Chemistry equations and general
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
n =
m / Mr
c x V
V / 24 (gas)
number of particles / 6.02 × 1023
pV=nRT
TOF mass spectrometry
t =
Answer should lie around: x10-5/-6/-7
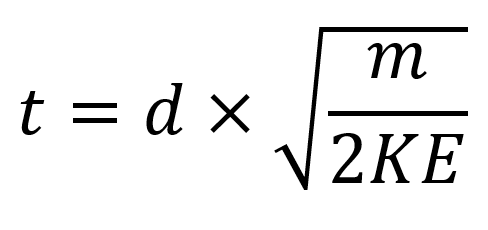
ThErmal cracking
High pressure - expensive and dangerous
High temperature - expensive
Produces:
Short chain alkanes
AlkEnes
Which can be used for feedstock and sold.
Catalytic Cracking
Slight pressure
High temperature
Zeolite catalyst
Products:
aromatic hydrocarbon
branched alkAnes
cycloalkanes
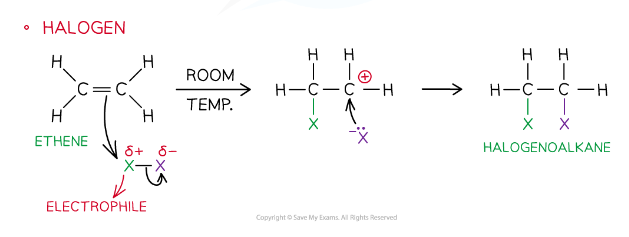
Examples of electrophiles
Dipole
Halogen: Br-Br
Hydrogen halide: H-Br
Sulfuric Acid: H2SO4
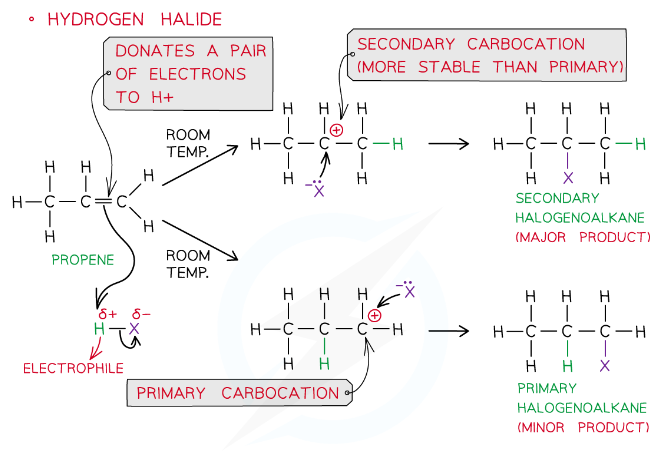
Electrophilic Addition to an unsymmetrical alkEne
Electrophilic Addition to a symmetrical alkEne
Examples of Nucleophiles
Lone Pairs
Ammonia: NH3
Potassium/Sodium hydroxide: OH- (aq)
Cyanide ion: CN-
Markovnikov's rule
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an asymmetric alkene, the hydrogen atom of the the hydrogen halide is more likely to bond to the carbon atom which is attached to the greater number of hydrogen atoms.
