27- Brainstem & Spinal Cord
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the is responsible for automatic survival functions
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
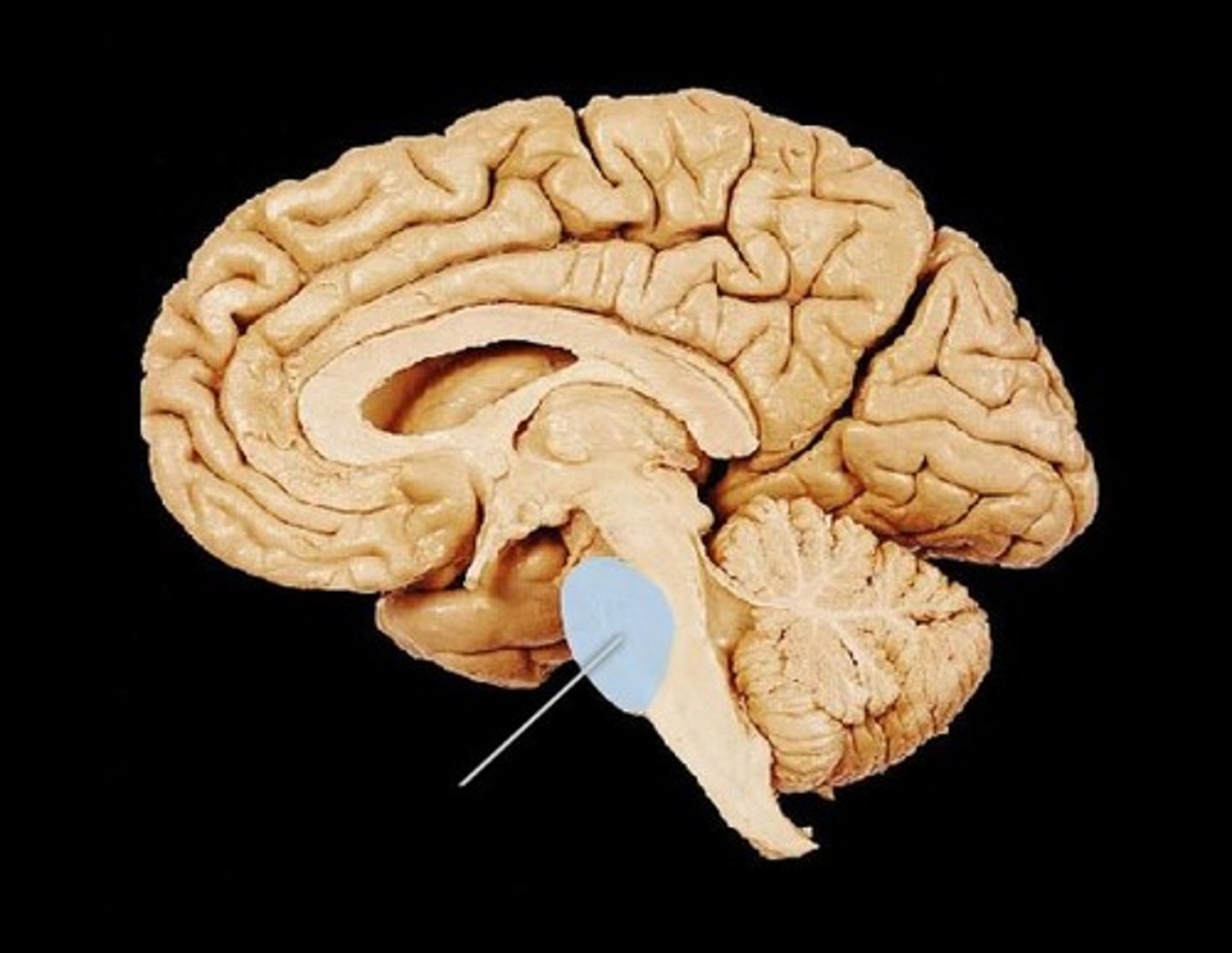
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
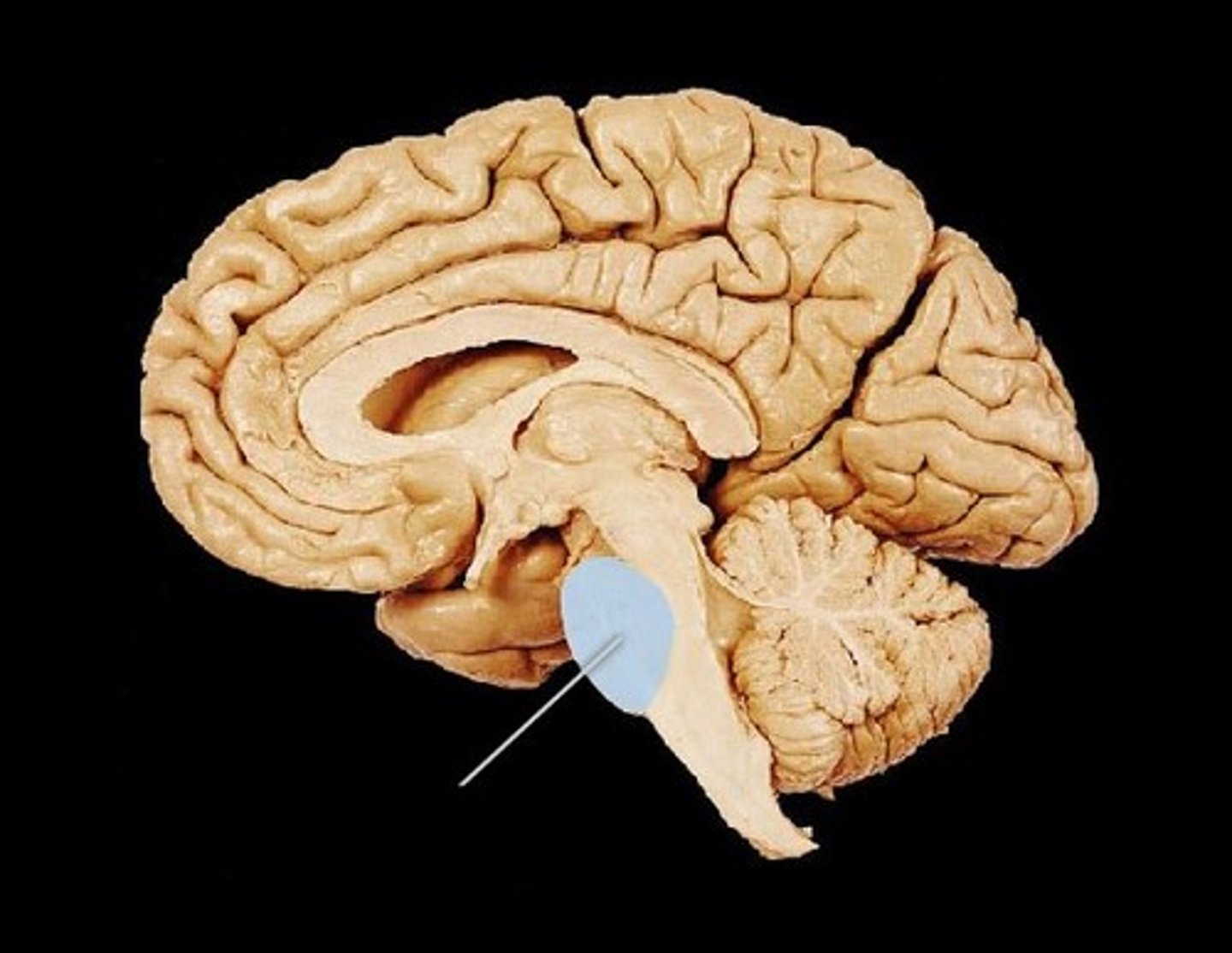
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
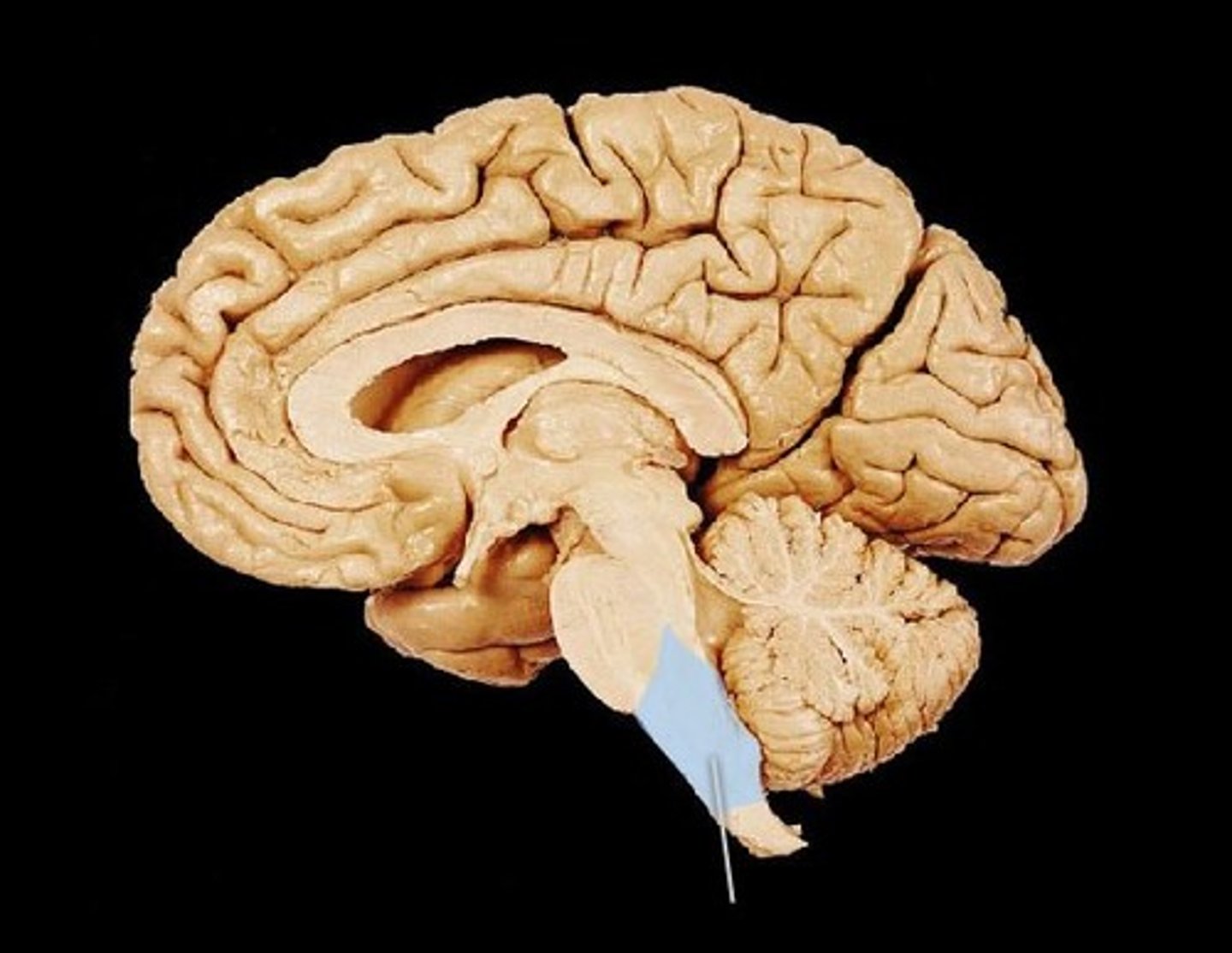
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
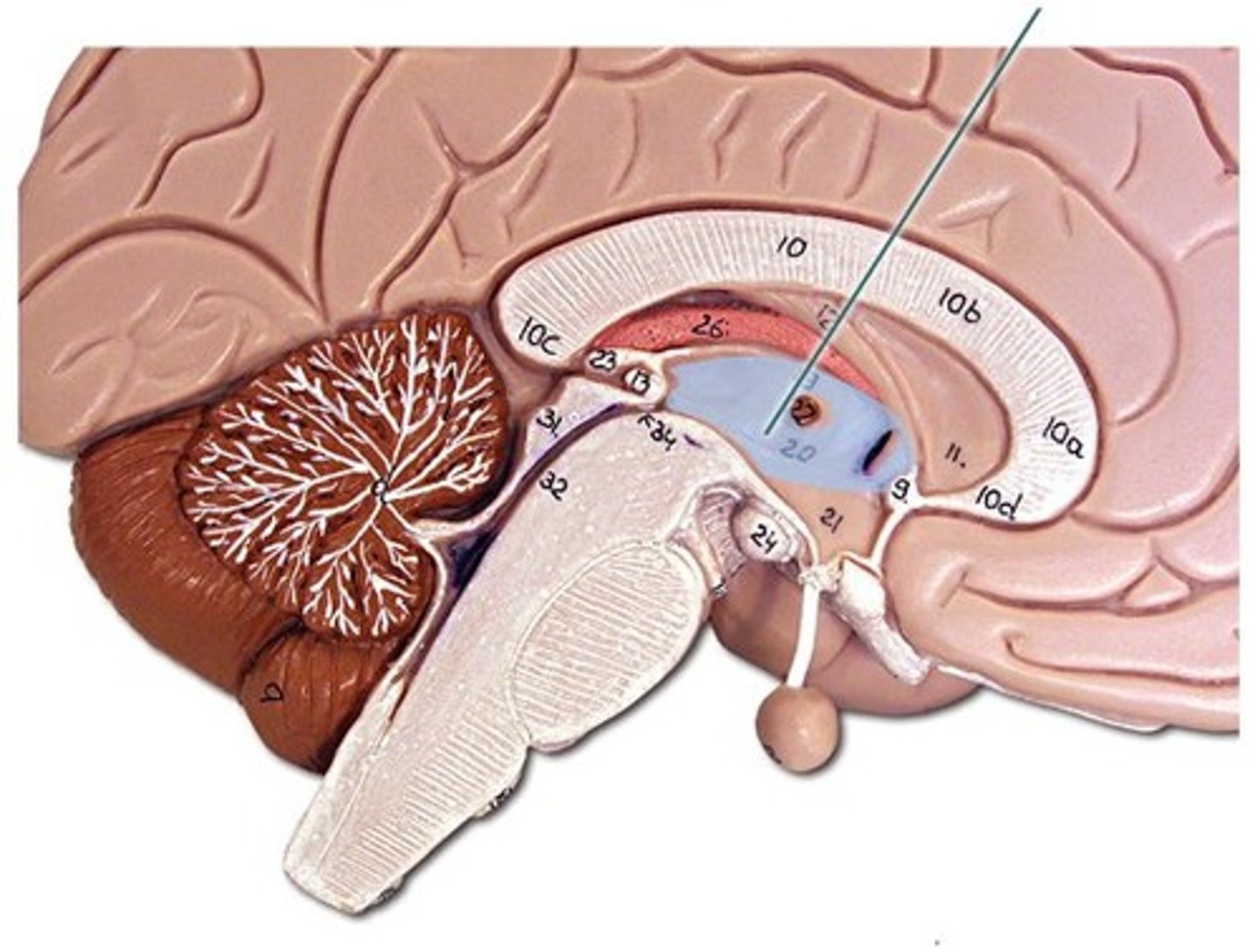
CN III and CN IV
What cranial nerves attach to the midbrain?
attaches to posterior midbrain
What is special about CN IV?
