Ch.1 The Airways & Alveoli
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what is the main function of the lungs?
bring atmospheric gases into contact with blood
what is ventilation?
process of moving gas into & out of the lungs
•has NOTHING to do with the oxygen
what is the main muscle of ventilation
diaphragm
what is respiration?
• moves O2 & CO2
what is external expiration?
movement between air in the lungs and the blood
what is internal respiration?
movement between capillaries & tissue
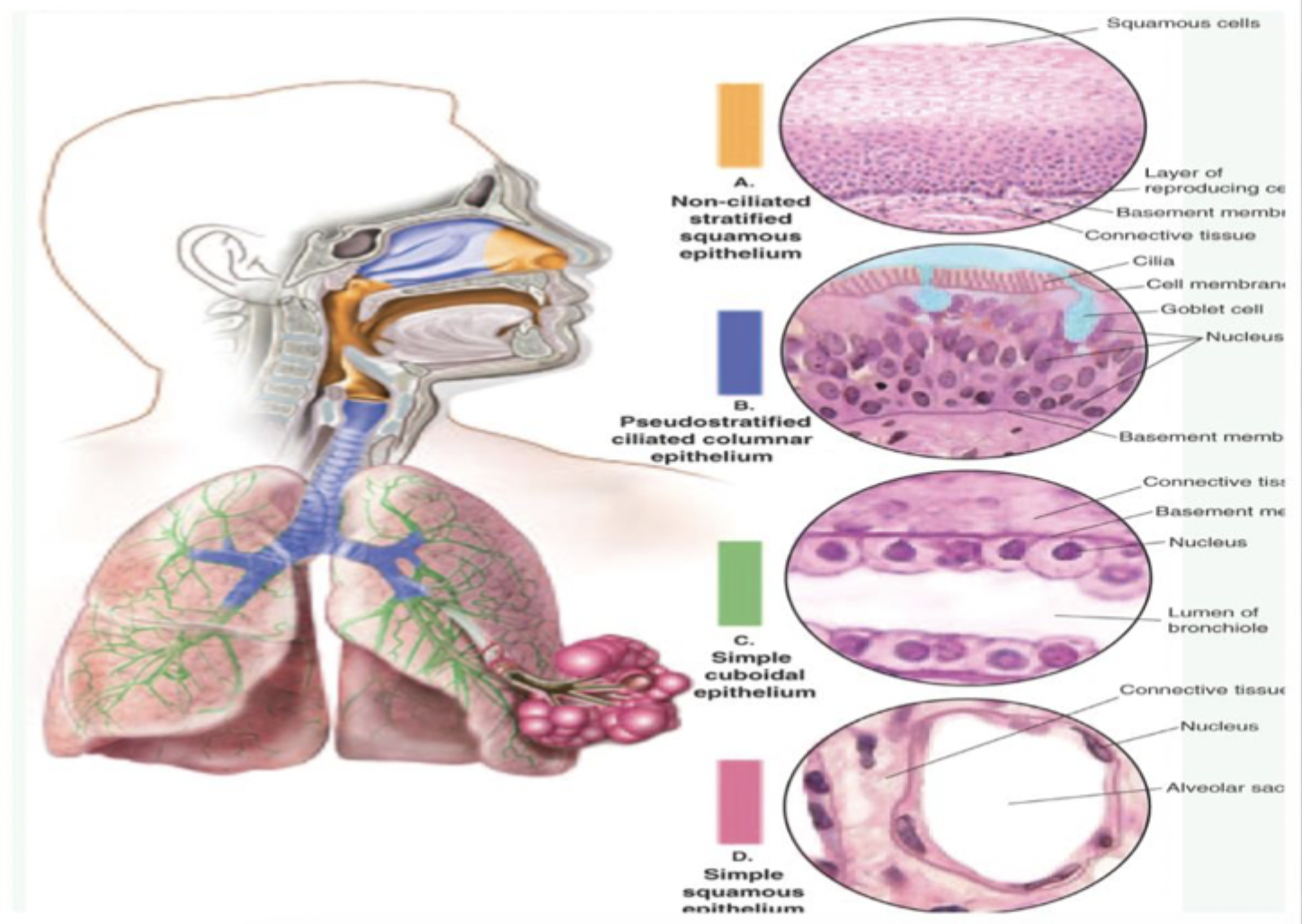
