11. Social Structure & Demographics (13%)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Social Structure
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
A system of people within a society organized by a characteristic pattern of relationships.
It's the framework—both micro (small groups, networks) and macro (societal institutions)—that organizes social life beyond individual whims.
Symbolic Interactionism
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
The study of how individuals interact through a shared understanding of words, gestures, and other symbols
Pioneered by George Herbert Mead
According to this theory, humans are different from lower animals in that lower animals simply respond to stimuli, while humans have the capability to interpret the stimulus first, then react
Symbols
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
Things to which we attach meaning
Can be an object, image, sound, or action
It is anything that carries meaning beyond its own existence
Social Constructs
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
Any idea that has been created and accepted by the people in a society
EX: symbols
Social Constructionism
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
Focuses on how individuals put together their social reality by communicating and working together to agree on the significance of a concept or principle
A theory that reality, knowledge, and meaning aren't inherent but are created and shaped by our social interactions, language, and cultural contexts, emphasizing that concepts like gender, race, and even health are shared understandings that evolve, not fixed truths.
It posits that we collectively build our understanding of the world through communication and agreement, influencing how we perceive ourselves and others.
Useful for explaining micro- and meso-level sociological phenomena
Rational Choice Theory
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
Focuses on decision-making in an individual
Claims that people weigh the costs and benefits when making choices, ranking their options based on maximizing perceived benefit
Influenced by the study of economics
An individual carefully considers all of the possible rewards and punishments of each social action and chooses the option that results in the greatest social benefit
Useful for explaining some micro- and meso-level sociological phenomena (except for charitable, illogical, selfish, or altruistic behavior)
Exchange Theory
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
Extension of rational choice theory that focuses on interactions in groups
People evaluate whether there is reciprocity and balance in social relationships
Views relationships as a cost-benefit analysis, where individuals seek to maximize rewards (companionship, support) and minimize costs (time, effort, conflict) in social interactions, deciding to maintain or end relationships based on perceived fairness and profitability
Conflict Theory
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
Focuses on how power differentials contribute to the maintenance of social order
Individuals in the group with more power attempt to preserve their power by shaping the structure of society itself
For the more powerful in society, maintenance of the status quo is usually desirable and, for the less powerful, change comes through disruption and revolution
Useful for explaining macro-level sociological phenomena
Based on the works of Karl Marx
Structural-Functionalism
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
The study of the structure and function of each part of a society
The inverse of Conflict Theory
Views society as interconnected parts (institutions like family, education) working together to maintain stability, much like organs in a body
Durkheim compared society to an organism and proposed that each group in society has a role to play in the overall health and operation of society
Dysfunctions
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Dysfunctions vs. Manifest Functions vs. Latent Functions
The harmful consequences of people's actions as defined by Structural-Functionalism
Negative consequences that destabilize the system (e.g., crime, drug abuse in schools).
Manifest Functions
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Dysfunctions vs. Manifest Functions vs. Latent Functions
The intended positive consequences of people's actions as defined by Structural-Functionalism.
The purpose is understood by society members and is clearly states and observable.
EX: A school’s purpose to educate; healthcare’s purpose to cure illness and promote wellness; law enforcement’s purpose to maintain public safety and enforce laws
Latent Functions
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Dysfunctions vs. Manifest Functions vs. Latent Functions
The unintended positive consequences of people's actions as defined by Structural-Functionalism.
The unintended, unrecognized, and often hidden consequences of social actions, institutions, or structures.
They aren't immediately obvious or acknowledged by participants.
EX: within education → teaching obedience, social skills, and serving as a matchmaking venue.
Feminist Theory
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
WORD BANK: Symbolic Interactionism, Rational Choice Theory, Social Constructionism, Conflict Theory, Exchange Theory, Feminist Theory, Structural-Functionalism
——
Critiques the institutional power structures that disadvantage women in society
Originally developed as an offshoot of conflict theory
Glass Ceiling
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Glass Escalator vs. Glass Ceiling
Processes that limit the progress of women to the highest job positions because of invisible social barriers to promotion, as defined by Feminist Theory
Glass Escalator
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Glass Escalator vs. Glass Ceiling
Invisible forces that sometimes push men up to higher positions even in cases where men do not seek to climb the job ladder, as defined by Feminist Theory
Social Institutions
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
Well-established social structures that dictate certain patterns of behaviors or relationships and are accepted as a fundamental part of culture
Regulate the behavior of individuals in core areas of society
Stable, enduring patterns of organized beliefs, behaviors, and relationships (like family, government, education, economy, religion) that meet fundamental societal needs, provide structure, regulate individual actions through norms, and form the framework for social order and cultural values.
