Fluid therapy 10
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
5 types of body fluid
•Intracellular fluid (ICF) – fluid found inside the cells of tissues
•Extracellular fluid (ECF) – fluid found outside the cells
•Intravascular fluid (IVF) – water contained in blood vessels (Part of ECF)
•Interstitial fluid (ISF) – fluid present in dense connective tissue and between cells (part of ECF)
•Transcellular fluid (TCF) – specialised fluid, gastro-intestinal secretions (part of ECF)
Fatty tissue contains…
Less water than other types of tissue
% of bodyweight that is water
about 60%
less as you get older
5 indications for fluid therapy

What does the body use water for?
•blood to circulate oxygen around, temperature control, transport medium, aids digestion, lubricant, assists in electrolyte balance.
2 types of water loss
•Sensible loss - can be seen, felt and measured e.g. urine, blood, diarrhoea, vomit
•In-sensible loss - lost by evaporation e.g. sweat, respiration
3 types of fluid
Isotonic – similar to blood make up. Electrolyte balance same as our blood.
Hypertonic –plasma volume – pulls water out of cells to increase the volume in circulation. Have to then add IVFT to replace the cells water content.
Hypotonic – contains lower conc of electrolytes, pulls water into cells. Hypernatremia, etc.
Water taken in via
drinking
eating
fluid loss increased in sick animals by
vomit
reflux
diarrhoea
blood loss
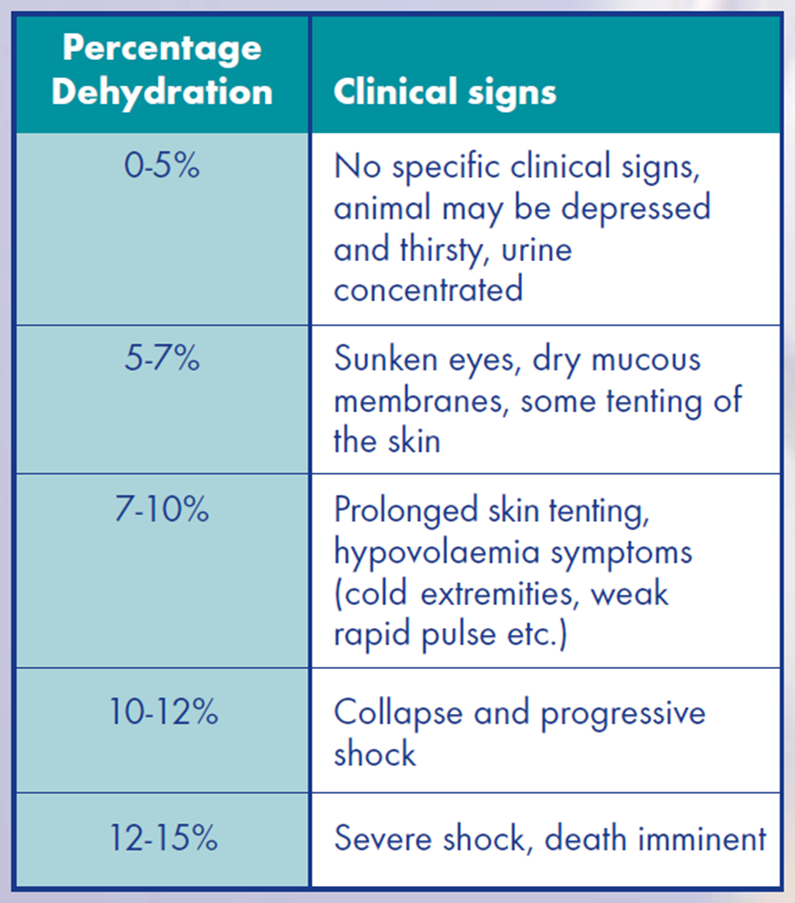
Clinical signs for each % dehydration
Normal PCV values
§Cats = 24 - 45%
§Dogs = 37 – 55%
§Rabbits = 36 - 48%
Normal total protein
§Dogs 50-70g/litre
§Cats 60–80g/litre
Normal urine output
1-2 mls/kg/hour
Normal specific gravity
•Cats = 1.035-1.060ug
•Dogs = 1.015-1.045ug
Maintenance fluid rate for small animals
50 mls/kg/24hrs
Maintenance rate in rabbits
60-100 mls/kg/24hours
Step by step for drops per min
maintetnace rate= 50 x BW x 24.
maintenace / no. of hours = mls per hour
/ 60= mls per in
x drip factor = drops per min
Fluid deficit calculation
fluid defict (%) = % dehdration x bodyweight x 10
total fluid requirement (ml) = maintenance fluid + fluid deficit
Anaesthesia support rate in healthy patients
dogs - 5ml/kg/hr
cats - 3ml/kg/hr
Management of the IV catheter and vein:
•Firmness or swelling of the vein
•Heat and/or pain of the vein
•Discharge or bleeding from the catheter site
•Vein patency
•Catheter patency
•Flush with heparinised saline (use 10,000IU heparin in 1litre saline which is 10IU/ml)
•Catheter damage
•Leaks
•Clots
•Check that the giving set is running and there are no kinks or blockages
•Missing stay sutures, tape or bandaging
•Contamination of extension sets, three way taps, and intravenous bungs
Monitoring patient on IVFT
•Demeanour
•Rectal and peripheral temp.
•Pulse rate and quality
•Respiration rate and sound
•CRT
•MM colour
•Urine output
Admkinistering blood - what for and indications