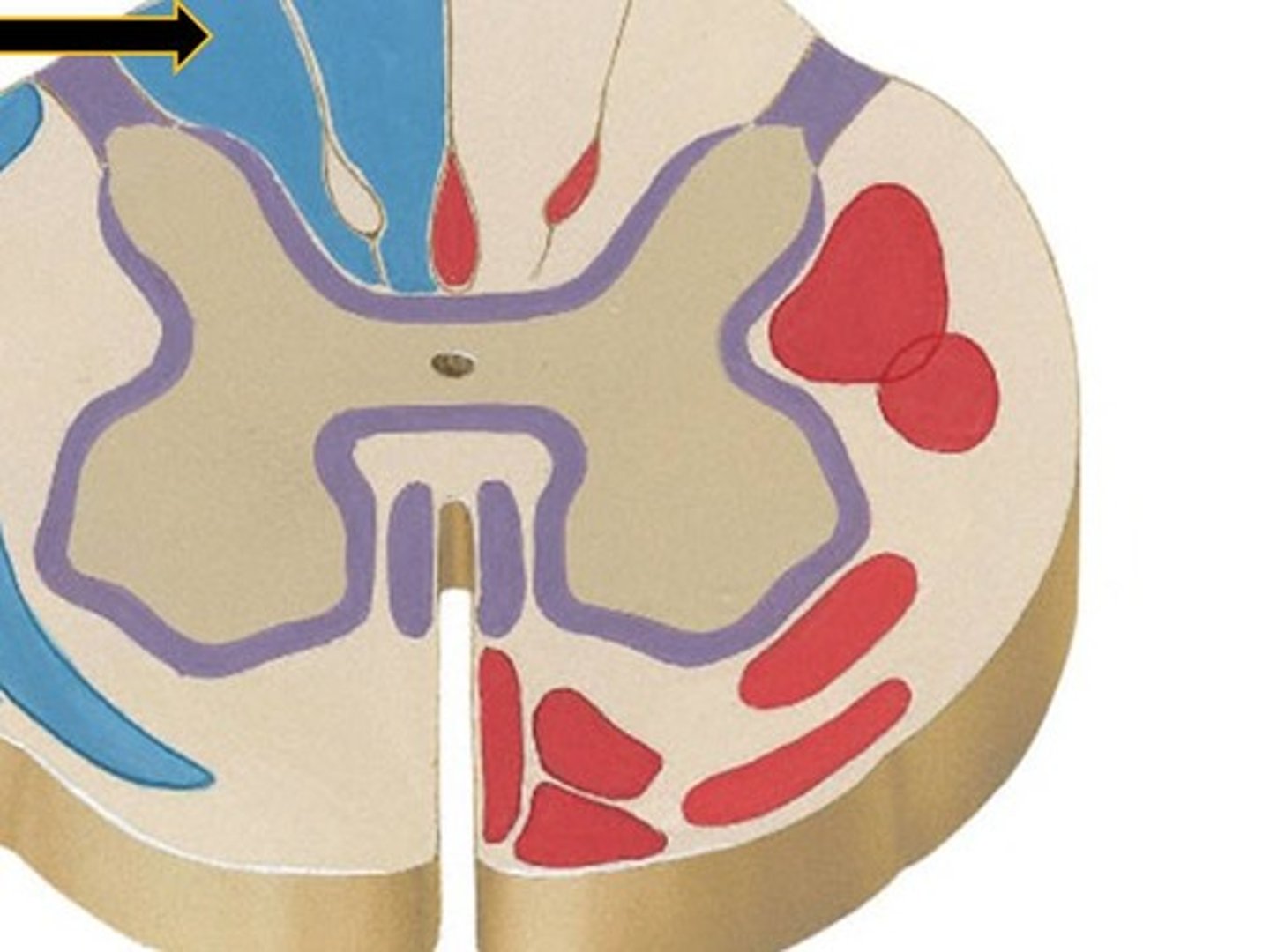
fasciculus gracilis
sensory tract for trunk and LE proprioception, 2 pt discrimination, vibration and graphesthesia
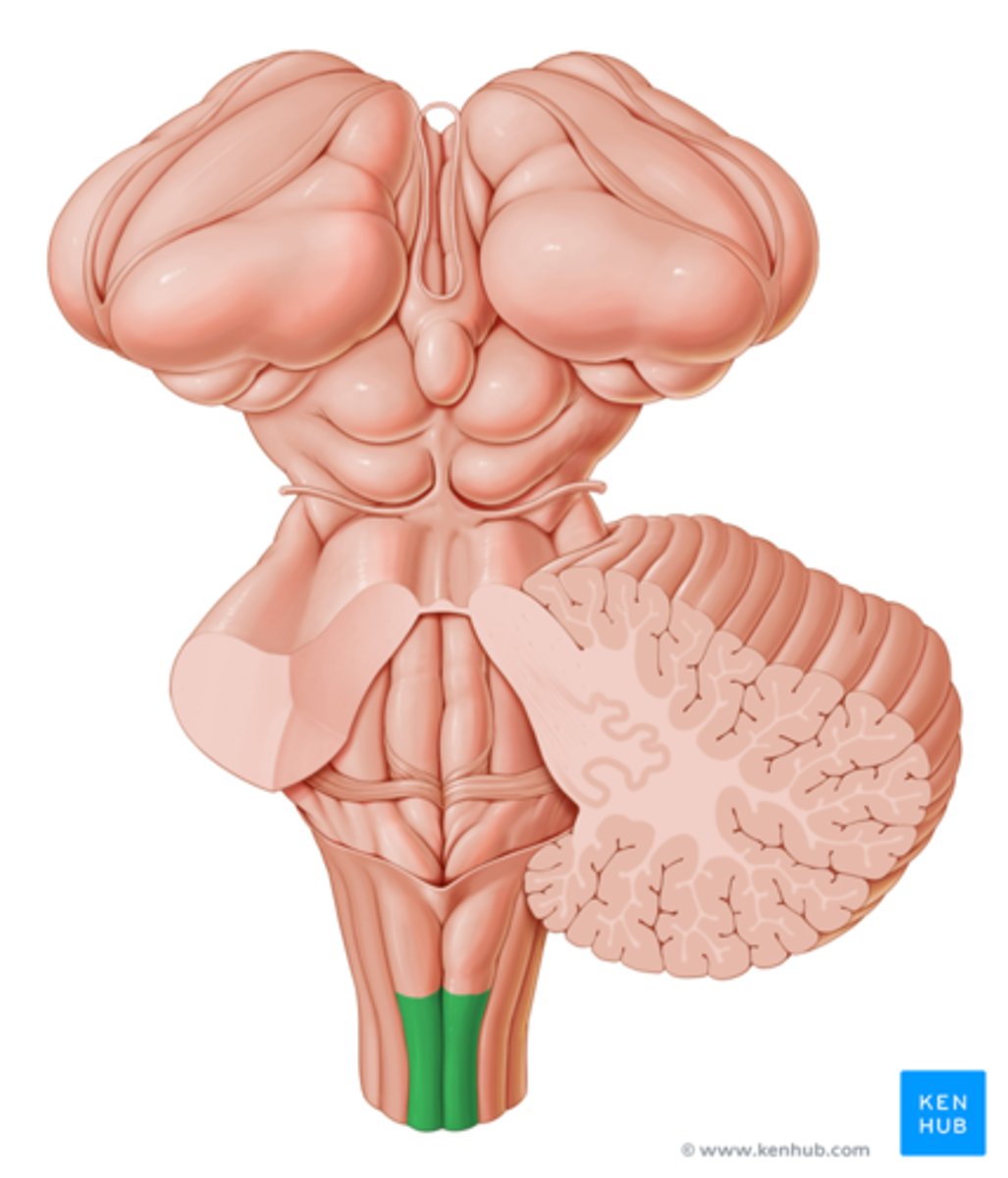
fasciculus cuneatus
A division of the Dorsal Columns System specifically dealing with the UPPER EXTREMITY
4
How many cranial nerves attach on the pons?
4
How many cranial nerves attach to the medulla?
reticular formation
-integrates sensory and cortical information
-regulates somatic motor activity, autonomic function, & consciousness
-widespread projections throughout brain and spinal cord
-involved in integration of activities
-modulates consciousness and behavior
3-12
What cranial nerves exit the brainstem?
basis pedunculi
Formed by cerebral peduncles & substantia nigra
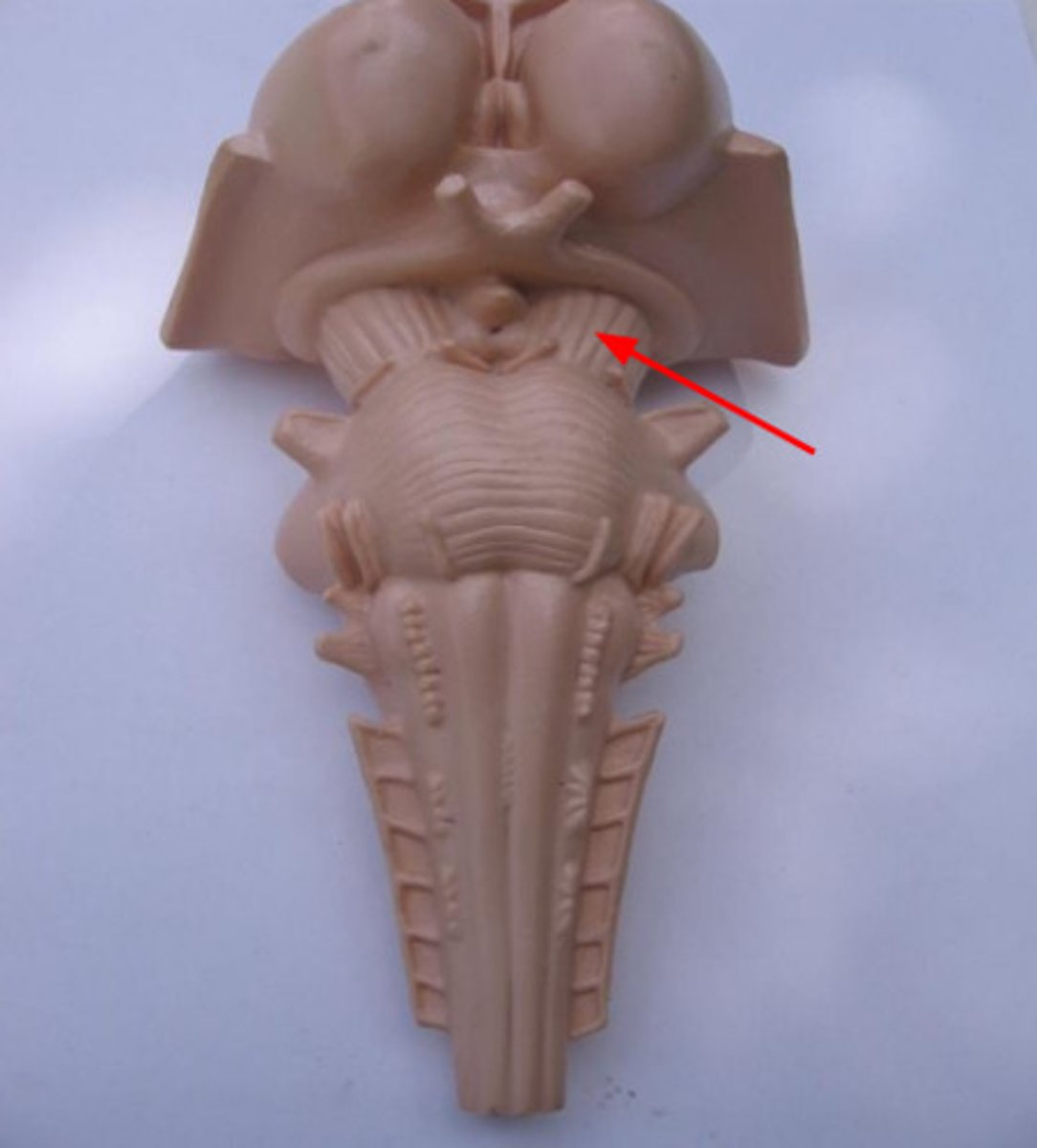
cerebral peduncles
contain fibers that carry motor output from cerebrum to other regions of CNS
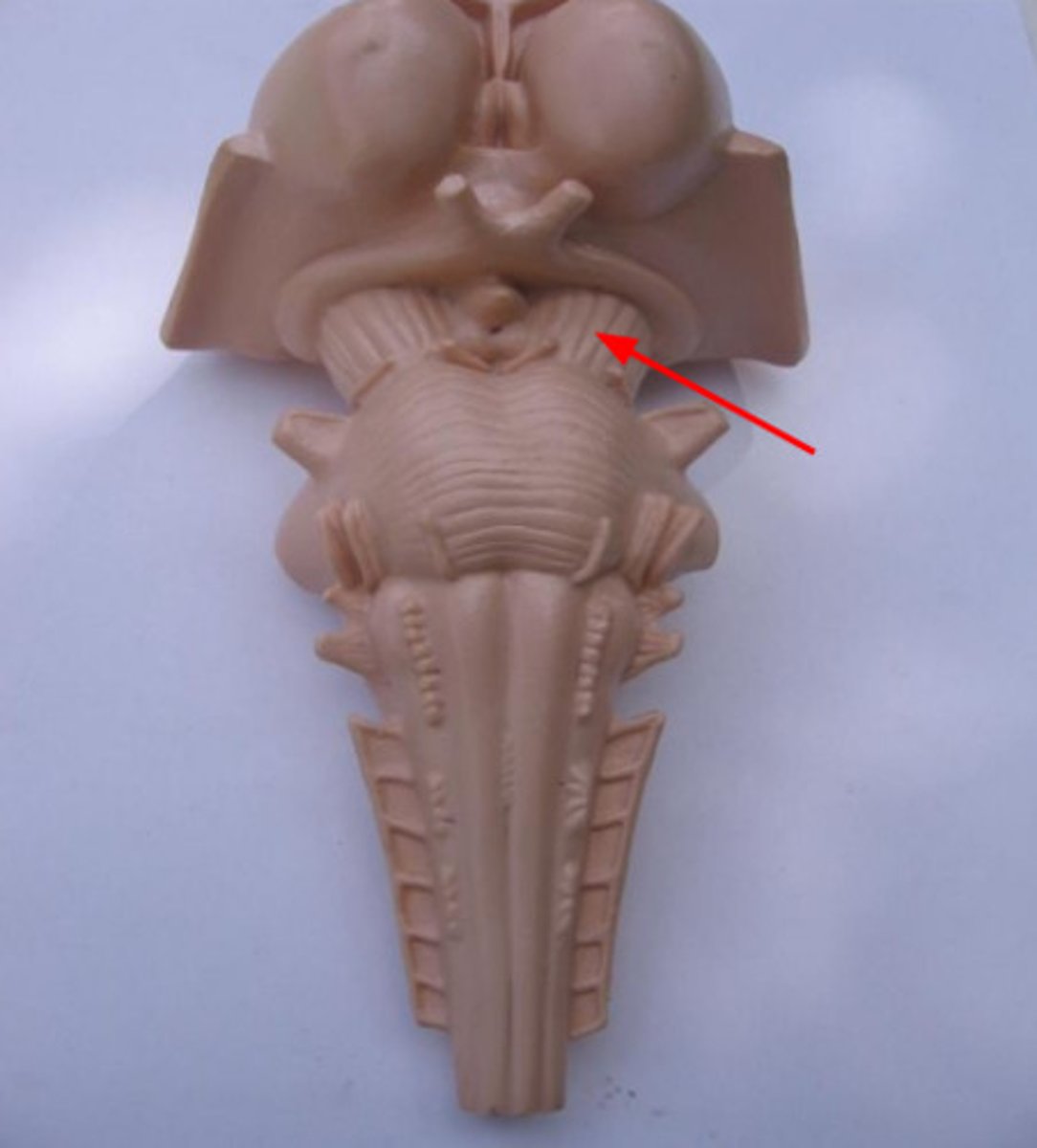
tectum
a part of the midbrain that orients an organism in the environment
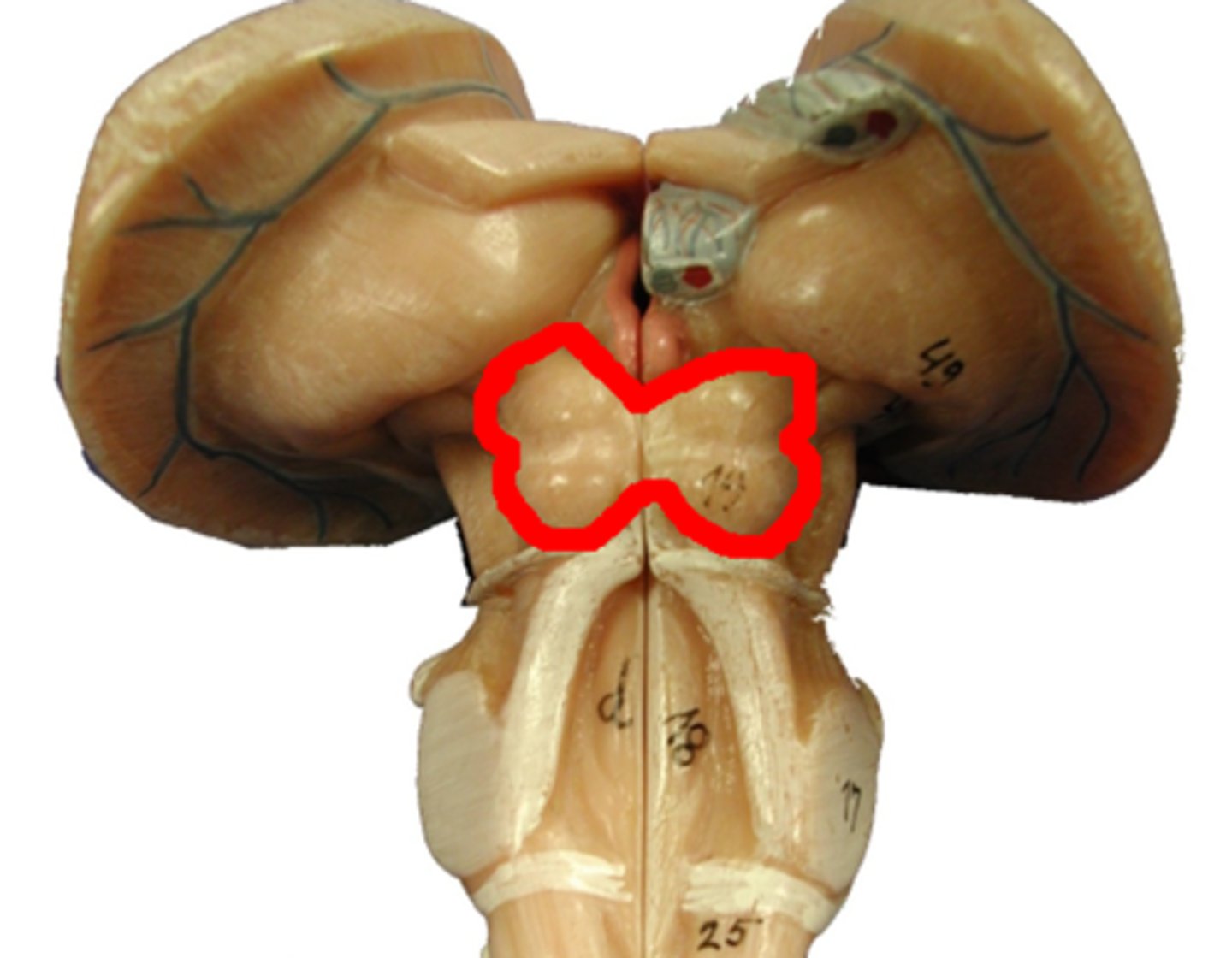
superior and inferior colliculi
Superior: Associated with visual reflexes
Inferior: Associated with Auditory reflexes
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
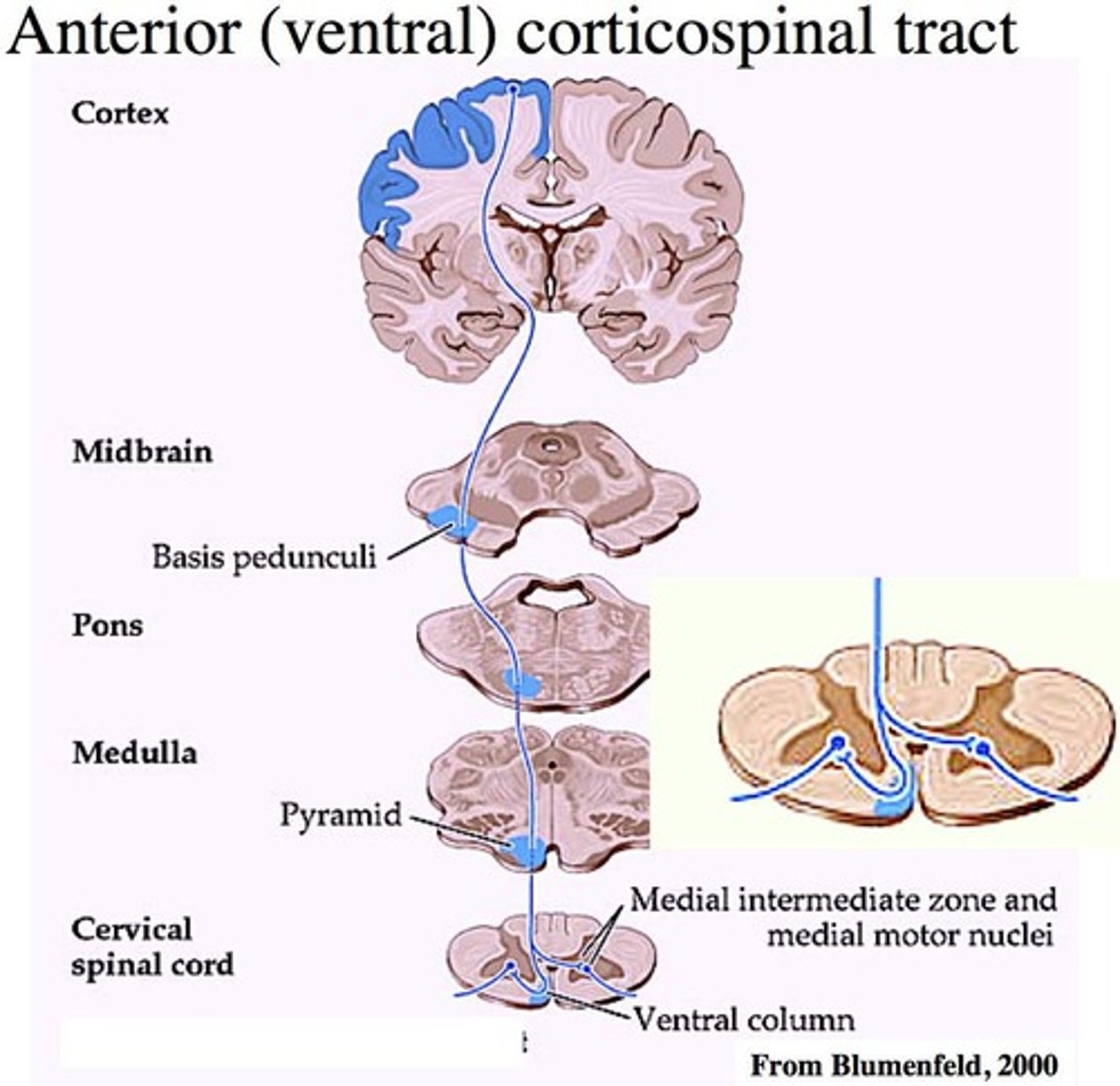
corticospinal tract
connections between brain and spine
corticopontine tract