They act as societal "backbones," guiding how people interact, learn roles (socialization), and understand their world, influencing self-perception and social justice.
Exist at the meso-level of sociological analysis
Hidden Curriculum
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
The social norms, attitudes, beliefs and other things that are not directly taught in schools but is inherently included within education.
Teacher Expectancy
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
The idea that teachers tend to get what they expect from their students
A teacher who places high demands on students but who also believes that students can rise to the challenge is more likely to see students succeed than a teacher who places the same demands but doubts that the students can achieve them
Religiosity
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
How religious a person considers themselves to be
Includes the strength of religious beliefs, engagement in religious practices, and attitudes about religion itself
Secularization
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
The movement from a world dominated by religion to a world dominated by science and rationality.
Fundamentalism
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
When a religion is rigid and resists secularization by strictly adhering to their religious code.
Sick Role
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
The role undertaken by patients who are ill
Such patients are not responsible for their illness and are exempt from social roles, but a patient has the obligation to want to become well and to seek out competent help
Beneficence, Nonmaleficence, Respect for Patient Autonomy, Justice
Sociology: Theories & Institutions
The 4 key tenets of American medicine.
Beneficence
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Key Tenets of American Medicine
WORD BANK: Nonmaleficence, Beneficence, Justice, Respect for Patient Autonomy
——
A physician is obligated to act in the patient's best interest.
Nonmaleficence
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Key Tenets of American Medicine
WORD BANK: Nonmaleficence, Beneficence, Justice, Respect for Patient Autonomy
——
Do no harm.
Respect for Patient Autonomy
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Key Tenets of American Medicine
WORD BANK: Nonmaleficence, Beneficence, Justice, Respect for Patient Autonomy
——
A physician must honor the decisions made by the patient.
Justice
Sociology: Theories & Institutions - Key Tenets of American Medicine
WORD BANK: Nonmaleficence, Beneficence, Justice, Respect for Patient Autonomy
——
A physician has the responsibility to treat similar patients with similar care, and to distribute resources fairly.
Material Culture
Culture
The physical items one associates with a given group such as artwork, emblems, clothing, jewelry, foods, buildings, and tools
Meaning of objects in a given society
Often a tangible embodiment of the underlying ideas of symbolic culture
Symbolic Culture (aka Nonmaterial Culture)
Culture
The shared, non-material aspects of a society—like language, beliefs, values, ideas, norms, gestures, and rituals—that people use to create meaning, communicate, and understand their world, differentiating humans and forming the core of social identity and interaction
May be encoded in mottos, songs, or catchphrases, or may simply be themes that are pervasive in the culture
Culture Lag
Culture
The gap or delay when symbolic culture (beliefs, norms, values) struggles to adapt to rapid changes in material culture (technology, physical inventions), leading to social problems, confusion, or conflict as old customs clash with new realities
EX: whereas American culture still prizes individuality and privacy, the development of smartphones and social media push toward a more community-oriented and less private world
Cultural Barriers
Culture
When a culture impedes interaction with others.
Obstacles from differing beliefs, values, norms, or communication styles that block understanding, leading to misinterpretation, mistrust, and conflict between people from different backgrounds
Ritual
Culture
A formalized ceremony that usually involves specific material objects, symbolism, and additional mandates on acceptable behavior
Tend to have a prescribed order of events or routine
Life Course Approach (or Perspective)
Demographics
Considering an individual’s age and cumulative life experiences when analyzing their personality, social status, health, and other social metrics
Gender Stratification
Demographics
Any inequality in access to social resources that is based on gender
May occur in the presence of gender inequality
Race
Demographics - Race vs. Ethnicity
Socially constructed groupings of people based specifically on inherited phenotypic characteristics.
