T2- menstruation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
mecharche
-first menstrual period in females life
-between 11 and 15
menstruation
-periodic shedding of the uterine lining
amenorrhea
-absence of menstruation
dysmenorrhea
painful menstruation
metorrhagia
-irregular uterine bleeding between expected menstrual periods
menorrhagia
-abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
oligomenorrhea
-infrequent menstrual periods
polymenorrhea
-frequent menstrual periods
follicular phase
-day 1-13
-hypothalamus releases GnRH
-pituitary secretes FSH and LH
-ovarian follicles develop, producing estrogen
-estrogen thickens
-oen follicle becomes dominant
ovulation phase
-day 14
-estrogen peaks and triggers LH surge
-dominant follicle ruptures, releasing egg
-egg enters fallopian tube
luteal phase
-day 15-28
-ruptures follicle becomes corpus luteum
-corpus luteum produces progesterone and some estrogen
-endometrium prepared for implantation
if fertilization occurs
-sperm fertilizes egg in fallopian tube
-zygote forms and begins cell division
-blastocyst implants in endometrium
-trophoblast cells produce hCG
-hCG maintains corpus luteum
-continued progesterone production sustains pregnancy
if fertilization does not occur
-unfertilized egg degeneration
-corpus luteum degenerates after 14 days
-estrogen and progesterone levels drop
-endometrium breaks down
-menstruation begins
primary sexual characteristic
-females: development of ovaries and uterus, menarche
-males: development of testes
secondary sextual characteristic
-females: breast development pubic and underarm hair growth, widening of hips, increased body fat in hips, thighs, and buttocks, changes in labia
-males: facial and chest hair growth, increased body hair, deepening of voice increased muscle and bone mass
tanner stages