goes to the pontine nuclei, which in turn project to the cerebellum
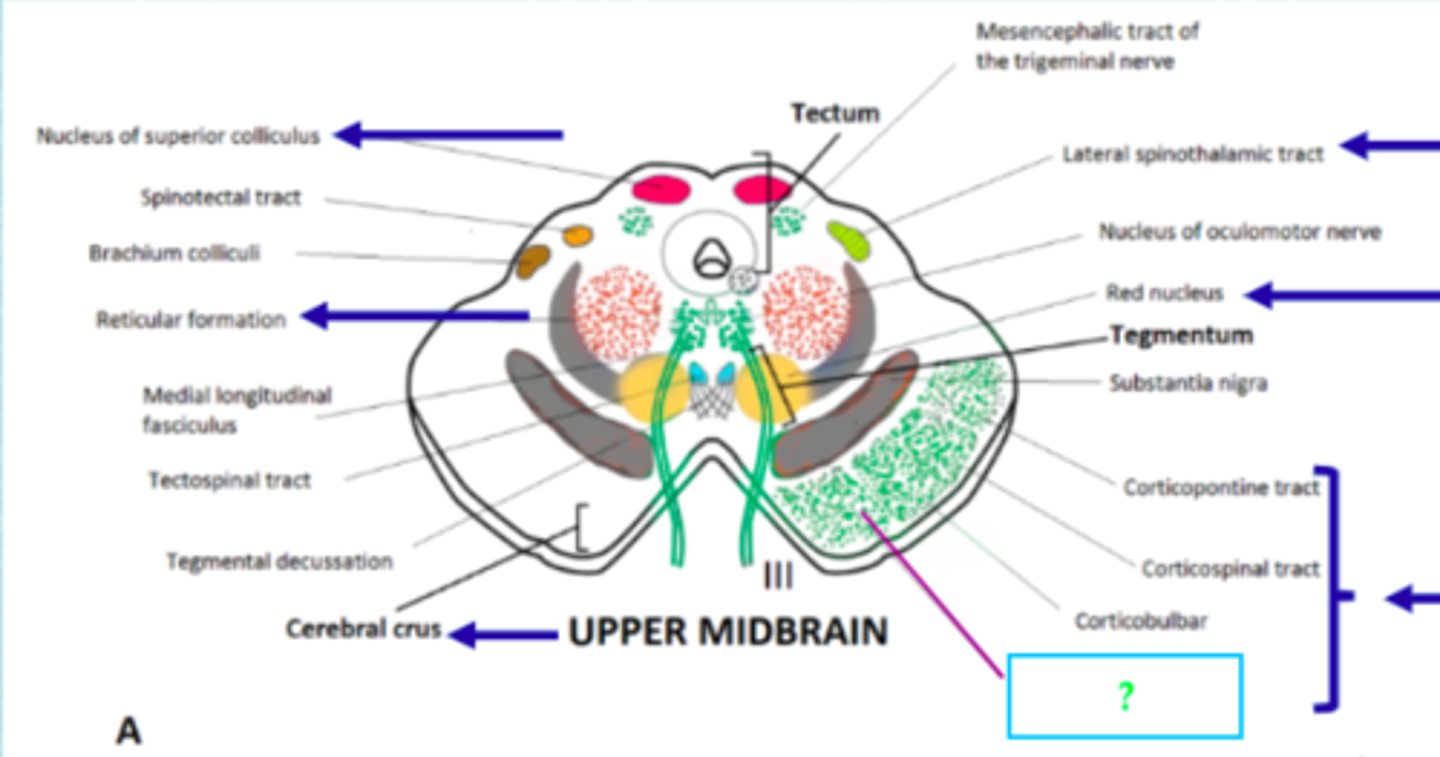
corticobrainstem tract
Arises from primary motor cortex in frontal lobe. passes through internal capsule. for voluntary control of muscles for speech production. it is an UMN. Synapses in LMN in cranial nerve nucleus in brainstem e.g., medulla for hypoglossal nerve. LMN then innervates muscles for speech: face, tongue, pharynx, larynx
pons
-processes motor information from cerebral cortex and relays it to the cerebellum
-sensation from face (5), facial expression (7), eye movement (6), chewing (7), audition & vestibular (8)
main sensory nucleus of trigeminal
Functional Category-General Somatic Sensory
Function-Receives touch & pressure via CN 5-- Similar to NG & NC
motor nucleus of trigeminal
this nucleus contains motor neurons that innervate the muscles of mastication
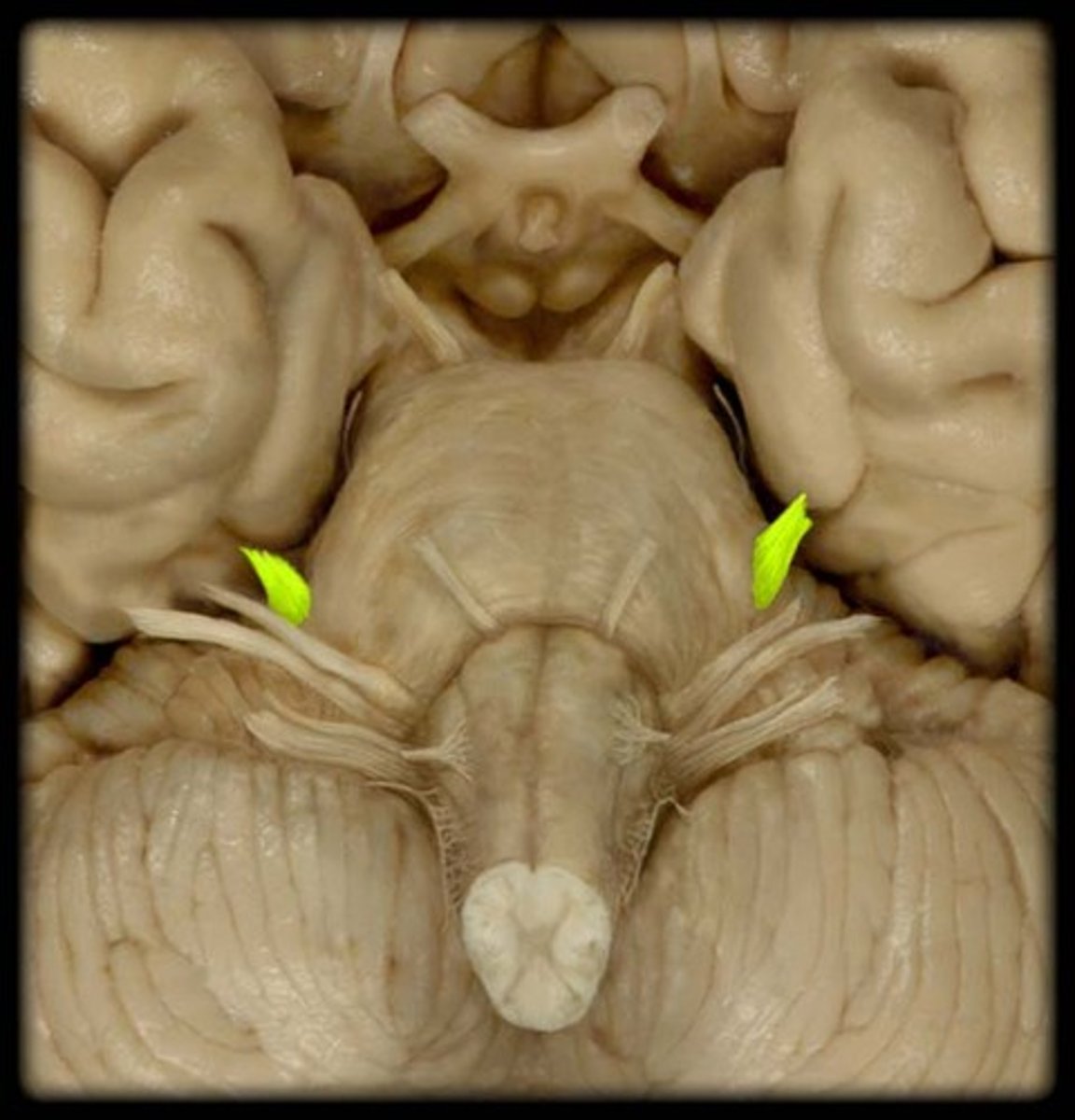
trigeminal nerve
spinothalamic tract
nerve pathway from the spine to the thalamus along which pain impulses are carried to the brain
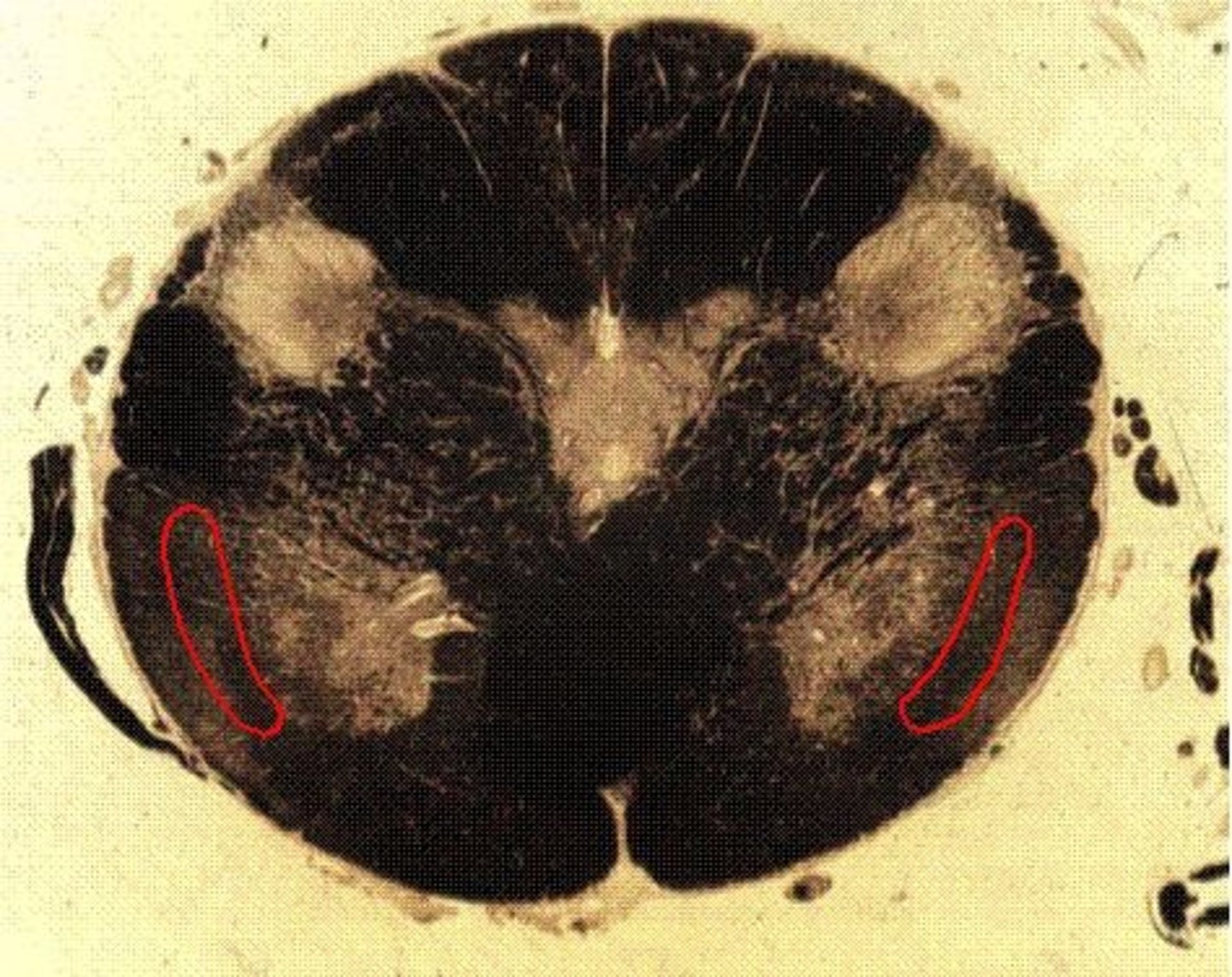
medulla
coordinate cardiovascular control (10), breathing (10), head movements (11) and swallowing (12)
spinothalamic tract in medulla
medial lemniscus
The somatosensory pathway between the dorsal column nuclei and the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus.
