Unit 1 Test Water Pollution Review
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

35 Terms
Sediment Pollution
Pollution by sand, soil and other minerals that are washed into streams and rivers after rainffall. (ex: logging, careless farming, mining)
Bacterial Pollution
Contamination of water by bacteria (ex : monure, human waste, spoiled food)
Toxic Pollution
Contamination of water by materials that Cause death, dis ease, or bir th defects (ex:gas,paint)
Nutrient Pollution
Contamination of water by excessive nutrients, usually nitrogen and phouphorus (ex: fertilizer, manure, human waste)
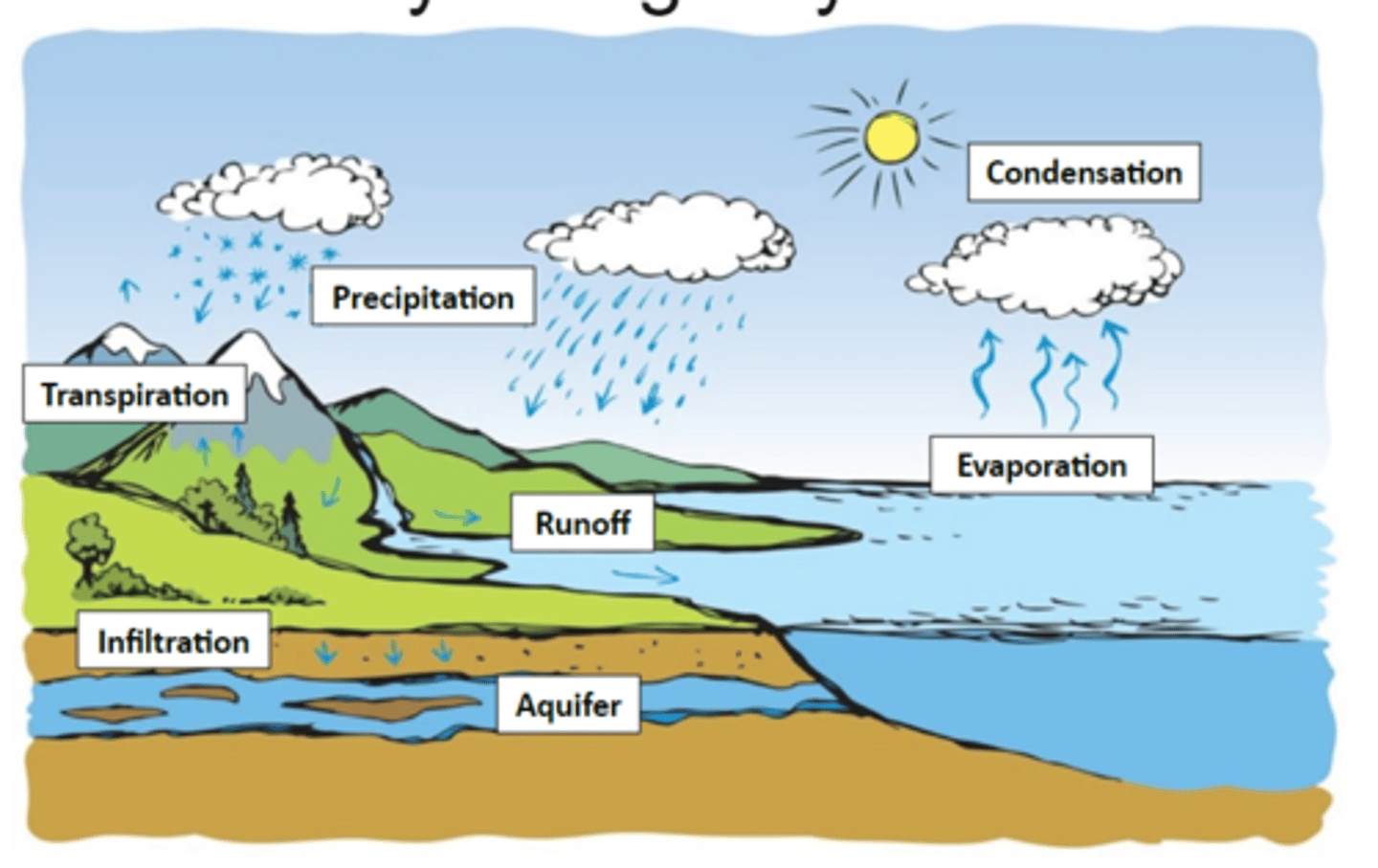
Aquifer
underground, permeable region of soil or rock that is saturated in water
Clean Water Act
the main U.S. federal Law that regulates water pollution
Watershed
land area surounding a body of water over which water such as rain could enter that bedy of water
Turbidity
the cloudiness of water
Ground Water Overdraft
wing water supply faster than can be replenished - causes a well to dry up
Point source pollution
pollution is coming fram a specific place and can be "pointed" to on map ex: chemicals from pipe draining into the river
Non-point source pollution
pollution does not come from any specific location ex: runoff from roads or careless farming
"biological treatment" of waste water?
Bacteria is used to break down waste and microorganisms + Plants remove nutrients (nitrgen, phasphorus, E. Coli)
Ppm
Parts per million
Ppb
Parts per billion (smaller than ppm)
Toxic Pollution examples
paint + paint thinner, gasoline leak oil
Sediment Pollution examples
trees being remared and soil washed into streams or rivers
Bacterial Pollution examples
living microbes (bacteria) washed down a drain
Nutrient Pollution example
washing clothes in a stream with detergent that contains phosphorus
Steps of Eutrophication (nutrient pollution)
1. Excess nutrients enter a body of water
2. Algea reproduces, using up oxygen and blocking sunlight
3. Underwater plants die
4. Bacteria consumes excess wastes and nutrients uaing up oxygen
Runoff
Water from precipitation that flows over the surface of land
Water Pollution
Anything that may degrade the quality of water making it difficult for organisms to live
Primary waste water treatment
treatment is a physical process that removes large particles with a screen
Secondary waste water treatment
treatment is a biological process that uses microorganisms to break down organic matter
When treatment marshes are used by sewage treatment facilities to treat wastewater, the treatment marsh is acting as a form of ——— treatment because it relies on the biological organisms in the marsh.
Secondary
Adding oxygen to water during secondary treatment is important because
It keeps bacteria alive and allows the bacteria to break down waste
Which practice requires the greatest amount of water in our homes?
flushing the toilet
Pollutant concentration is highest where?
Closest to the source of pollution
Traditional water treatment
Used for big cities and starts by using screens to clear debris (-) it uses chemicals to treat the water (+) treats water very quickly and efficiently
Wetland water treatment
Uses screens to clear debris at the start of the process. Uses marshes to purify water (+) more natural and eco-friendly process that does not use chemicals (-) takes longer to process water and not as efficient as traditional water treatment
Flint water crisis
1. City switched water source over to Flint River Water
2. The river was highly corrosive
3. Switched back to Detriot water system but damage already done to pipes in Flint
4. Pipes leak lead into water going into homes and businesses of Flint
Point Source Pollution
Pollution in which the source can be identified. Example: Smoke from a factory smokestack, waste water from a factory pipe
Non-Point Source Pollution
Pollution in which the source cannot be identified. Example: runoff from a farm field, golf course, or housing development
Dissolved Oxygen
The amount of oxygen in the water
Chlorine
Not naturally found in water at any appreciable levels but is added to public water systems and swimming pools as a bactericide
Know the parts of the water cycle