Visual Processing: Ganglion Cells and Color Perception
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are ganglion cell responses?
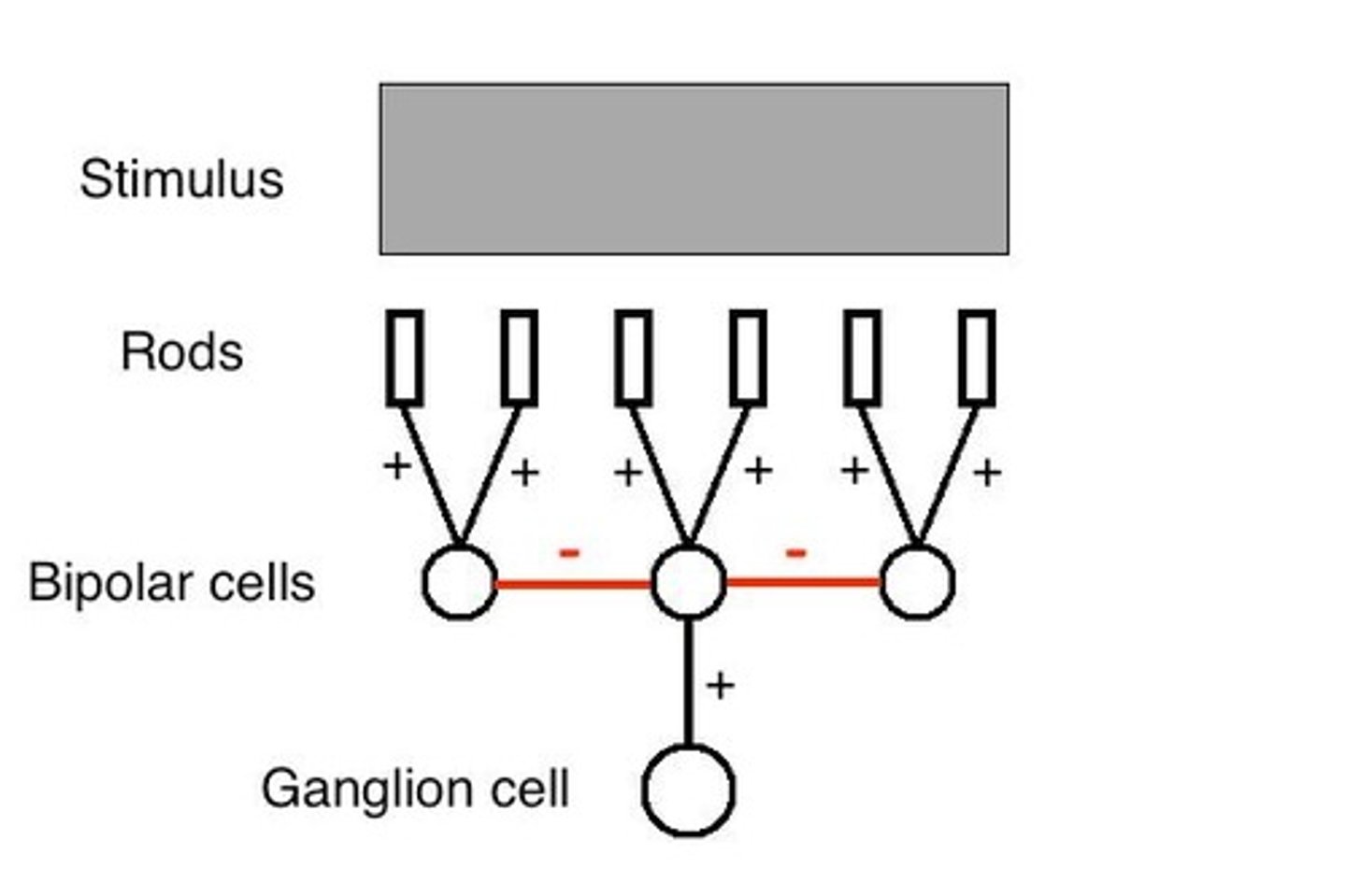
Ganglion cells respond to visual stimuli, particularly to edges and regions of high contrast, acting as contrast detectors.
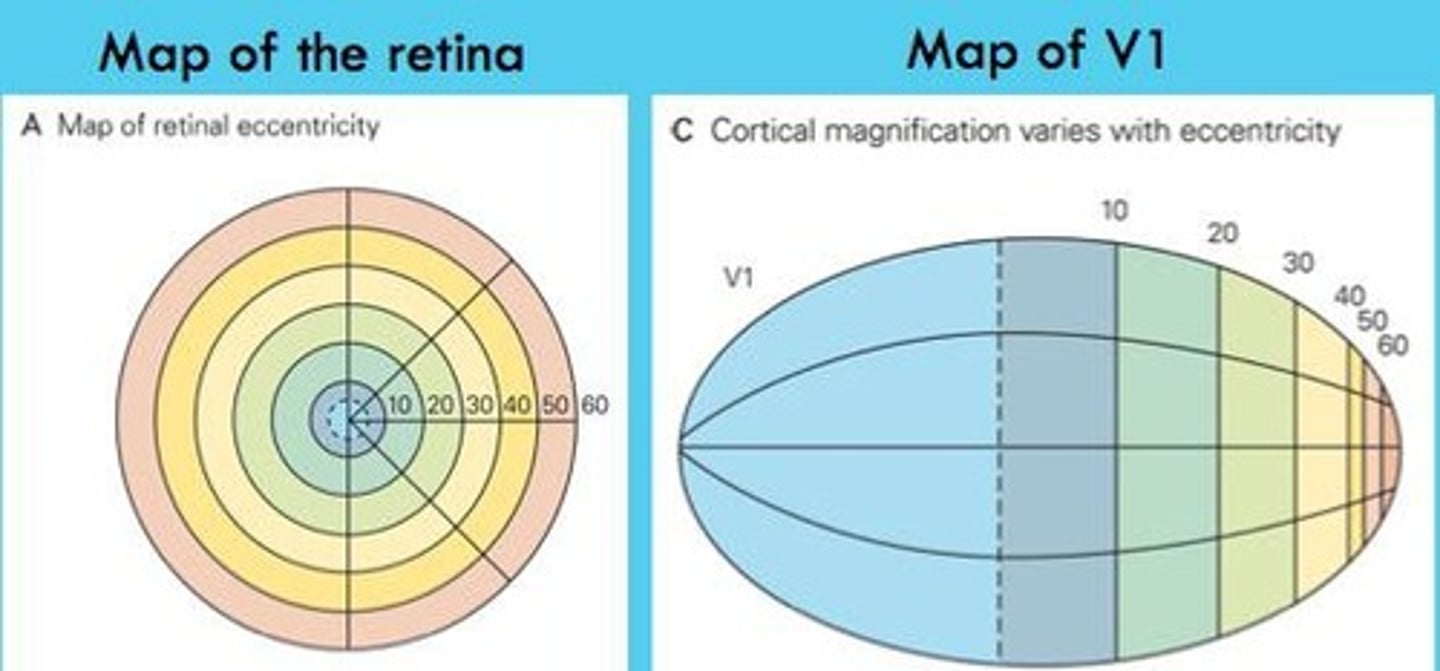
What is the large scale organization of V1?
