Lecture 4: Forebrain
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
forebrain
made up of the telencephalon and diencephalon
telencephalon
part of brain that is involved in higher order functions like learning and memory
diencephalon
part of brain that integrates all information passing from brainstem to cerebral cortex and some visceral and motor activities
dorsal
top or superior
ventral
inferior or bottom
anterior
front, towards the forehead
posterior
back or towards back of head
epithalamus
more of a region above the thalamus
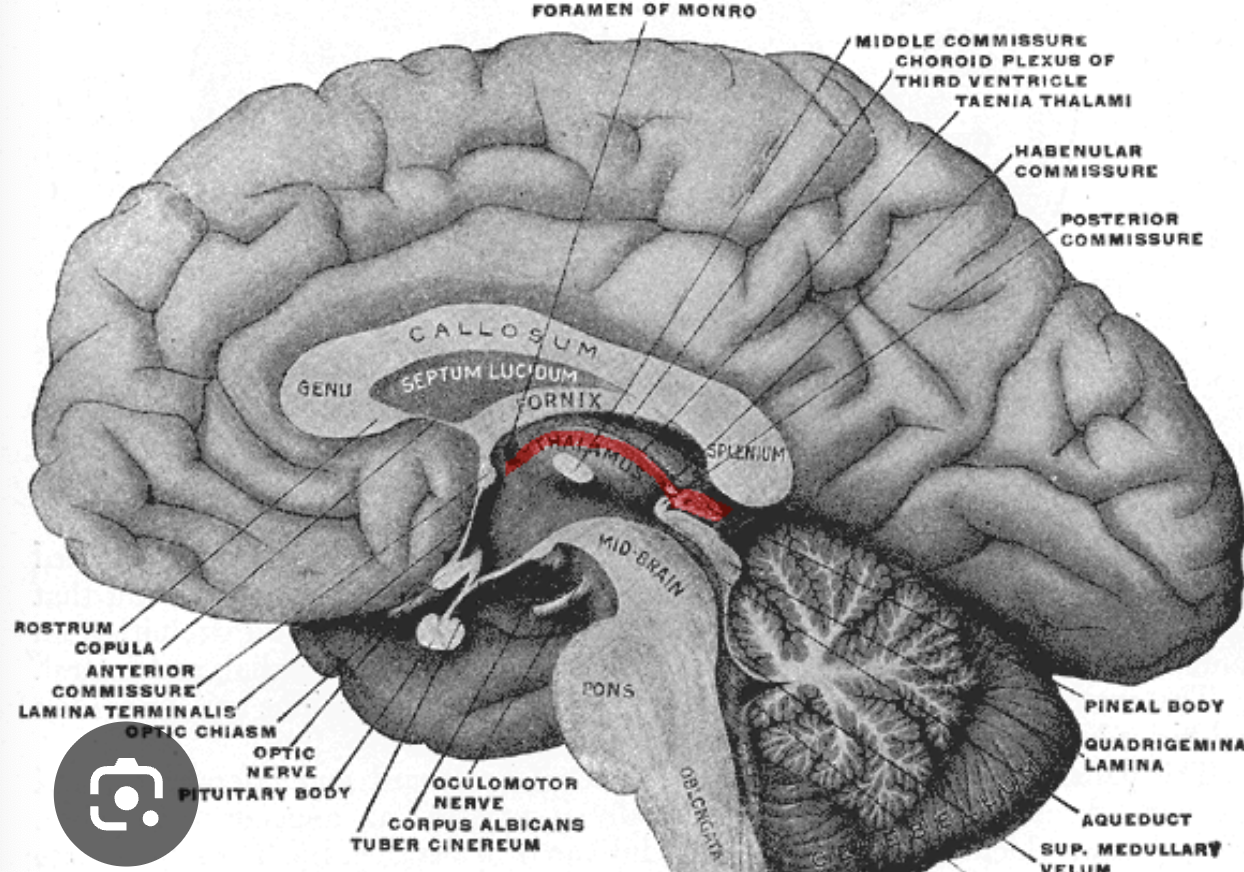
pineal gland
produces and secretes melatonin
parenchymal cells
similar history to rods and cones - main cells of epithalmus
non-parenchymal cells
astrocytes in the epithalamus
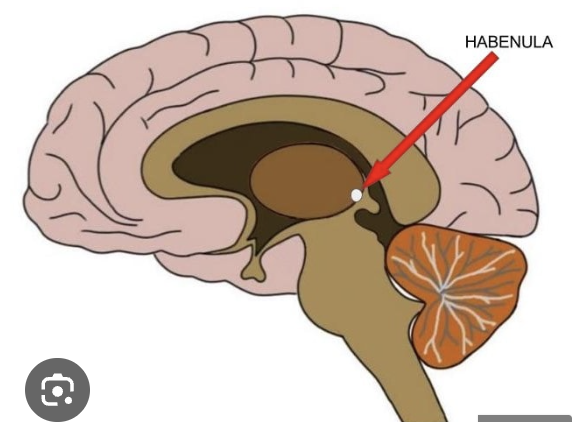