Ethnicity
Demographics - Race vs. Ethnicity
Socially constructed groupings of people based on cultural factors such as shared language, cultural heritage, religion, and/or national origin
Symbolic Ethnicity
Demographics
A specific connection to one's ethnicity in which ethnic symbols and identity remain important, even when ethnic identity does not play a significant role in everyday life
EX: Irish Americans in the US celebrating St. Patrick’s Day
Demographic Shifts
Demographics
Changes in the makeup of a population over time
Can be measured considering the population density
Fertility Rate
Demographics
The average number of children born to a woman during their lifetime in a population
In many parts of the world, this is the primary driver of population expansion
Mortality Rate
Demographics
The number of deaths in a population per unit time
Serve as a significant brake on population growth in many parts of the world
Migration
Demographics
The movement of individuals into or out of a place
Contributor to population growth
Can be motivated by both pull factors and push factors
Immigration
Demographics - Immigration vs. Emigration
Migration INTO a place.
Emigration
Demographics - Immigration vs. Emigration
Migration OUT OF a place.
Pull Factors
Demographics - Pull vs. Push Factors
Positive attributes of the new location that attracts new residents
Influences immigration
Push Factors
Demographics - Pull vs. Push Factors
Negative attributes of the old location that encourage existing residents to leave
Influences emigration
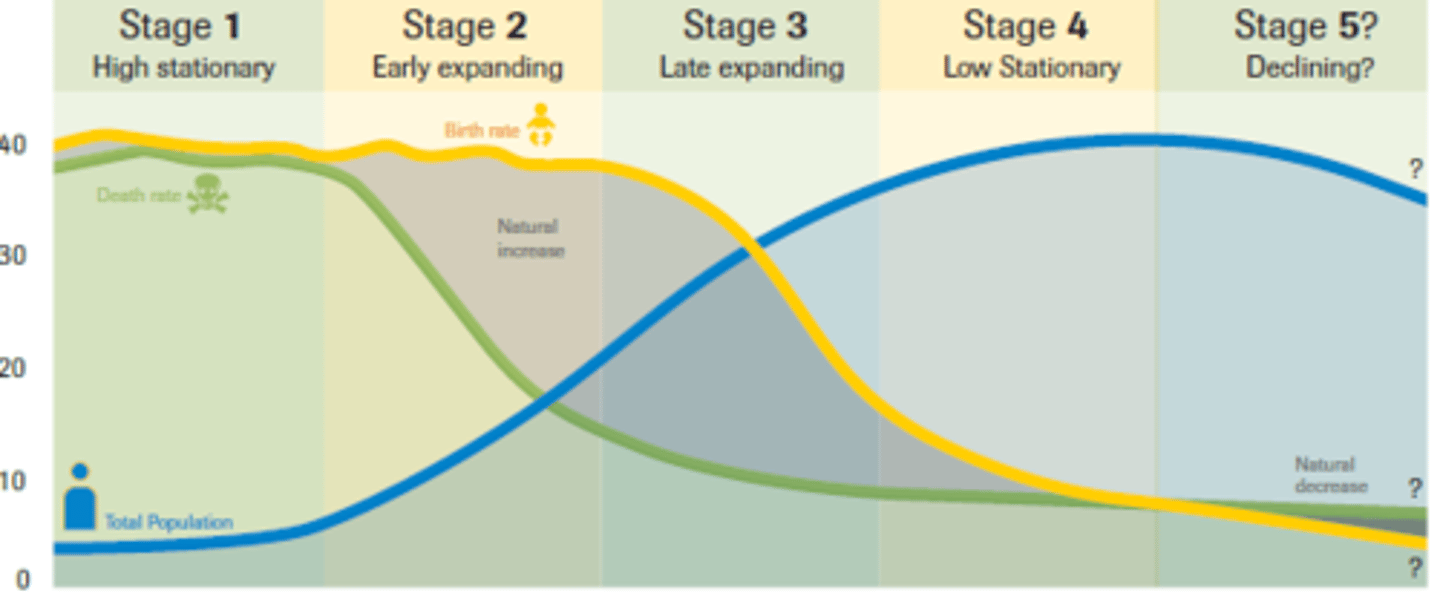
Demographic Transition
Demographics
A specific example of demographic shift in which a country moves from high birth/death rates to low birth/death rates through time.
Can be seen when a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrial economic system.