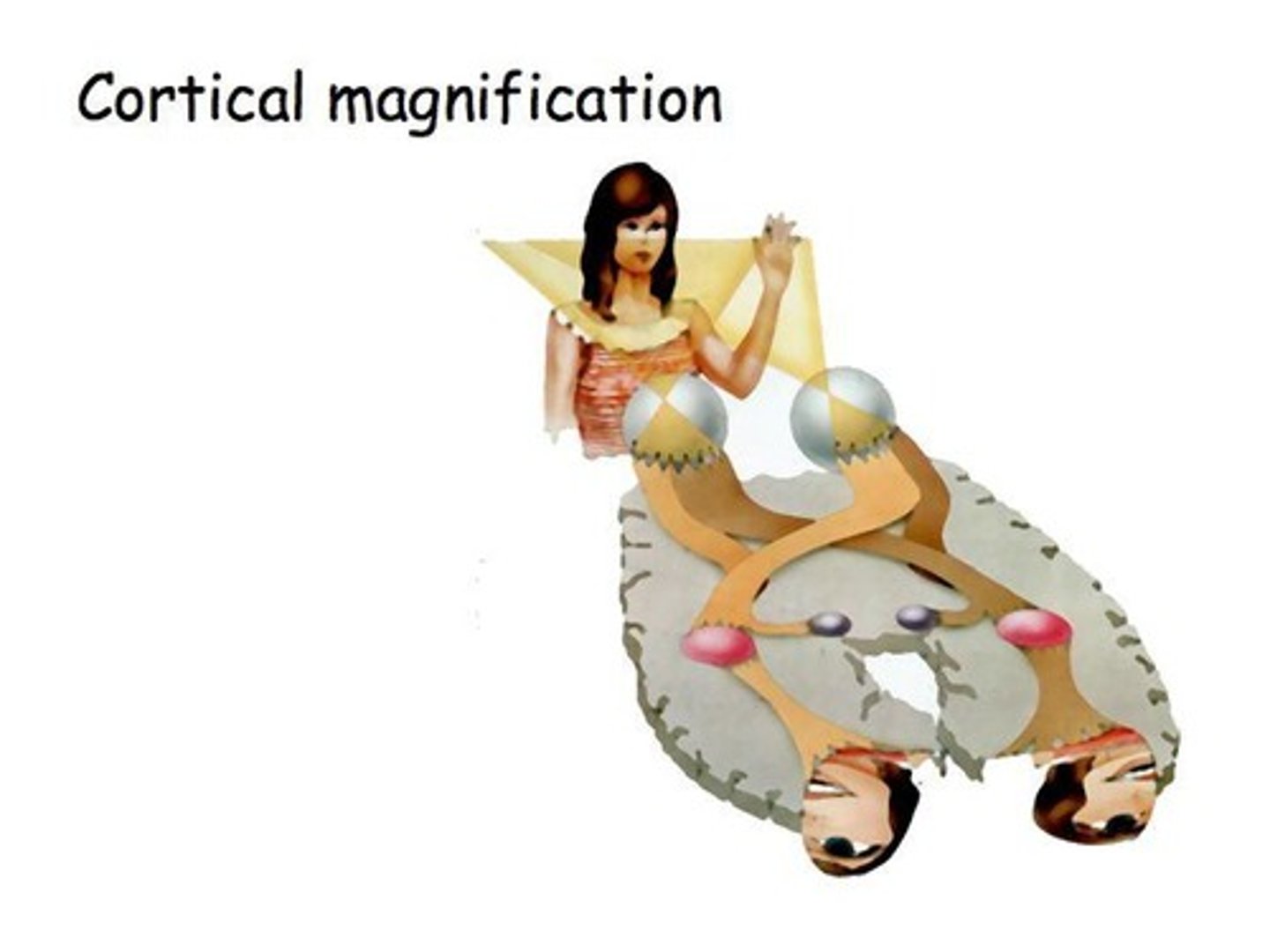
The retinotopic map in V1 is distorted, with the central 10 degrees of the visual field occupying roughly half of V1, a phenomenon known as cortical magnification.
What is cortical magnification?
Cortical magnification refers to the distortion in the retinotopic map of V1, where more cortical area is dedicated to processing the central visual field compared to the peripheral field.
What is the small scale organization of V1?
V1 is organized into functional columns, including location columns and orientation columns.
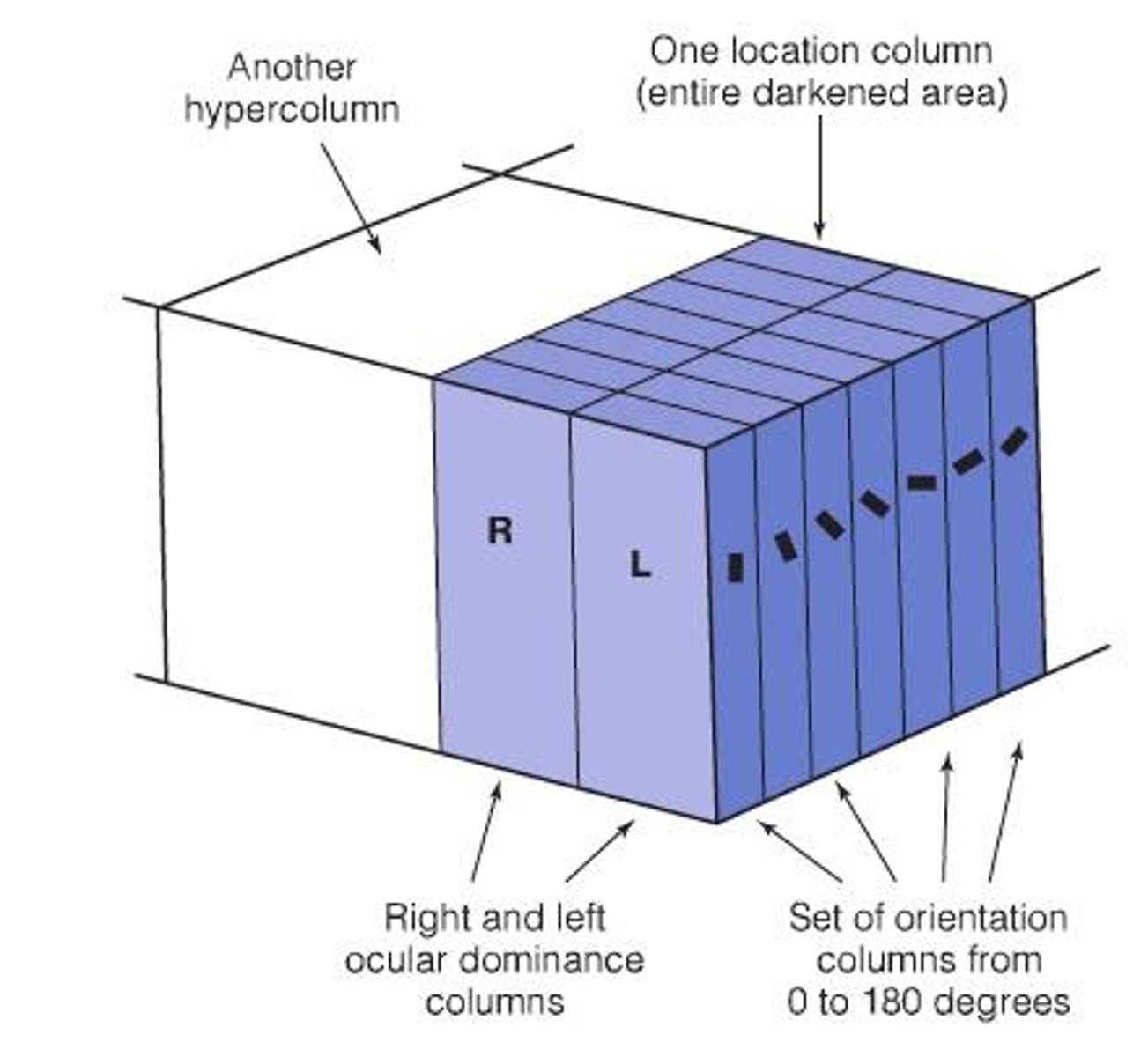
What are location columns in V1?