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4
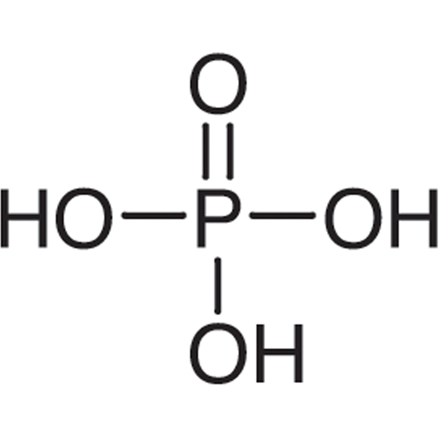
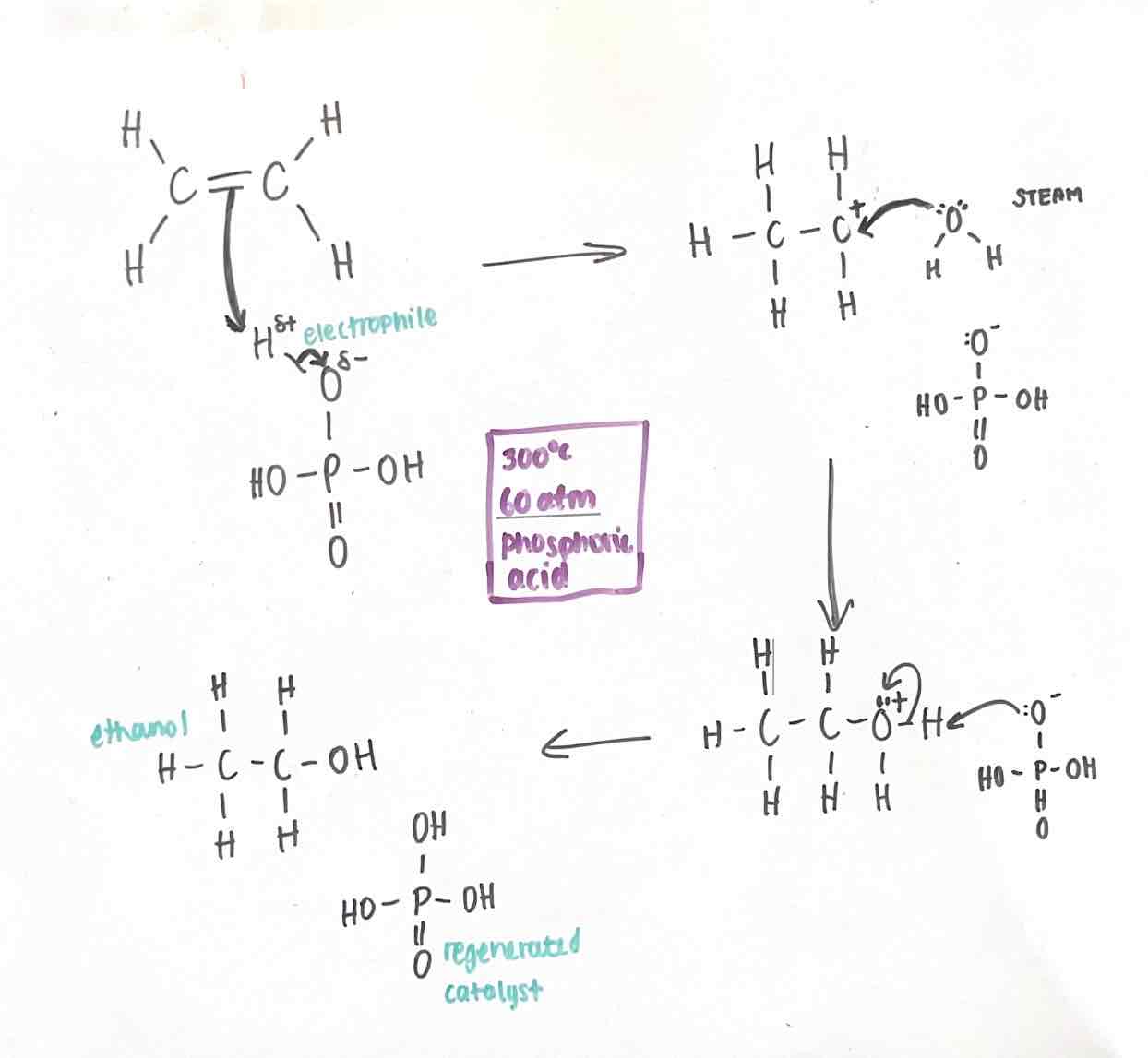
Hydration of alkenes conditions
300oC
60 atm
phosphoric acid catalyst
Hydration of alkenes mechanism
5 curly arrows
Carbocation intermediate
O+ with 1 lp, in second intermediate
Regenerated H3PO4
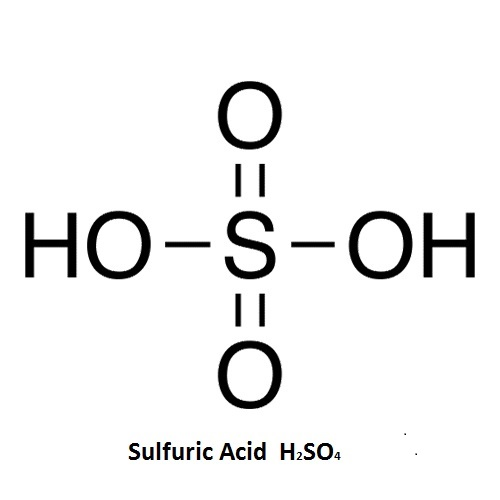
Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4
Plasticiser
A small molecule that fits between polymer chains, causing them to move further apart. This weakens IMF between chains so they can now move over one another, resulting in a more flexible polymer.