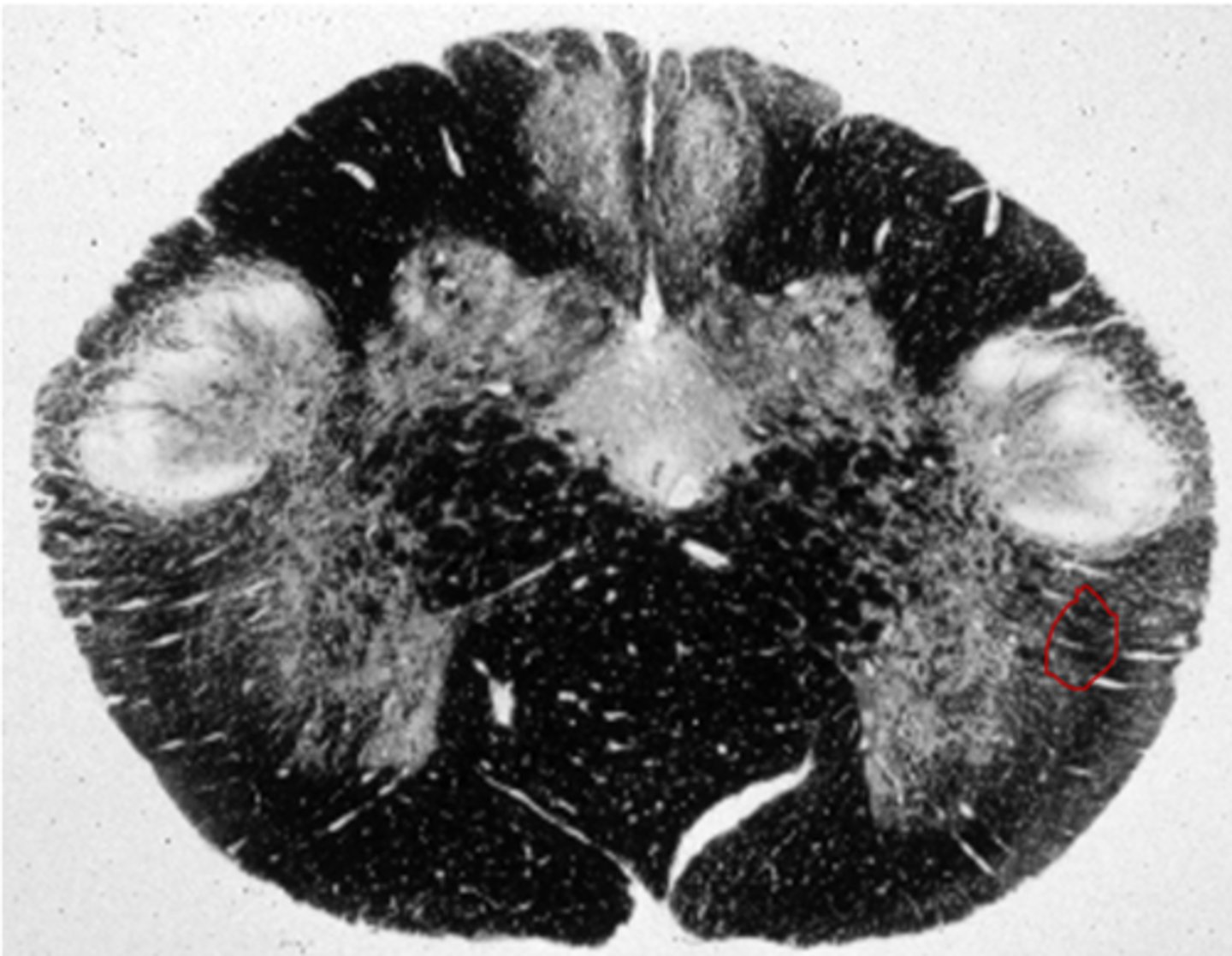
corticospinal tract in pyramid
-carries voluntary motor activity to the somatic muscles of the body
-C
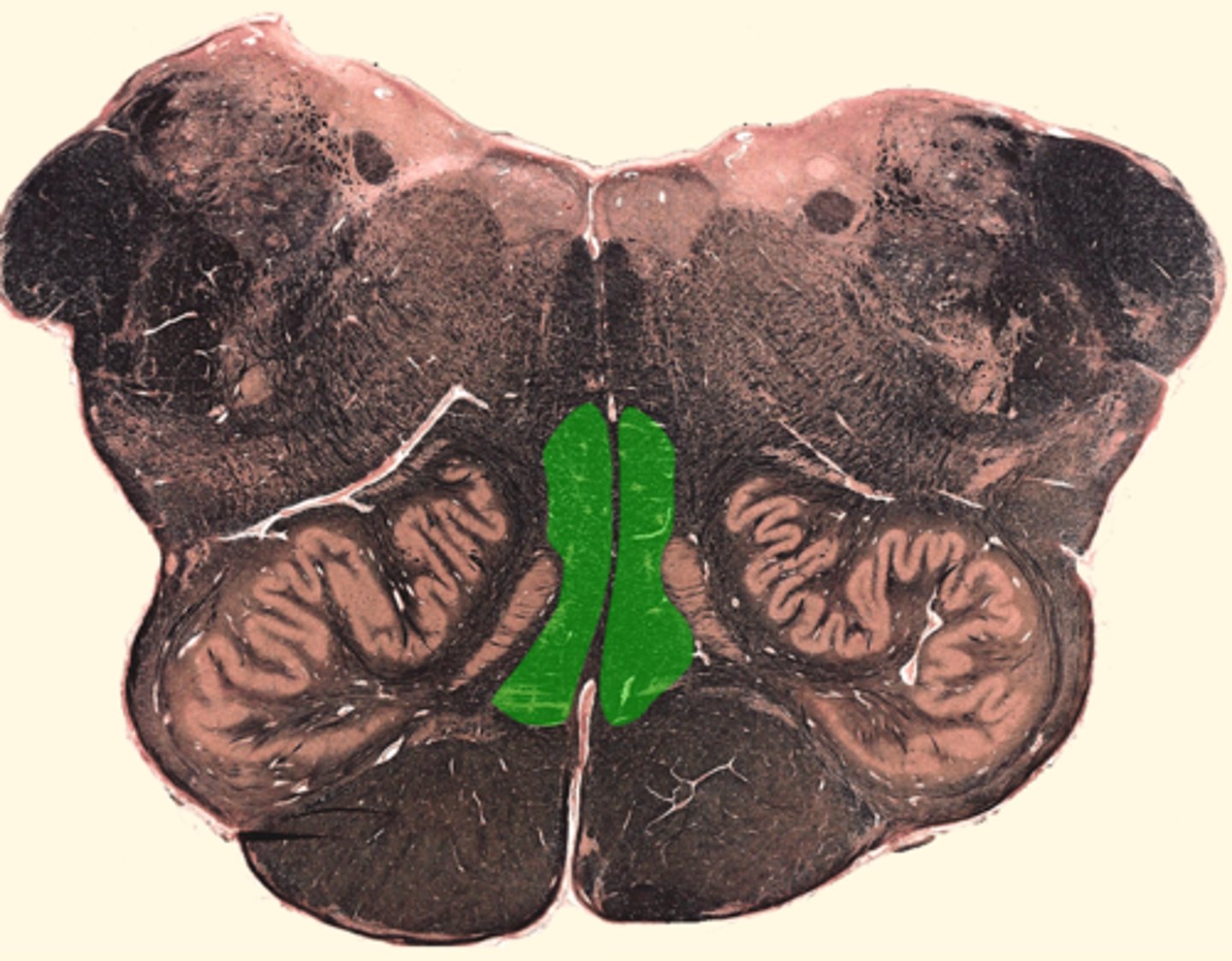
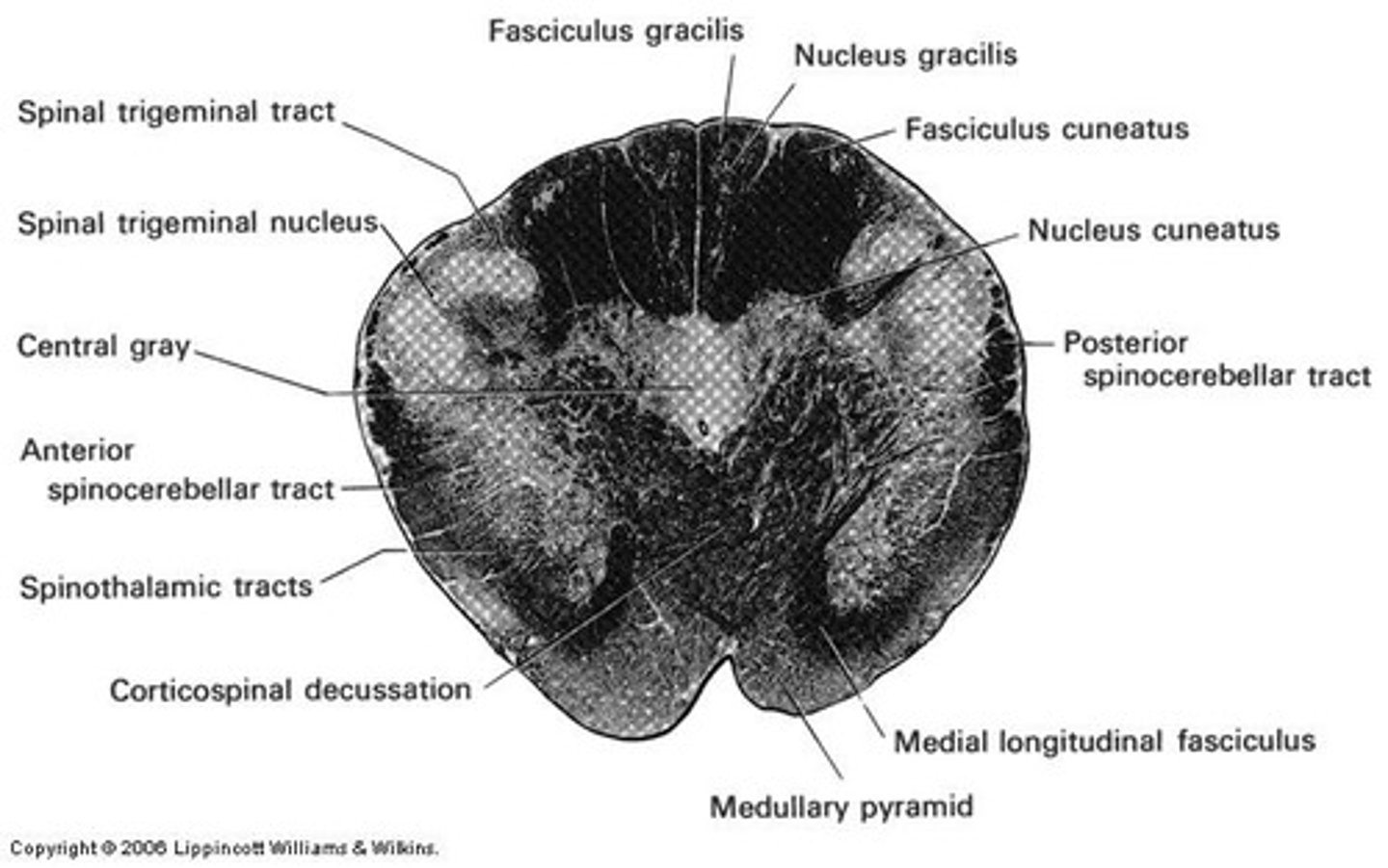
dorsal columns in medulla
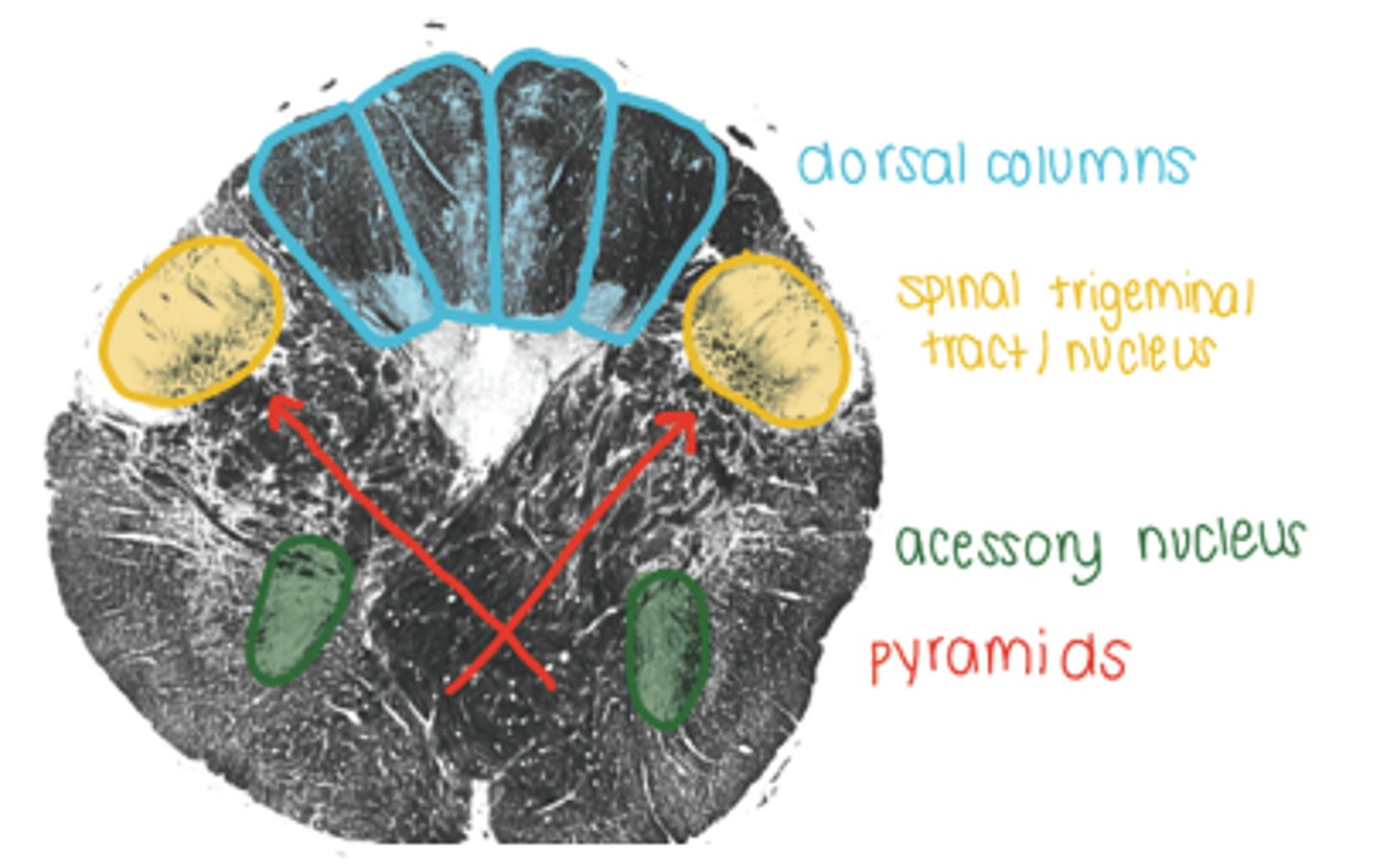
lateral column in medulla
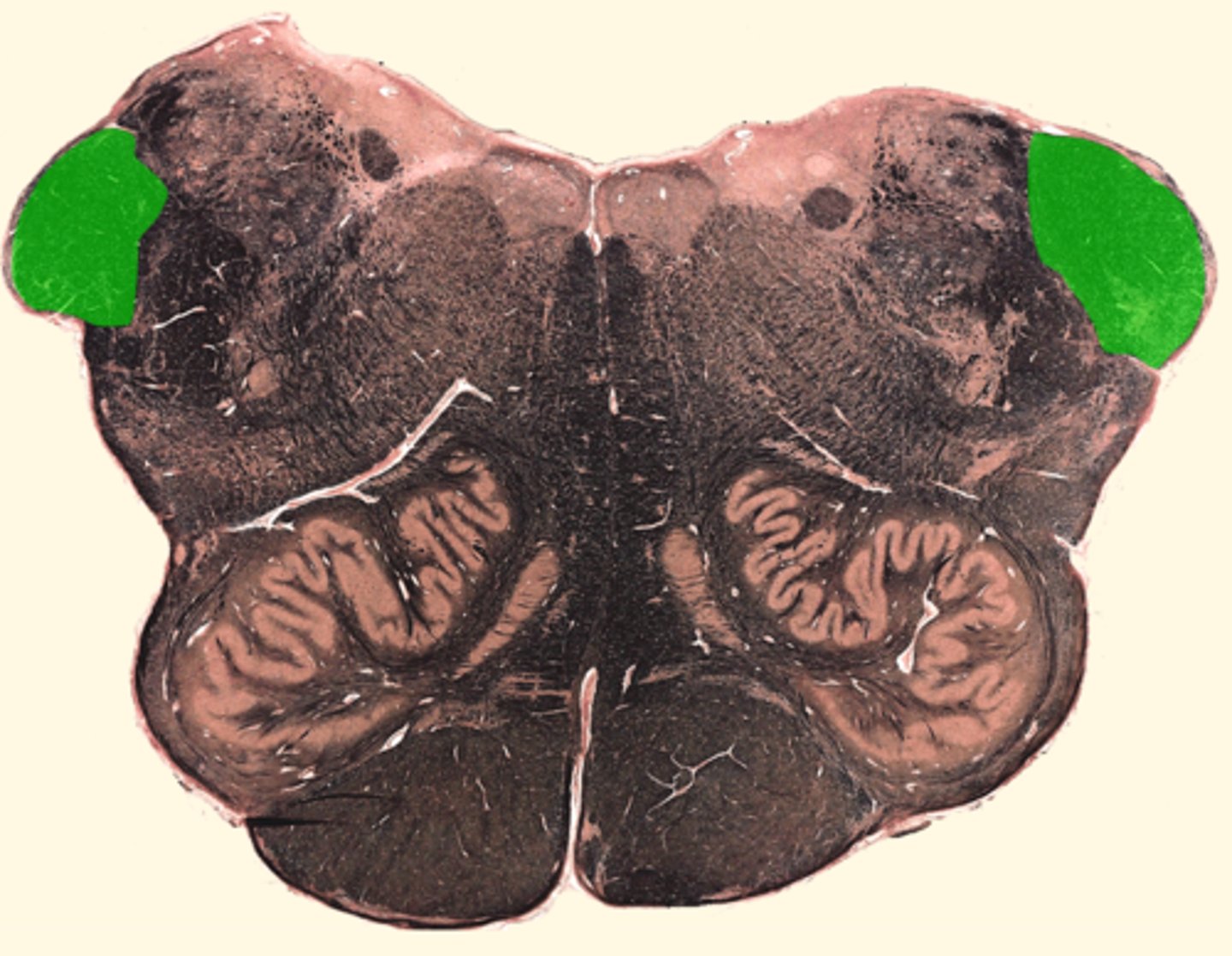
inferior cerebellar peduncle
connects the cerebellum to the medulla oblongata
9-12
What cranial nerves exit from the medulla?
