Comprehensive Guide to Accounting Principles and Standards
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What is the definition of accounting?
Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to permit informed judgment and decisions by users of information.
What are the three important activities in accounting?
1. Identifying - analyzing events and transactions to determine if they will be recognized. 2. Measuring - assigning numbers, usually in monetary terms, to economic transactions. 3. Communicating - transforming economic data into useful accounting information for users.
What are external events in accounting?
External events involve an external party and can include reciprocal transfers, non-reciprocal transfers, and other changes in economic resources or obligations caused by an external source.
What are internal events in accounting?
Internal events do not involve an external party and include production (transforming resources into finished goods) and casualty (unanticipated losses from disasters).
What are some measurement bases used in accounting?
1. Historical cost 2. Fair value 3. Present value 4. Realizable value 5. Current cost 6. Inflation-adjusted costs.
Which measurement base is most commonly used in accounting?
Historical cost is the most commonly used measurement base.
What is the basic purpose of accounting?
The basic purpose of accounting is to provide information about economic activities that is useful for making economic decisions.
What is general-purpose accounting information?
General-purpose accounting information is designed to meet the common needs of most statement users and is governed by the Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRSs).
What is special-purpose accounting information?
Special-purpose accounting information is designed to meet the specific needs of particular statement users, provided by types of accounting such as managerial accounting or tax basis accounting.
What is the double-entry system in accounting?
The double-entry system records each accountable event in two parts: debit and credit.
What does the going concern concept imply?
The going concern concept assumes that the entity will carry on its operations for an indefinite period of time.
What is the separate entity concept in accounting?
The separate entity concept treats the entity as distinct from its owners.
What does the stable monetary unit concept state?
The stable monetary unit concept states that amounts in financial statements are stated in a common unit of measure, ignoring changes in purchasing power.
What is the time period concept in accounting?
The time period concept divides the life of a business into a series of reporting periods.
What is the materiality concept?
The materiality concept states that information is material if its omission or misstatement could influence economic decisions.
What is the cost-benefit concept in accounting?
The cost-benefit concept asserts that the cost of processing and communicating information should not exceed the benefits derived from it.
What is the accrual basis of accounting?
The accrual basis of accounting recognizes the effects of transactions when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
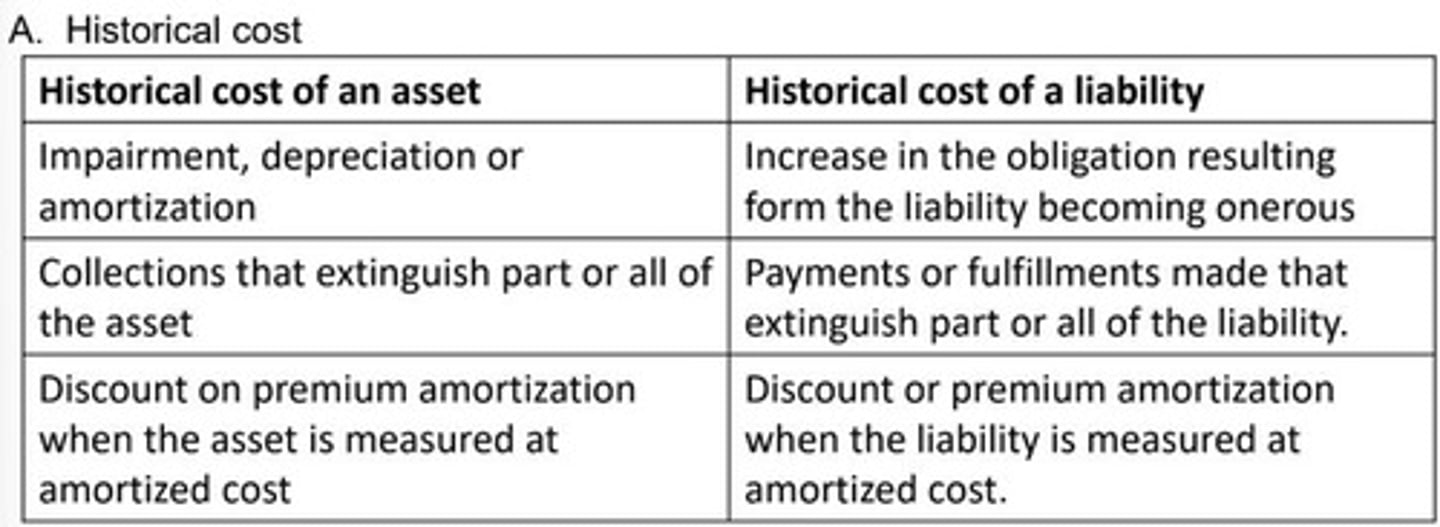
What is the historical cost concept?
