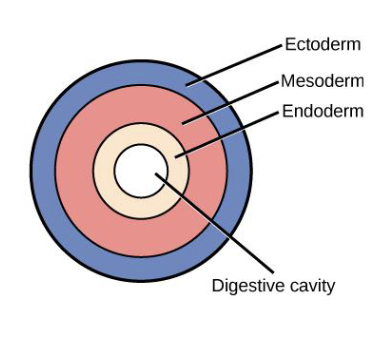
pseudocoelomate
coelom lined by (in between) endoderm and mesoderm
eucoelomate
true coelom;
completely lined with mesoderm
3 processes of animal development
cleavage
coelom formation
fate of blastopore
Differences in animal development separate Nephrozoa into…
protostomes and deuterostomes
cleavage stage for protostomes
spiral and determinate
spiral cleavage
planes of division are diagonal to the vertical axis
determinate cleavage
developmental fate is rigid;
if a cell is removed → adult lacks parts
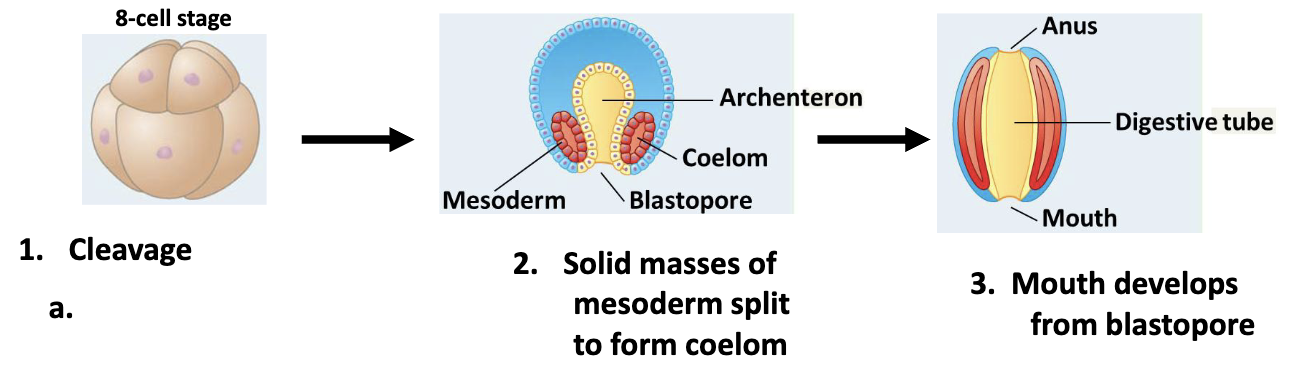
protostomes 3 stages
cleavage
solid masses of mesoderm split to form coelom
mouth develops from blastopore
draw protostome development
cleavage stage for deuterostomes
radial and indeterminate
radial cleavage
planes parallel or perpendicular to the vertical axis
indeterminate cleavage
each cell in early divisions is able to develop into a complete embryo
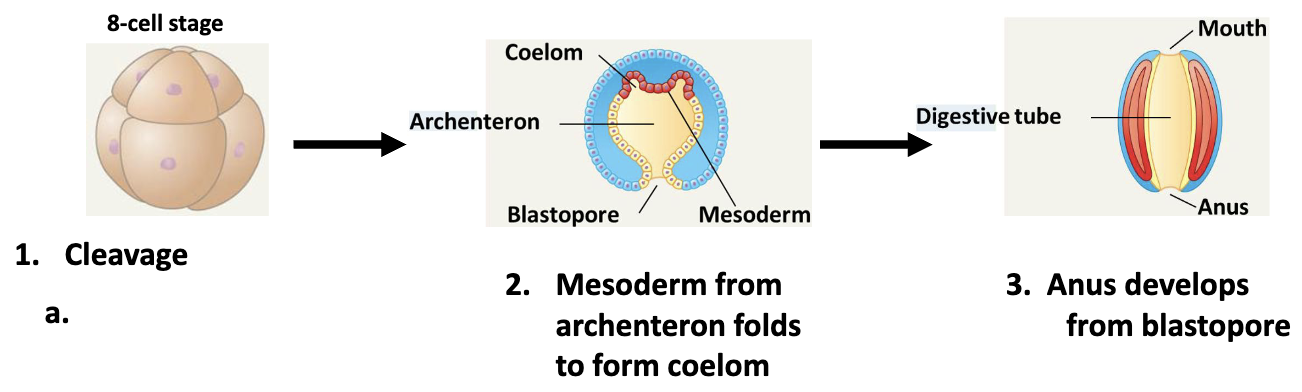
deuterostome 3 stages
cleavage
mesoderm from archenteron folds to form coelom
anus develops from blastopore
draw deuterostome development
choanoflagellates
protists
sister taxon to animals
CA of all animals lived…
770 mya
Sponges originated around…
700 mya
basal taxon of clade metazoa
phylum porifera
basal taxon of clade eumetazoa
phylum cnidaria
basal taxon of clade bilateria
phylum acoela
Cambrian explosion
535 - 525 mya;
rapid diversification
When were most of the current phyla established?
~ 500 mya
metazoa clade
porifera
cnidaria
acoela
echinodermata
chordata
platyhelminthes
rotifera
mollusca
annelida
nematoda
arthropoda
metazoa basal taxon
porifera
metazoa SDC
ECM
porifera SDC
asymmetry
no specialized tissues