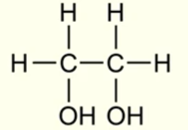
IUPAC name for this molecule
Ethane - 1,2 - diol
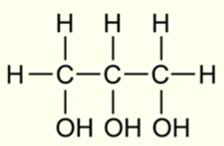
IUPAC name for this molecule
Propane - 1,2,3 - triol
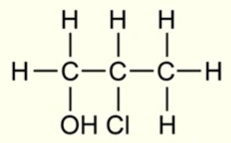
IUPAC name for this molecule
2-chloropropan-1-ol
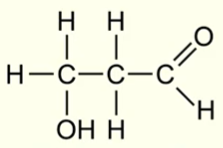
IUPAC name for this molecule
3-hydroxypropanal
(aldehyde group takes priority over alcohol group, alcohol is represented by ‘hydroxy’)
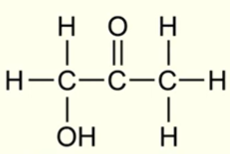
IUPAC name for this molecule
1-hydroxypropan-2-one
(ketone group takes priority over alcohol group, alcohol is represented by ‘hydroxy’)
Oxidation and reflux of alcohols
Oxidation | Reflux | |
|---|---|---|
Primary | Aldehyde | Carboxylic acid |
Secondary | Ketone | / |
Tertiary | / | / |
Name an oxidising agent used for alcohols
Colour change
Acidified potassium dichromate and warmed.
K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4(aq)
Orange dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) are reduced to green Cr3+ ions.
SO must be primary or secondary alcohol.
Aldehyde can be distilled off as it has a lower bp than alcohol or can be refluxed with excess K2Cr2O7 to form a carboxylic acid.
Elimination reaction of alcohols
Alcohol → alkEne + water
H2SO4(l) Catalyst H+
2 lp on O
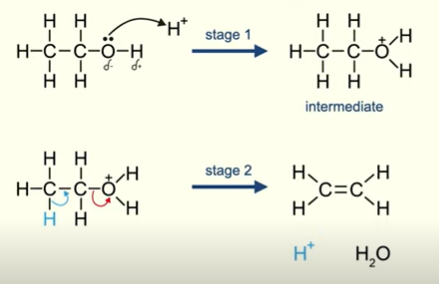
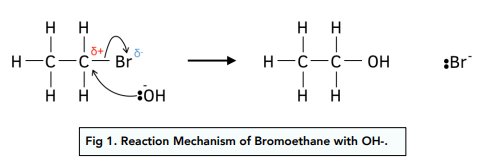
Nucleophilic substitution OH-
Conditions
Halogenoalkane must be dissolved in ethanol to make it able to react with aqueous OH-.
Heat under reflux to increase rate.
Acid
Proton donor
Base
Proton acceptor (H+)
When investigating rate of nucleophilic substitution of different halogenoalkanes, we use nucleophile…
H2O, not OH- as they would react with AgNO3 to form insoluble silver hydroxide.
Rate of nucleophilic substitution of different halogenoalkanes
Iodoalkanes > Bromoalkanes > Chloroalkanes
Chloroalkanes have the highest bond enthalpy.