-stage 1: no glandular tissue, elevated nipple only, no pubic hair
-stage 2: breast buds forms, small area of surrounding glandular tissue, sparse growth of long, downy hair labia
-stage 3: breasts and areola enlarge but no contour separation, darker, coarser and more curled hair, spreading sparsely over pubic symphysis
-stage 4: areolar and nipple form secondary mound above breast tissue, adult type but less in distribution so spread to medial thigh
-stage 5: mature contour, with nipple projecting and areolar recessed into general breast contour, adult distribution in quantity and type, spread to medial thigh
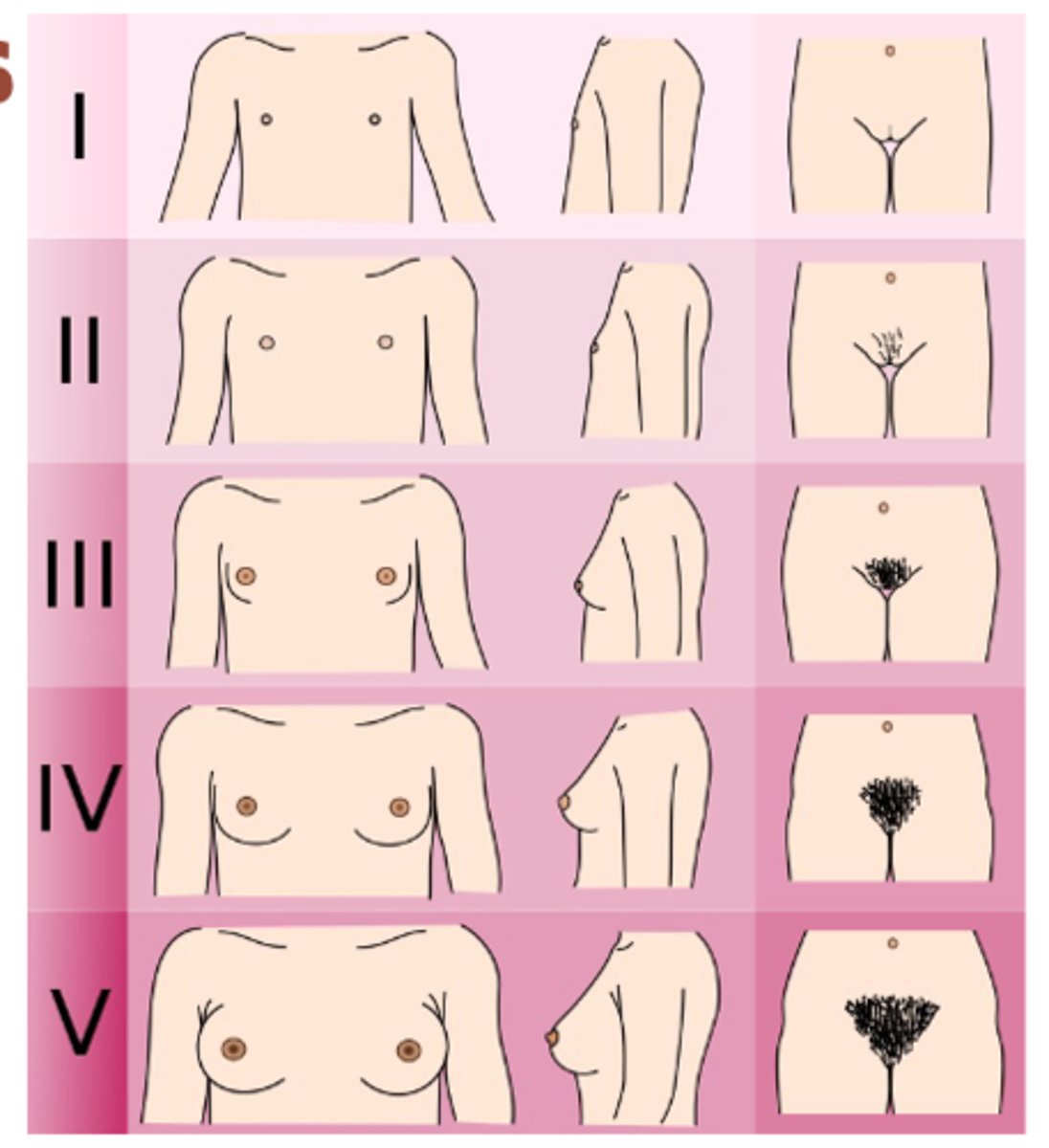
menarche typically occurs in
-late stage 3 or early stage 4 tanner
precocious puberty
-begin usually at age 8
-early than the normal age
-primary: from the brain
-secondary: something else in the body is causing this
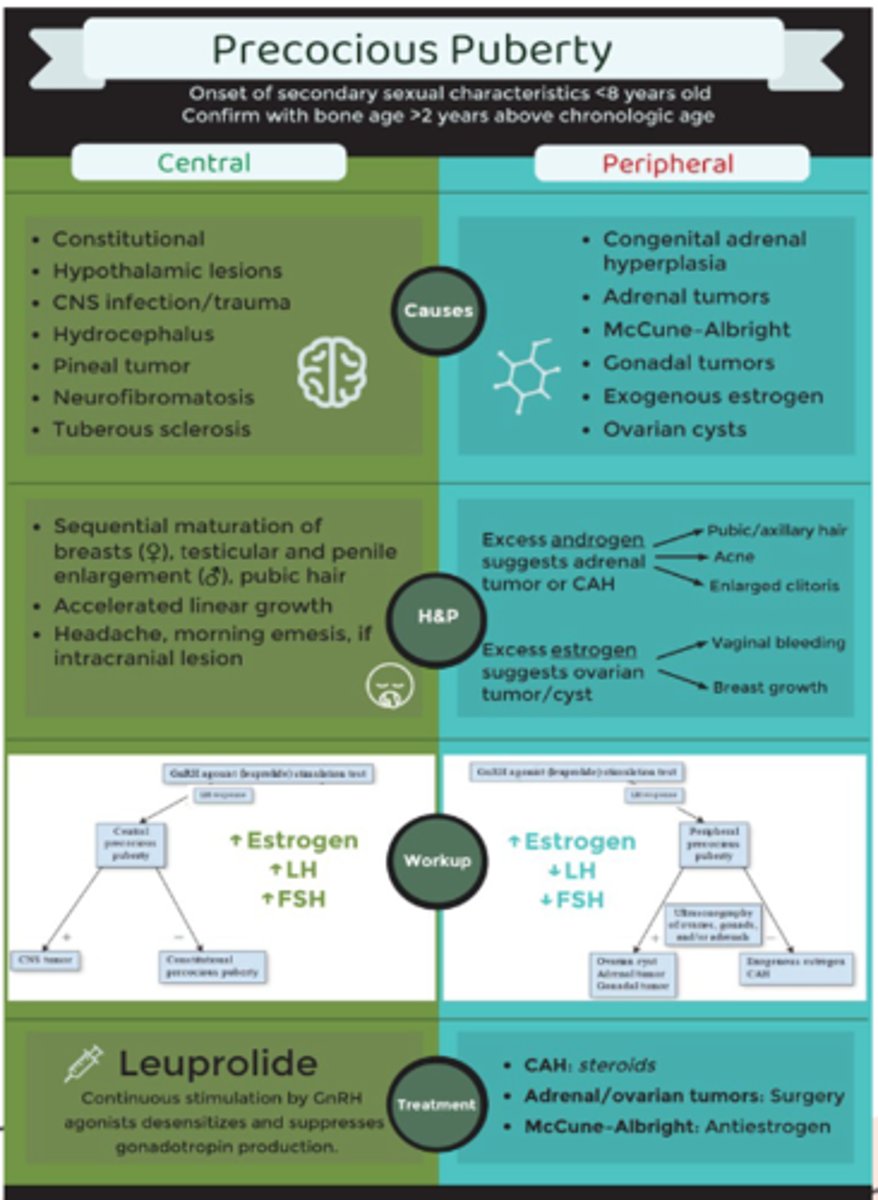
primary amenorrhea
1. at age 14 years if neither menarche nor any breast development has occurred or if height is in the lowest 3% for ethnicity
2. at age 16 if menarche has not occurred
primary amenorrhea causes
-gonadal dysgenesis (turner syndrome)- 43%
-mullerian agenesis- 15%
-physiologic delay of puberty (chronic systemic disease, acute illness)- 14%
-PCOS
-isolated GnRH deficiency
-weight loss
-hypopituitarism
gonadal dysgenesis (turner syndrome)
-chromosomal disorder affecting females, absence of all or part of one X chromosome
-features: short stature, ovarian failure, lack of secondary sextual characterisitcs, webbed neck, low hairline
-45, X karyotype
-associated with cardiovascular abnormalities, kidney problems, autoimmune
-tx: growth hormone therapy, estrogen replacement, regular health screening
mullerian agenesis
-congenital absence or underdevelopment of the uterus and upper two thirds of the vagina (MRKH) syndrome
