Chapter 9 - DNA Structure
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Structure / proteins / inert
Fill in the blank…
The genetic functions of DNA flow directly from its ( ); knowledge of DNA makes it possible to understand biochemical processes of genetics. All of the genetic functions of DNA depend on specialized ( ) that read the information in a DNA sequence. DNA itself is chemically ( ).
Nuclein / acidic / phosphorus / DNA / chromosomes
Fill in the blank…
Meischer extracted ( ) from nuclei of human white blood cells that was weakly ( ) and ( )-rich. Chemical analysis showed that its major component was ( ) and staining of cells showed that DNA localized exclusively within ( ).
Nitrogenous bases / nucleotides / four / protein
Fill in the blank…
Around 1900, both DNA and RNA were found to contain ( ). By 1910, ( ) had been discovered. Regardless, it was felt that DNA was too simple to be the genetic material since it was made up of only ( ) different subunits. Protein is made up of 20 different subunits, so it was thought that it had more potential for creating different combinations. Protein was also thought to be the genetic material because chromosomes contained more ( ).
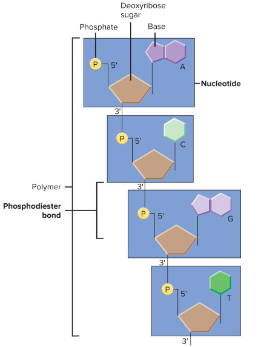
Nucleotides / phosphodiester bonds
Fill in the blank…
DNA contains four kinds of ( ) linked in a long chain by ( ), or covalent bonds joining adjacent nucleotides.
Virulent / non-virulent / transformed / dead
1) Died
2) Lived
3) Lived
Fill in the blank…
F. Griffith did experiment with two strains of S.pneumoniae that differed in morphology and biological activity. The smooth (S) strain was ( ) while the rough (R) strain was ( ). The R cells could be ( ) by genetic material transferred from dead S cells and become S. This was discovered when mice were injected with a mixture of dead S cells and living R cells and ( ) mice were found to contain living S cells.
Also, what happened to the mice when they were…
1) Injected with S cells
2) Injected with S cells that mutated to R
3) Injected with heat-killed S cells
The transforming principle was purified from extracts. The component was exposed to degradative enzymes and techniques that degraded different cellular components (protease, RNase, DNase, and centrifugation). After exposure, the component was added to R cells to test if they were still transformed into S cells by the transforming principle. All samples except that treated with DNase turned the R cells into S, implicating DNA as the transforming principle
How did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty prove that DNA was the transforming principle in the R and S cells?
Bacteria / equal
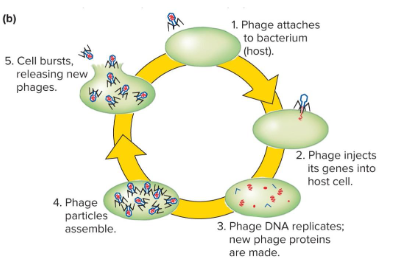
Fill in the blank…
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect ( ). They contain ( ) amounts of protein and DNA. After infecting a host, the “ghost” of the phage remains attached to the outer membrane of the cell and the phage genetic material is injected into the bacterial cell.
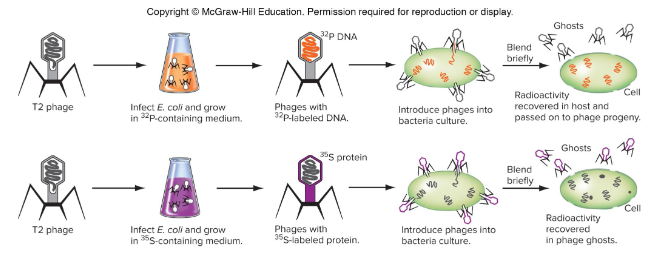
1) Grew T2 phages in two different E.coli mediums: P-containing and S-containing
2) Allow T2 phages to infect E.coli, producing phages containing P-labeled DNA and phages containing S-labeled protein
3) Introduce each phage type into a bacterial culture
The phages with S-labeled protein never transferred the material into the bacteria (radioactivity studies only saw material in the phage). The phages with P-labeled DNA transferred material into the bacteria and phage progeny were observed to have the material as well.
How did the Hershey-Chase blender experiment work and prove DNA was the genetic material?
Nucleic Acids
Chemically linked chains of nucleotides.