habenula
connection between thalamus and brainstem just rostral to pineal gland; input from thalamus, output to midbrain RF
subthalamus
subthalamic nuclei
part of basal nuclei
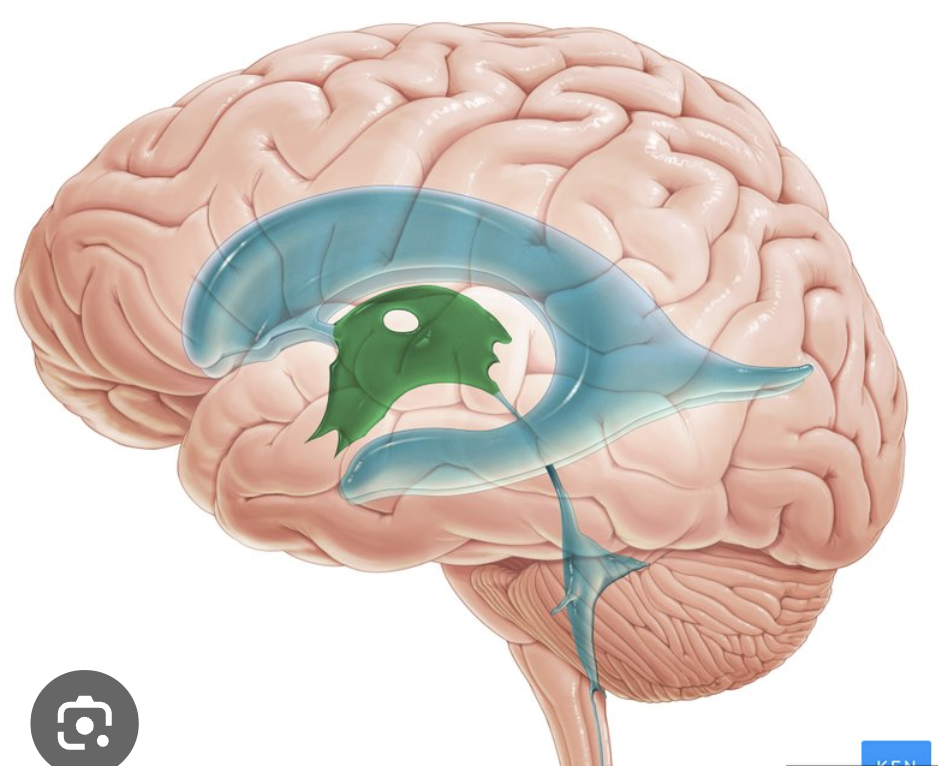
thalamus
“egg-shaped” inner chamber that makes up most of the diencephalon; forms mass bordering lateral aspect of third ventricle; “gatekeeper” for all sensory information goig to cerebral cortex
