Criminology Test 3, Ch. 8, 12 + 13
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the basic premises of the link between socialization and crime?
Everyone has the potential to become a criminal.
Criminality is a function of individual socialization.
Crime is not limited to the poor and under-class.
We need to examine the agents of socialization such as family, school, peer groups, and religion.
What factors of family relations may contribute to criminal behaviour?
Conflict and tension.
Separation and divorce.
Single parenthood.
Inconsistent discipline.
Parent-child relations.
Parental mental health problems.
Drug abuse.
Child abuse and neglect.
Graph: Types of self-reported criminal victimization experienced during adulthood, by victims of childhood physical and/or sexual abuse, Canada, 2014
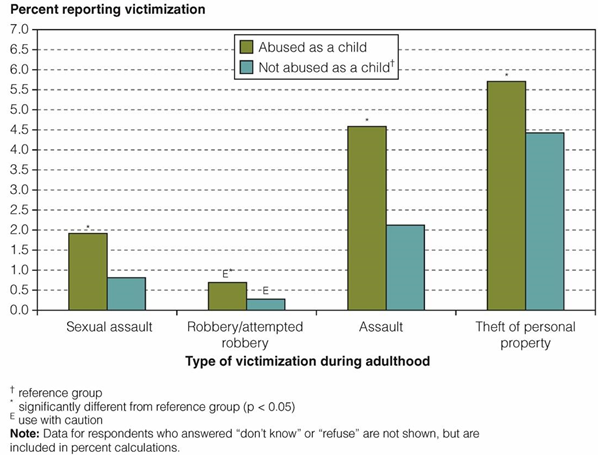
What factors of educational experience may contribute to criminal behaviour?
Poor academic achievement.
“Streaming” or tracking.
Dropping out.
What factors of peer relations may contribute to criminal behaviour?
Acceptance and popularity affects
Falling in with a “bad crowd”
Antisocial friends
Gang activity
What factors of institutional involvement and belief may contribute to criminal behaviour?
Religious beliefs and values.
Religious participation.
Evidence is mixed.
What are three theories that describe the effects of socialization on crime?
Social learning theory
Crime learned through interaction with criminal peers.
Social control theory
Criminal tendencies are controlled by bonds to society.
Social reaction theory
Criminality is result of labelling by significant others.
What is ‘differential association’?
Edwin H. Sutherland
Challenged the stereotype of crime as a lower-class phenomenon.
Criminal attitudes and skills are learned:
through interaction.
with significant others.
Criminal learning includes skills and motives.
Attitudes, values, language.
Significant others give definitions favourable or unfavourable to law-breaking.
Too many definitions favourable to breaking the law results in deviance.
Criminal behaviour is learned just like non-criminal behaviour.
Criminal behaviour results from general needs and values, not special needs and values.
Research shows that differential association is related to:
Violent behaviour.
Substance abuse and drug trade.
Career patterns of crime.

What is ‘differential reinforcement theory’?
Akers and Burgess
Combines differential association theory with operant conditioning
Deviant behaviour starts as imitation.
Maintained through reinforcement
Weakened through punishment
Rewards and rationalization.
Main influence
Groups that control reinforcement and punishment
Akers’ research of teen drug behaviour
Kids who believe they will be rewarded for deviance by those they respect are most likely to be deviant.
Associates may be chosen because they reinforce deviant behaviour.
What is ‘neutralization theory’?
Sykes and Matza (1957)
People “drift” between conventional and deviant behaviours.
Techniques of neutralization of conventional values paves the way for further deviance and crime.
Evidence of conventional values
Techniques of Neutralization:
Criminals neutralize their conventional values through:
Denial of responsibility.
Denial of injury.
Denial of victim.
Condemnation of the condemners.
Appeal to higher loyalties.
What is ‘social control theory’?
Key Issue:
All people are tempted to be deviant.
Emphasis:
Self-concept, self-esteem and self-control.
Criminality is a product of weak self-concept and poor self-esteem.
Testing Social Control Theory:
Supportive research
Non-delinquent youth versus delinquent view
Deviant behaviour results in weakened social bonds.
Image: Hirschi’s Social Bond (1969)

What is ‘social reaction theory’?
Also known as Labelling Theory
People are given labels which may define the whole person.
Labels about one trait may be generalized.
Negative labels stigmatize.
E.g. Mentally ill are thought to be dangerous.
Agents of social control may maintain and amplify criminal behaviour.
E.g. police, courts.
Crime and Labelling Theory:
Crime is not a behaviour but how we respond to a behaviour.
Social groups create deviance by making rules.
Moral entrepreneurs
What is ‘differential enforcement’?
Law are differentially enforced, based on social status and social distance.
Poor and minorities predominate in crime statistics.
What are the consequences of labelling?
Stigma
Changing self-image
Reflective role-taking.
Joining deviant cliques
Common bond with other outcasts.