Location columns are organized such that neurons along the column have similar spatial receptive fields.
What are orientation columns in V1?
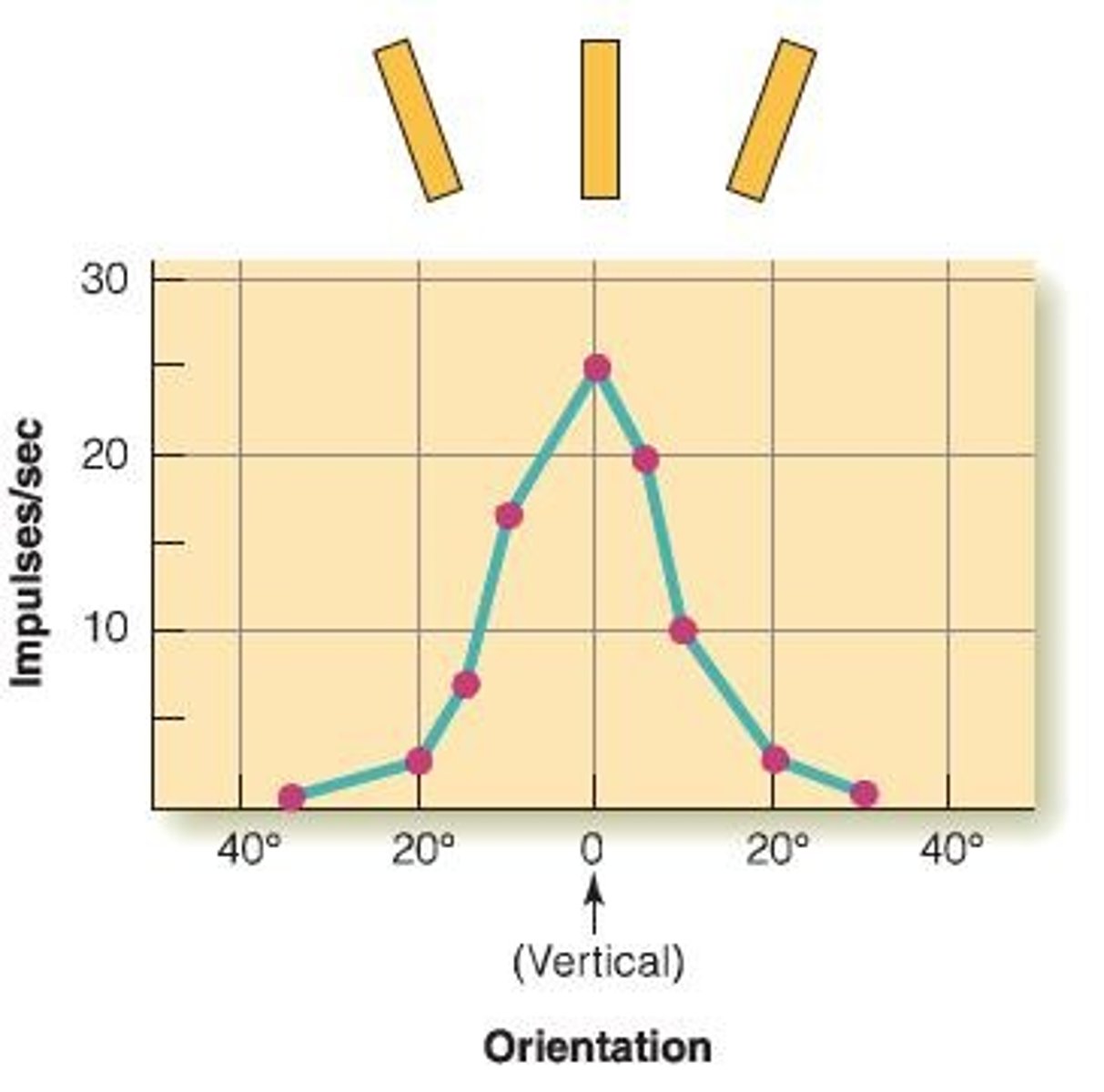
Orientation columns consist of neurons that have similar orientation selectivity, with the entire range of orientation preferences represented across nearby columns.
What is the trichromatic theory?
The trichromatic theory suggests that color perception is based on the activity of three types of cones sensitive to different wavelengths of light.

What is the opponent processes theory?
The opponent processes theory posits that color perception is controlled by opposing pairs of colors, and is supported by evidence from color adaptation and contrast.
What is the function of color vision?
Color vision allows for the discrimination of different wavelengths of light, aiding in object recognition and environmental interaction.