Non-ciliated stratified squamous epithelium
No hair like structures
location
Nares
Oropharynx
Larynx
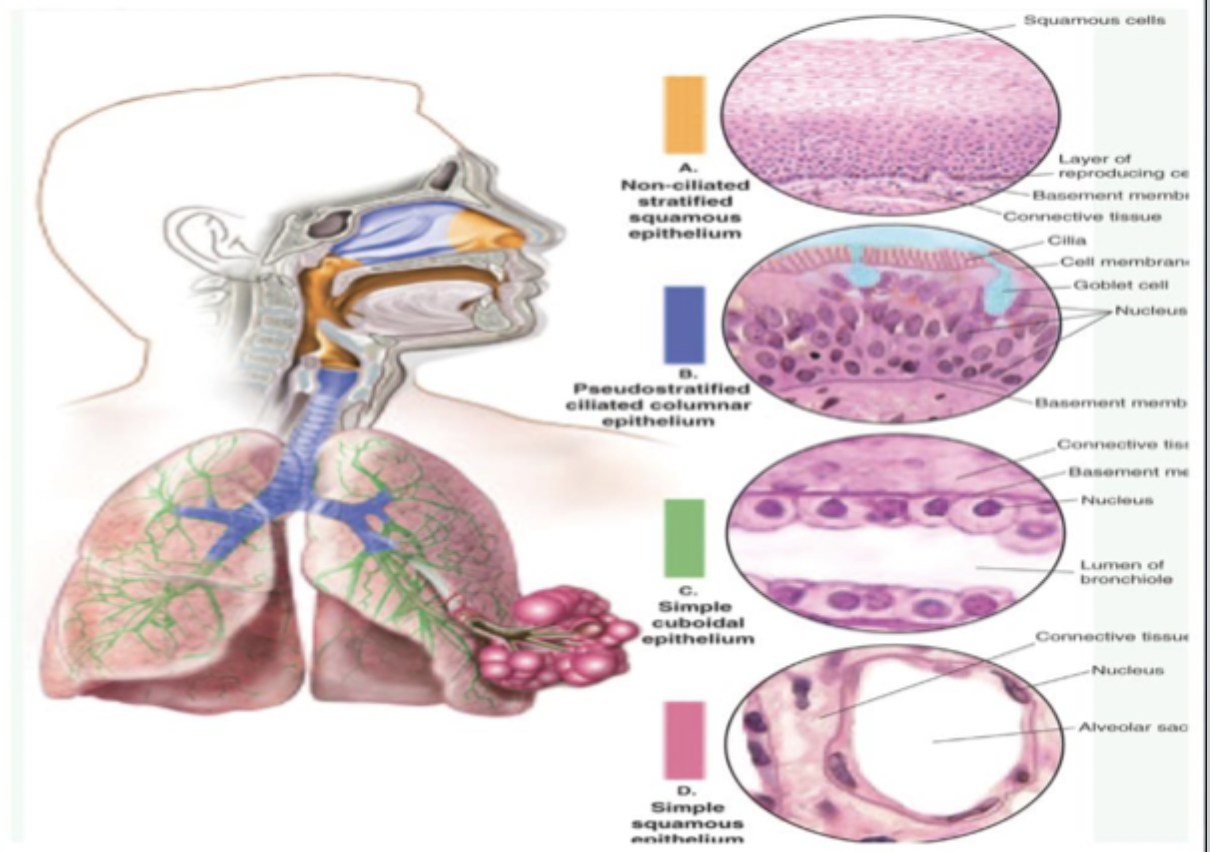
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Ciliated
Must be able to move
Mucus helps move cilia
location
Nasal passages
Trachea to bronchi
Cilia (hairlike structures)
Cilia must be able to move
Moves through mucus (must be moist)
Important for gas
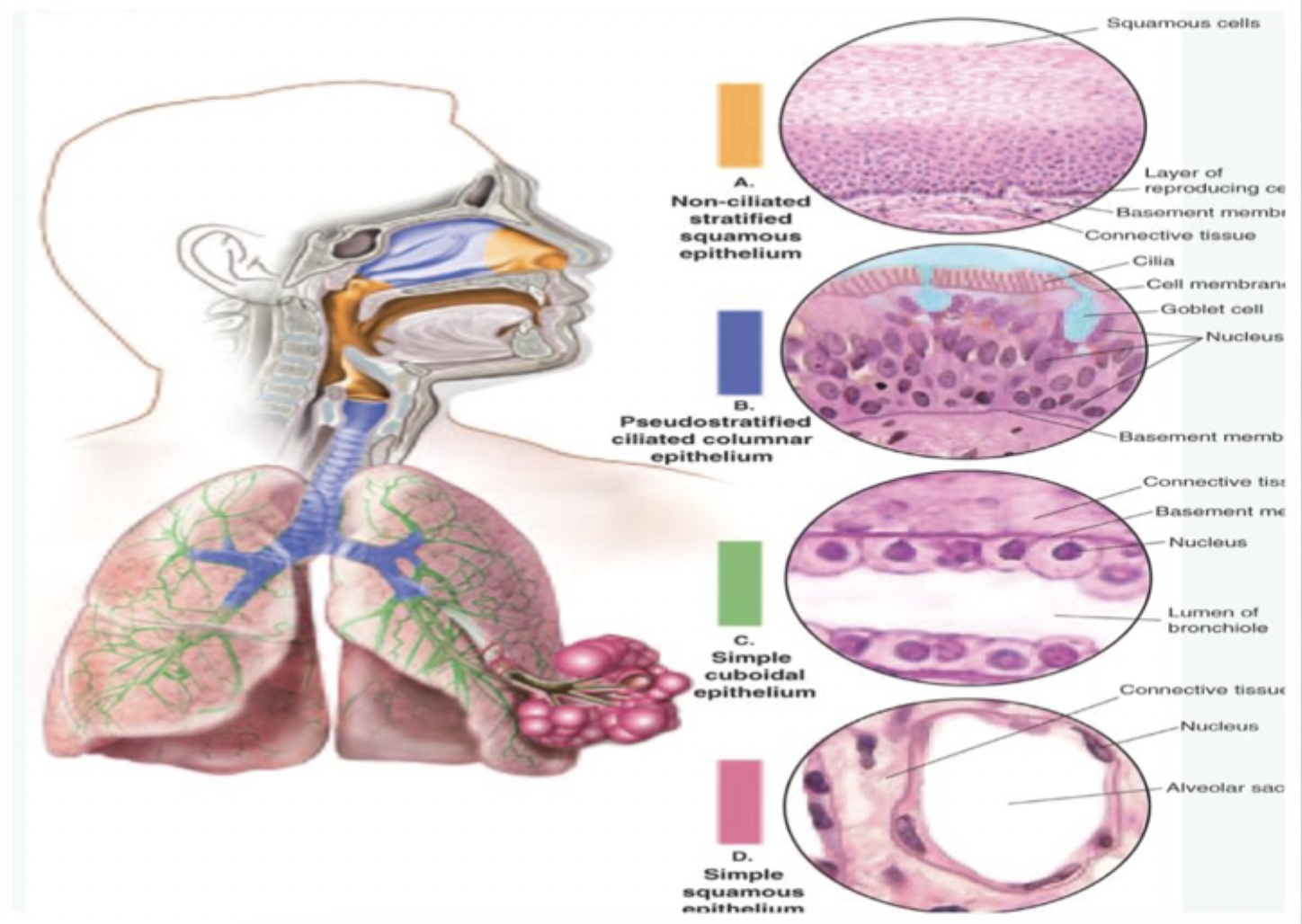
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Location
Terminal bronchiole