-feature: primary amenorrhea, normal external genitals and ovarian function, absent or rudimentary uterus and upper vagina
-sporadic, but some familial cases
-associated with renal abnormalities, skeletal anomalies
-tx: nonsurgical vaginal dilation or surgical creation of neovagina, psychological support
secondary amenorrhea
-amenorrhea for 3 month after previously having regular cycle
-amenorrhea 6 months when cycle were previously irregular
secondary amenorrhea causes
-PREGNANCY IS MOST IMPORTANT TO R/O
-hypothalamic pituitary causes (low FSH)
-hyperandrogenism (low FSH)
-uterine causes (normal FSH)
-premature ovarian failure (high FSH)
-menopause (high FSH)
-scarring or stenosis: asherman syndrome (intrauterine adhesions or scar resulting from uterine surgery, preventing normal endometrial growth and menstrual shedding)
-primary ovarian insufficiency: ovaries stop function normally before 40
functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA)
-anorexia nervosa, exercise, stress
-women's menstrual cycle stops due to suppression of HPO axis, trigger by stress, low body weight, excessive exercise
-low estrogen levels and absent or infrequent ovulation
pituitary dysfunction
-prolactinomas = most common
primary dysmenorrhea
-painful menses in the absence of disease that could account for sx
-cramping during period
-pain usually begins 1-2 years after menarche and becomes more severe
-pain is from uterine vasoconstriction and sustained contraction mediated by prostaglandins
-low midline wave like pain
-lasts 1 or more days
secondary dysmenorrhea
-painful menses in females with a disorder that could account for their sx
-endometriosis, adenomyosis, fibroids
abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)
-refers to menstrual bleeding of abnormal quantity, duration, schedule
