Small Ruminant Medicine - Ram Fertility & Internal Parasites
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
When should you perform a BSE?
10-12 weeks prior to joining
2
New cards
Briefly describe your approach to perform a ram breeding soundness examination.
Check the 5Ts
1. Toes → check for lameness
2. Torso → BCS should be 3.5-4
3. Teeth → age and wear
4. Testicles → check the skin, contents and wool cover
5. Tossle > check the penis
1. Toes → check for lameness
2. Torso → BCS should be 3.5-4
3. Teeth → age and wear
4. Testicles → check the skin, contents and wool cover
5. Tossle > check the penis
3
New cards
What is the desirable minimum scrotal circumference of a normal 2-year-old Merino ram for good semen quality and quantity?
32cm = 400ml testicular volume
4
New cards
Define cryptorchidism and monorchidism.
**Cryptorchidism:** one or both testes fails to descend into scrotum
**Monorchidism:** only one testis or only one descended into scrotum
**Monorchidism:** only one testis or only one descended into scrotum
5
New cards
What agent causes pizzle rot and describe its pathogenesis?
Corynebacterium renale
Pizzle rot may develop when bacteria are present + high concentration of urea in urine (protein rich diet, alkaline urine)→ bacteria produce ammonia → cytotoxic → damage spizzle membranes and external skin
Pizzle rot may develop when bacteria are present + high concentration of urea in urine (protein rich diet, alkaline urine)→ bacteria produce ammonia → cytotoxic → damage spizzle membranes and external skin
6
New cards
Outline the aetiology, treatment and management of pizzle rot in wethers.
Corynebacterium renale
* Isolate the infected animals
* Flushing pizzle with mild antiseptic
* Acidy the urine by restricting protein rich diet
* Move to less clover (protein-rich)
* Ammonium chloride in the water
* Slit the pizzle to drain urine and pus if severe
* Isolate the infected animals
* Flushing pizzle with mild antiseptic
* Acidy the urine by restricting protein rich diet
* Move to less clover (protein-rich)
* Ammonium chloride in the water
* Slit the pizzle to drain urine and pus if severe
7
New cards
What agent causes knob rot and describe its pathogenesis?
Trueperella pyogenes
Paraphimosis (foreskin stuck behind glands penis)→ necrosis and ulceration of penis often with extensive blood clots in prepuce
Paraphimosis (foreskin stuck behind glands penis)→ necrosis and ulceration of penis often with extensive blood clots in prepuce
8
New cards
What causes testicular degeneration in rams?
Increased temperature → increased testicular degeneration
1. Hot weather
2. Overweight rams
3. Fever
4. Septicaemia
5. Excessive wool over the scrotum
6. Scrotal thickening
1. Hot weather
2. Overweight rams
3. Fever
4. Septicaemia
5. Excessive wool over the scrotum
6. Scrotal thickening
9
New cards
How is Brucellosis ovis transmitted?
Transmitted venereally or sexual behaviour
* By joining
* By homosexual activity (ram to ram)
* By rams snigging vulvas (intranasal infection)
* By joining
* By homosexual activity (ram to ram)
* By rams snigging vulvas (intranasal infection)
10
New cards
What is the pathogenesis of B. ovis?
* Initially swelling in the tail of epididymis, may form granulomas or develop into abscesses → **epididymis is enlarged & hard**
* Rams show no signs of sickness
* Semen quality from infected rams **may vary**
* Rams show no signs of sickness
* Semen quality from infected rams **may vary**
11
New cards
You suspect B. ovis in your ram flock. How would you deal with a possible breakdown in flocks accredited free from *B.ovis?*
**THERE IS NO TREATMENT FOR B.OVIS**
1. **Test and slaughter:** palpate ALL rams and kill those positive for serology
2. **Total replacement:** sell ALL and replace with brucellosis-free rams
3. **Two-flock system:** separate infected flock with new flock
1. **Test and slaughter:** palpate ALL rams and kill those positive for serology
2. **Total replacement:** sell ALL and replace with brucellosis-free rams
3. **Two-flock system:** separate infected flock with new flock
12
New cards
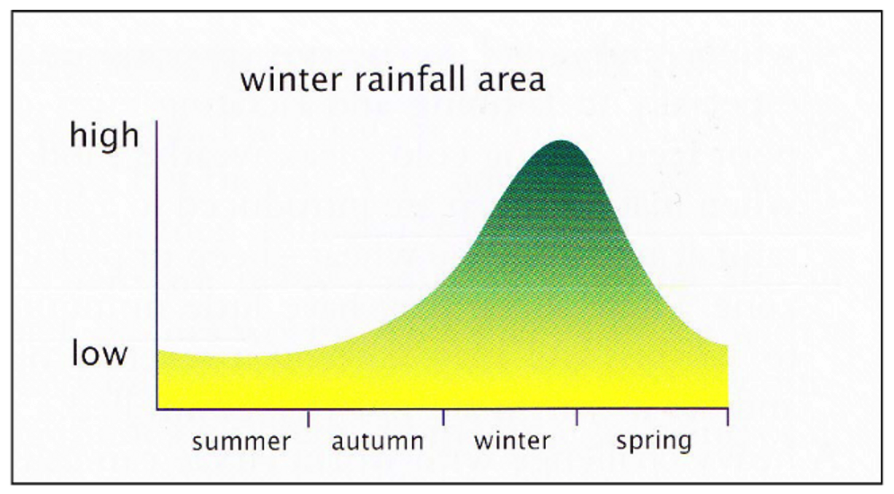
Which parasites are of concern in this zone?
