Proteins: Structures and Diversity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Name the subunits (monomers) of proteins
Animo acids
Generalized amino acid structure
Alpha carbon, Amino group, Hydrogen, Carboxyl group (COOH), Variable R side Chain
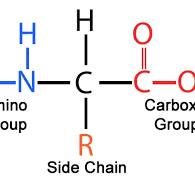
In one amino acid, the central carbon atom (also known as alpha carbon) is bound by a single covalent bond to an H atom and to three other groups of atoms which are ______, ______, ______
Amino, Carboxyl, Side or R
How many different amino acids are found commonly in living things?
20
Primary structure of protein
The type, number, and order of animo acids in the chain which varies from protein to protein.
The linear sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain
Primary structure of protein
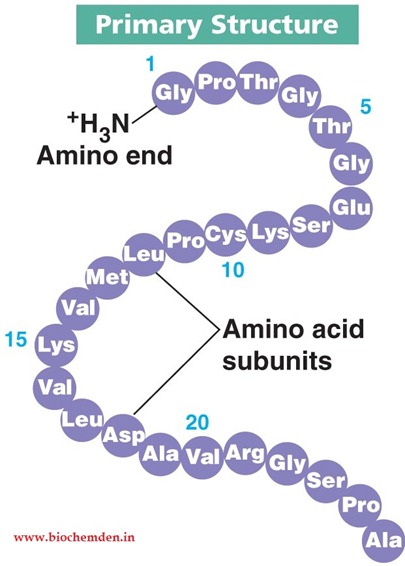
The secondary protein structure
when various function groups (R groups) exposed on the outer surface of the molecule interact by forming hydrogen bonds
The hydrogen bonds cause the amino acid to twist into a coiled configuration called the _____ _____ or to fold into an accordion pattern called a ___ ____ _____
Alpha helix
Beta-pleated sheet
How can one amino acid and another amino acid within the same polypeptide join together through hydrogen bonding to make a helix or pleated sheet
They are held in shape by hydrogen bonds that form between the Carbonyl O & Amino H
Tertiary structure
additional bonds between functional groups in secondary structure to form a 3D mass
Where does the interaction occur in teriatry structure
R groups
What kind of bond makes tertiary structure stable
covalent disulfide bonds
Quaternary Structure
more than one polypeptide form a large, multiunit protein
_______ structure is typical of antibodies and some enzymes that act in cell synthesis
Quaternary
Can proteins perform their normal functions when they are denatured?
No
How do enzymes affect the reaction rate?
Increase the rate of reaction
Catalysts
What can denature proteins?
heat, acid, alcohol, and some disinfectants disrupt (denature) the stabilizing bonds within the chains
What is lactase an example of?
An enzyme
What does lactase break down in the body? (disaccharide)
Lactose
Lactase breaks down Lactose into which two monosaccharides?
Glucose and Galactose
What are defense proteins?
antibodies
What hormone (protein) allows glucose from the blood to endter the body
insulin
What type of bonds are formed between adjacent amino acids?
Peptide
Are all proteins enzymes?
NO