Criminal labels
Create a master status.
Become basis of personal identity.
Process is referred to as the “dramatization of evil”.
Labelling is associated with chronic offending
What is the ‘General Theory of Deviance’?
Kaplan (1992)
Some people are unable to meet social expectations and face social sanctions.
e.g., lack desirable skills or traits
Social sanctions lead to
Self-rejection
Deviant peer associations
Deviance amplification
What is the ‘Social Development Model (SDM)’?
Community-level risk factors
Poverty, disorganization, weak institutions
Socialization to develop pro-social bonds to family and friends through four routes:
Perceived opportunities for involvement in activities and interactions with others
Degree of involvement and interaction with others
Development of skills needed to participate
Perceived reinforcement (feedback) as a result of participation
What is ‘white-collar crime’?
Illegal activity for profit through legitimate business transactions
Edwin Sutherland
Wealthy classes use their positions in business for personal gain
i.e. price-fixing, false advertising
Committed by individuals who use the marketplace for their criminal activity
How serious is it?
Much higher cost than street crime
Destroys property and lives
Destroys trust and confidence
An international problem
Controlling white-collar crime:
Prosecution is rare
Compliance strategies
Economic incentives to obey the law.
Deterrence strategies
Detect crimes, convict and punish offenders as a warning to others.
Judges don’t see them as real criminals
They are subject to civil rather than criminal law
What are the seven types of white-collar crime?
Swings and swindles
Financial
Phony investments
Religious
Donations for non-existent causes
Chiselling
Cheating company or customers
E.g. Substituting generic drugs.
Securities fraud
Insider trading
Individual exploitation of position
Government
Industry
Influence peddling and bribery
Government
Criminal justice system
Business
Theft and employee fraud
Use position for personal gain
Blue-collar fraud
Pilferage
Management fraud
Client frauds
Health care fraud
Unnecessary services
Bank fraud
False property evaluation
Tax evasion
GST, PST
Corporate crime
Committed by people who control companies to further their business interests.

What are the four types of corporate crime?
Illegal restraint of trade and price-fixing
Deceptive pricing
False claims and advertising
Environmental crime
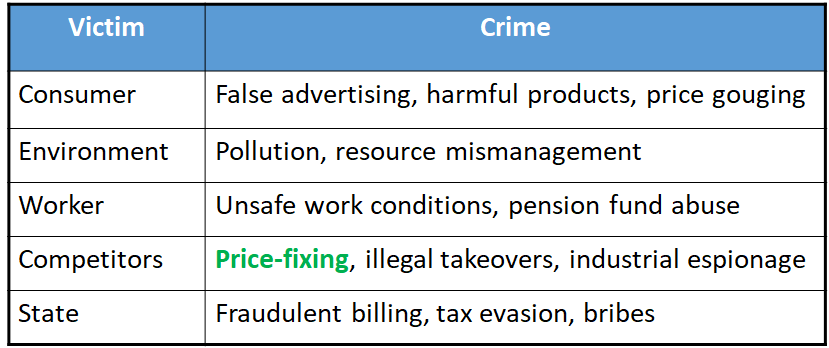
What is ‘organized crime’?
Illegal activity for profit through illegitimate business enterprise
Structured organization, which systematically provides illegal goods and services.
Prostitution
Gambling
Drugs
Pornography
Conspiratorial
Coordinated specialties, hierarchical.
Goals:
Profits and power, monopoly on illegal goods and services.
Also involved in businesses that seem legitimate
Money laundering, land fraud, computer crimes, protection rackets.
Predatory tactics:
Intimidation, violence, corruption.
Appeals to greed.
Control and discipline members.
Demotion, death sentences.
Many different groups besides Mafia.
What are some types of organized crime groups?
Asian-based
Drugs, migrant smuggling, street gangs, credit card fraud.
East European-based
Sophisticated Internet and financial frauds, phony credit cards, prostitution, drugs.
Italian-based
Sicilian mafia, Cosa Nostra.
Primarily narcotics, gambling, extortion and loansharking.
Outlaw motorcycle gangs
Hell’s Angels, Outlaws, Bandidos.
Drugs, escort services, extortion, intimidation, murder, etc.
Native outlaw gangs
Street gangs, cross-border smuggling.
What are the similarities between white-collar crime and organized crime?
Focus on enterprise
Taint and corrupt free market system
May involve violence
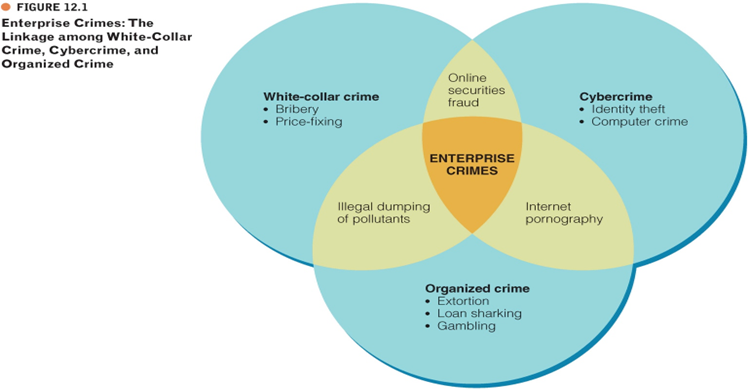
What are the two types of independent crime organizations?