5-8
What cranial nerves exit from the midbrain
4th ventricle
true
t/f spinal cord gray matter contains cell bodies and white matter contains axons
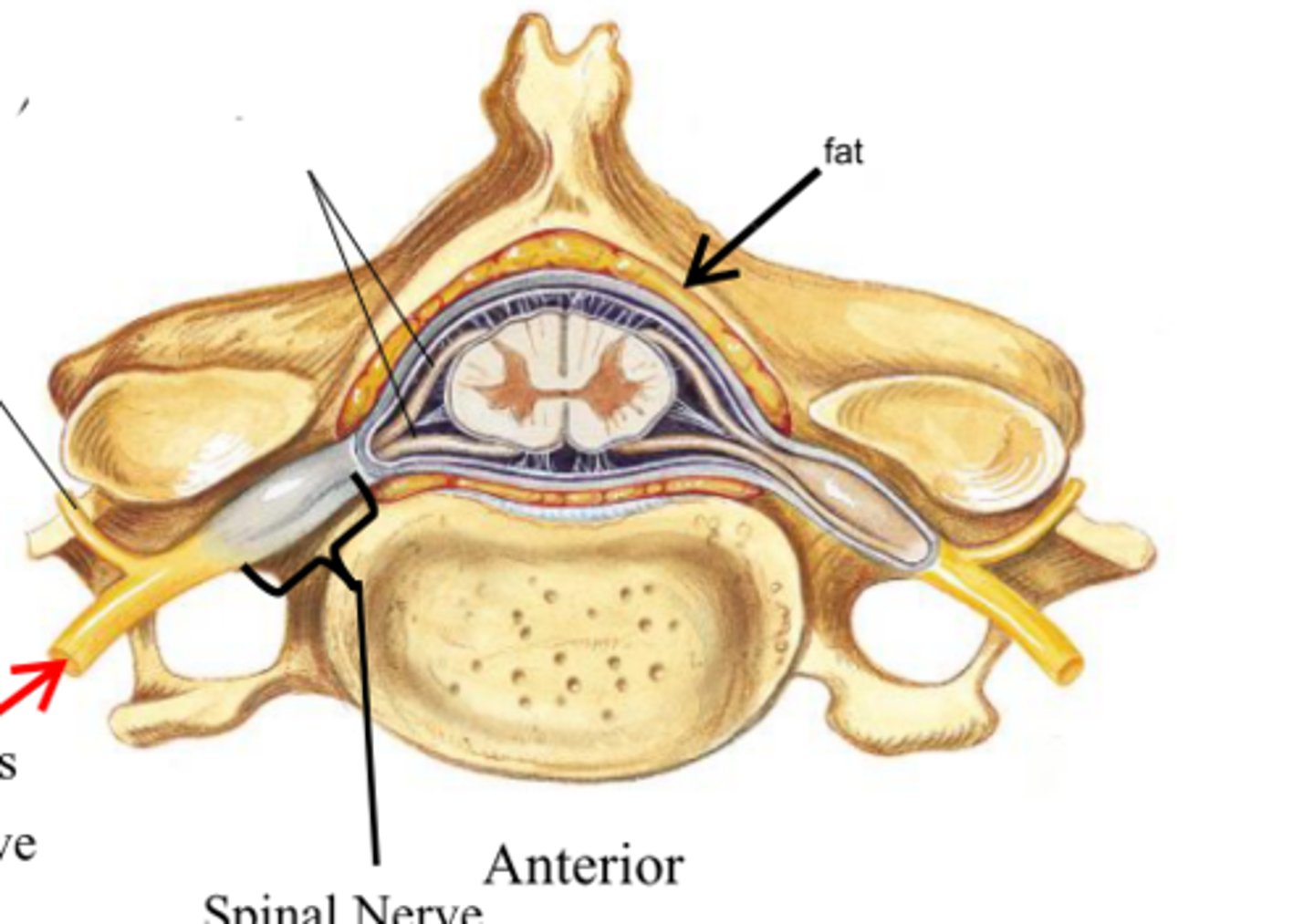
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
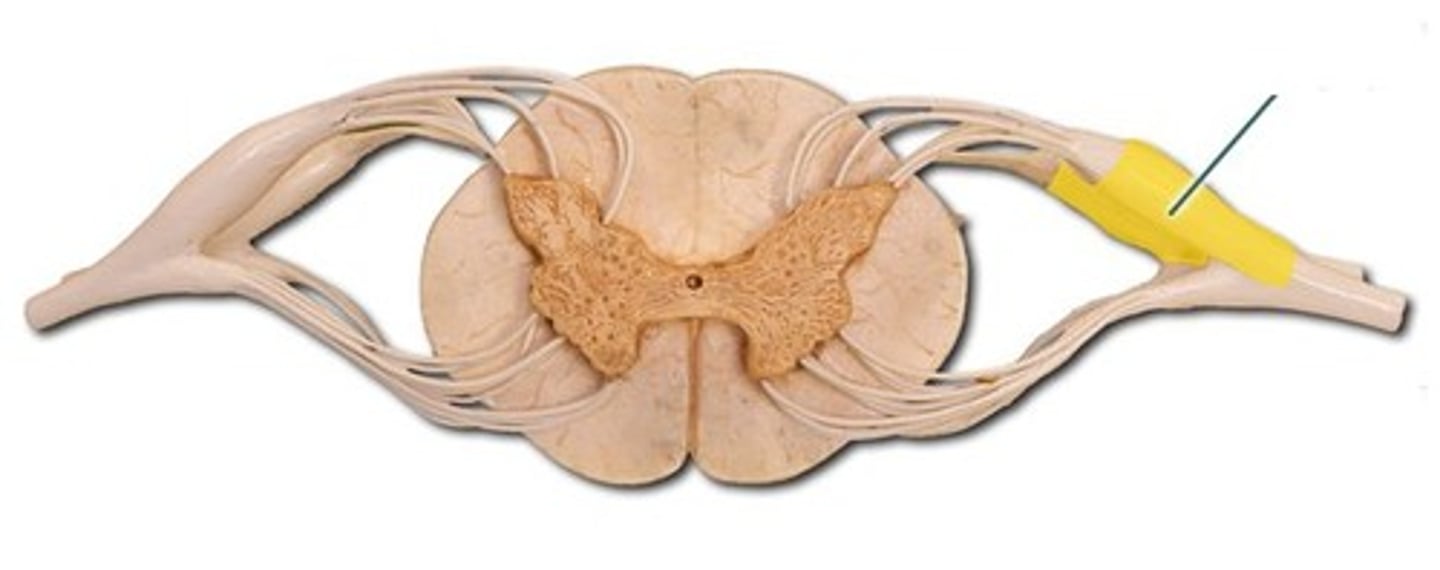
dorsal root
the sensory branch of each spinal nerve
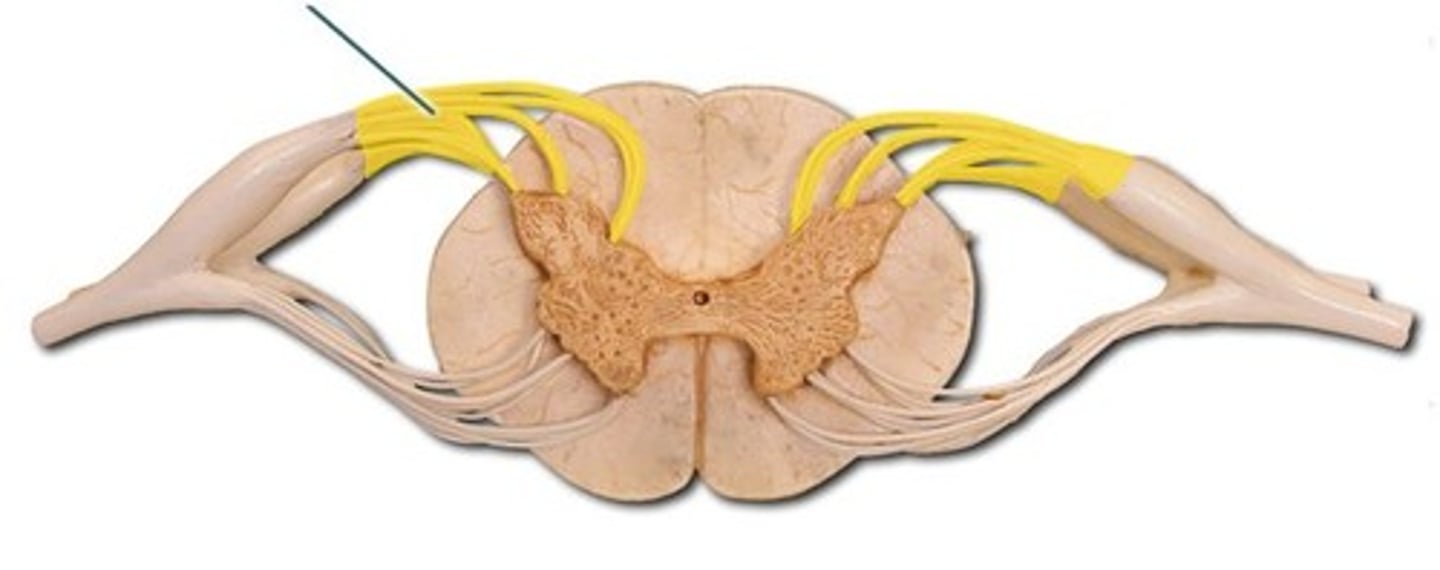
vertebral lamina
expanded transverse process on the sixth cervical vertebra
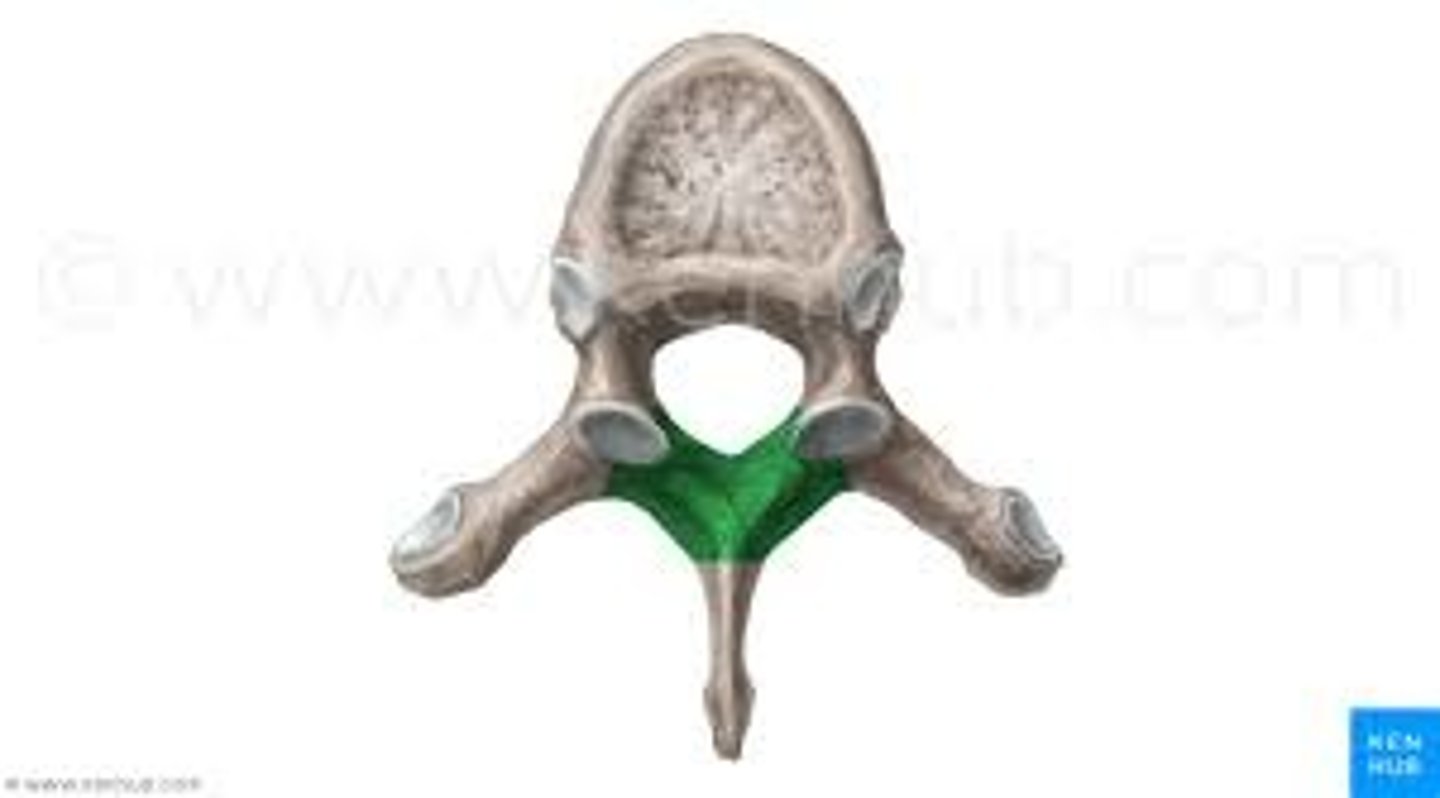
dorsal ramus
the division of posterior spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior trunk muscles and relay sensory impulses from the skin of the back
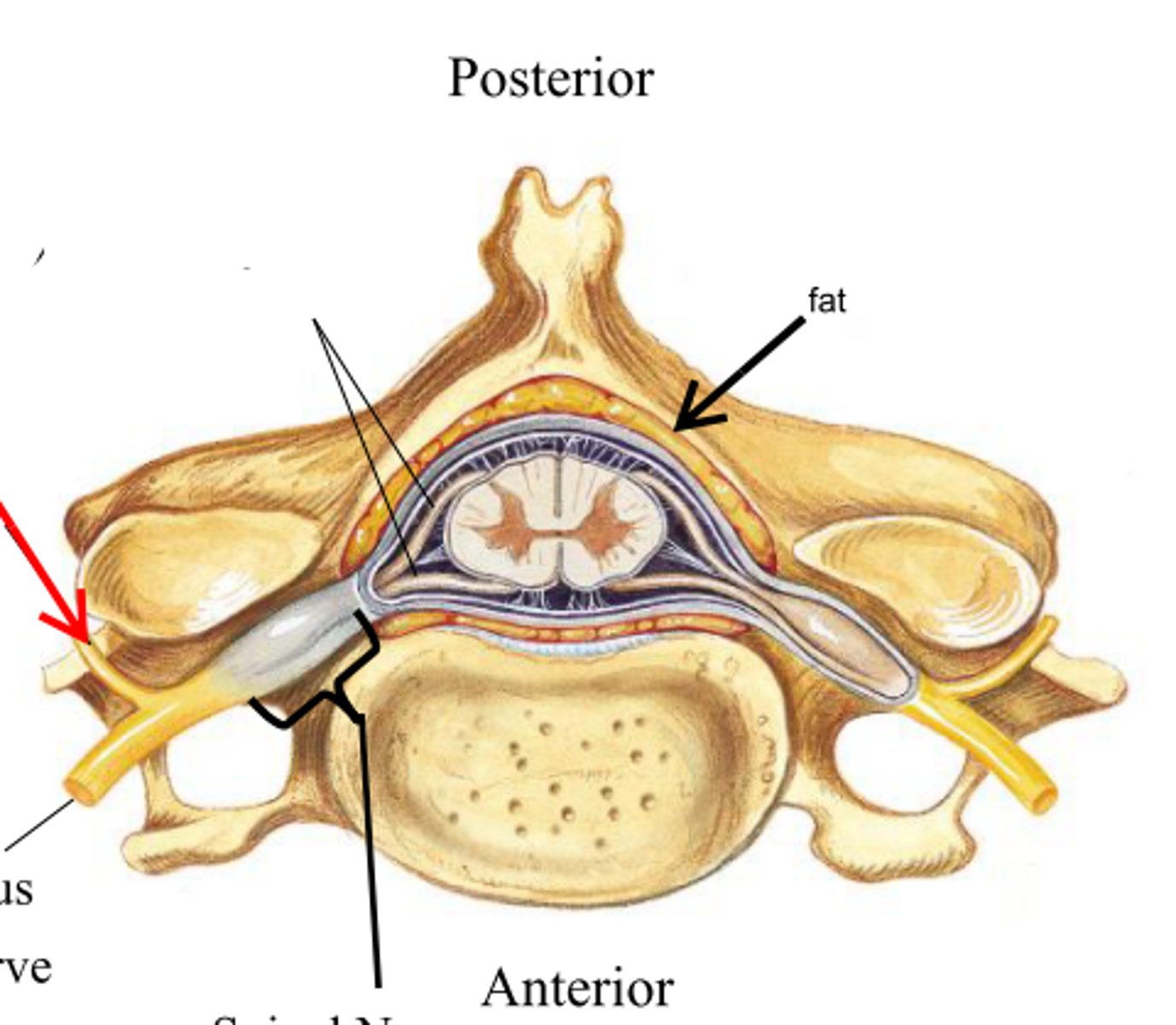
ventral ramus
the anterior division of spinal nerves that communicate with the muscle and skin of the anterior and lateral trunk
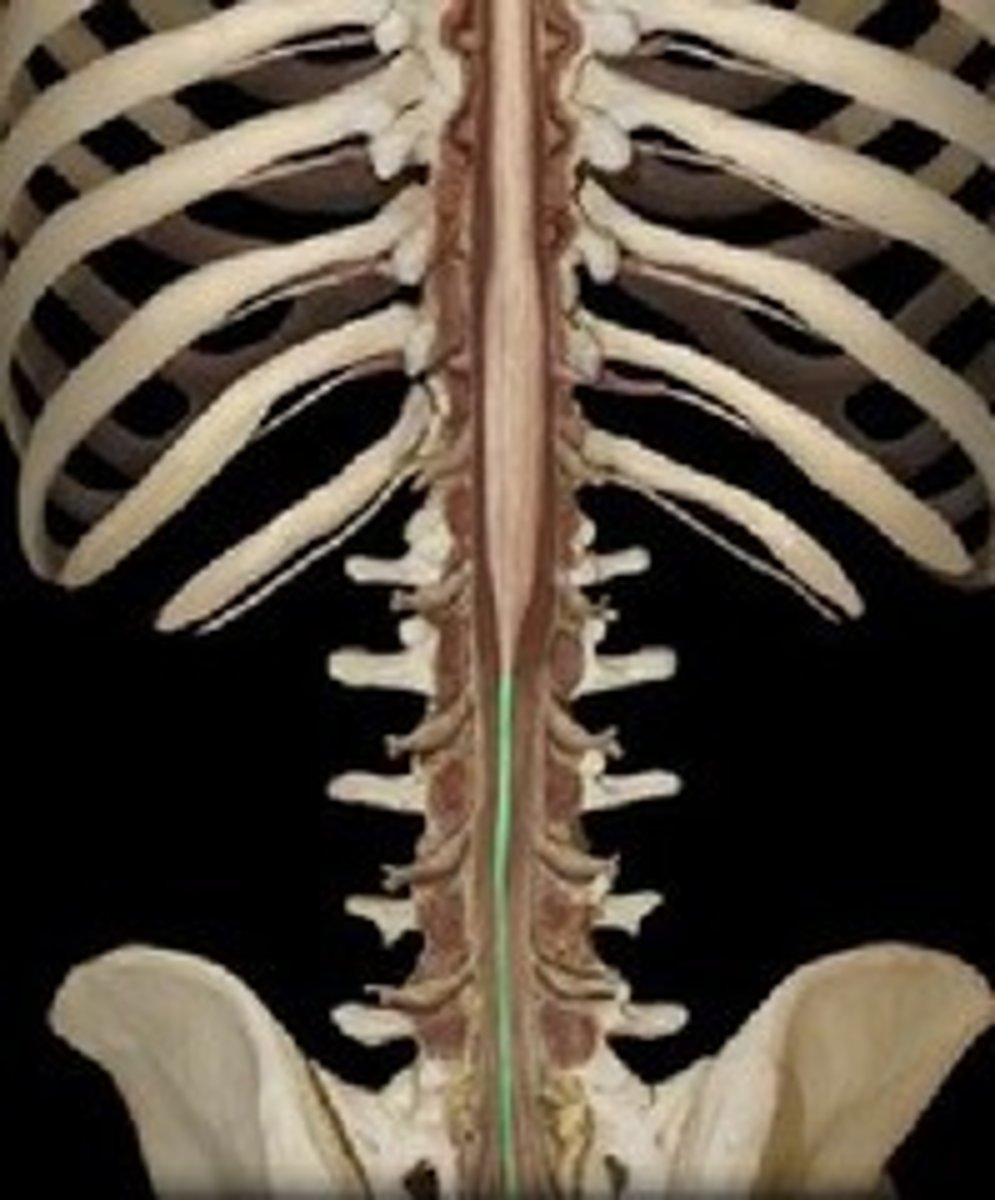
spinal cord
-enlargements in cervical and lumbar regions
-cauda equina made up of lumbar and sacral roots that extend caudal
L1-L2
Where does the spinal cord terminate at?
filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
intervertebral foramen
How do spinal nerves exit?
superior to vertebrae except C8
Where do the nerves exit in the cervical region?
inferior to vertebrae
Where do the nerves exit in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions region?
cervical spinal cord
-more white matter
-overall large size
-large ventral horns
-dorsal column separation
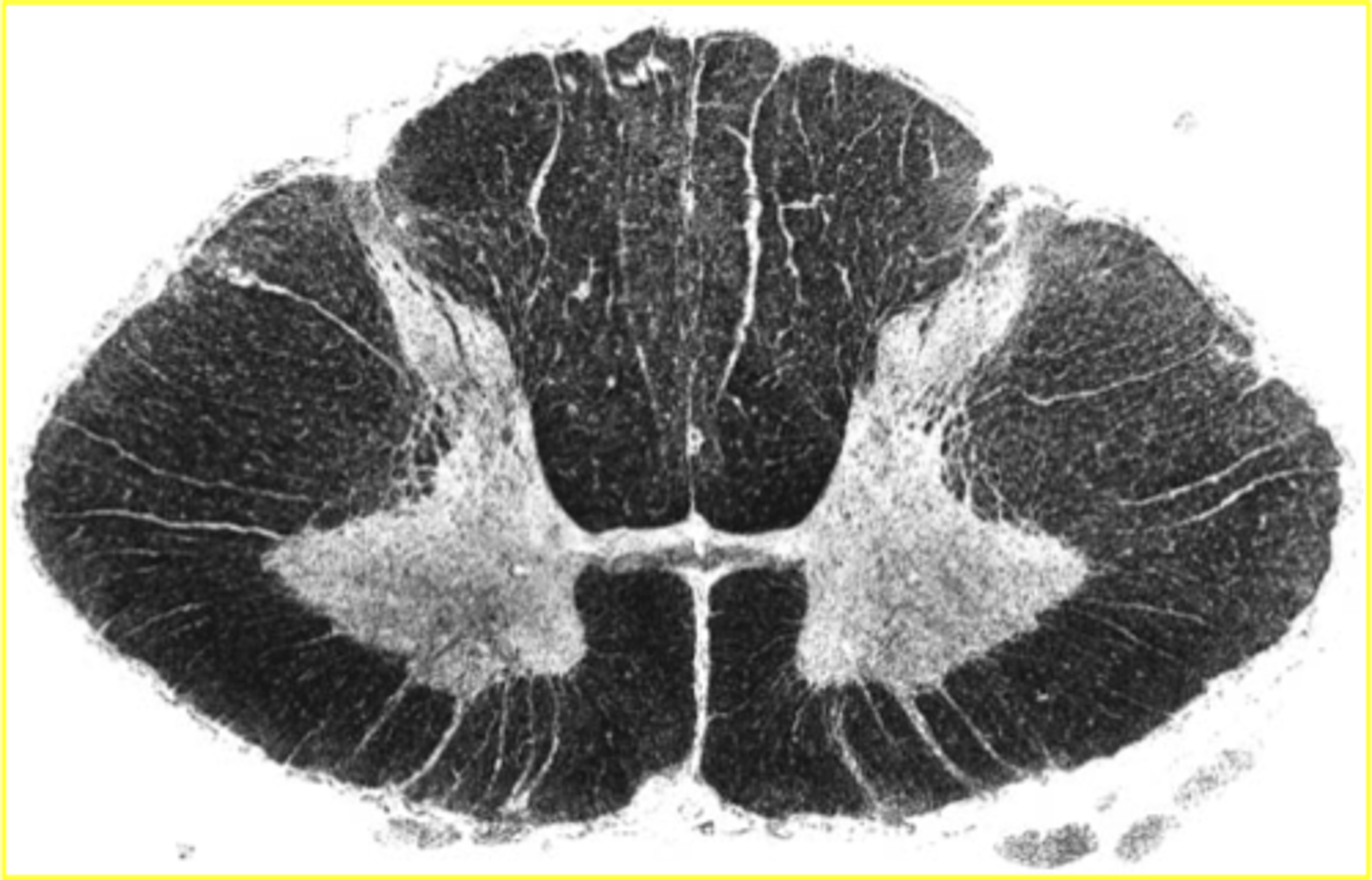
thoracic spinal cord
-most white matter (compared to gray matter)
-small ventral horns
-prominent lateral horn
-dorsal column separation
-less motor control here
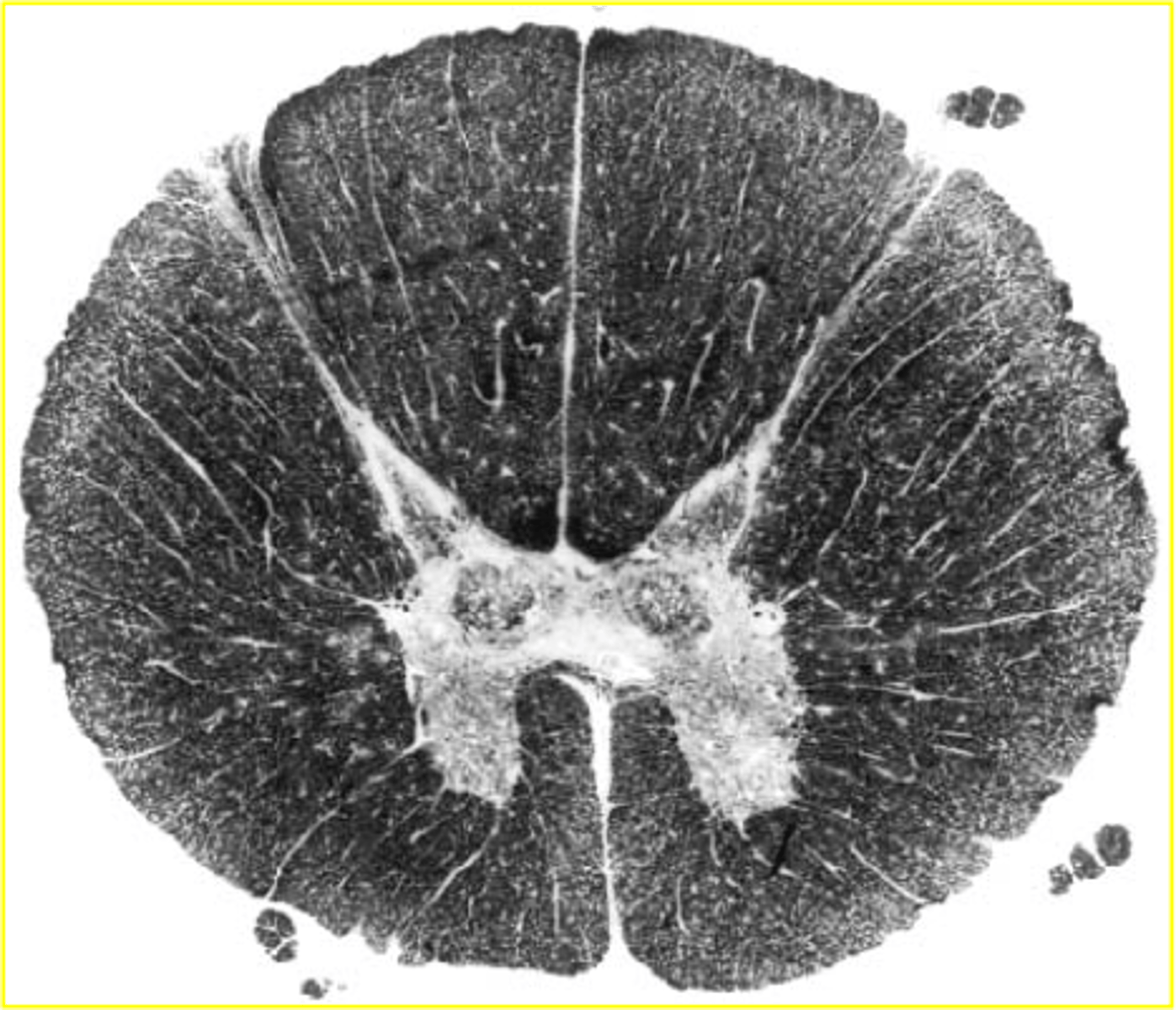
lumbar spinal cord
-WM=GM
-More round shape
-large ventral horns
-no dorsal column separation (fasciculus gracilis only)
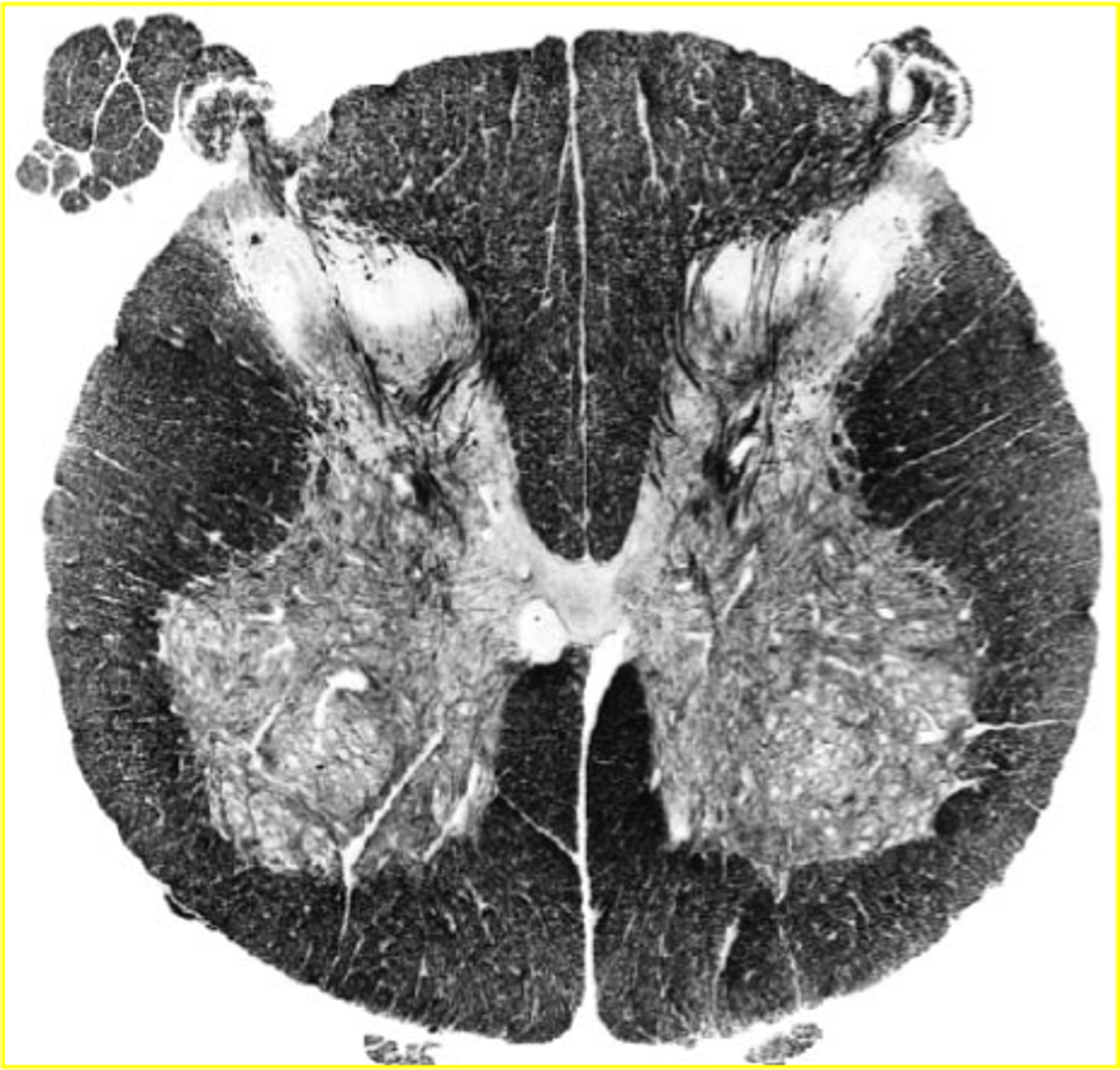
sacral spinal cord
-WM
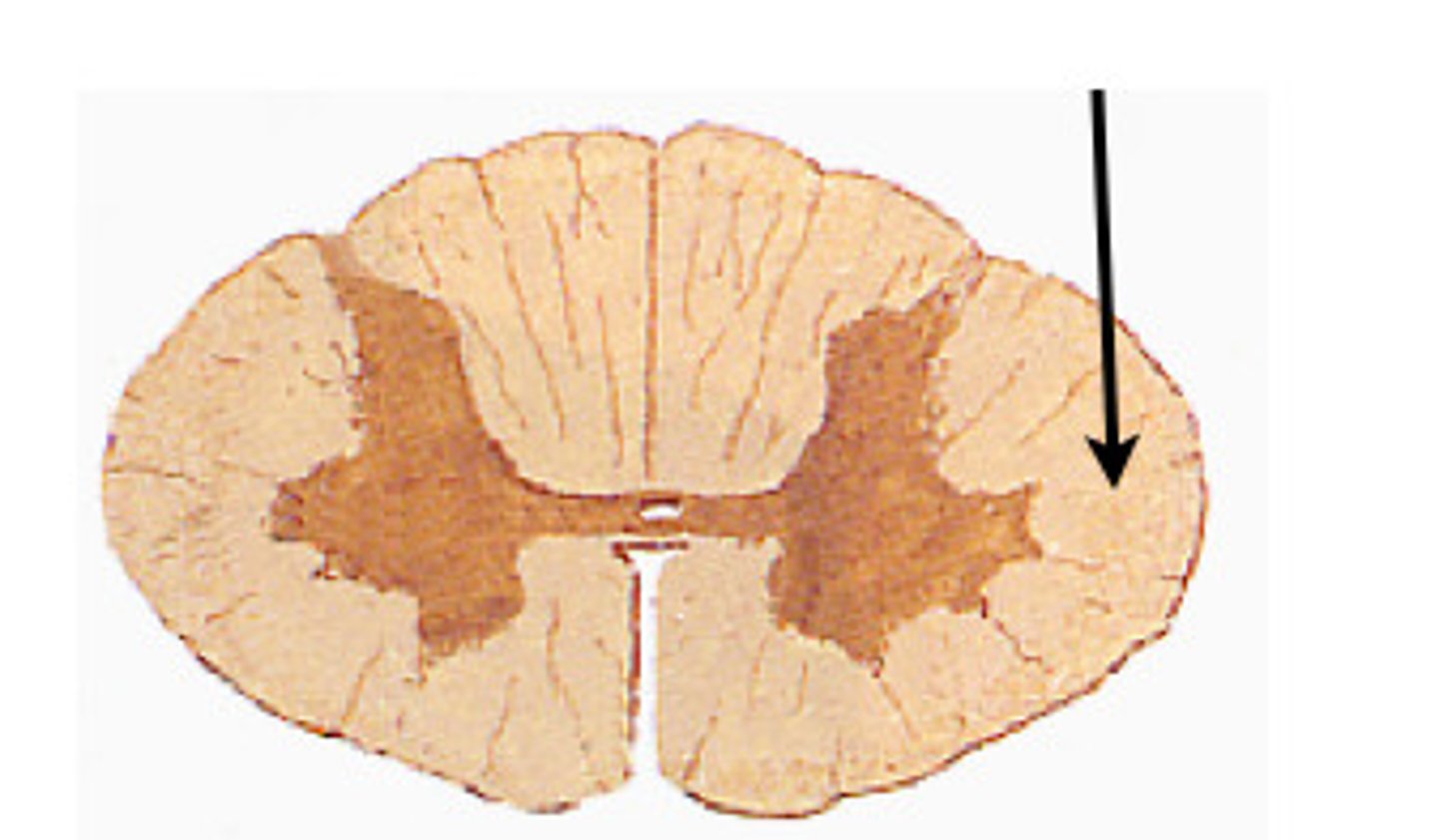
funiculi
columns of white matter
dorsal column medial lemniscus system
The division of the somatosensory system that ascends in the dorsal portion of the spinal white matter and carries signals related to touch and proprioception
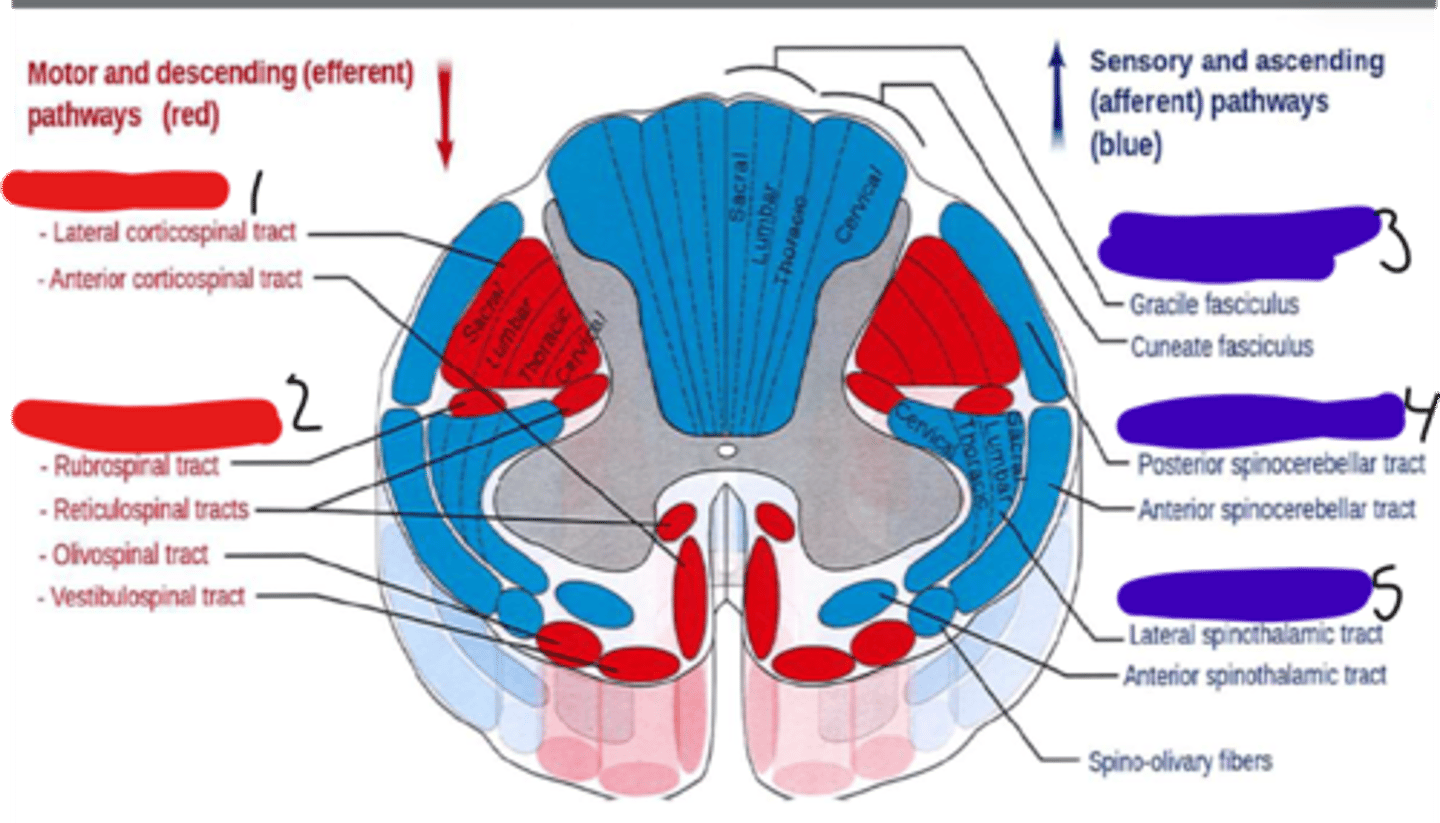
spinocerebellar tracts
carry information about muscle or tendon stretch to the cerebellum; postural; unconscious
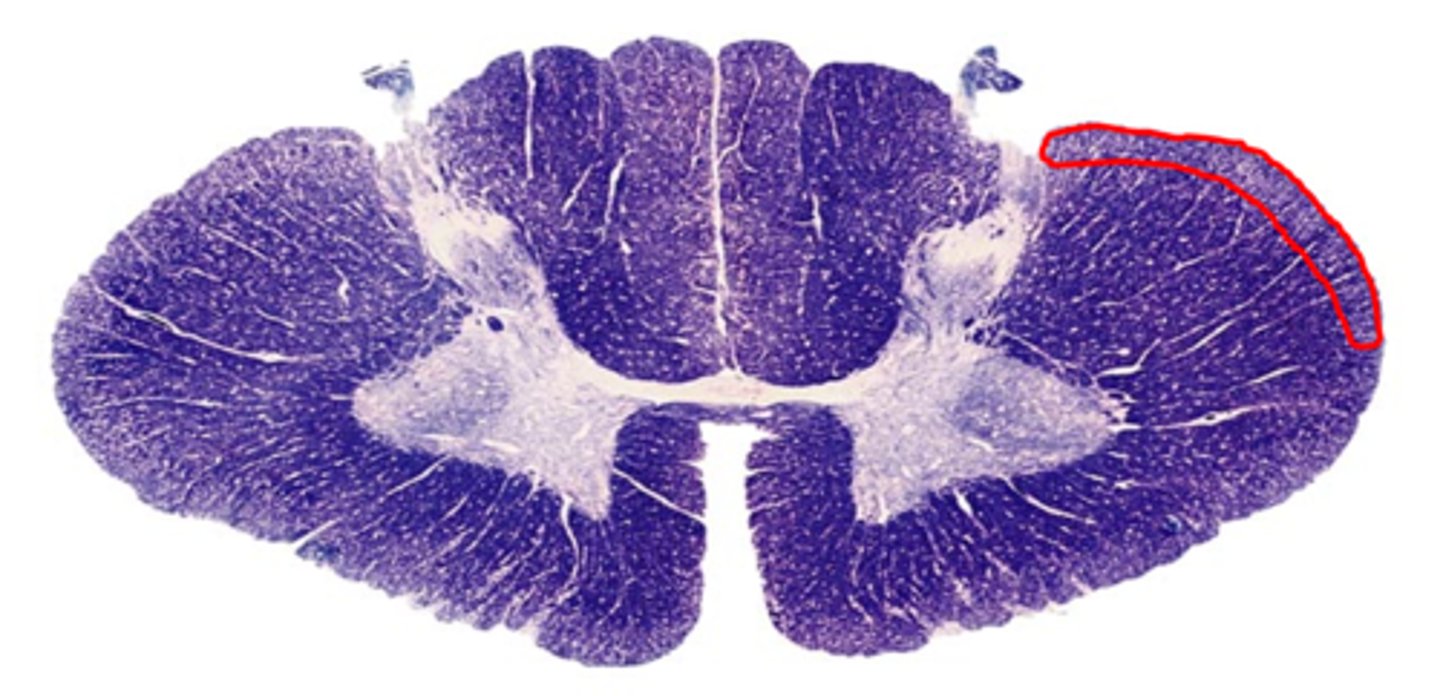
anterolateral system
a somatosensory system that carries most of the pain information from the body to the brain
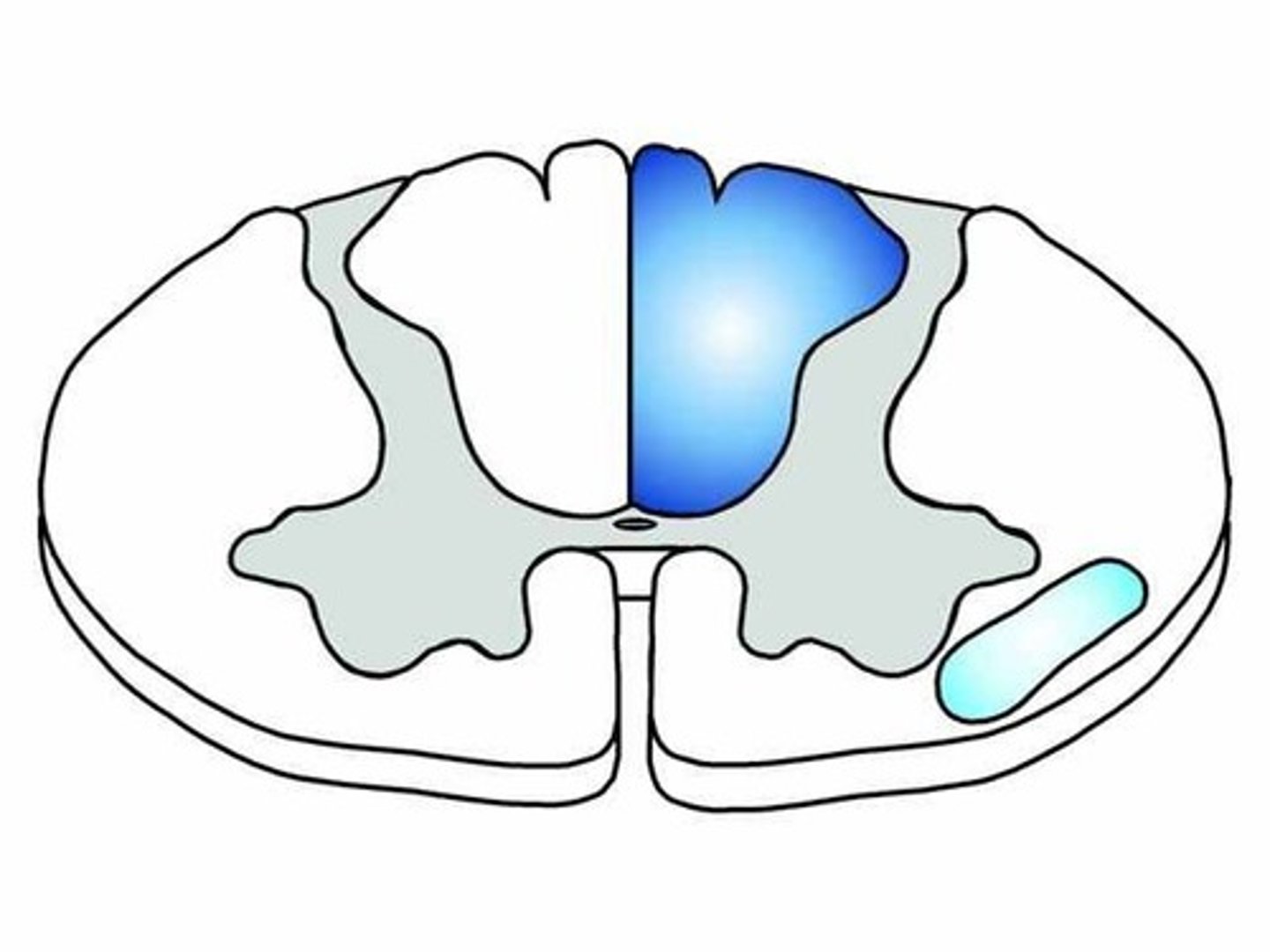
fasciculus gracilis
lower limb and trunk
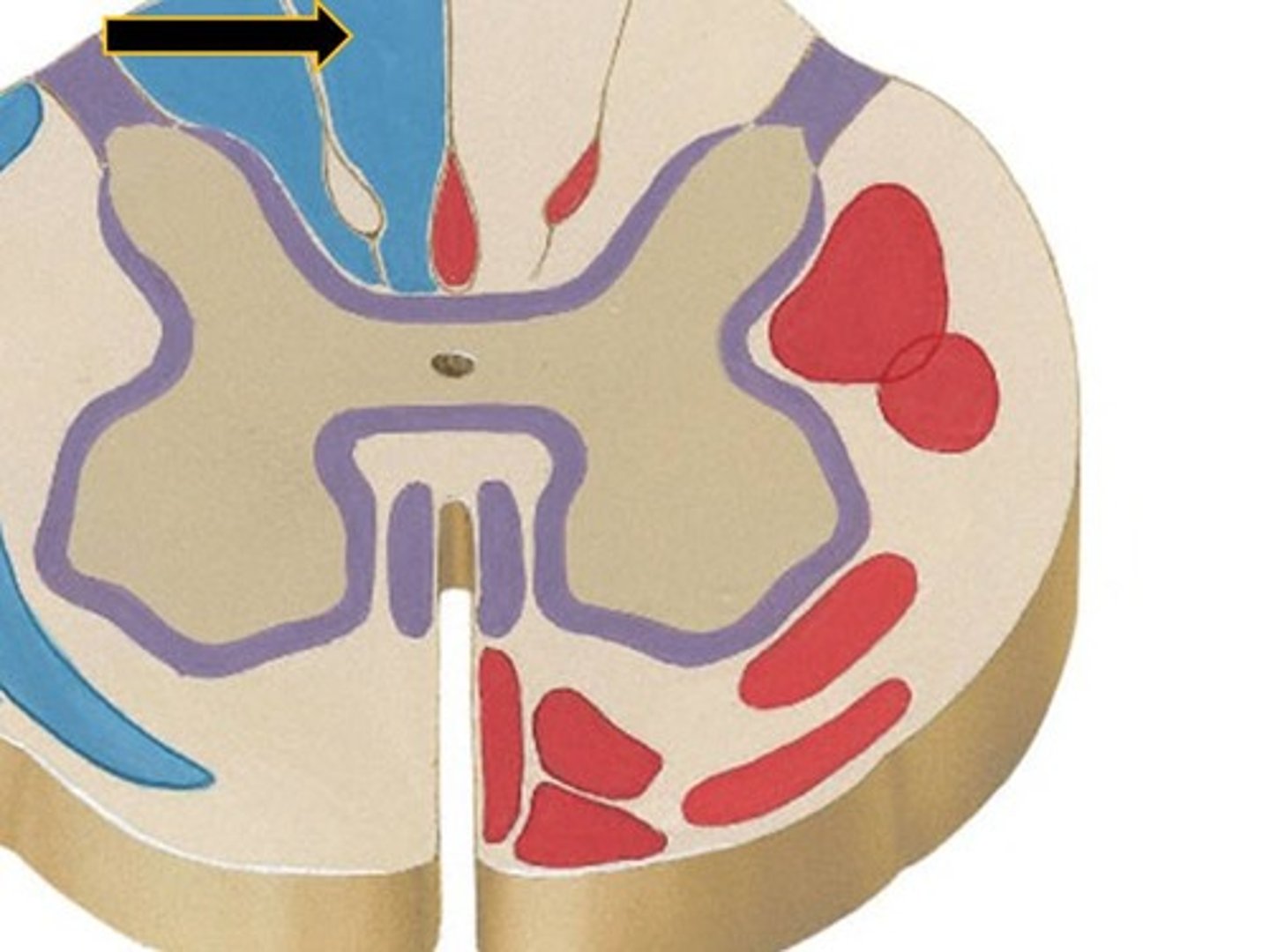