Respiratory bronchiole
Smaller bronchiole
Lumen open in between (airway)of bronchiole between
Thick
Contains connective tissue
Oxygen goes through but is too thick to go through until it reaches simple squamous epithelium
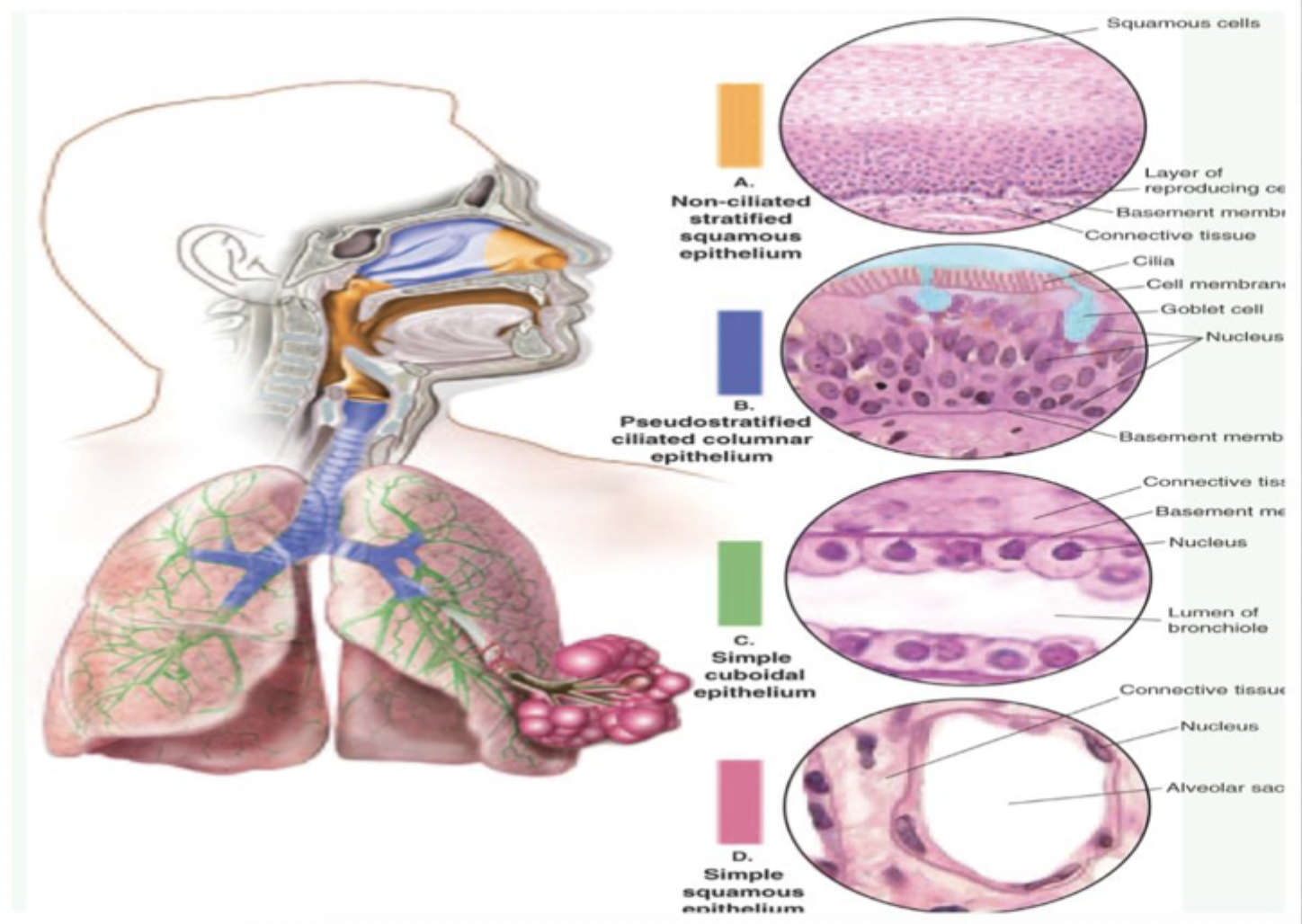
Simple squamous epithelium
Thin, gas can enter
Gas diffusion
Oxygenation
Alveoli
**what structures are located in the upper airway?
•nose
•oral cavity
•pharynx (throat)
•larynx (voice box) ; marks transition between U & L airways
**what structures are located in the lower airway?
•trachea (wind pipe)
•L&R mainstem bronchi
•bronchioles
•alveoli
•lungs
**what are the main functions of the nose?
•warms
•humidifies
•filters inspired air
**what are other functions of the nose?
•greater airway resistance
•contain turbinates that create airflow turbulence (↑ SA of the nasal cavity)
•produce secretions that contain immunoglobulins & inflammatory cells (1st line of defense)
what happens by the time the inspired air reaches the nasopharynx?
gain considerable water vapor & heat
what helps humidify the following inspiration?
