Particles and nuclides
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Electron info
Electrons orbit nucleus, electron is a fundamental particle
Plum pudding model
Represented atoms as tiny electrons embedded in positively charged background of uniform density
Specific charge
Ratio of charge to mass Q/m
What has largest specific charge
Electrons
Notation
A on top - protons and neutron's (mass number)
Z on bottom - number of protons (proton number)
An isotope
An atom of an element with a specific number of neutrons
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons and different number of neutrons
Ions
Have different number of protons to electrons
Diameter of nucleus
Is of the order 10^-15m
Diameter of an atom
10^-10m
Repulsion and attraction strong nuclear force
Repulsive between 0 and 0.5fm
Attraction between 0.5fm and 3fm
Strong nuclear force function
Holds the nucleus together
How does nucleus stay together
Positive protons repel each other through electrostatic force
So held together by a stronger force through strong nuclear
This attracts neutrons to each other within a small range of distance between them
Types of radioactive decay
Alpha decay
B- decay
B+ decay
Alpha decay
Nucleus emits 4 2 a alpha particle with 2 protons 2 neutrons
Thing becomes new element bc dif number of protons
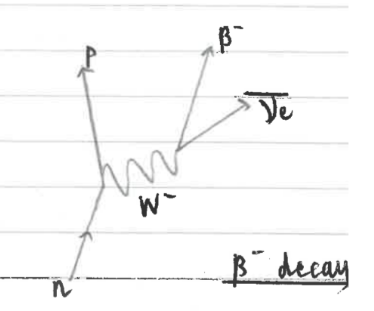
B- particle
high energy electron
emitted from neutron rich nuclei
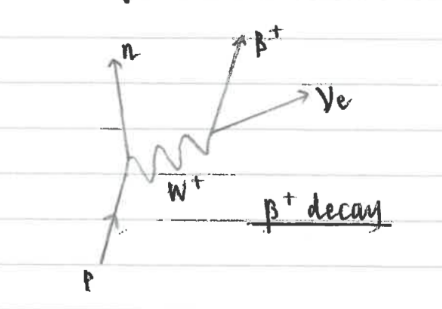
B+ particle
B+ particle is an antimatter electron, a positron
Emitted from proton rich nuclei
Need for neutrino
B particles have range of energies
Neutrino also emitted to carry away missing energy and momentum
Existence of neutrino hypothesised to account for conservation of energy and momentum in beta decay
Gamma radiation
High energy penetrating electromagnetic radiation
Gamma decay
Nucleus loses energy but doesn't change to a different isotope
Antiparticles
Equal mass but opposite properties
eV to J
x 1.6x10^-19
energy of photon equation
rest energy of particles + surplus energy (appears as kinetic energy)
Pair production conditions
if the energy of a photon is greater than 2mc squared (total rest energy)
what happens during pair production
photon converts all its energy into particle-antiparticle pair
annihilation
a particle and corresponding antiparticle collide and their mass becomes energy in two gamma photons travelling in opposite directions (to conserve momentum)
example of application of annihilation
PET scanner
four fundamental interactions
strong nuclear (strong interaction)
weak nuclear
electromagnetic
gravity
what do 4 fundamental forces act through
exchange particles
exchange particle for strong nuclear
pions moving between nucleons
exchange particles for weak nuclear
W bosons
exchange particles for electromagnetic force
virtual photons
strong nuclear force details
can be experienced by particles that contain quarks
involved in production of kaons
weak nuclear force
involved in B decay and in decay of particles with strangeness and where strangeness isn’t conserved
B+ decay diagram
B- decay diagram
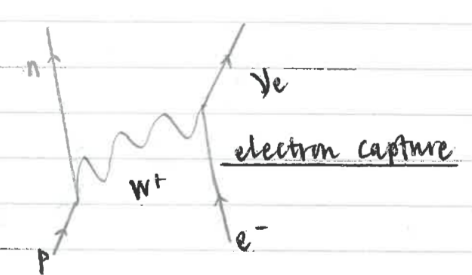
electron capture diagram
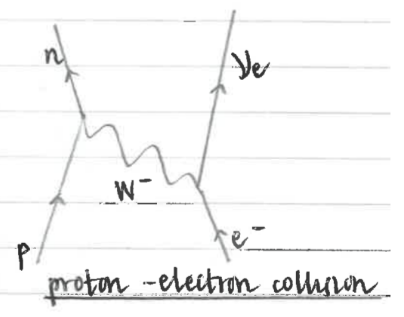
proton-electron collision diagram
electron capture
proton in nucleus captures inner shell electron - decays into a neutron
electron capture features
occurs in nuclei which are proton rich
after, x-ray photon is emitted because an electron falls down energy levels to fill vacancy left by captured electron, releasing energy as a photon
electron capture equation thing
AZ X + 0-1 e- becomes A Z-1 Y + neutrino
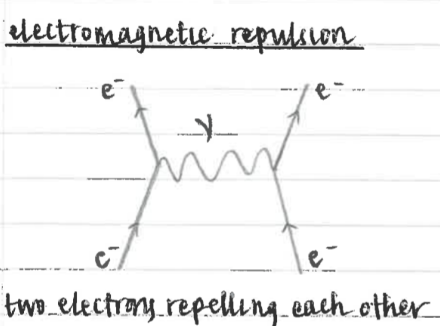
two electrons repelling each other diagram
two positrons repelling each other diagram
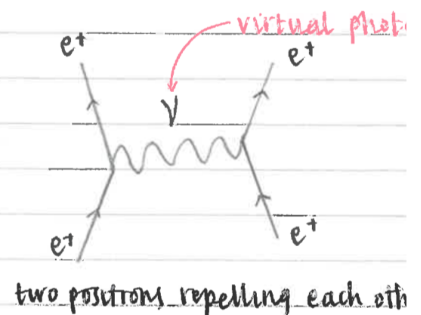
what are feynman diagrams used for
representing reactions or interactions in terms of particles going in and out, and exchange particles
2 classifications of a particle
hadron and lepton
2 classifications of hadron
mesons and baryons
free neutron info
unstable
decay via weak interaction forming proton, B- particle and electron antineutrino
quarks in B- and B+ decay
B- d quark changes into u quark, B+ u quark into d quark
what are virtual particles
real particles that exist for a very short time