Seedless and Seedless Vascular Plants
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Most common ancestor of plants
Archaeplastida→Charophytes
Green Algae and Plants: Shared Characteristics
Chlorophytes, Charaphytes and Plants share:
multicellularity
cell walls with cellulose
chloroplasts with the same pigments (a+b)
Storage molecule is starch
Chlorophyte (Ulva), Charophyte (Chara), plant (moss)
Challenges from water to Land
Desiccation (drying out is a constant danger for an organism exposed to air)
Both gametes and zygotes must be protected from dessication
Plants needs to form structural support in a medium that does not give the same lift as water
Male gametes must reach the female gametes using new strategies, swimming is no longer possible
Benefits from water to Land
[CO2] is higher
light intensity is higher
more minerals
no herbivores
no competition
From land to water: Adaptations
Life cycle: alternation of generations
Apical meristem tissue in roots and shoots
Waxy cuticle to resist dessication
Cell walls with lignin to support structures off ground
Alternation of generations: bryophytes
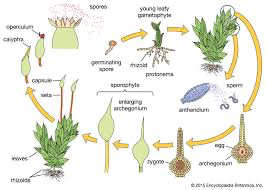
archegonium
where fertilization occurs
protects egg
the female part of the plant
gametangia (multicellular gamete)
where zygote formation occurs
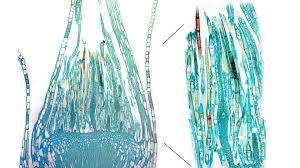
Apical Meristems
continuously dividing cells
roots and shoots grow towards resources
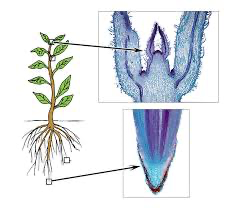
Waxy Cuticle
stop desiccation
pores needed in this to allow CO2/O2 exchanges

Sporopollenin
Protects haploid spores when there’s dispersal through air
made with multicellular sporangium
Antheridium
gametangia
protect sperm
male part of the plant
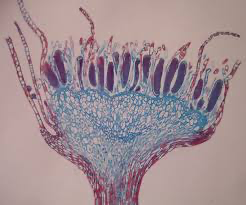
Why Charophyte life cycle if different from plants
The zygote is unicellular and not multicellular when going from meiosis to fertilization
Stomata
Holes for gas exchange in plant leaves below cuticle
Secondary metabolites
Chemicals adapted in plants to deter, repel or poison competitors, herbivores, and parasites
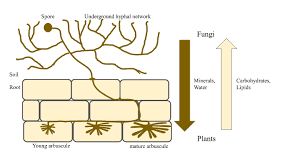
Mycorrhizae
Mutualism w/ fungi; helps plants get water and absorb minerals
dates back to the first land plants (before true roots)
Seedless Nonvascular Plants (SNP)
Bryophytes
Non-woody, small, ground-covering plants that require water for reproduction
Have rhizoids (Not true roots)
Phyla of Bryophytes
Liverworts (Hepaticophyta group)
Hornworts (Anthocerotophyta group)
Mosses (Bryophyta group)
Seedless Nonvascular Plants
Homosporous
Bryophyte characteristics: Gametophyte
Haploid gametophyte dominant
makes eggs and flagellated sperm
most are small, low growing, in moist areas
Bryophyte characteristics: sporophyte
Sporophyte depends on gametophytes for food and water
Grows w/in archegonium of gametophyte
sporangium makes many haploid sperms
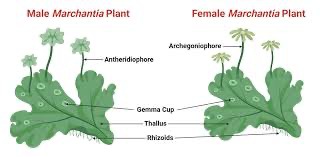
Liverworts
Most have elevated gametophytes that resemble miniature trees (Marchantia)
Reduced over very small sporophytes; some thalloid some leafy
Marchantia, thalloid=gametophyte
Plagiochilla deltoids, leafy= gametophyte
Bryophytes
Bryophytes, hepaticophyta
Hornworts
common name refers to the horn-like long tapered shape of sporophyte
good colonizers of moist soils
symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria
Bryophytes, Anthocerotophyta

Mosses
The most numerous of the non-vascular plants
inhabit extreme environments such as mountain tops, tundra, and deserts
Sporophyte grows up from female gametophytes to gain elevation for spore dispersal (polytrichum commune, hair-cap moss)
Pioneer species in nutrient-poor soils
primary producers in cold/high-altitudes
Sphagnum/Peat Moss; important in wetlands, also harvested for food
Some peatlands preserve corpses for thousands of year
Bryophytes, Bryophyta