The historical cost concept determines the value of an asset based on its acquisition cost.
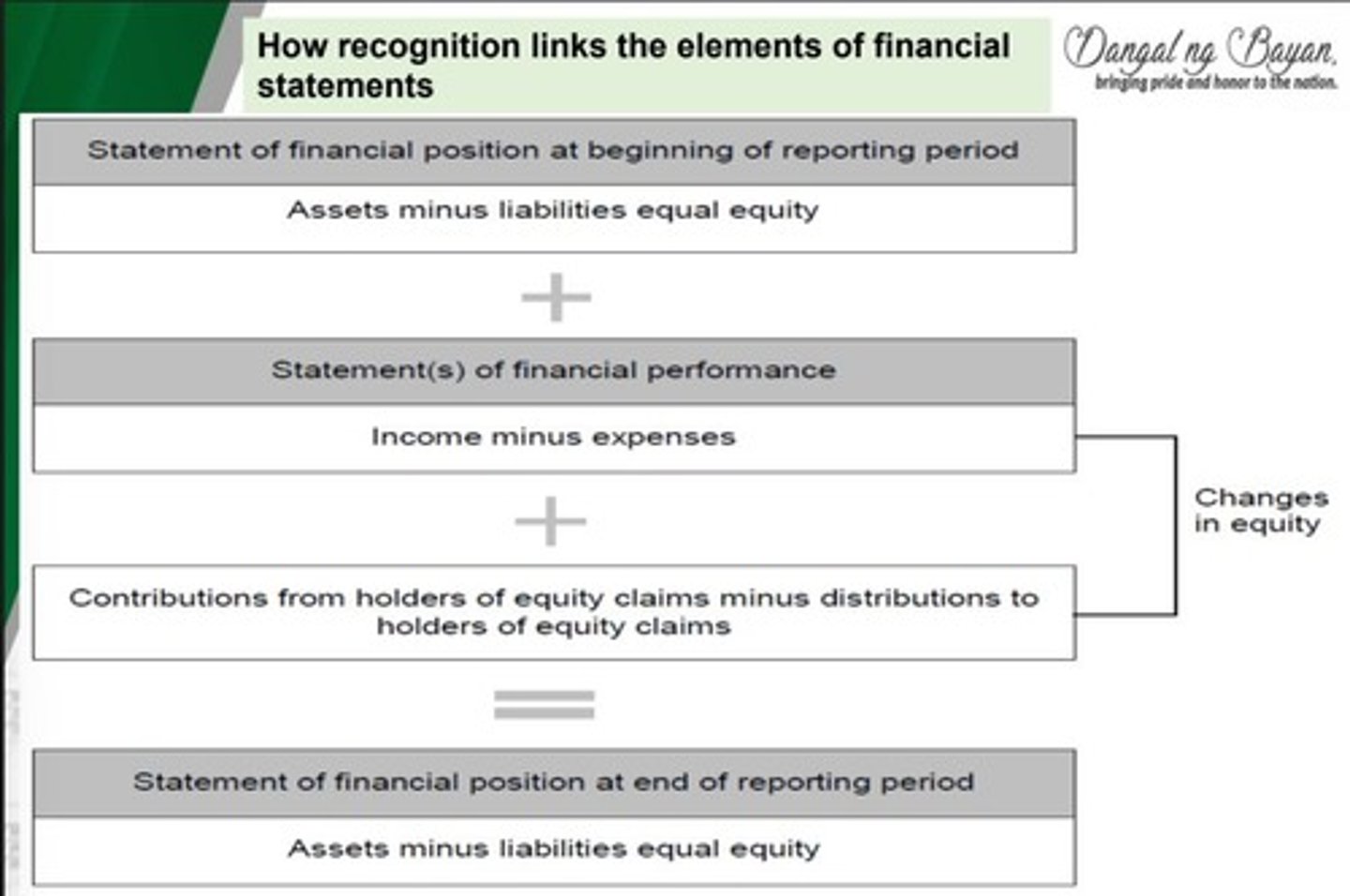
What is the concept of articulation in accounting?
The concept of articulation states that all components of a complete set of financial statements are interrelated.
What is the full disclosure principle?
The full disclosure principle requires financial statements to provide sufficient detail to disclose important matters while remaining understandable and considering the costs of preparation.
What is the consistency concept in accounting?
Financial statements are prepared based on accounting policies applied consistently from one period to the next.
What does the matching principle in accounting state?
Costs are recognized as expenses when the related revenue is recognized.
What is the residual equity theory?