exhaled air cools & leaves the nose → causing water vapor to condense on its internal surfaces
**what are the 3 divisions of the pharynx?
•nasopharynx
•oropharynx
•laryngopharynx
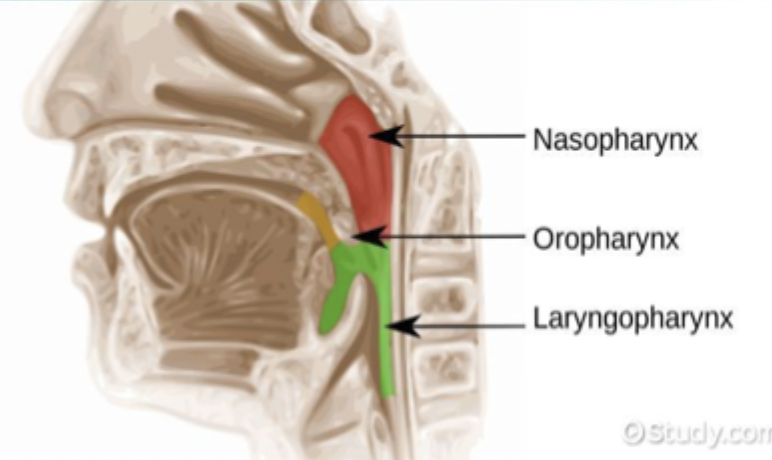
where is the nasopharynx?
behind nasal cavity down to the soft palate
where is the oropharynx?
behind the oral cavity from the soft palate to the base of the tongue
where is the laryngopharynx?
below the base of the tongue & above the larynx
why is pharyngeal musculature important?
helps prevent respiratory aspirations (anything in the lungs that shouldn’t be there) such as food and water
what are some functions of the pharynx?
•pharyngeal reflex
•gag & swallow reflex
•pharyngeal anatomy & upper airway obstruction
what does the pharyngeal reflex consist of?
•sensory (glossopharyngeal nerve IX)
•motor (vagus nerve X)
where is the voice box located?
in the larynx
what are the main functions of the larynx?
•generates sound for speech
•protection against aspiration of food & liquids
what is the thyroid cartilage?
•main cartilage of the larynx
•aka adams apple
**what is the purpose of the epligottis?
•upper movement of the larynx towards the base of the tongue pushes the epiglottis downward → diverts food away from glottis and into esphagus
•protective flap that prevents food and liquid from entering the windpipe and lungs during swallowing
• protect the airways from food, liquid, and debris
**what position is the epiglottis at rest?
remains in an upright position covering the soft palate, allowing air to pass freely into the larynx and lungs
**what position is the epiglottis when working?
folds backward to cover the airway entrance when you swallow
**what are the 3 layers of the tracheobronchial tree? (Dichotomous branching)
•trachea
•bronchi
•bronchioles
Inner to outer
Mucosa (traps & clears foreign material, contains Resp epithelium)
Submucosa (contains CT, glands, C shaped rings in trachea & large bronchi)
Adventitia (dense CT, support & protection of airway)
what does the trachea consist of?
•8-20 C-shaped rings
•located from C6-T5'
•11cm long in adults
when does _____ get replaced with ____ muscle as it goes down?
cartilage; smooth
located @ bronchioles
what is the carina?
•bifurcation of trachea into R & L bronchi
•R → deviates 20-30 degrees, 2x longer → straighter, wider
•L → deviates 45-55 degrees from midline, more angle, thinner
which bronchi stem is the ETT likely to enter
right side
what are optimal conditions of effective mucocilliary clearance?
•produce 100 mL of mucus/day
•functional glottis for aspiration
•ciliated epithelial cells (250 cilia beating @ 1300x per minute → moves 2cm per minute to pharynx)
•intact cough mechanism
this removes microbes & inhales particles
• RA 22 C; RH 50% (10mg H2O)
•ISB below trachea @ 37 C, RH 100% (44 mg H2O)
**what is part of the conducting airway?
(NO GAS EXCHANGE, DEADPACE)
•all airways from the trachea down to the level just before the terminal air sacs/ or alveoli: Trachea → terminal bronchioles
trachea
bronchi (cartilage)
bronchioles (no cartilage)
terminal bronchioles (smooth muscle) ← end of conduction zone
•only directs air to alveoli
**what marks the beginning of the respiratory zone/gas exchange zone?
alveoli (respiratory bronchioles) -300mil
**what are parts of the respiratory zone?
GAS EXCHANGE OCCURS
respiratory bronchioles
alveolar ducts (opened into blind terminal units of alveolar sacs & alveoli)
alveolar sacs (Clusters of alveoli)
alveoli (Tiny air sacs surrounded by capillaries.)
what is the functional respiratory unit of the lungs?
acinus (all alveoli)
•each terminal bronchiole give rise to the acinus
what connect adjacent alveoli with one another?