Seedless Vascular Plants Characteristics (SVP)
Branched sporophytes that are independent of gametophytes for nutrition
diploid sporophyte dominates life cycle
Transport in the xylem and phloem (vascular system)
Evolution of true roots
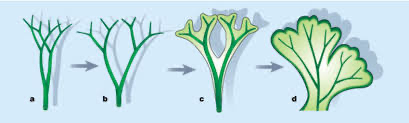
Evolution of true leaves
Microphyll Leaves
small, spine-shaped leaves
supported by a single strand of tissue
SVPs
Ex: Krauss’ spike moss, selaginella kraussiana
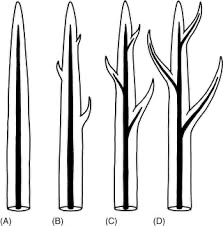
Megaphyll
leaves supported by a branched vascular system
Greater photosynthetic productivity
Ex: Tumbridge filmy fern, hymeniphylllum tumbrigense
SVPs
Sphorophylls
Leaves modified to bear sporangia
Developed in SVPs
Ex: Sori on ferns
Sphorophylls: Homosporous
Sporangium on sporophyll → single type of spore → typically bisexual gametophyte → Eggs/Sperm
Sphorophylls: Heterosporous
Megasporagnium on megasporophyll →Megaspore → Female gametophyte → Eggs
Microsporangium on microsporophyll → Microspore → Male gametophyte → Sperm
SVPs
Lycophytes (club mosses and relatives)
Pterophytes (ferns and relatives)
Lycophytes
small, tropical, and temperate
Sporophylls are modified to be cone-like strobilus
Only phyla to have microphyll leaves
Seedless Vascular Plants
Mainly monoecious
Sporophyll: cone-like structure/ central stalk
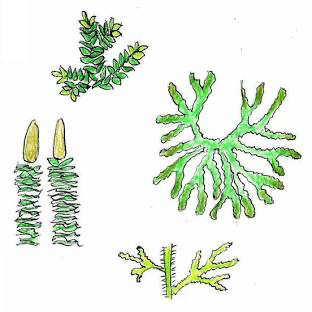
Lycophytes: Homosporous
Club mosses
Lycophytes: Heterosporous
quillworts and spike mosses
Pteridophytes
Horsetails, whisk ferns, and ferns
Homosporous → monoescious
Heterosporous → diescious
Sorophyll: Sori
Whisk Ferns
dichotomous branching
no true leaves or roots
homosporous
photosynthesis occurs in the stem
Pteridophytes, SVP
Monilphyte
Psilotum

Horsetails
Joined stems with tiny leaves
Strobili
Homosporous
Photosynthesis occurs in stems
Pteridpohytes, SVPs
Monilophytes

Ferns
most widespread and diverse
Homosporous
large megaphylls
sori on the underside of sporophylls
mostly in understory or as epiphytes
SVPs
Pteridophytes
Monilophyte group

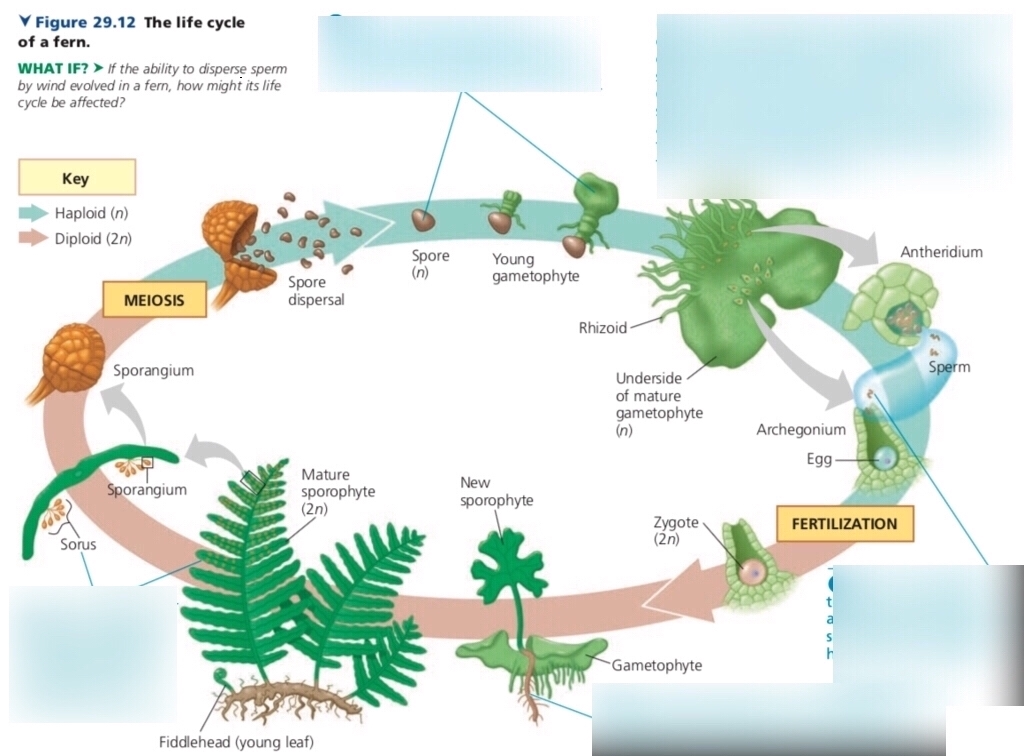
Fern Life Cycle
Importance of Seedless Plants (SVPs and Bryophytes)
The disappearance of mosses→Biological indicator of environmental pollution
Ferns→ Promotes Weathering of rocks → accelerates topsoil formation
Ferns→ Used as food
Peat Moss → used as fuel (renewable resources)
Peat Moss → Soil conditioner
Extinct SVPs → Coal → Energy source