16. session: instruments, altimetry
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Altimetry definition
The science that determines our vertical position with respect to a given surface or point
Why is knowledge on altitude important for the flight
Avoidance of Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT)
Separation with other aircraft
Some levels are more suitable than others in terms of
Efficiency
Safety: weather, avoiding turbulence and ice
Altitude definition
Vertical distance between the vehicle and Sea Level (AMSL)
AMSL stands for
Above Mean Sea Level
Height definition
Vertical distance between the vehicle and terrain (AGL)
AGL stands for
Above Ground Level
Elevation
The vertical position of a given obstacle placed on the surface of the Earth with respect to Sea Level
Which elements have a declared elevation?
Aerodromes
Certain thresholds
Radioaltimeter definition
An instrument that we use to measure height (vertical distance between vehicle and terrain)

How does the radioaltimeter work
Using a transmitter that sends a signal downwards and expects an echo.
When this echo is produced, the signal travels again upwards against the belly of the aircraft
A receiver can write down a timestamp
By measuring the difference of time between the meeting and receiving signals we can determine the distance between the aircraft and terrain, knowing that the wave is traveling at speed of light

Typical range of the altimeter, when important?
2500 ft, when next to the ground (during approach and take-off maneuvers)D
What does GPWS stand for
Ground Proximity Warning System
Radioaltimeter: connection with GPWS
The radio altimeter is a basic input in the Ground Proximity Warning System
The Ground Proximity Warning System will alert the crew when flying against an obstacle
When measuring a decrease in the height of the aircraft without any other meaningful input, such as extending the landing gear or extending the flaps, then the Ground Proximity Warning System may alert the crew that it is inadvertently flying against an obstacle, such as a mountain.
Radio altimeter is important during approach maneuvers (ILS approach)
Altimeters are
Barometers
Barometers definition
Instruments thatmeasure outside static pressure
Most important layers of atmosphere and its boundary
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Tropopause
The instruments we will use will be calibrated using the…, so we will have
ISA atmosphere, errors
QFE stands for
The static pressure at a given point on the surface of the earth, typically a runway threshold
What is QNE
Vertical distance of aircraft and the ficticious 1013.2 mb
P at SL ISA
Pref= 1013.2 mb
Flight levels
measured in flight levels: 100s of feet
Transition layer definition
The spacing between the Transition Altitude and Transition Level
T. Altitude lower than T. Level
It has to have at least 1000ft
Transition limits
Lowest (T. Level)
Highest (T. Altitude)
Which transition changes every day, Altitude or Level?, Why?
Transition Level, because it’s a function of QNH
What is QNH
MSLP (Mean Sea Level Pressure)
The vertical separation lowers when
Accuracy increases
Ability increases
Minimum separation of
1000 ft
The higher the altitude/FL, the ___ the accuracy of the instruments/altimeter
lower
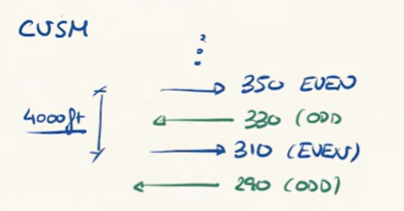
CVSM stands for
Conventional Vertical Aeparation Minimum
CVSM values
1000 ft for up to FL290
2000 ft for FL290 or above
RVSM stands for
Reduced Vertical Aeparation Minimum
Which FL where the most congested in the 1990s?
FL340 - FL400
RVSM values
1000ft up to FL410
2000ft if FL410 or above
To go from CVMS to RVSM
needs certification (aircraft, crew)
Even/Odd criteria
Set a direction as even and the other one as odd
Segment the odd and even flights in different FLs
Above FL410 it can be confusing, careful!
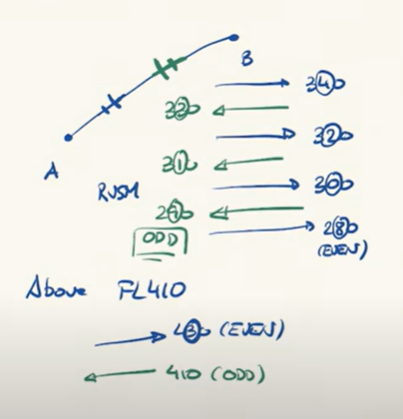
in CVSM the Even/Odd criteria is more confusing
very inneficient
Level Bust definition, minimum of
unauthorized vertical deviation on ATC clearance (Air Traffic Control)
Minimum value
CVSM: more than 300ft
RVSM: more than 200ft
Causes of Level Bust
Misunderstanding of read back in ATC clearance
wrong selection of FL in cockpit
misunderstanding of QNH QNE or the whole static ref P system
A Level Bust might induce a …
Airprox
Airprox definition
Air Proximity Incident: loss of separation between aircrafts
TCAS triggered
What does a variometer show, units?
Vertical speed, fpm
Artificial horizon
Instrument to measure the attitude of the plane (pitch and bank angle)
How does the artificial horizon work?
It has a spinning gyroscope inside, which maintains the rotation axis cte
PFD stands for
Primary Flight Display
PFD has
all the relevant information in terms of dynamic and navigation variables for the flight
what do PFD contain
altimeter
variometer
compass
artificial horizon
anemometer
autopilot selections, different flight modes
ND stands for
Navigation Display
ND shows
the relative position of the aircraft with respect to the selected route, with waypoints
Anemometry definition
the science behind the determination of the true airspeed of the aircraft (the speed of a/c wrt the mass of air around it)
the determination of TAS is strongly related to
the static pressure (Pt)