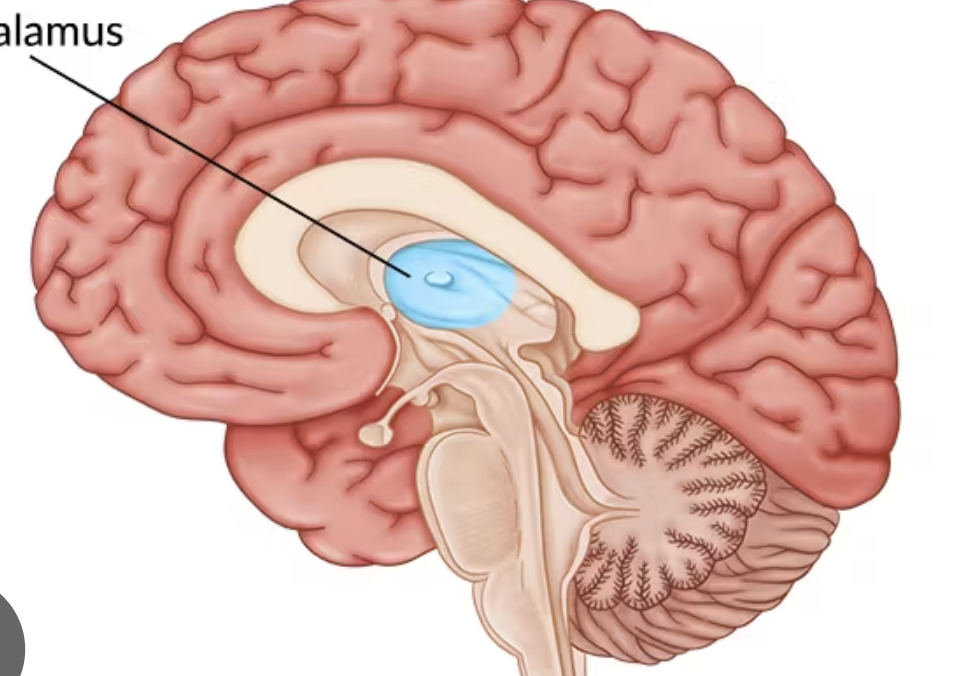
anterior thalamus
has anterior nucleus
medial thalamus
DM nucleus
lateral thalamus
two tiers, dorsal and ventral
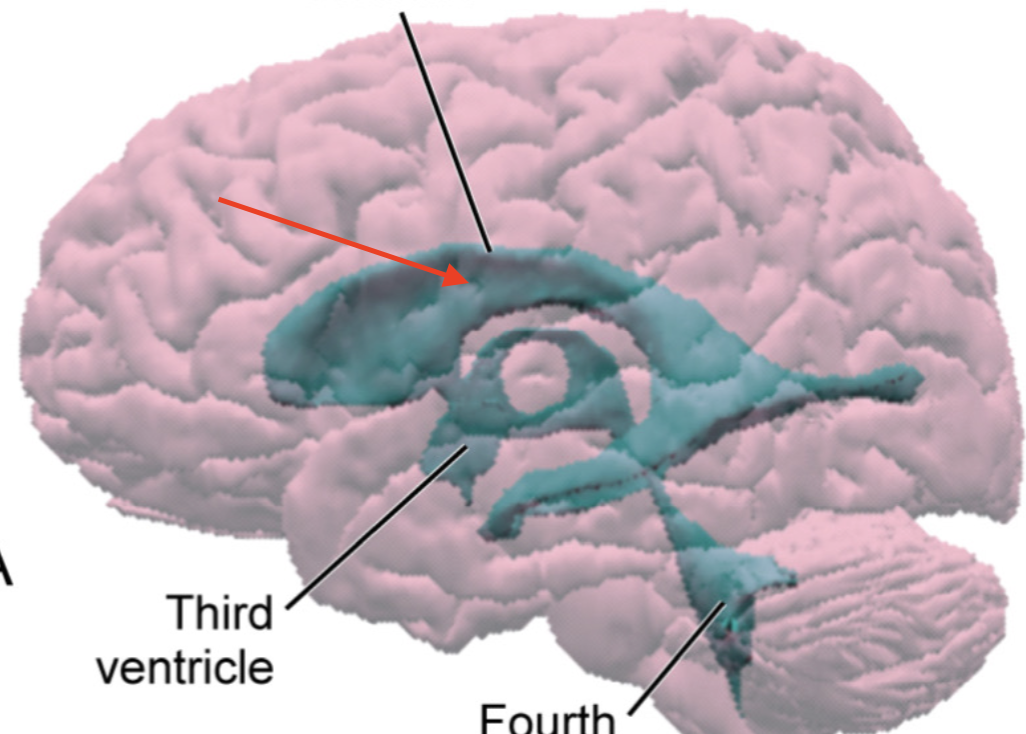
third ventricle
fluid-filled cavity; continuous with cerebral aqueduct and lateral ventricles
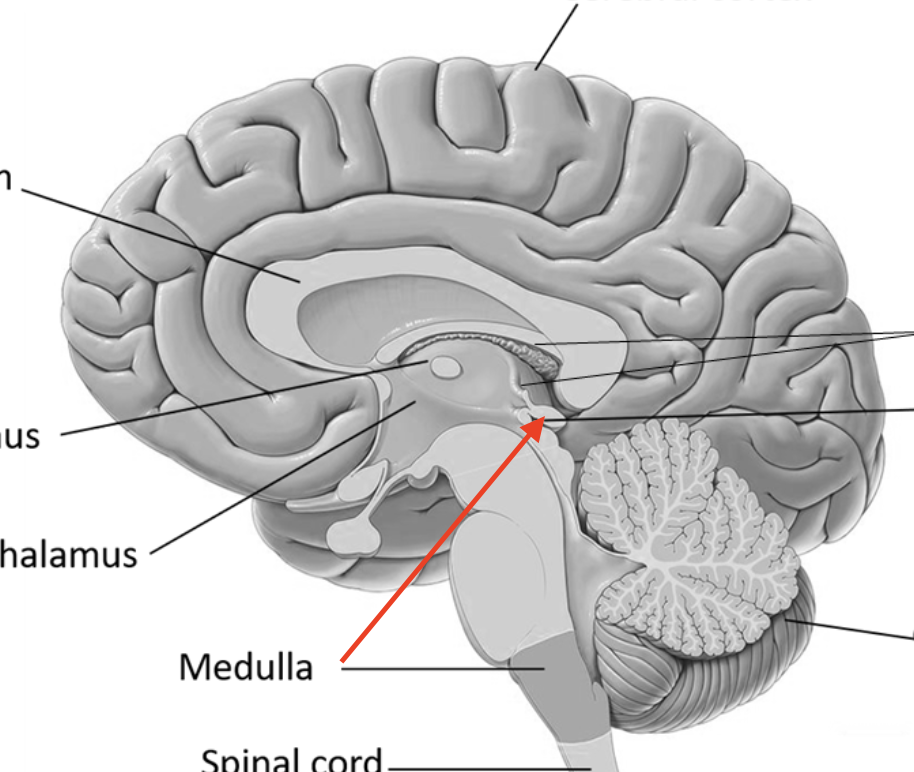
hypothalamus
orchestrates visceral and drive-related activities