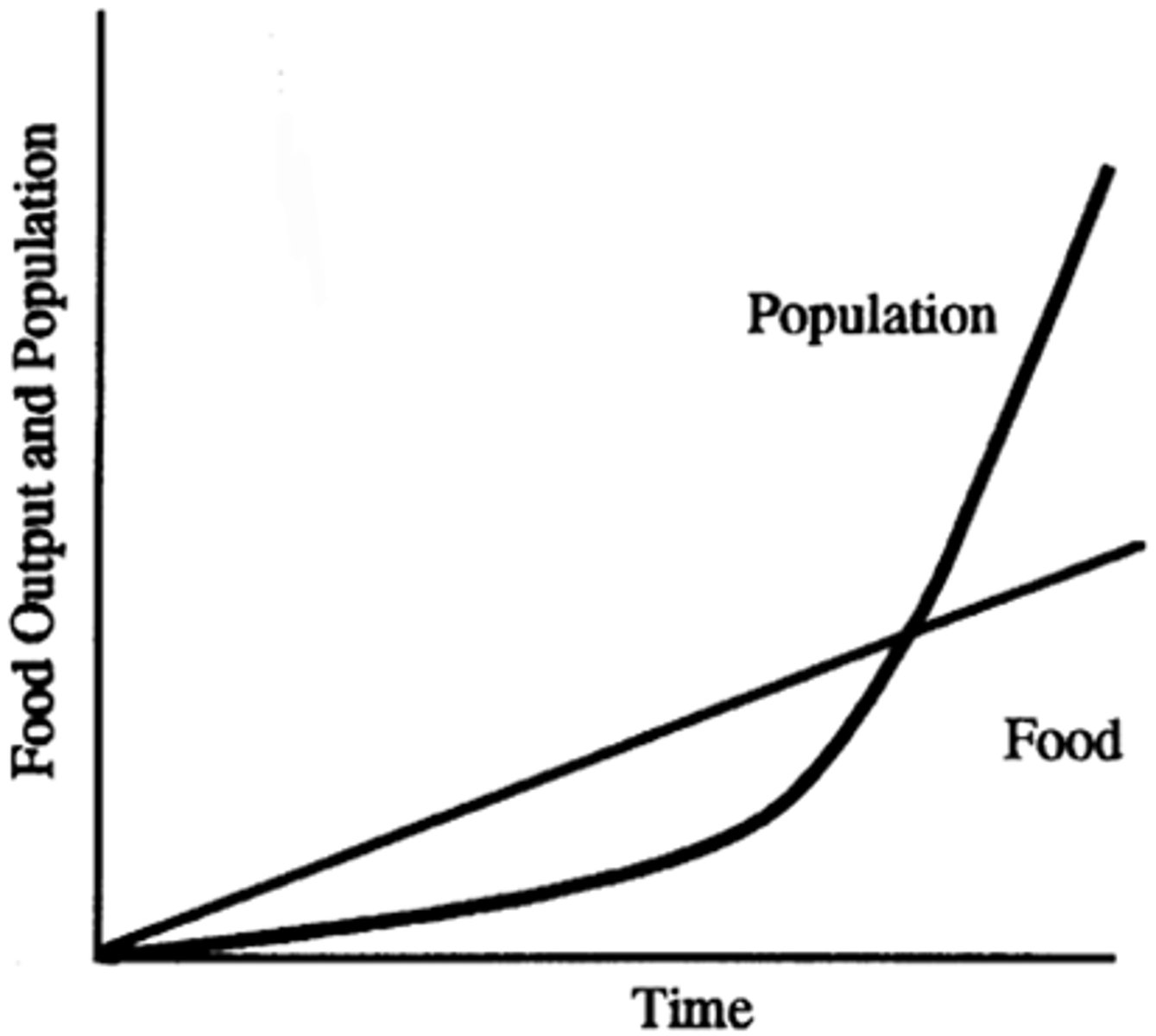
Malthusian Theory
Demographics
Theory focusing on how the exponential growth of a population can outpace the growth of food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder, resulting in a hypothetical mass starvation.
Similar to the death phase in bacteria when resources in the environment have been depleted.
Relative Deprivation
Demographics
A decrease in resources, representation, or agency relative to the whole of society, or relative to what the group is accustomed to in the past
Often motivates social movements
Proactive
Demographics - Proactive vs. Reactive
Describes social movements that PROMOTE social change.
Reactive
Demographics - Proactive vs. Reactive
Describes social movements that RESIST social change.
Globalization
Demographics
The practice of integrating the global economy with free trade and the tapping of foreign markets
Leads to a decrease in the geographical constraints on social and cultural exchanges and can lead to both positive and negative effects