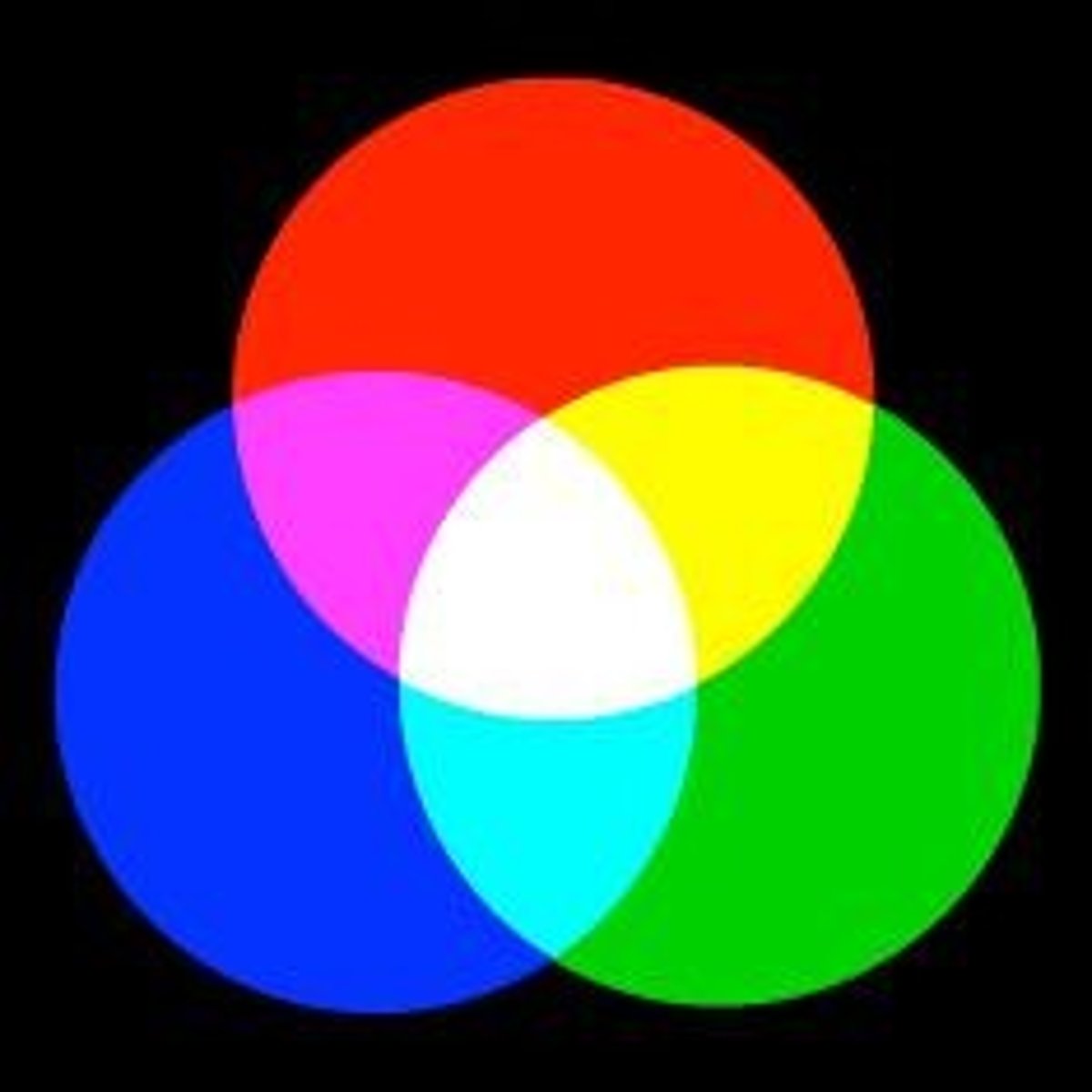
How does color mixing differ between lights and paints?
Mixing lights is additive (combining wavelengths), while mixing paints is subtractive (removing wavelengths from white light).
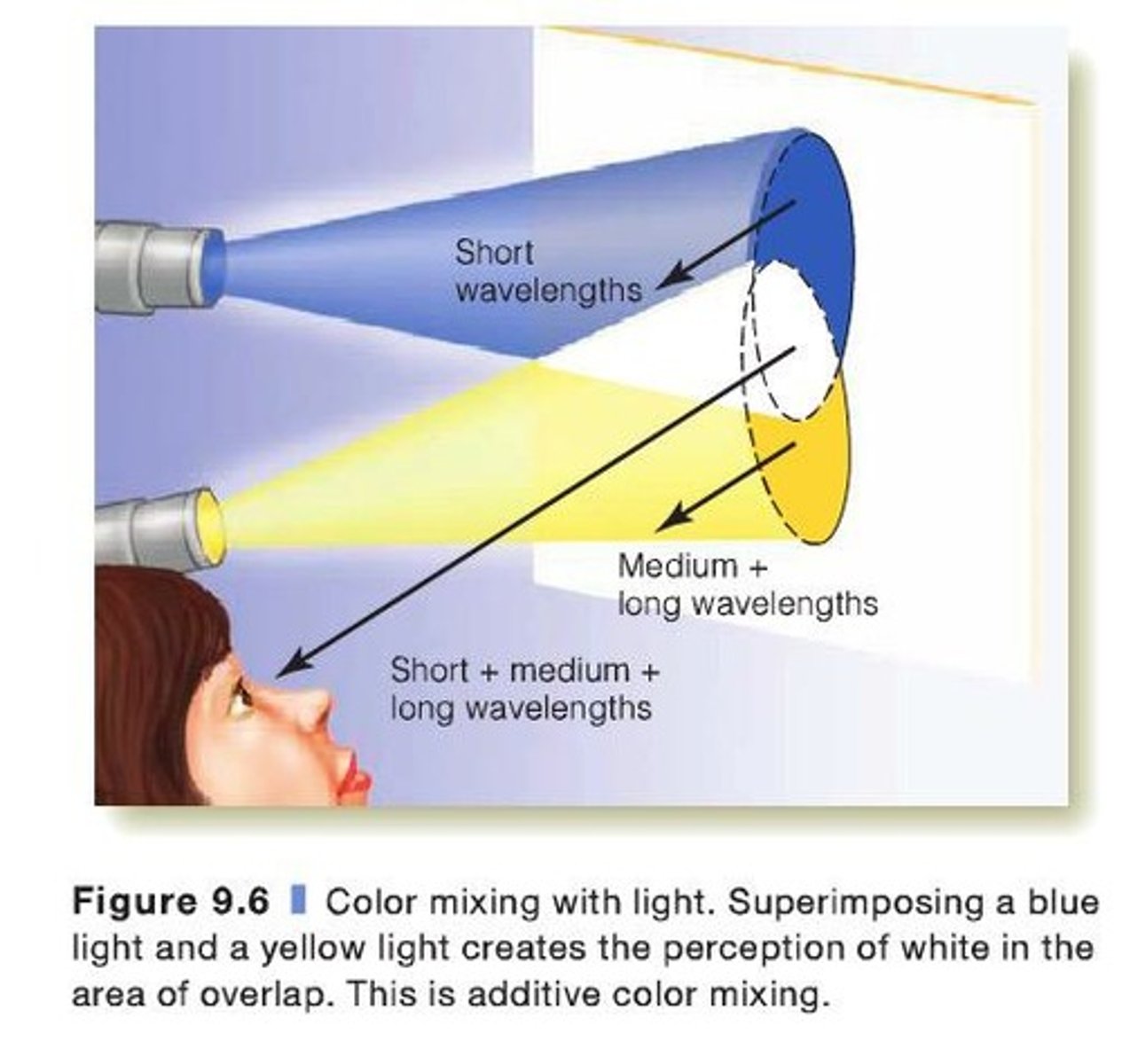
What is color blindness?