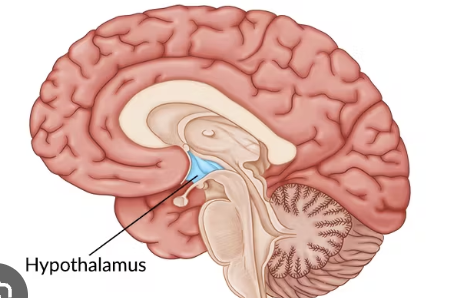
anterior hypothalamus
region above the optic chiasm
tuberal hypothalamus
region most directly superior to infindibulum
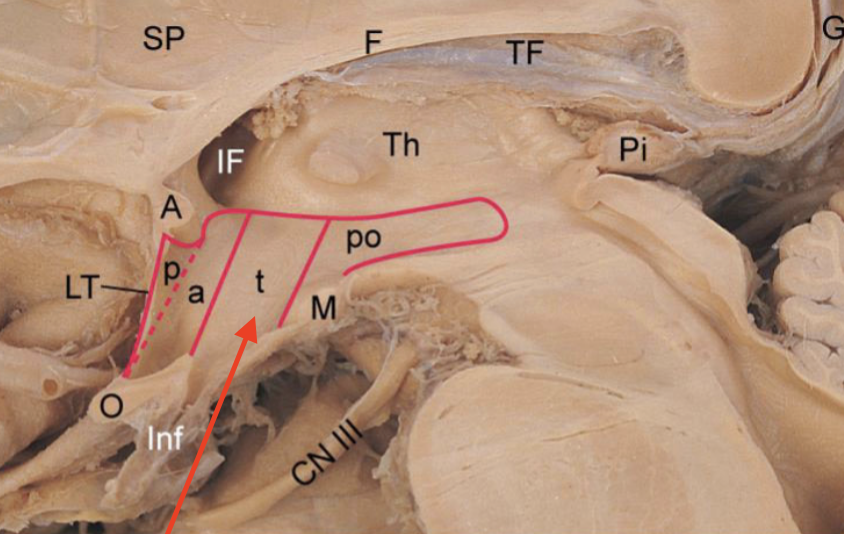
posterior hypothalamus
portion of hypothalamus that contains mammillary bodies
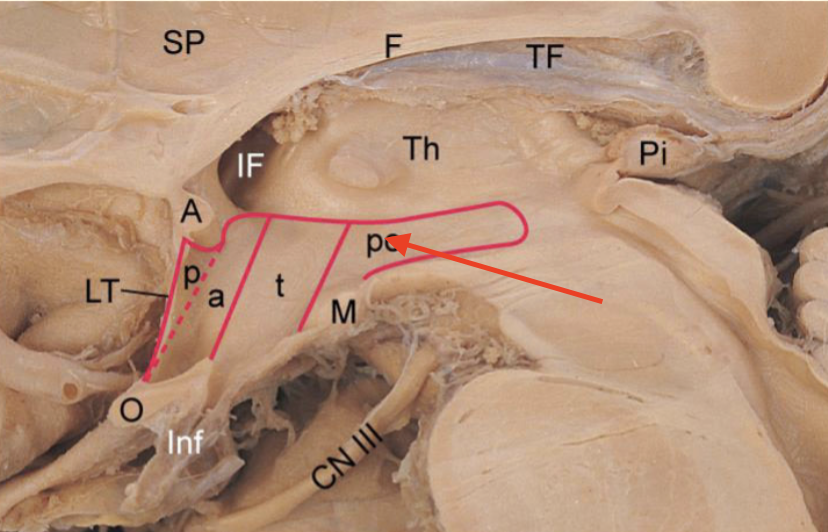
infindibulum
fibery stalk that connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