This theory applies when there are two classes of shares, ordinary and preferred, and is expressed as 'Assets - Liabilities - Preferred Shareholders' Equity = Ordinary Shareholders' Equity.'
What is the focus of fund theory in accounting?
The accounting objective is the custody and administration of funds.
What does realization refer to in accounting?
The process of converting non-cash assets into cash or claims for cash.
What is the principle of prudence (conservatism) in accounting?
It involves exercising caution in judgments to ensure assets or income are not overstated and liabilities or expenses are not understated.
What is financial accounting?
It focuses on general purpose financial statements.
What is management accounting?
It focuses on special purpose financial reports for use by an entity's management.
What does cost accounting involve?
The systematic recording and analysis of the costs of materials, labor, and overhead related to production.
What is the purpose of auditing?
To evaluate the correspondence of certain assertions with established criteria and express an opinion thereon.
What does tax accounting encompass?
The preparation of tax returns and rendering of tax advice, including determining tax consequences of business endeavors.
What is government accounting?
It refers to accounting for the government and its instrumentalities, emphasizing the custody of public funds and accountability.
What is the practice of public accountancy?
It involves rendering audit or accounting-related services to multiple clients on a fee basis.
What does practice in commerce and industry entail?
Employment in the private sector requiring professional accounting knowledge and typically necessitating CPA certification.
What is the focus of practice in education/academe?
Employment in educational institutions teaching accounting, auditing, finance, business law, and related subjects.
What does practice in government involve?
Employment in a government accounting professional group or government-owned corporation requiring professional accounting knowledge.
What are Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRSs)?
Standards and Interpretations adopted by the Financial Reporting Standards Council, including PFRSs, Philippine Accounting Standards (PASs), and Interpretations.
Why is there a need for reporting standards in accounting?
Entities should follow a uniform set of generally acceptable reporting standards to avoid misleading financial statements.
What does 'generally acceptable' mean in the context of accounting standards?
It means the standard is established by an authoritative accounting rule-making body or has gained acceptance through practice over time.
How are financial accounting standards established?
Through a democratic process where a majority of practicing accountants must agree on a standard before it is implemented.
What is the purpose of the Conceptual Framework in accounting?
To assist the International Accounting Standards Board in developing consistent Standards, help preparers create consistent accounting policies, and aid in understanding and interpreting the Standards.
What are the three main contributions of the Conceptual Framework to financial reporting?
It promotes transparency, strengthens accountability, and contributes to economic efficiency.
How does a single, trusted accounting language benefit capital markets?
It lowers the cost of capital and reduces international reporting costs.
What is the hierarchy of reporting standards in accounting?
1. PFRS Accounting Standards 2. Judgment.
What assumption is financial reporting typically based on regarding the entity's future?
The going concern assumption, which assumes the entity will continue operations for the foreseeable future.
What defines a reporting entity?
A reporting entity is an entity that is required or chooses to prepare financial statements.
What are the three aspects of the definition of an asset?
1) Right 2) Potential to produce economic benefits 3) Control.
What criteria must be satisfied for a liability to exist?
1) The entity has an obligation 2) The obligation is to transfer an economic resource 3) The obligation is a present obligation resulting from past events.
How is equity defined in relation to an entity's assets and liabilities?
Equity is the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities.
What are the two types of claims that constitute equity?
1) Shares issued by the entity 2) Obligations of the entity to issue another equity claim.
What constitutes income in financial reporting?
Increases in assets or decreases in liabilities that result in increases in equity.
What should management consider when making judgments about financial reporting?
Requirements in other PFRSs dealing with similar transactions and the Conceptual Framework.
What additional resources may management consider in financial reporting?
Pronouncements from other standard-setting bodies and other accounting literature and industry practices.
What is the objective of general-purpose financial reporting?
To provide financial information about the reporting entity that is useful for existing and potential investors, lenders, and other creditors.
Who are the primary users of financial reporting?
Existing and potential investors, lenders, and creditors.
What is one specific objective of financial reporting?
To provide information useful in making decisions about providing resources to the entity.
What is the significance of the Conceptual Framework for preparers of financial statements?
It assists them in developing consistent accounting policies when no Standard applies or when a choice of accounting policy is allowed.
How does the Conceptual Framework enhance the quality of financial information?
By promoting international comparability and transparency.
What role does the Conceptual Framework play in reducing the information gap between capital providers and management?
It strengthens accountability by providing clearer financial reporting.
What is the relationship between the Conceptual Framework and economic efficiency?
It helps investors identify opportunities and risks, improving capital allocation.
What is the reporting period in financial statements?
The specified period for which financial statements provide information on assets, liabilities, and equity.
What does the going concern assumption imply for financial statements?