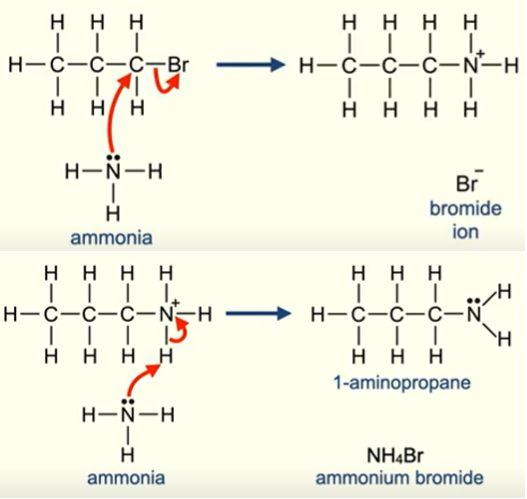
Nucleophilic substitution NH3
1lp on N in aminoalkane
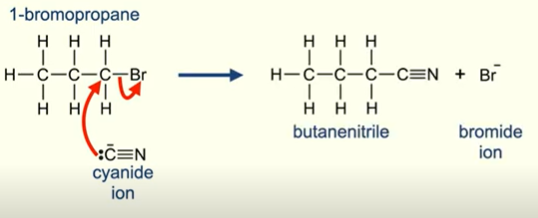
Nucleophilic Substitution CN-
Very useful reaction as it allows an increase in length of carbon chain!
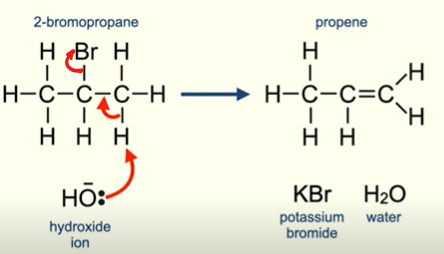
Elimination of a halogenoalkane
KOH (ethanolic)
NaOH (ethanolic)
Reflux
In absences of water it acts as a base.
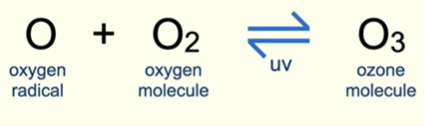
Ozone & UV light equation
Amount stays constant due to reverisble reaction
(Initiation) photodissociation equation

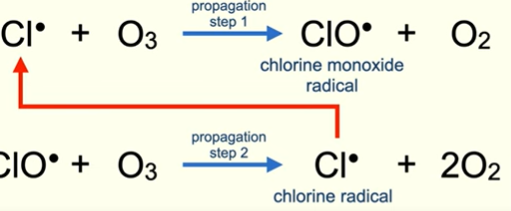
Chlorofluorocarbon + ozone propagation steps
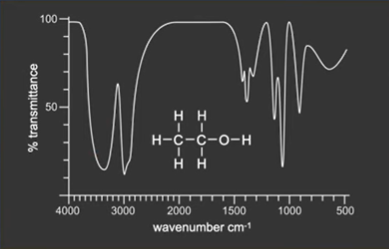
Infrared Spectroscopy
Bonds vibrate at different rates, which is slower between heavier atoms.
Bonds absorb radiation at the same frequency as they vibrate - which lies within the infrared region of electromagnetic spectrum for organic molecules.
An absorption spectrum is produced.
Fingerprint region is complex (<1500).
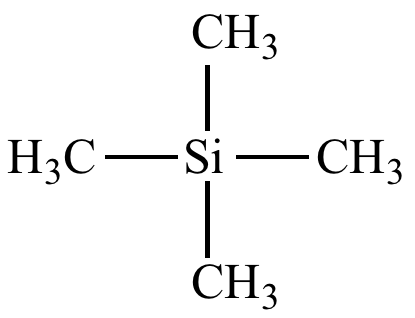
TMS name and structure
Tetra Methyl Silicane
How many H environments does TMS have?
1
Why is TMS a good reference?
Only a small amount needed as there are 12H in the same environment - so gives a strong signal.
Singlet pattern as only one H environment.
Contains silicon so chemical shift different to any organic compound so we can compare.
It is inert so doesn’t react with what we are analysing.
Non-toxic.
Volatile so can easily distil off and reuse.
Can use for both 1H and 13C n.m.r.