Enterprise syndicates providing services
E.g. drugs, gambling, prostitution.
Power syndicates
Extortion, terror to gain power in legitimate business.
What are ‘high tech crimes’?
Traditional crimes using a computer:
Money laundering
Illegal gambling
Child pornography
Internet fraud
Hate propaganda
What are ‘pure high tech crimes’?
Hacking
Spreading viruses
Motivations:
Malice
Revenge
Voyeurism
“Open access” philosophy
Showing off
What is ‘mal prohibitum’?
An act that is not inherently immoral but is prohibited by statute (via Cornell Law School)
Public Order Crimes
What are ‘public order crimes’?
May be regarded as victimless crimes
Are victimless crimes victimless?
E.g. runaways and prostitution.
Violate the prevailing moral rules.
Prohibit the sale and distribution of selected goods and services (e.g., sex, drugs).
What are some examples of the relationship between criminality and morality/immorality?
Some non-criminal behaviour may be very harmful.
E.g. tobacco.
Some criminal behaviour may not be very harmful.
E.g. marijuana.
What are ‘moral crusaders’?
Moral entrepreneurs
Howard Becker
Undertake “moral crusades” to have their values incorporated into law.
E.g. same-sex marriage opponents.
Encourage “moral panics.”
What is ‘prostitution’?
Consensual exchange of sex for money.
Not a crime per se.
Sections 211 - 213 of Criminal Code includes
Solicitation (communicating for purposes of prostitution).
Procurement (act as a pimp)
Earlier in 2012, the Ontario Court of Appeal made a ruling on prostitution, resulting in significant changes to the prostitution laws.
It is now legal for prostitutes to hire drivers, bodyguards and support staff
It is now legal for prostitutes to work in organized brothels or “bawdy houses”
“Exploitation” of sex workers by pimps is illegal, as is openly soliciting customers on the street
Prostitutes and customers:
Limited information, mostly focused on female street prostitutes.
Customers:
Almost exclusively male.
Mostly white.
Blue-collar workers most common occupational group.
Higher status more likely to use escort services, call girls.
What are the five different types of prostitutes?
Streetwalkers
Runaways, ethnic minorities, high incidence of drug abuse.
Bar girls
In military towns, transient populations.
Brothel (bordello) workers.
Run by madams (former prostitutes).
Call girls
Independent or escort services.
Often high-income earners.
Circuit travelers
Groups of two or three.
Visit lumber camps, truck stops.
Some are enslaved by pimps.
What are some reasons for becoming a prostitute?
Troubled families.
Conflict with school.
Poor grades.
Dislike of discipline of traditional work.
Drug abuse
Heroin, cocaine.
Desire for money, luxuries.
Easy money.
Few are coerced into prostitution.
What is ‘pornography’?
Difficult to define
What is obscene? Who decides?
Supreme Court definition:
Media which links sex with undue exploitation, violence, or degrading or dehumanizing treatment and which has no redeeming social value.
What is ‘child pornography’?
Use of children in sexually explicit material.
Under 18 (or depicted as being under 18).
Visual depiction
Written material advocating sex with minors.
What have been some attempts at controlling sex for profit?
Vibrant industry, $10 billion worldwide.
Get tough policy
Increases profits.
By-laws may regulate and license activity.
Zoning by-laws.
Restricting the number of licenses.
How have technological changes impacted sex crimes?
Technology increases ability to communicate.
Guarantees privacy.
Internet interactive sex services.
Bill C-15A
Internet luring.
Child pornography.
What is ‘illegal gambling’?
Not well controlled, continues to be popular.
Section 207 of the Criminal Code
Province has exclusive rights.
Need permission from government to operate lotteries, make or take bets, hold a pool.
Gambling over the Internet is illegal if website is outside of Canada.
Social costs of gambling:
Problem gamblers (3 - 5% of the population).
Suicide (10% are gambling-related).
Crimes to support habit (theft, fraud).
Domestic violence and family breakdown.
Debt and bankruptcy.
What are some drug control strategies?
Source Control.
American approach to Latin America, Middle East; the War on Drugs.
High stakes, violent action and reaction.
Devastated economies (Afghanistan).
Can’t control designer drugs.
Border checks.
Law enforcement.
Target drug rings, go undercover.
Punishment.
Jail, fines.
Community.
Block watches.
Pioneer Canada:
Opium widely used in medicines.
Moral crusaders.
1908 Criminalization of opium.