Color blindness is a condition where individuals have difficulty distinguishing certain colors, often due to the absence or malfunction of specific cone types.
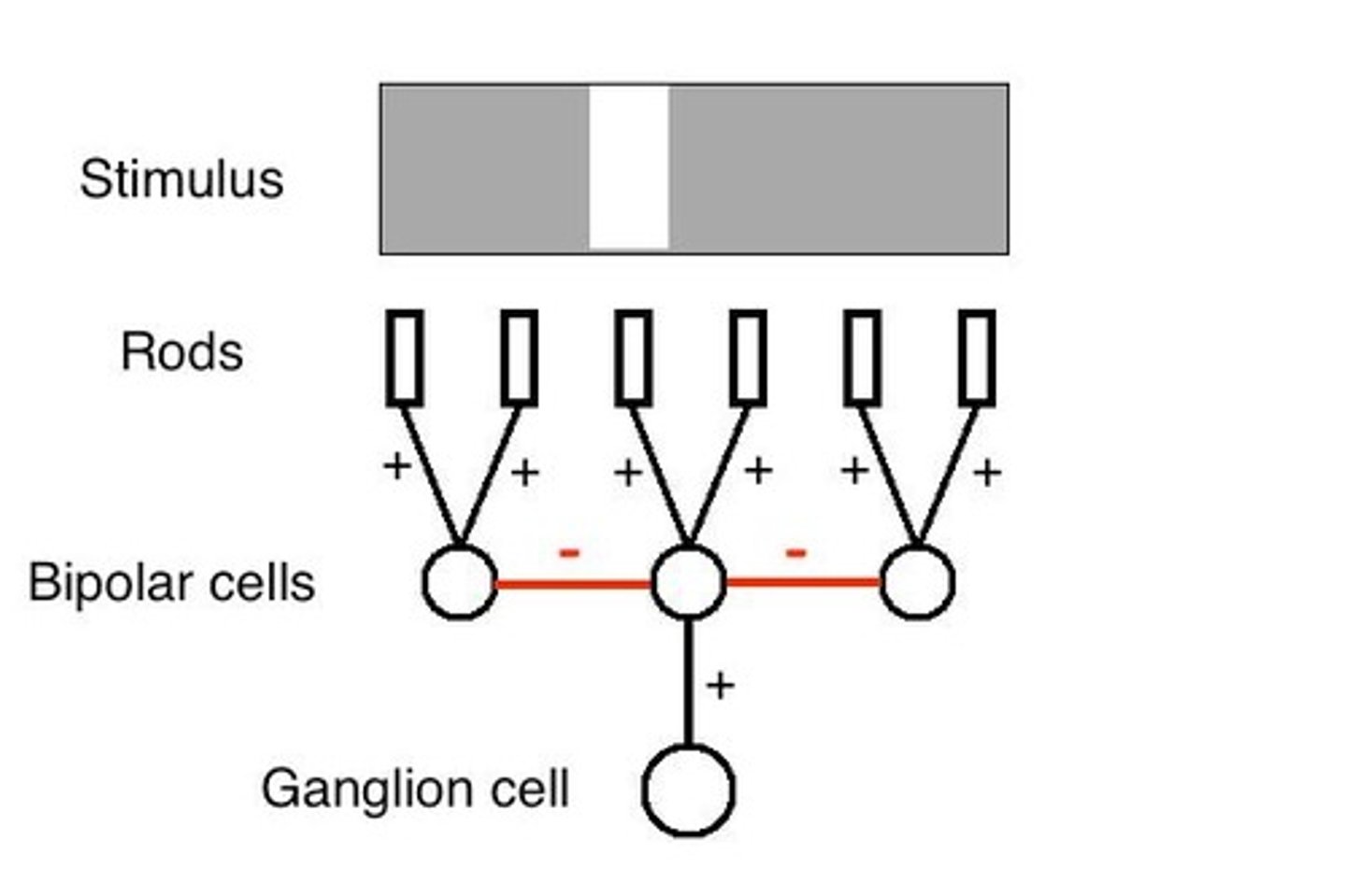
What is lateral inhibition?
Lateral inhibition is a process where the activation of one neuron reduces the activity of neighboring neurons, enhancing contrast in visual perception.
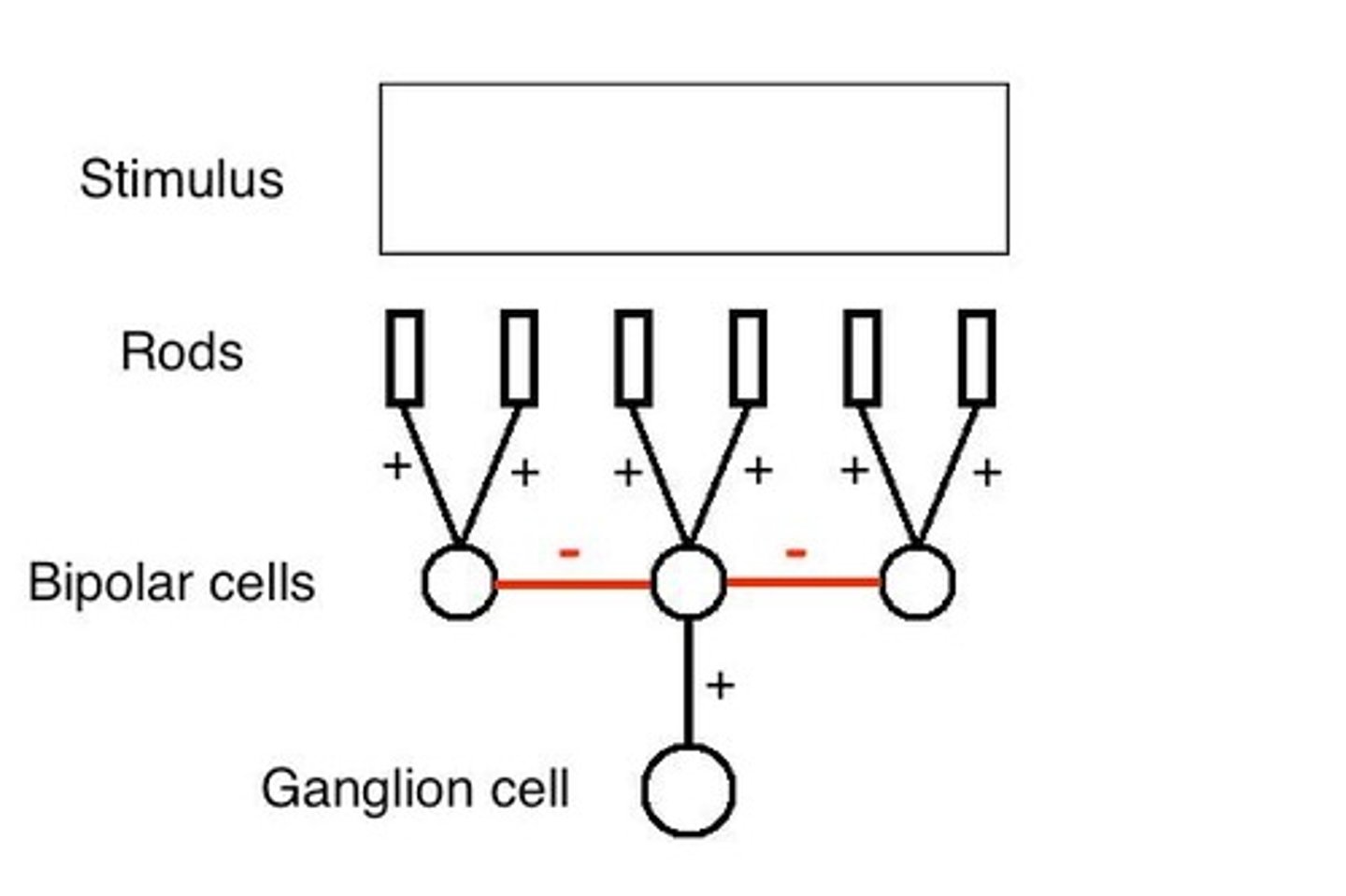
What are Mach bands?