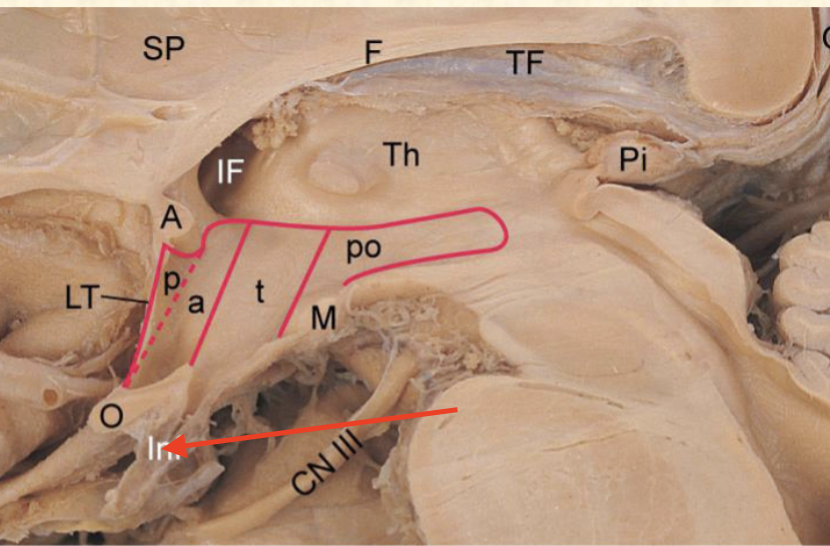
telencephalon
the “highest” thinking part of the brain
gyri
swellings
sulci
grooves
lateral sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes from other lobes “Sylvian fissure”
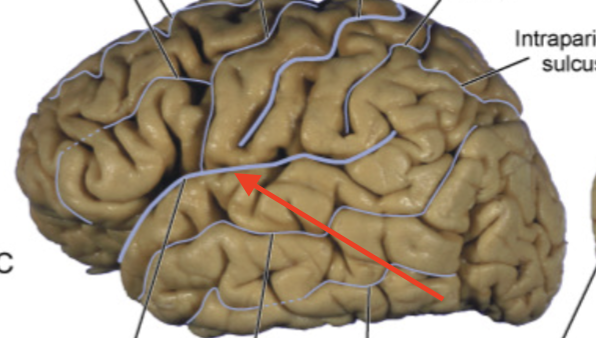
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes “fissure of Ronaldo”
