Exam 3 Intro to Animal Science Study Guide
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the marbling scores discussed in class for beef?
Slight to moderately abundant or BMS 1 to BMS 12
What were the four main impacts of the Federal Meat Inspection Act on the US meats industry?
1. Antemortem inspection of all livestock before slaughter 2. Postmortem inspection of every carcass. 3. Sanitary conditions in all meat processing facilities 4. Authorize the USDA to monitor and inspect all harvesting and processing operations.
What are growth implants, beta-agonists, and antibiotics? Why are all three of these compounds used in the livestock industry?
Growth implants are hormones used to increase rate of growth and weight gain. Beta-agonists are chemicals used to shift nutrients away from fat production to promote lean muscle growth. Antibiotics are a treatment used to prevent and treat illnesses in livestock animals. These compounds are used because they impact cutability and meat quality. Important from farm to processor.
What are the six nutrients horses need for survival?
water, protein, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, vitamins
What are the yield grades for beef, pork, and lamb?
Beef: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Pork: 1, 2, 3, 4
Lamb: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
What are the quality grades for beef, pork, and lamb?
Beef: prime, choice, select, standard, utility, cutter, canner
Pork: U.S, U.S utility
Lamb: Prime, choice, good, utility, cull
What are the three components of a syringe? Please describe each component as well.
Needle: a sharp hollow piece of metal which pierces the skin
Barrel: where the medication is held
Plunge: a device that pushes the medication or vaccine through the needle into the animal
What are the three common injection methods utilized in livestock? Please describe each technique.
Intramuscular: given in the animals muscle
Subcutaneous: given under the skin but above the muscle
Intravenous: given in the jugular vein
What are the three different types of vaccinations discussed in class? Please describe each type of vaccination along with giving an example of that type of vaccination.
Inactivated: contains bacteria or viruses which have been inactivated by heat or chemicals ex. Ingelvac
Subunit: are created using new combinations of DNA ex. Porcine circovirus type 2
Modified-live: contains live viruses ex. Bluetounge vaccine type 10
What differentiates a “horse” from a ‘pony’?
14.2 hands divides the horse from the pony

Below, you need to identify the different face markings.
Star

Below, you need to identify the different face markings.
Snip

Below, you need to identify the different face markings.
Stripe

Below, you need to identify the different face markings.
Blaze
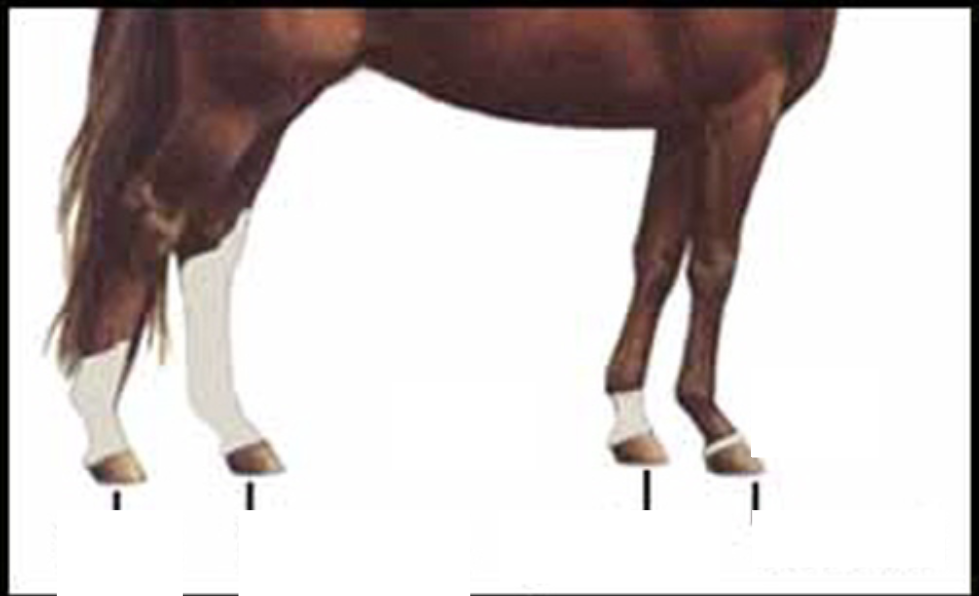
Below, you need to properly identify the different leg markings.
Sock, stocking, pastern, coronet
What is a sign in each of the following livestock species (cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses) that a female is in estrous?
Cattle: redness of vulva, restlessness
Sheep: standing to be ridden by a male
Pigs: vocalization, erect ears
Horses: nervousness, frequent urination
What is the gestation length for the following species in days, not months? cows, ewe/doe, sow, and mare
Cow: 275 days
Ewe/doe: 147 days
Sow: 114 days
Mare: 336 days
Please define hormones and give two different ones for females and males discussed in class.
Hormones are a chemical substance that is carried by the blood stream to target an organ and elicit a consistent response. Two examples are luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
T or F: An intact male horse is a gelding.
false
T or F: Horses are classified as non-ruminant hind gut fermenters
true
T or F: Quarter horses make up the largest horse population in the U.S
true
T or F: The largest part of the digestion tract for a horse is the small intestine
false
T or F: The federal meat inspection act paved the way for the FDA
false
T or F: Meat palatability includes the following attributes: tenderness, juiciness, and flavor
true
T or F: Grass tetany is a nutritional disease in cattle
true
Where did the Brahman cattle originate from?
two of the above
What are the breeds that compose the composite breed Beefmaster?
brahman, hereford, shorthorn
What segment is responsible for producing breeding stock?
purebred/seedstock
What segment feeds high energy diets in confinement?
feedlot