facsiculus cuneatus
upper limb, upper trunk, and neck
dorsal root ganglion
First order neuron cell body for the medial lemniscus pathway
nucleus cuteatus or gracilis
Second order neuron cell body for the medial lemniscus pathway
VPL nucleus of thalamus
Third order neuron cell body for the medial lemniscus pathway
anterolateral columns
-nociception and temperature
-can enter at any level
-primary location is at a specific level
-synapses in dorsal horn, crosses and ascends in anterolateral, goes to thalamus and processes and realys, then goes to sensory cortex
medial motor tracts
synapse with motor neurons that innervate postural and girdle muscles
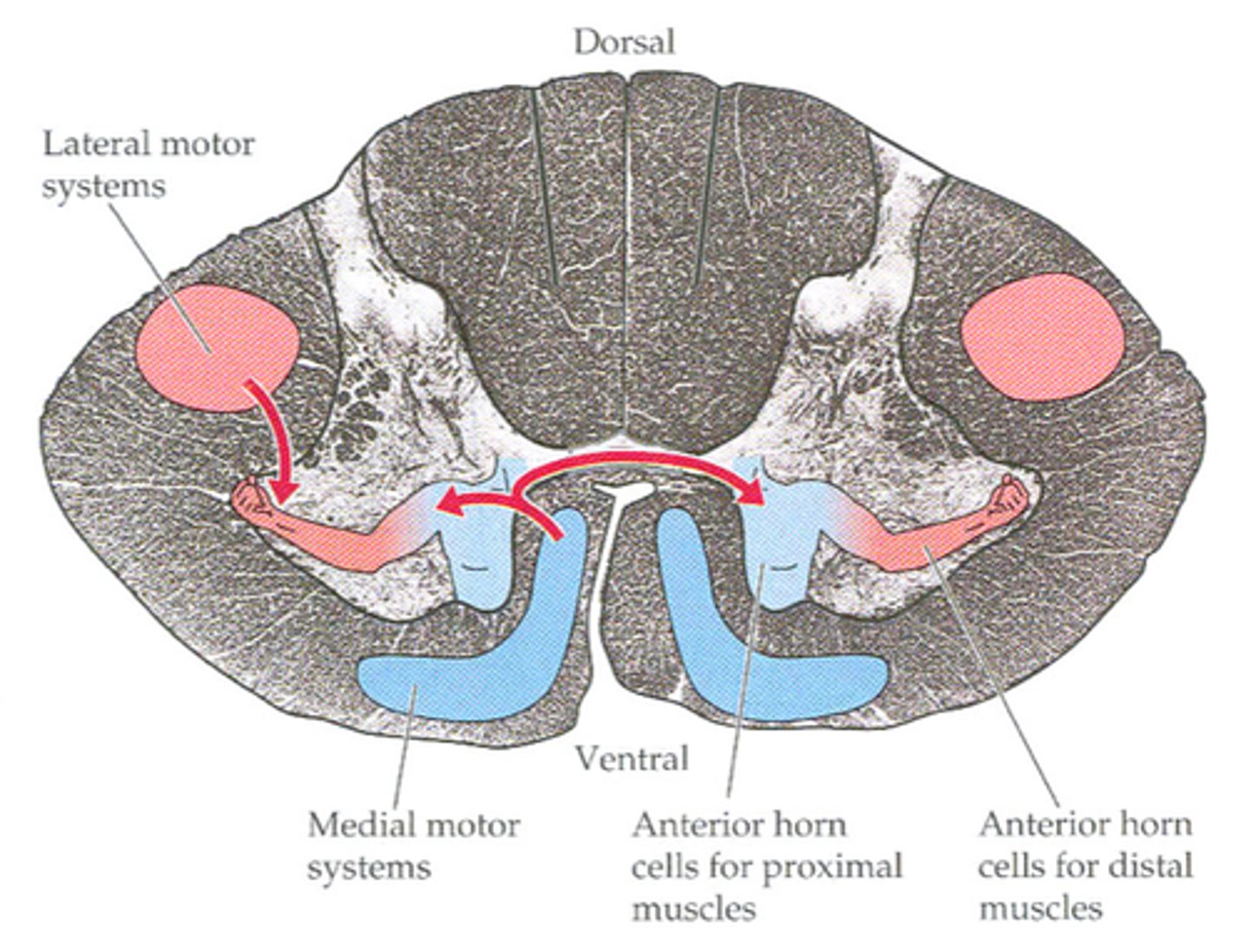
reticulospinal tract
-a tract of axons arising from the brainstem reticular formation and descending to the spinal cord to modulate movement
-bilateral postural control and gross limb movement
-whole brainstem
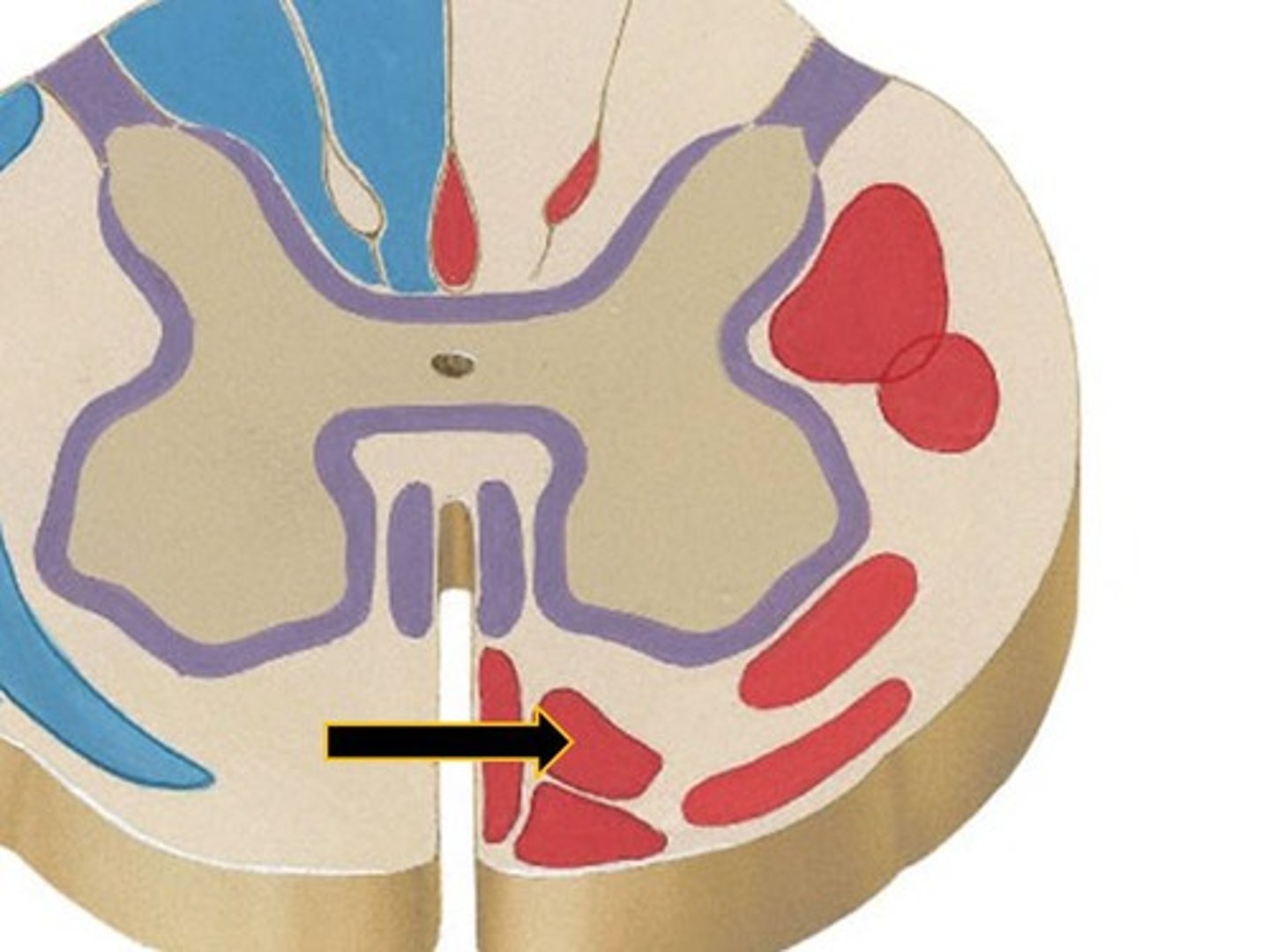
vestibulospinal tract (Medial)
• arises in the medial vestibular nucleus
• terminates on LMN circuit neurons of cervical and upper thoracic
levels
o controlling the neck muscles (tandem with corticobulbar
tract)
o stabilizing the head
o coordinating head movements with eye movements
vestibulospinal tract (lateral)
• arises in the lateral vestibular nucleus
• Stimulate extensor muscles
• Inhibits flexor
• serves to mediate postural adjustments
-ipsilateral postural muscles in trunk and limbs
medial corticospinal tract