pores of kohn
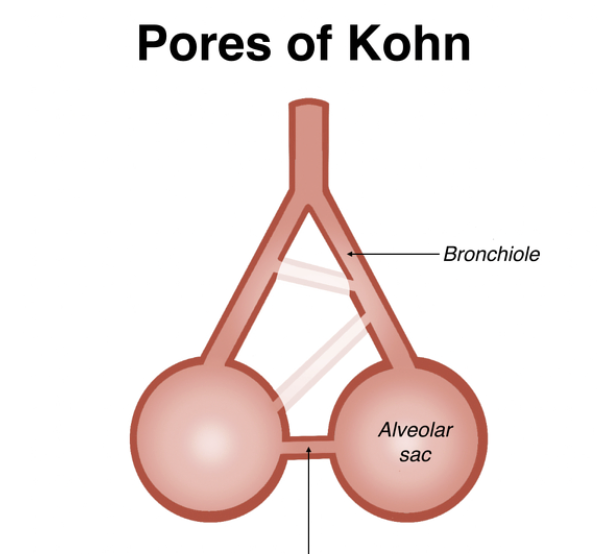
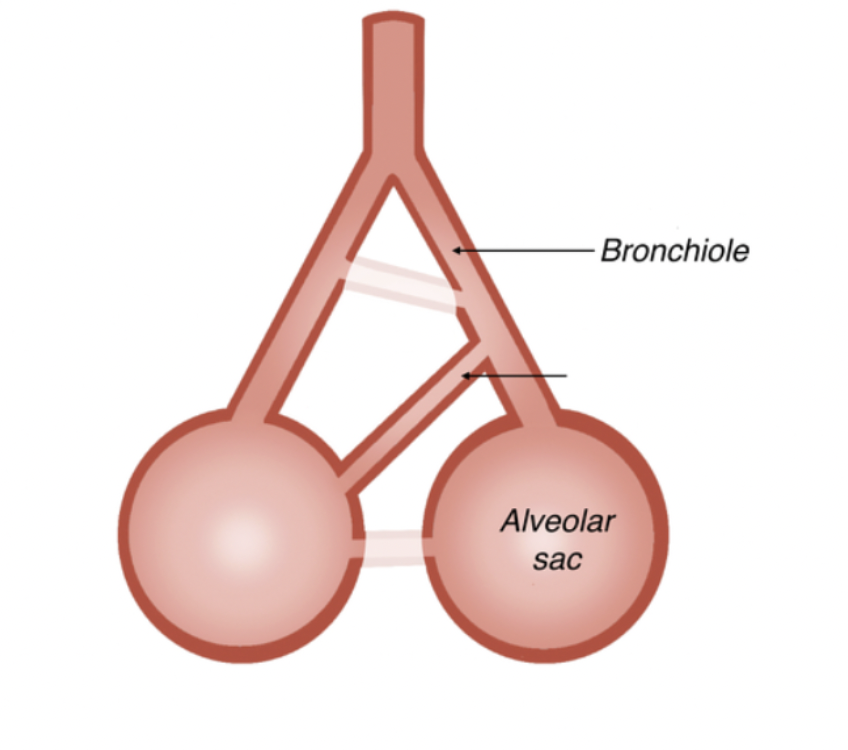
what connects terminal bronchioles with nearby alveoli?
canals of lambert
**what is the AC membrane?
alveolar-capillary membrane
Site of gas exchange
alveolar epithelium contains:
•type 1 cells
•type 2 cells
•alveolar macrophages
**what are type I alveolar cells?
•comprise most of alveolar SA
•flat
**what are type 2 alveolar cells?
•compact, polygonal shaped
•protrude into alveolar airspace
•contain lamellar bodies to secrete surfactant → reduced surface tension & keeps alveoli open (important fas newborn babies don’t secrete surfactant)
what do the adjoining basement membranes of the alveolar ____ & capillary _____ form?
•epithelium(highly permeable to respiratory gas); endothelium (more permeable to water)
•extremely thin blood-barrier, less than 0.5 μm thick in the flattest regions of the type I cell
what is the space between the ____ epithelium & _____ endothelium
interstitium
what are alveolar macrophages?
•large migratory phagocytes → wanders through alveolar airspace & interstitium
•engulf & digest microorganisms & foreign material → major lung clearance mechanism distal to the terminal bronchiole