Ex) DNA and RNA
1) Five-carbon sugar
2) A phosphate group
3) One of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, guanine, thymine/uracil, or cytosine
Nucleotides have what three parts?
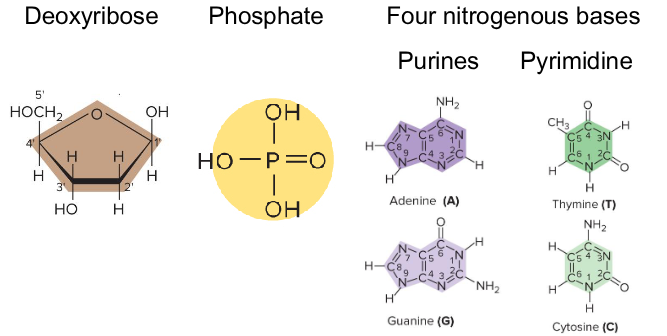
2-deoxyribose
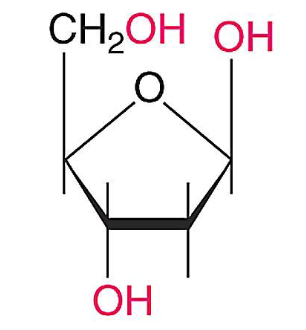
Ribose
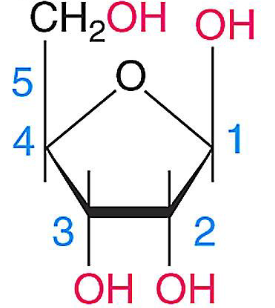
1) Deoxyribose
2) Ribose
What are the two kinds of five-carbon sugars in DNA/RNA?
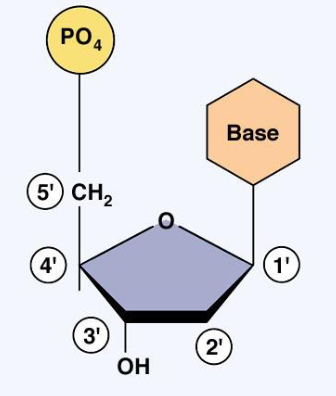
Nucleoside
3’ / 5’ / 5’ / 3’
Fill in the blank…
Phosphodiester bonds always form a covalent link between the ( ) carbon of one nucleotide and the ( ) carbon of the next nucleotide. DNA is always read in the ( ) to ( ) direction.
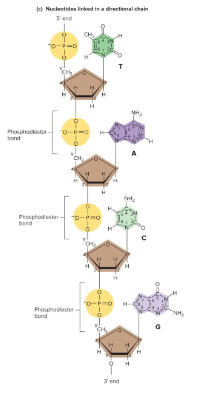
Backbone
This hydrophilic component of DNA is comprised of the sugar and phosphate parts of nucleotides.
Glycosidic
Fill in the blank…
Bases are linked to sugars by ( ) bonds.
Nucleotides
Components of nucleic acids. They provide chemical energy for the cell, act as cofactors, and have a wide range of regulatory functions.
E. Chargaff
Studied the base composition of DNA from many organisms and found that the ratio of A to T is 1 to 1 and the ratio of G to C is 1 to 1. He also found that different tissues from the same species have the same base composition and that base composition doesn’t change during an organism’s life.
R. Franklin and M. Wilkins
Determined the X-ray diffraction pattern of DNA and found that DNA is a helical structure with 20 A diameter, has 3.4 A spacing between repeating units, and undergoes a complete turns every 34 A.
Hydrogen bonds / shape / size
Fill in the blank…
Base pairs consist of ( ) between a purine and pyrimidine, which was consistent with Chargaff’s rules. Each base pair has the same ( ) and ( ).
1) Strands are antiparallel
2) Sugar-phosphate backbone on outside
3) Base pairs in middle
4) Two chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between A-T and G-C base pairs
Overall, what are the major characteristics of the DNA double helix structure?
Stack / reduce
Fill in the blank…
In water, DNA wants to form the double helix. The bases ( ) to ( ) contact with water.
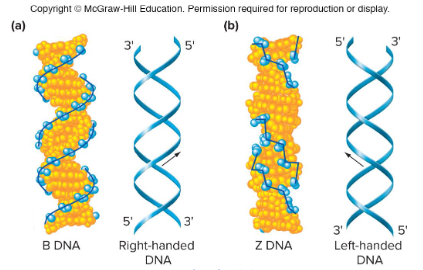
B-DNA
The main form that DNA assumes in cells. It is a right-handed helix and it has 10 bases per turn. Was described/discovered by Watson and Crick.