Mach bands are optical illusions that enhance the perception of edges, where adjacent areas of different brightness are perceived as having greater contrast.
What is the response strength of ganglion cells to visual stimuli?
Ganglion cells show heightened responses to edges and regions of high contrast, with varying response strengths based on the visual stimulus.
What is the orientation tuning curve in V1?
The orientation tuning curve illustrates how individual V1 neurons respond preferentially to specific orientations of visual stimuli, with graded responses to similar orientations.
What is the significance of the center-surround receptive fields of ganglion cells?
Center-surround receptive fields allow ganglion cells to detect contrast by responding differently to light in the center versus the surrounding area.
What is the role of high-level cues in color illusions?
High-level cues can influence color perception, leading to illusions where colors appear differently based on context and surrounding colors.
What evidence supports the trichromatic theory?
Psychophysical evidence from color matching experiments demonstrates that people can match colors using three primary colors, supporting the trichromatic theory.
How do ganglion cells contribute to visual processing?
Ganglion cells process visual information by detecting contrast and edges, sending signals to the brain for further interpretation.
What is the relationship between ganglion cells and photoreceptors?
Peripheral ganglion cells pool over hundreds of photoreceptors, while foveal ganglion cells pool over just a few, contributing to the distortion in V1.
What is the primary role of V1 in visual processing?
V1 is responsible for processing basic visual information, such as orientation and contrast, before it is sent to higher visual areas.
What is the significance of the graded response of V1 neurons?
The graded response indicates that V1 neurons can respond to a range of stimuli, not just their preferred orientation, allowing for more nuanced visual processing.
What are ocular dominance columns?
They are columns in the brain where neurons have the same ocular dominance, responding to input from one eye or the other.
What happens to ocular dominance columns in a patient who has lost an eye?
In a patient who has lost an eye, only the neurons responding to the active eye are active, as seen in the dark stripes of a stained brain.
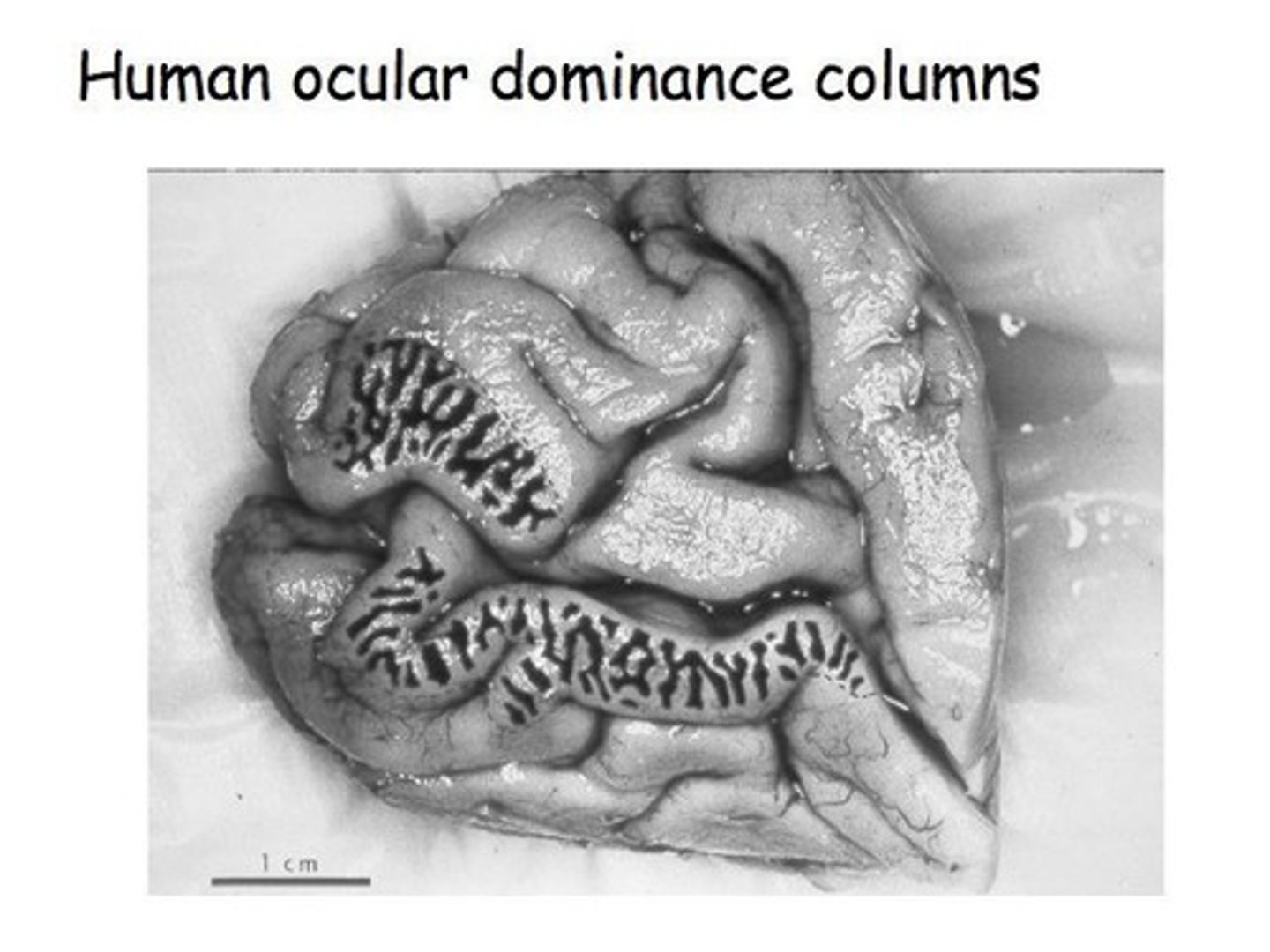
What do the dark and light stripes in a stained brain represent?