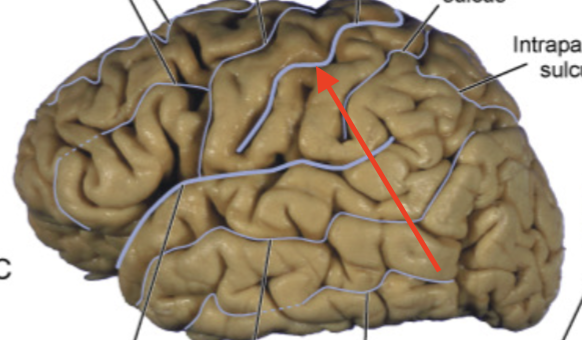
pre-central & post-central gyri
anterior and posterior to central sulcus, respectively
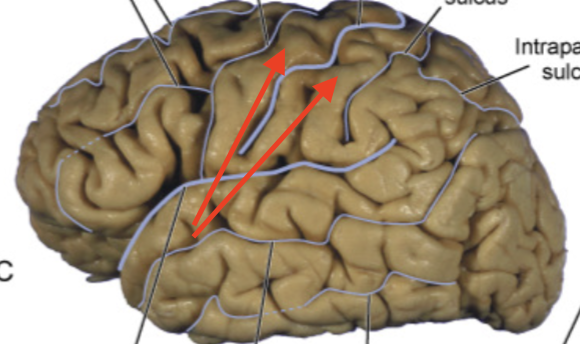
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
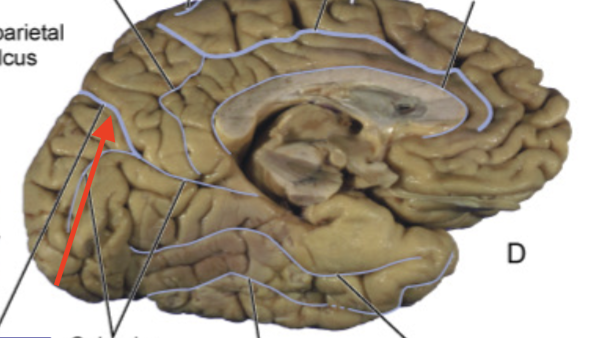
cingulate sulcus
demarcates cingulate gyrus
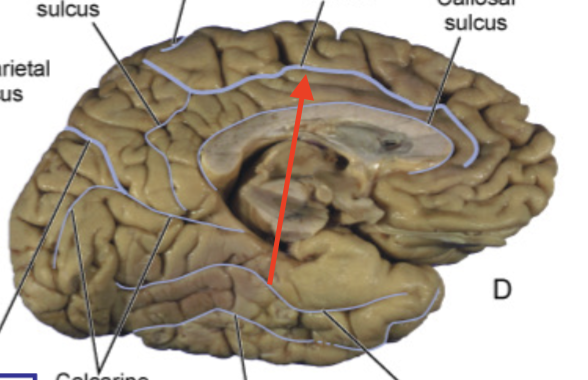
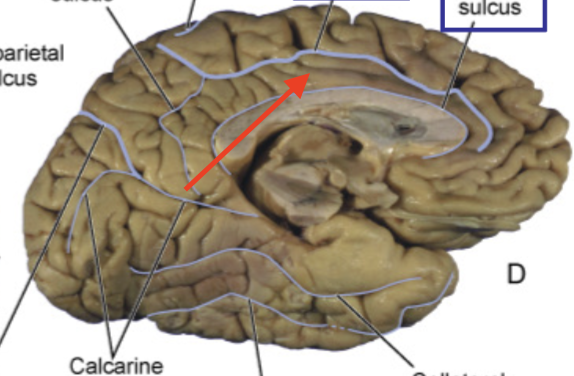
callosal sulcus