That the reporting entity is expected to continue its operations in the foreseeable future.
What are the elements of financial statements?
Assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses.
What is the importance of the definition of an asset in financial reporting?
It establishes the criteria for recognizing economic resources controlled by the entity.
What is the purpose of providing information in financial reports?
To assist in decision-making regarding resource allocation, assess cash flow prospects, and provide details about entity resources and claims.
What are the fundamental qualitative characteristics of useful financial information?
Relevance (including predictive and confirmatory value) and Faithful Representation (including completeness, neutrality, and freedom from error).
What does relevance in financial information entail?
It includes predictive value and confirmatory value.
What does faithful representation in financial information require?
It requires completeness, neutrality, and being free from error.
What are the enhancing qualitative characteristics of financial information?
Comparability, verifiability, timeliness, and understandability.
What is the objective of financial statements?
To provide financial information about the reporting entity's financial position and performance.
How are expenses defined in financial reporting?
Expenses are decreases in assets or increases in liabilities that result in decreases in equity, excluding distributions to equity holders.
What is recognition in financial reporting?
The inclusion of an item in the financial statements that meets the definition of one of the financial statement elements.
What is derecognition in financial reporting?
The removal of all or part of a recognized asset or liability from the statement of financial position.
What does measurement refer to in financial statements?
The quantification of financial statement elements in monetary terms.
What is fair value in the context of current value measurement?
The price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
What is value in use for assets?
The present value of the cash flows or other economic benefits expected to be derived from the use of an asset and its ultimate disposal.
What is current cost in financial measurement?
The cost of an equivalent asset at the measurement date, including consideration and transaction costs.
What is the role of presentation and disclosure in financial reporting?
To communicate information about assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses effectively.
What are the principles of effective communication in financial statements?
Focus on presentation and disclosure objectives, classify similar items, and aggregate information without obscuring details.
What is classification in financial reporting?
The sorting of assets, liabilities, equity, income, or expenses based on shared characteristics for presentation and disclosure.
What does offsetting mean in financial reporting?
Recognizing and measuring both an asset and liability separately but reporting them as a single net amount.
What is aggregation in financial reporting?
The addition of assets, liabilities, equity, income, or expenses that share characteristics and are included in the same classification.
What is the financial concept of capital?
Capital is regarded as the invested money or purchasing power, including equity, net assets, and net worth.
How is physical capital defined?
Physical capital is regarded as the entity's productive capacity, exemplified by units of output per day.
What constitutes financial capital maintenance?
A profit is earned only if the financial amount of net assets at the end of the period exceeds that at the beginning, excluding distributions and contributions from owners.
In what units can financial capital maintenance be measured?
Financial capital maintenance can be measured in nominal monetary units or units of constant purchasing power.
What is physical capital maintenance?
A profit is earned only if the physical productive capacity at the end of the period exceeds that at the beginning, excluding distributions and contributions from owners.
What are general purpose financial statements?
General purpose financial statements are intended to serve users who do not have the authority to demand tailored financial reports, catering to a wide range of external users.
What is the requirement for measuring assets in financial statements according to PAS 1?
Assets must be measured net of valuation allowances, such as obsolescence allowances, allowances for doubtful accounts, and accumulated depreciation.
How often must an entity present a complete set of financial statements?
An entity must present a complete set of financial statements at least annually.
What must an entity disclose when changing the end of its reporting period?
The period covered by the financial statements, the reason for using a longer or shorter period, and the fact that amounts presented are not entirely comparable.
What is required regarding comparative information in financial statements?
An entity must present comparative information for the preceding period for all amounts reported in the current period's financial statements.
What is the consistency of presentation in financial statements?
An entity must retain the presentation and classification of items from one period to the next unless a significant change in operations or a PFRS requires a change.
When is an additional statement of financial position presented?
It is presented when an entity applies an accounting policy retrospectively, makes a retrospective restatement, or reclassifies items, and the effect is material.
What are the two types of presentation for a statement of financial position?
A statement of financial position may be presented as classified (distinguishing current and noncurrent items) or unclassified (based on liquidity).
What criteria classify an asset as current?
An asset is classified as current if it is expected to be realized or consumed in the normal operating cycle, held for trading, or expected to be realized within twelve months after the reporting period.
What is management's responsibility regarding financial statements?
The financial statements are fundamentally the responsibility of the company's management.
What is the significance of the Conceptual Framework and PFRSs?
They provide the guidelines and standards for the preparation of general purpose financial statements.
What must be excluded when calculating financial capital maintenance?
Distributions to and contributions from owners during the period must be excluded.
What is the effect of not presenting comparative information?
It may lead to a lack of context and comparability for users analyzing the financial statements.