The dark stripes represent brain regions that have been recently metabolically active, corresponding to ocular dominance columns.
What is the organization of V1 neurons regarding orientation preferences?
V1 neurons show a gradual variation in orientation preferences, covering the entire range of orientations.
How is the organization of V1 at the individual neuron level characterized?
At the individual neuron level, V1 neurons show a preference for oriented edges and possibly moving in particular directions.
What is cortical magnification in V1?
Cortical magnification is the over-representation of the central region of the fovea in the spatial organization of V1, due to the convergence properties of rods and cones.
What are the functional columns in V1 responsible for?
Functional columns in V1 respond to different aspects of visual stimuli, including ocular dominance, orientation, and color.
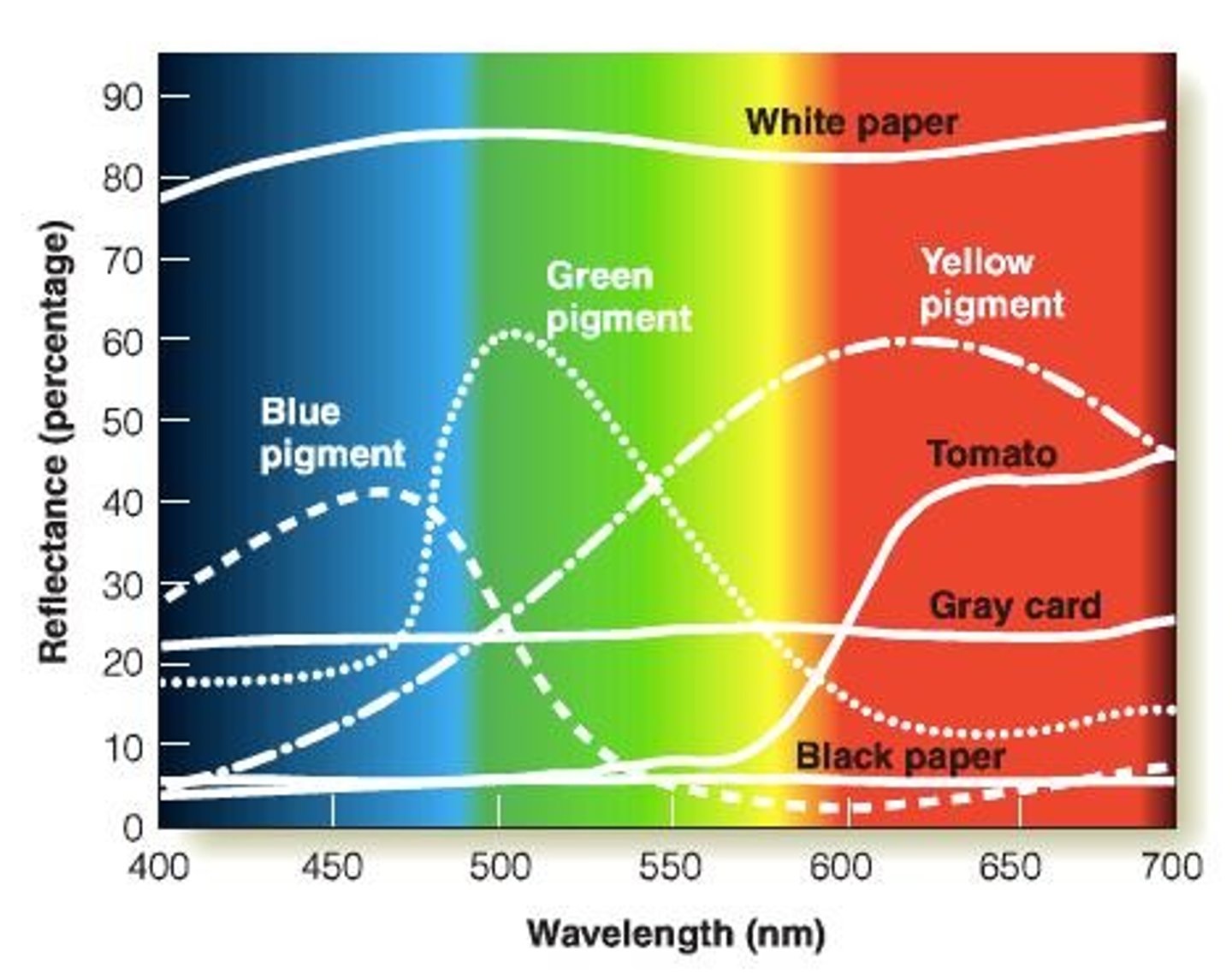
What is the visible spectrum?
The visible spectrum refers to the range of wavelengths that an object reflects, which determines the color we attribute to it.
What is selective reflection?
Selective reflection is the phenomenon where different objects reflect different ranges of wavelengths.
What is additive color mixing?
Additive color mixing occurs when different colors of light are combined, resulting in a new color.
What is subtractive color mixing?
Subtractive color mixing occurs when different pigments are mixed, absorbing certain wavelengths and reflecting others.
What is the trichromatic theory of color perception?
The trichromatic theory, proposed by Young and Helmholtz, states that there are three types of color receptors in the human visual system.
What did Young and Helmholtz conclude from their color matching experiments?
They concluded that three lights were sufficient to match all colors, providing a unique solution for every color match.
What types of cones were identified in the retina?
Three types of cones were identified that respond preferentially to short (419nm), middle (531nm), and long (558nm) wavelengths.
What is the typical distribution of cones in the retina?
The typical distribution includes three types of cones that correspond to different wavelengths of light.
How prevalent are color deficits in the population?
Color deficits affect about 1 in 12 men and 1 in 200 women, and they are present on the X-chromosome.
What are the types of color blindness?
There are various types of color blindness, which can affect how individuals perceive colors.
How do people with color deficits perceive colors differently?
People with color deficits see colors differently due to the absence or malfunction of certain types of cones in the retina.