-bleeding or spot between periods
-bleeding after sex
-heavy bleeding
-longer than 35 days or shorter than 21 days
-irregular
-not having period for months
-bleeding after menopause
what causes AUB
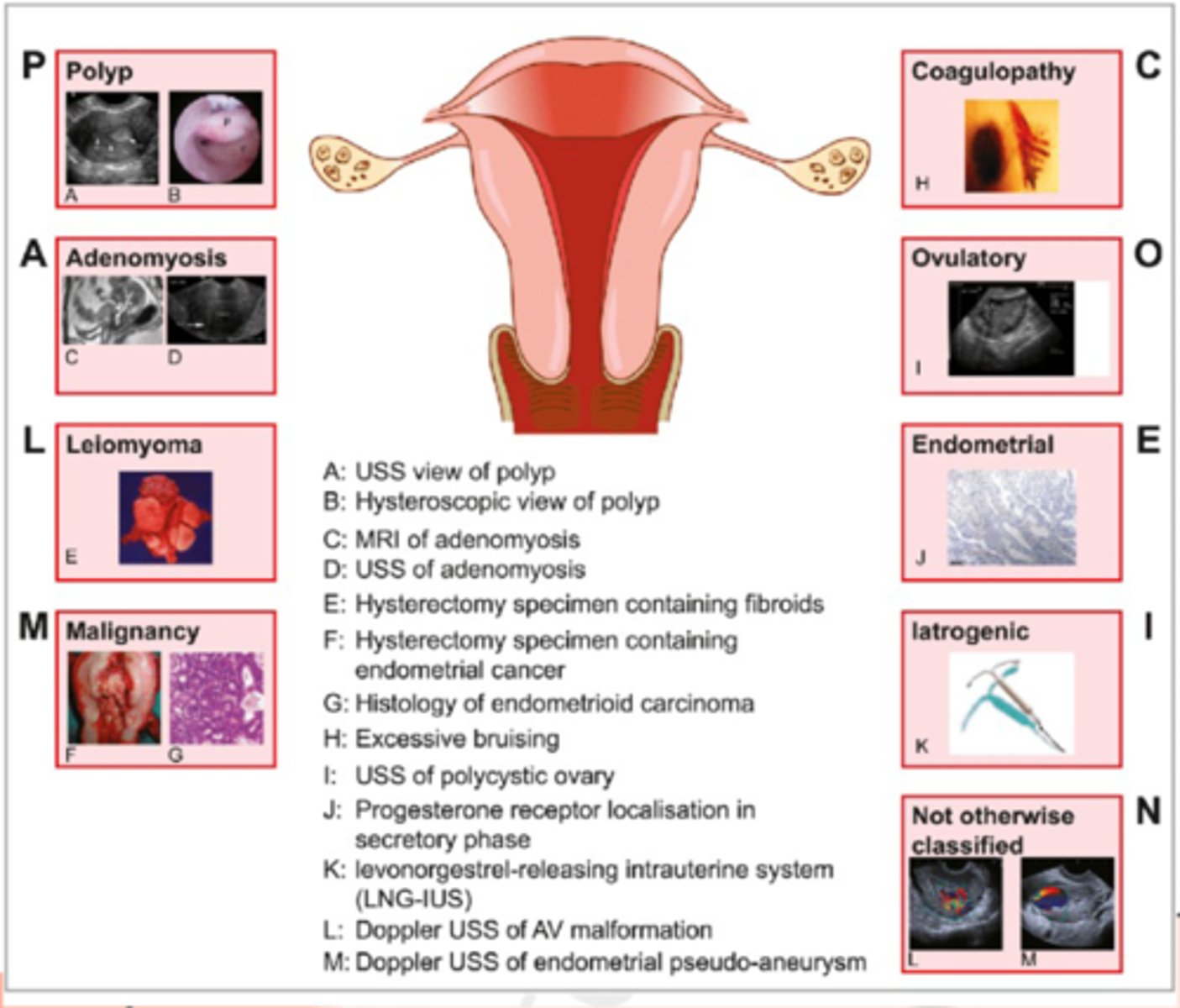
-PALM-COEIN
structual causes
-polyp
-adenomyosis
-leiomyoma
-malignancy and hyperplasia
non-structural causes
-coagulopathy
-ovulatory dysfunction
-endometrial
-latrogenic
-not classified yet
AUB in adolescents
-anovulation due to immaturity of the HPO axis
-oce regular menses have been established > ovulatory dysfunction
AUB in women 19-39 is often a result of
-pregnancy
-structural lesions
-anovulatory cycles
-use of hormonal contraception
-endometrial hyperplasia
AUB post menopausal
-bleeding requires work up for endometrial or cervical cancer!!
-once ruled out move on to other causes
AUB dx
-HCG
-pap if over 21
-STI screening
-labs: CBC, TSH, coag panal
-imaging: pelvic ultrasound, saline initiated sonography
AUB tx
-depends on cause
-structural: removal vs hormonal tx
-adenomyosis: hormonal tx, hysterectomy
-cancer: refer to gyn oncologu
-coag: refer to heme
-STI: abx
PMS
-sx present 5 days before
-must end within 4 days after
Abdominal bloating
Breast tenderness
Headaches
Hot flashes
Fatigue
Mood swings
Irritability
Anxiety/depression
Increased appetite/food craving
PMDD
-five or more sx present during the week prior to menese, resolving within a few days after menses starts
-preceding year
sx: Difficulty concentrating
Change in appetite, food cravings, overeating
Diminished interest in usual activities
Easy fatigability, decreased energy
Feeling overwhelmed or out of control
Breast tenderness, bloating, weight gain, or joint/muscles aches
Sleeping too much or not sleeping enoug
PMS/PMDD tx
-NSAIDs
-spironolactone
-SSRI