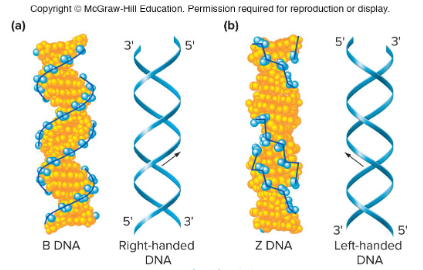
Alpha DNA
A form of DNA that forms when DNA is dehydrated or in a solution with little water. The bases tilt more, resulting in 11 bases per turn. DNA/RNA hybrids and double stranded RNA assume this structure.
Can also be seen in some DNA/protein interactions.
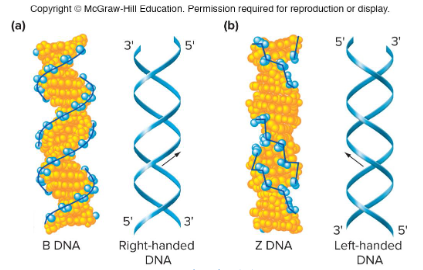
Z-DNA
A form of DNA that is left-handed. It tends to form in G/C rich regions and it occurs in particularly transcriptionally active regions of cells. It can form under very high salt concentrations and has an irregular backbone.
1) Lacking a hydroxyl group in the five-carbon sugar of RNA
2) Uracul replaces thymine in RNA
3) RNA is single-standed while DNA is double-stranded
What are the three main chemical differences between RNA and DNA?
Secondary / same
Fill in the blank…
RNA can form a lot of ( ) structure, so it has a lot of structural variety. It does so by forming base pairs within other parts of the ( ) molecule.
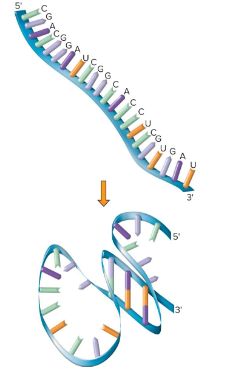
Double-Stranded RNAs
RNAs that are antiparallel and tend to assume a right-handed alpha helix. They can, however, have irregular base pairings and some single-stranded regions.
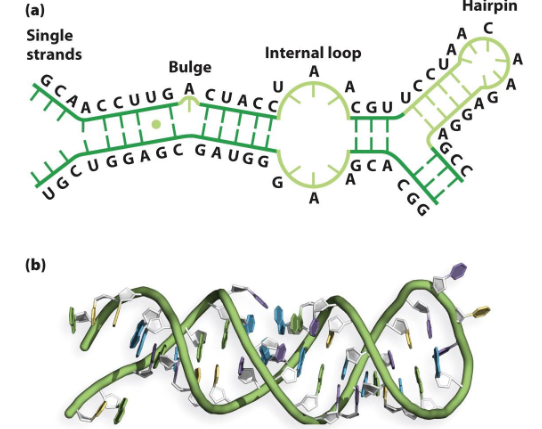
Ribonucleo-Proteins
RNAs that will only fold into three-dimensional structures when in the presence of proteins.
Single-stranded DNA absorbs more light at 260 nm than double-stranded DNA
How is denaturation of DNA measured?
Heat / pH / reversible / cool/ annealing
Denaturation of DNA occurs when DNA is exposed to ( ) or high ( ) and the hydrogen bonds that hold the double-stranded DNA together are broken. This process, however, is ( ) and DNA will become double-stranded again when allowed to ( ), a process known as ( ) or re-naturing.
Tm Point
The point at which half the DNA of a sample is denatured. This is affected by G-C content as well as salt concentration.
Cot Curves
Measure the reassociation of DNA. In this process, DNA is denatured and allowed to renature under constant salt and temperature before absorbance is measured.
Hybridization
When DNA from different species will anneal with each other to produce novel combinations. It is a widely used technique in molecular biology.
Probe
The known piece of single-stranded DNA or RNA that is used in a hybridization experiment to hybridize with other pieces of DNA or RNA. It is usually labeled in such a way that it can be detected.
Southern Blot
Used to detect DNA sequences.
Northern Blot
Used to detect RNA sequences.