Main Peak → decreases due to dilation effect as grass volme increases (proportion of grass is higher than worms)
* Telodorsagia circumcincta (Small Brown Stomach Worm)
* Trichostrongylus spp. (Black Scour Worm)
* Telodorsagia circumcincta (Small Brown Stomach Worm)
* Trichostrongylus spp. (Black Scour Worm)
13
New cards
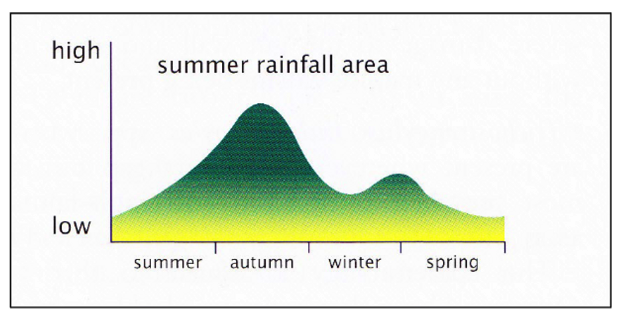
What parasites are of concern in this zone?
Main Peak → drops in winter due to decreased temperature
* Haemonchus contortus (Barber’s pole worm)
Winter Peak
* Telodorsagia circumcinta
* Trichostrongylus spp.
* Haemonchus contortus (Barber’s pole worm)
Winter Peak
* Telodorsagia circumcinta
* Trichostrongylus spp.
14
New cards
What are the three types of rainfall pastoral zones?
1. Winter Rainfall
2. Summer Rainfall
3. Low Rainfall
15
New cards
What are examples of parasitic drugs in drenches with sustained activity/persistent and when should you use them?
You should use persistent drugs when you have animals that you won’t have access to for prolonged preiods of time i.e. pre-lambing ewes
* Closantel
* Moxidectin
\
* Closantel
* Moxidectin
\
16
New cards
Which parasitic drug in drenches has no recorded anthelmintic resistance so far?
Derquantel (only available in combination with abamectin)
17
New cards
What defines as ‘anthelmintic resistance’?
The ability of parasites to survive doses of drugs that would normally kill parasites of the same species and stage
18
New cards
How does anthelminthic resistance develop?
1. Underdosing
2. Freqeunt dosing
3. Using the incorrect drug
4. Use of single active drenches
5. Persistant anthelmintics
19
New cards
What is ‘refugia’?
The population of parasites that are not exposed to the drug i.e. in the enviornment or in untreated animals
20
New cards
How would you detect and control anthelmintic resistance on your property?
* Regular drench resistance testing → DrenchCheck and Drench Test (worm egg count reduction test)
* Use effective productions, and in combination (multi-active > single active)
* Compare WEC and larval differentiations from treatment group to untreated group
* Do not underdose
* Do not use short-acting products
* Quaratine drench any introduced sheep in a secure quaratine paddock
* Minimise drenching and maintain good refugia
* Genetic selection for parasite immunity (moderately heritable)
* Maintain good BCS
* Use effective productions, and in combination (multi-active > single active)
* Compare WEC and larval differentiations from treatment group to untreated group
* Do not underdose
* Do not use short-acting products
* Quaratine drench any introduced sheep in a secure quaratine paddock
* Minimise drenching and maintain good refugia
* Genetic selection for parasite immunity (moderately heritable)
* Maintain good BCS
21
New cards
Define a ‘smart drench’ and a ‘tactical/therapeutic drench’.
**Smart Drench**: given at a **critical time** to reduce worm larval contamination **irrespective to worm egg counts**
**Tactical/Therapeutic Drench**: given when sheep are suffering from effects of worms and **based on worm egg counts**
**Tactical/Therapeutic Drench**: given when sheep are suffering from effects of worms and **based on worm egg counts**
22
New cards
Which combinations of anthelminthics is the least likely to show resistance when used to control Telodorsagia (ostertagia) circumcincta in sheep in south east SA?
Use a combination of minimum 4 unrelated drench active with at least one of these being the ‘newest’ drench actives: monepantel or derquantel ± liver fluke treatment
1. Albendazole
2. Levamisole
3. Abamectin
4. Derquantel or Monepantel
1. Albendazole
2. Levamisole
3. Abamectin
4. Derquantel or Monepantel
23
New cards
*Haemonchus contortus* is most commonly found in the?
Abomasum
24
New cards
Use of which of the following products is most likely to cause the development of anthelmintic resistance by sheep nematodes?
A. Moxidectin injections
B. Levamisole oral drench
C. Ivermectin oral drench
D. Napthalophos oral drench (organophosphate)
A. Moxidectin injections
B. Levamisole oral drench
C. Ivermectin oral drench
D. Napthalophos oral drench (organophosphate)
Broad spectrum benzidimazoles and levamisoles
B. Levamisole oral drench
B. Levamisole oral drench
25
New cards
Resilience and resistance play an important part in developing a sustainable worm program in an intensive sheep production system.
What is the difference between resistance and resilience?
What is the difference between resistance and resilience?
**Resilient:** large number of parasites based on fecal egg count testing and does not have to be dewormed based on FAMACHA and other clinical signs
**Resistant:** does not have a lot of parasites despite being exposed to a large number of parasite eggs
**Resistant:** does not have a lot of parasites despite being exposed to a large number of parasite eggs
26
New cards
Aside from leaving a paddock destocked, outline TWO (2) other methods you could use to make a paddock low worm-risk?
1. Use cattle or horses to graze on the paddock
2. Exclude sheep, goats or alpacas from the paddock
3. Grow a crop or make hay/silage