-set of axons from many parts of the cerebral cortex, midbrain, and medulla; responsible for control of bilateral muscles of the neck, shoulders, and trunk
-bilateral postural control of muscles for anticipatory control of intended movements
lateral corticospinal tract
-a set of axons from the primary motor cortex, surrounding areas, and midbrain area that is primarily responsible for controlling the peripheral muscles
-controls contralateral muscles
-innervates motor neurons (excitation) in ventral horn and interneurons (inhibition)
rubrospinal tract
-Extrapyramidal motor tract responsible for motor input of gross postural tone, facilitating activity of flexor muscles, and inhibiting the activity of extensor muscles
-controls contralateral muscles
-innervates wrist and finger extensors
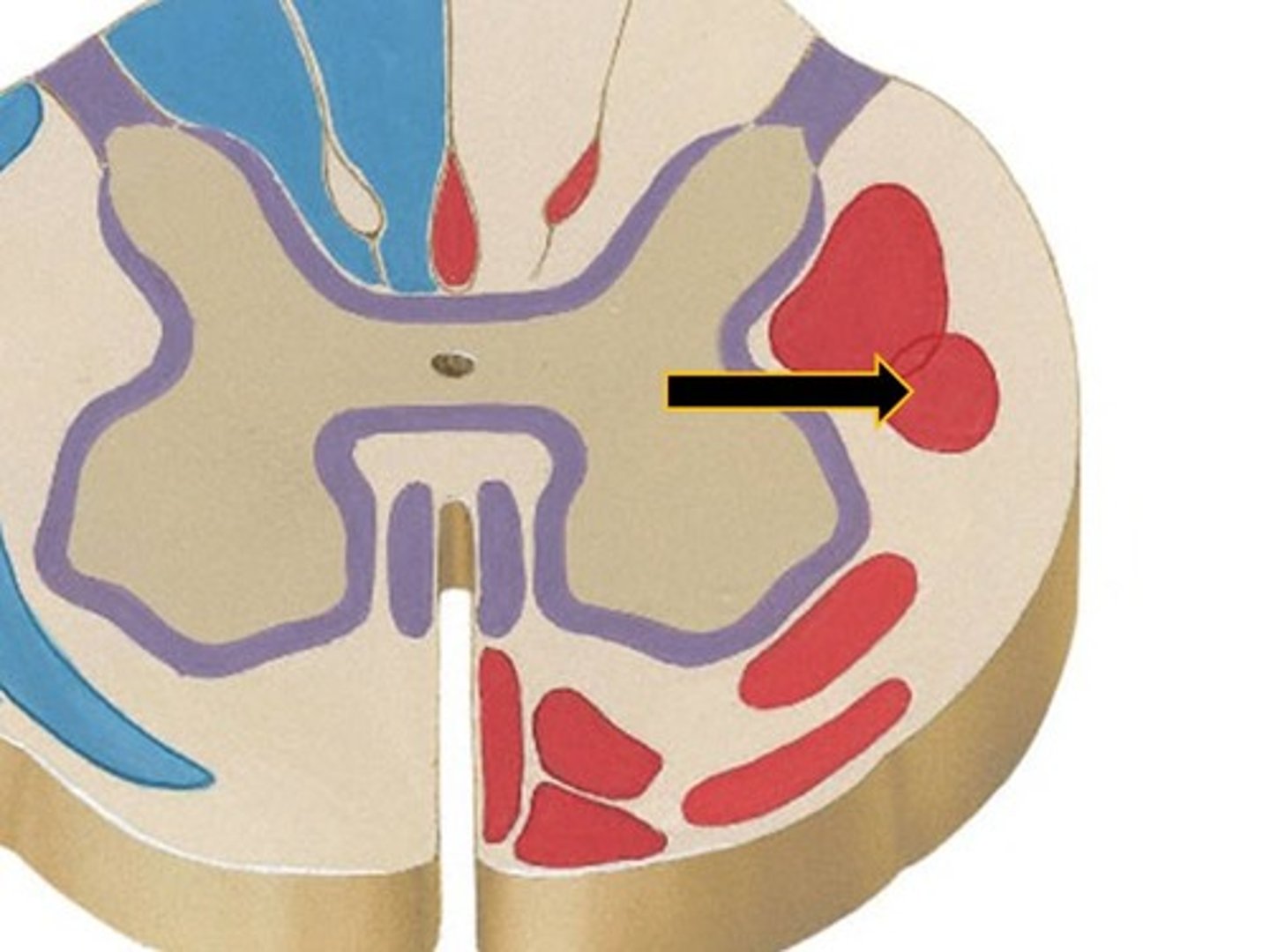
fractionation
ability to activate muscles independently of other muscles
corticopontine
axons synapse with nuclei in pons
corticoreticular
axons synapse with reticular formation
corticobrainstem
Axons synapse with cranial nerve nuclei in brainstem
corticospinal
no modification
trigeminal lemniscus
second order neurons in the main sensory nucleus and spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve and decussate
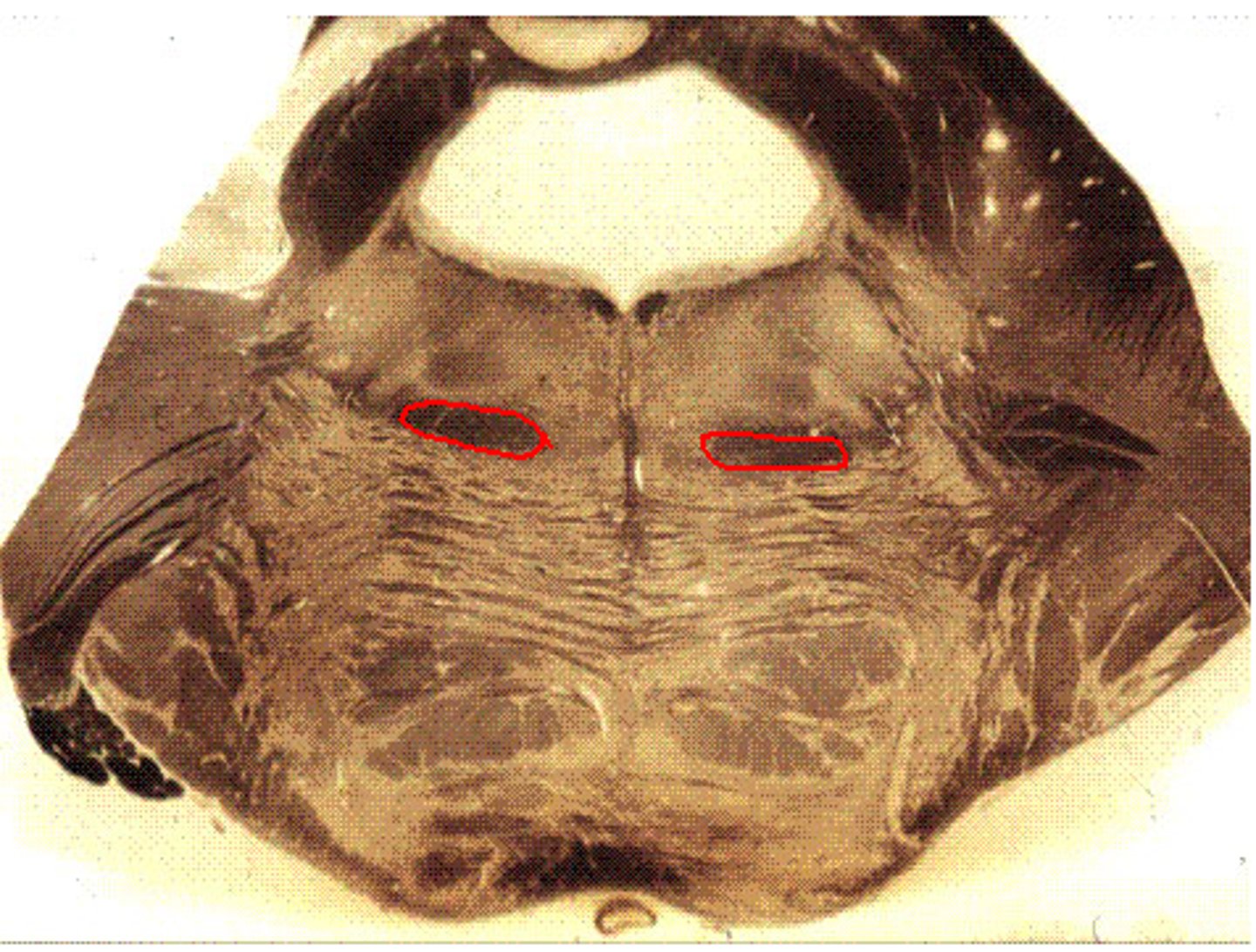
spinocerebellar
exit brainstem via inferior & superior cerebellar peduncles
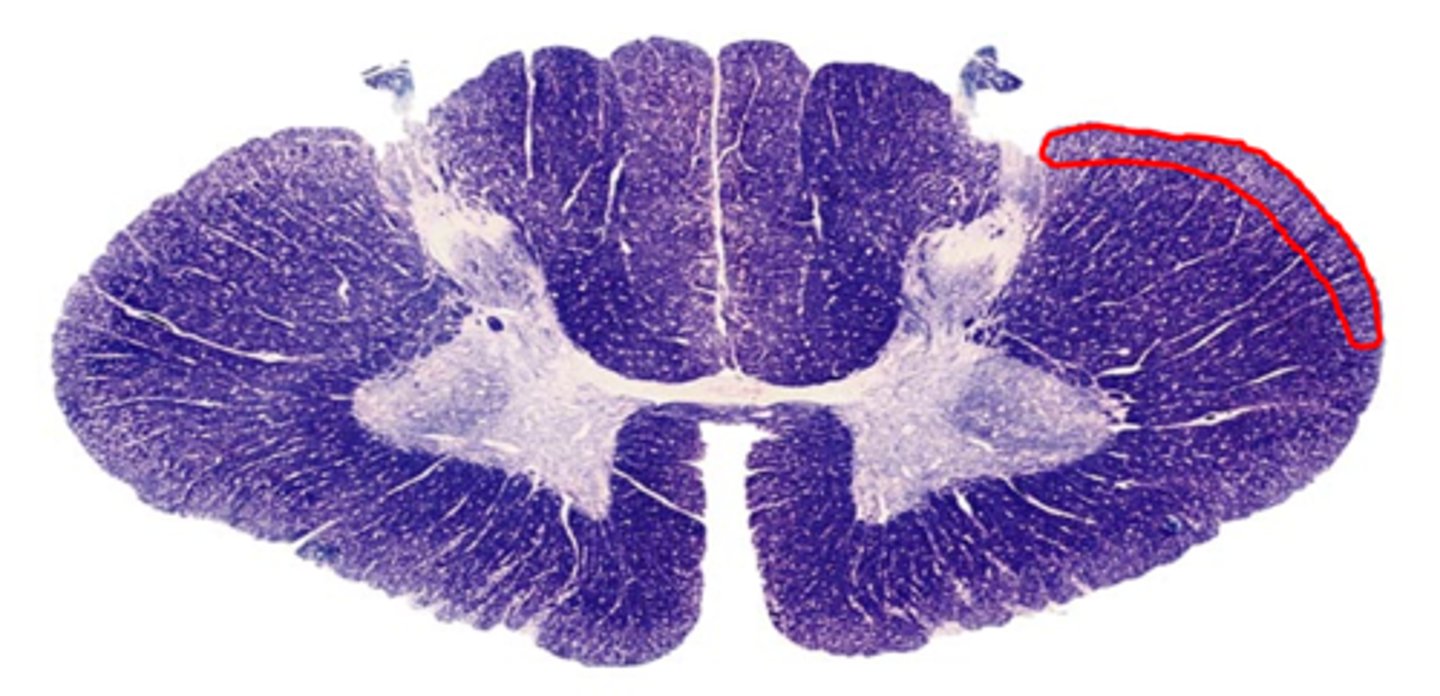
dorsal column
synapse in nucleus gracilis or cuneatus, decussate to form medial lemniscus
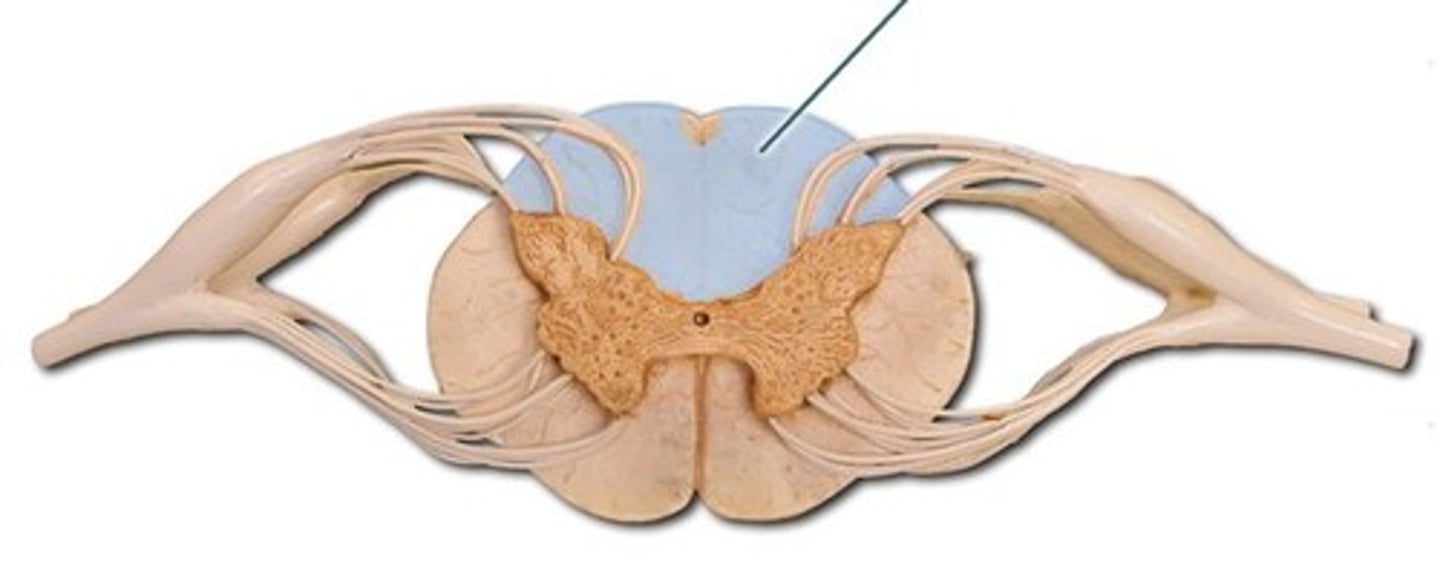
spinothalamic
no modification; goes to thalamus