Indications for Plasma transfusion
•Contains clotting factors and plasma proteins
•Indicated for:
•Albumin loss
•Intravascular volume expansion
•DIC – to supply additional clotting factors
Benefit of dog blood transfusion
can collect and store
have blood banks - not for cats
Average amount of blood

dog blood groups
•DEA 1.1 (most common), 1.2. 1.3 (DEA = Dog Erthyrocyte Antigen)
•DEA 3
•DEA 4 (all dogs possess the DEA 4 red cell protein)
•DEA 5
•DEA 7
•All dogs have some DEA 4, but ones that are pure 4 are universal donors as they don’t have as many antigens to react. (A lot of greyhounds are pure DEA 4)
cat blood groups
•3 major blood groups - ABC blood group system (C formerly known as AB)
•Type A have a low anti-B-antibody titre (generally most common (around 99%))
•Type B have a high titre of anti-A-antibodies
•Type C cats do not form anti-A-antibodies nor anti-B-antibodies (rarer)
•If type A cat – wouldn’t cope with type B or C – fatal. In an emergency you can give dogs blood temporary as they don’t have the antigens against it, would kill it off slowly enough for you to manage. Cannot give cat blood to dogs.
blood typing
•The membrane of each red blood cell contains millions of antigens that are ignored by the immune system.
•A blood type is a classification of blood, based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of RBCs
•Antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins or glycolipids
•Antibodies = protein produced by the immune system
•Negative = no antigens present
•Positive = antigens present
•Content of RBCs (i.e. Blood Type) is inherited from parents
•Antigens – proteins produced by WBC’s in immune system.

cross matching bloods
•Not necessarily required for a first or an isolated blood transfusion
•Identifies the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of RBCs
•Used to detect existing antibodies against red cell antigens
•Detects serological incompatibility
•Blood donor essentials:
•Healthy
•Vaccinated
•Not pregnant
•Use a microscope and mix the blood with - agglutination test to decide if blood would work. Positive: Clumping (agglutination) indicates the presence of the target substance.
Negative: No clumping indicates the absence of the target substance.
always match cats
collection of blood donor
•Taken from a vein
•Collected into a prepared blood collection bag
•Collection bag may contain either Acid Citrate Dextrose (ACD) or Citrate Phosphate Dextrose (CPD)
storage of bloods
•Ideally use within 6 hours to reduce inactivation of platelets and clotting factors, and risk of bacterial growth
•Blood collected in ACD collection bags may be stored at 1-6˚C for 21 days
•Blood collected in CPD collection bags may be stored at 1-6˚C for 28 days
•Packed red blood cells (plasma has been removed) can be stored at 1-6˚C for 21 days (or up to 42 days if an additive had been used)
administration of blood transfusion
•The transfusion should not exceed 20% of the total blood volume
no longer than 4 hour as blood will deteriorate in bag
calculation for blood required
up to 20ml/kg dog
up to 10-15ml/kg cat
administration rates
slowly at 0.1ml/kg for 10 mins (monitor)
5-10ml/kg/hr
plasma collection and storage
Collection:
•Collected in the same manner as blood
•Plasma collection kits are available
•Blood can be centrifuged, or allowed to settle
and the plasma is decanted off
Storage:
•Freeze within 8 hours of collection
•Plasma can be frozen at -30˚C for up to 12 months
transfusion reactions
•Increased HR
•Increased RR
•Pyrexia
•Emesis
•Trembling
•Restlessness
•Urticaria
•Collapse
•Any reaction, the transfusion is stopped immediately, then get the vet.
•If severe, take the catheter/ aspirate to get rid of residue so you can push medication through and not more RBC’s.
parental nutrition 2 types
•Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
•Amino Acids (protein)
•Dextrose (carbohydrate)
•Lipids (fat)
•Partial Parenteral Nutrition (PPN)
•Amino Acids (protein)
•Dextrose (carbohydrate)
•TPN is light sensitive
•High nutritive value of the solution as a medium for fungi and bacteria
•The lipid component should be added last (Acid pH of carbs will destabilise the lipid but protein presence buffers this reaction)
•Would use the jugular/ central vein for this.
•Access to water.
•Vitamins and minerals would need to be supplemented. Fluid spiked, etc.
•High nutritive value – aseptic technique when mixing is essential to prevent bacteria and fungi.
•Super mega expensive!!!