What are the types of color blindness based on the distribution of cones on the retina?
Normal retina, Protanope retina.
How do people with color deficits perceive colors differently?
It is very hard to assess from verbal reports, but rare cases of unilateral dichromats can provide insight.
What can be inferred about color deficits based on color ratings?
We can make guesses based on the sets of colors that individuals with color deficits rate as similar or dissimilar.
What is the role of S cones and L cones in deuteranomaly?
Color vision in deuteranomaly depends on S cones and two forms of long-wave cones (L, Lʹ) that have different spectral sensitivities.
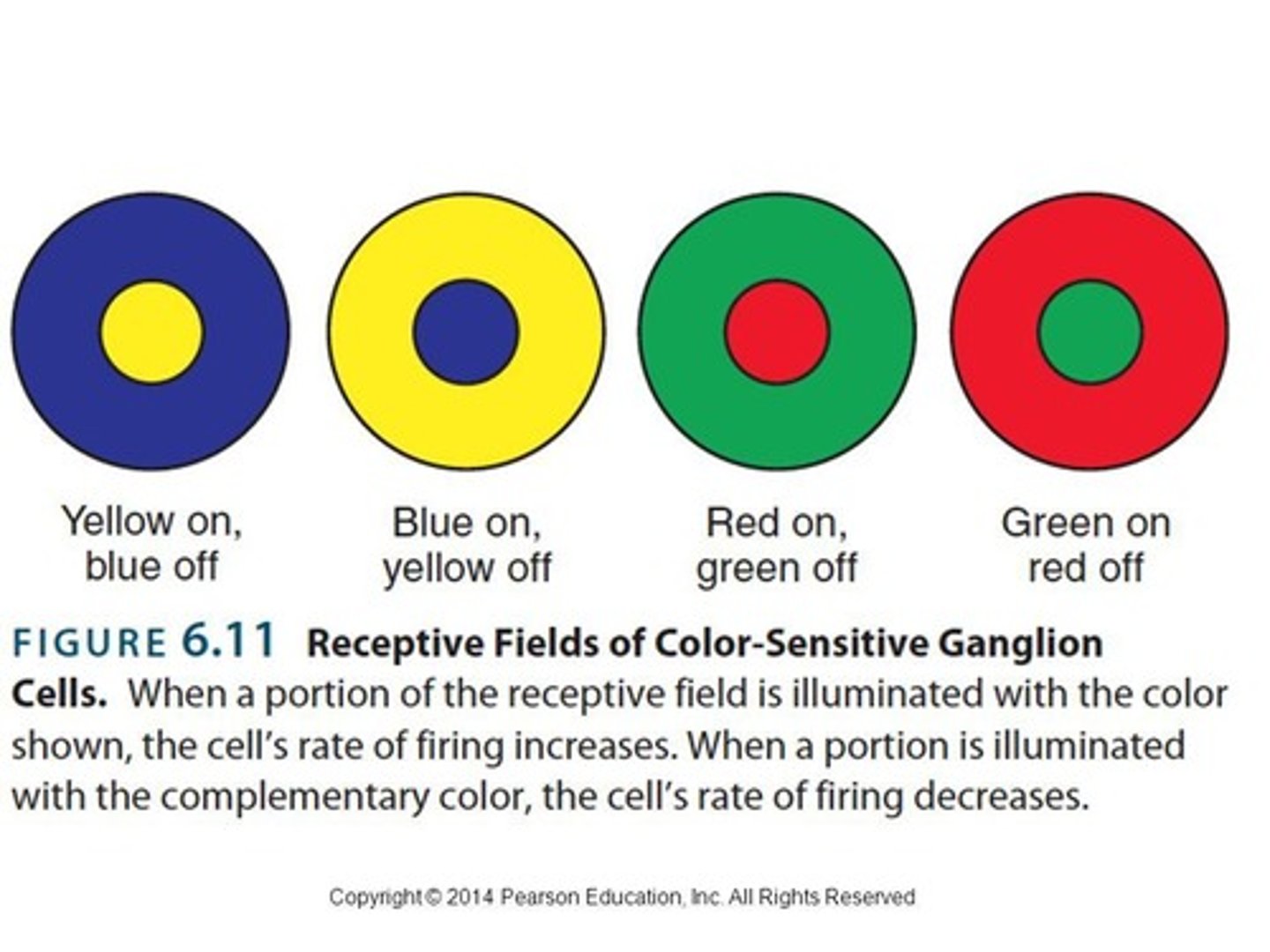
Who proposed the opponent-process theory of color vision and what are its three types of opponent channels?
Ering proposed the theory, which includes Black-White, Red-Green, and Blue-Yellow channels.
What evidence supports the opponent-process theory of color vision?
Evidence comes from color imagery, color aftereffects, and simultaneous color contrast.
What is an example of an exercise to demonstrate evidence from imagery?
Imagining the color red and then modifying it to be more yellowish or bluish.
What color aftereffects can be observed after staring at a black dot?
Green appears red, red appears green, blue appears yellow, and yellow appears blue.
What is the summary of color perception?
The relative responses of three types of cones give rise to basic color experience, influenced by excitatory and inhibitory processes with ganglion cells.
What is color constancy?
Color constancy is the ability to perceive colors consistently under varying lighting conditions.
What is the checker-shadow illusion and who created it?
The checker-shadow illusion, created by Ted Adelson, demonstrates how context affects color perception.
How does prior knowledge influence color perception?
Prior knowledge can create top-down influences on how colors are categorized and discriminated.
What effect does language have on color categorization?
The language spoken can affect how individuals categorize and discriminate colors, as shown in studies like Winawer et al. (2007).
What is a newer color illusion mentioned in the notes?
The afterimage after the image, by Rob van Lier & Mark Vergeer (2008).
What is the significance of color contrast effects?
Color contrast effects involve excitatory and inhibitory processes with ganglion cells, influencing how we perceive colors.
What is the relationship between higher-level processes and color perception?
Higher-level processes can influence how we perceive colors, even with the underlying mechanisms of color vision.
What are the implications of color vision deficiency tests?
They help in understanding how individuals with color deficits perceive and discriminate colors.
What is the challenge in assessing color perception in individuals with deficits?
It is challenging to assess color perception accurately through verbal reports.
What is the role of ganglion cells in color perception?
Ganglion cells are involved in the excitatory and inhibitory processes that contribute to color contrast effects.
What can be inferred from the study of color vision in deuteranomaly?
It suggests that the interaction between different types of cones can provide a useful chromatic signal.
What is the importance of color discrimination tests?
They reveal how individuals with color vision deficiencies perceive color differently from those with normal vision.
What is the homework assignment mentioned in the notes?
Homework 1 is due tomorrow (Friday) by midnight.
What chapter should be read for the next class?
Chapter 8 on motion perception.