separates cingulate gyrus from corpus callosum
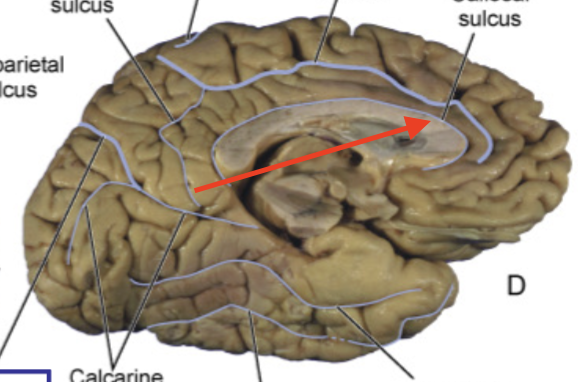
cingulate gyrus
part of limbic lobe
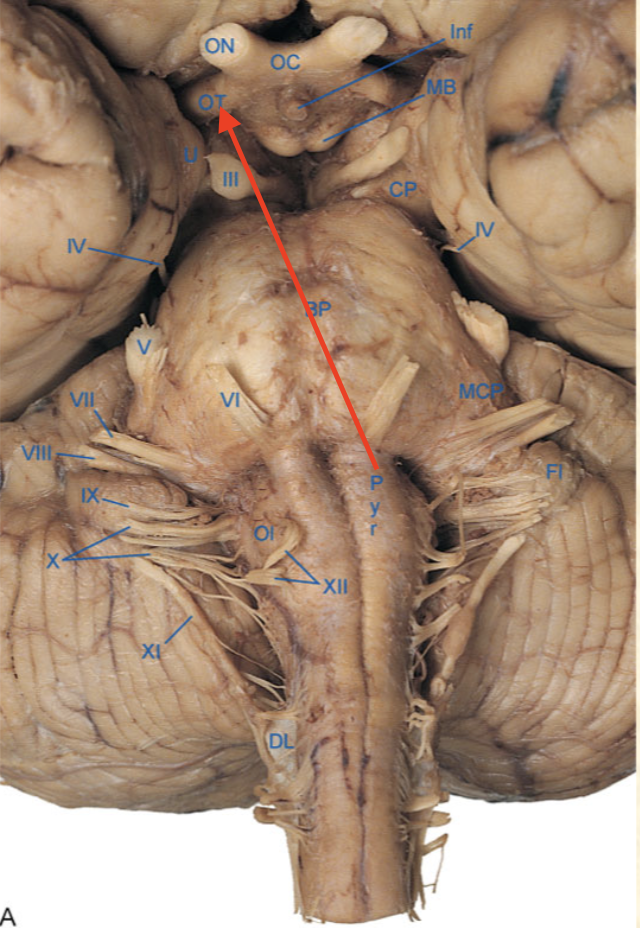
olfactory bulb
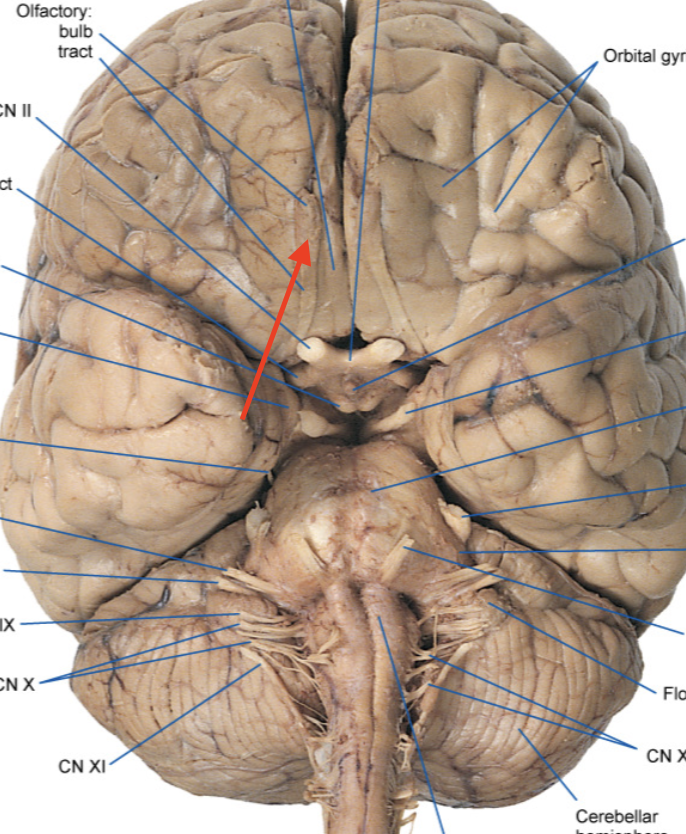
olfactory tract
mammillary body
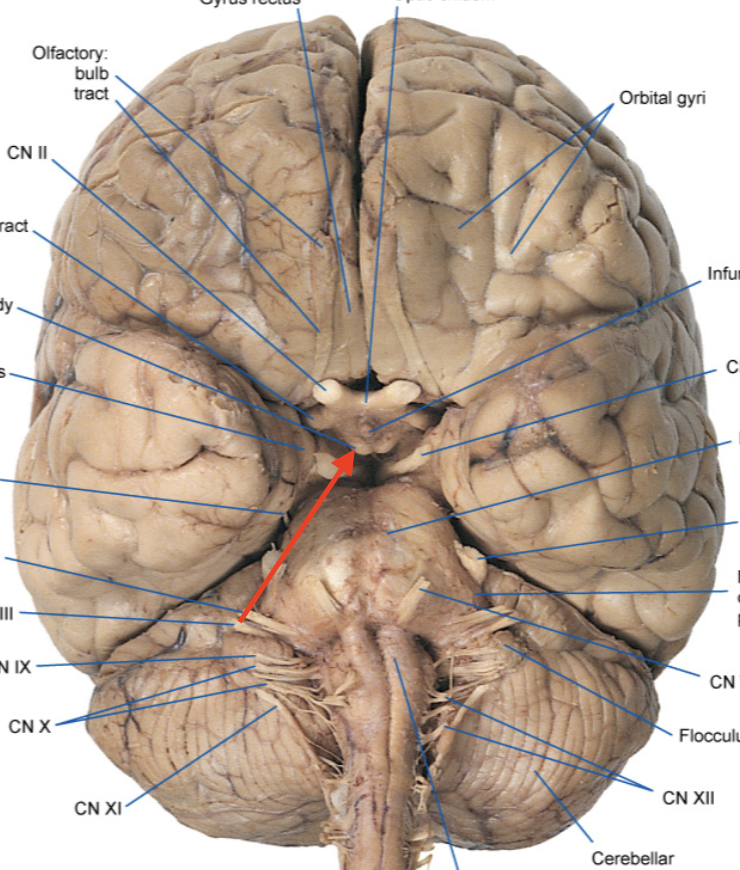
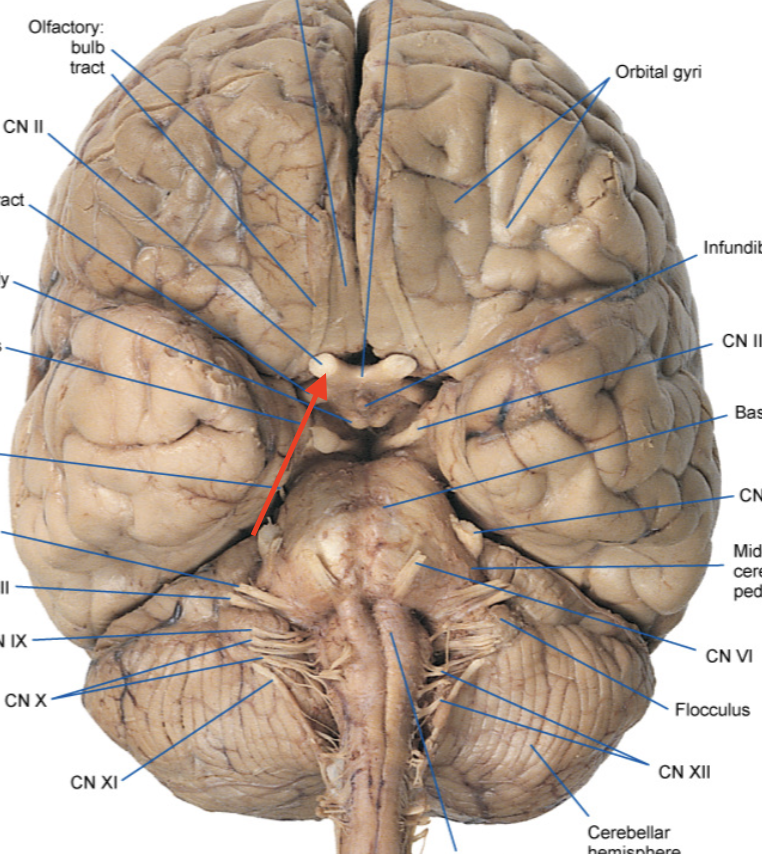
optic chiasm
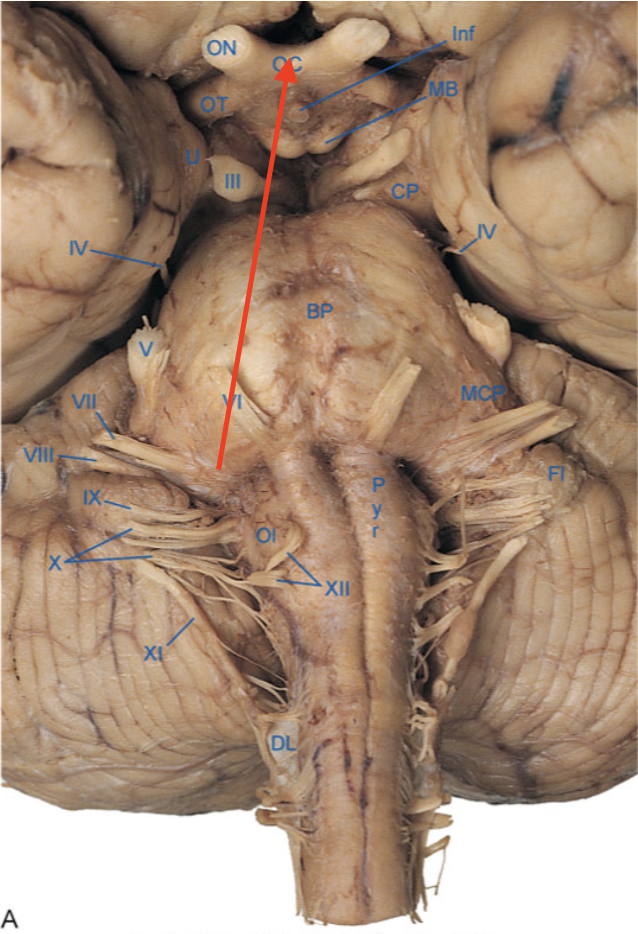
optic nerve
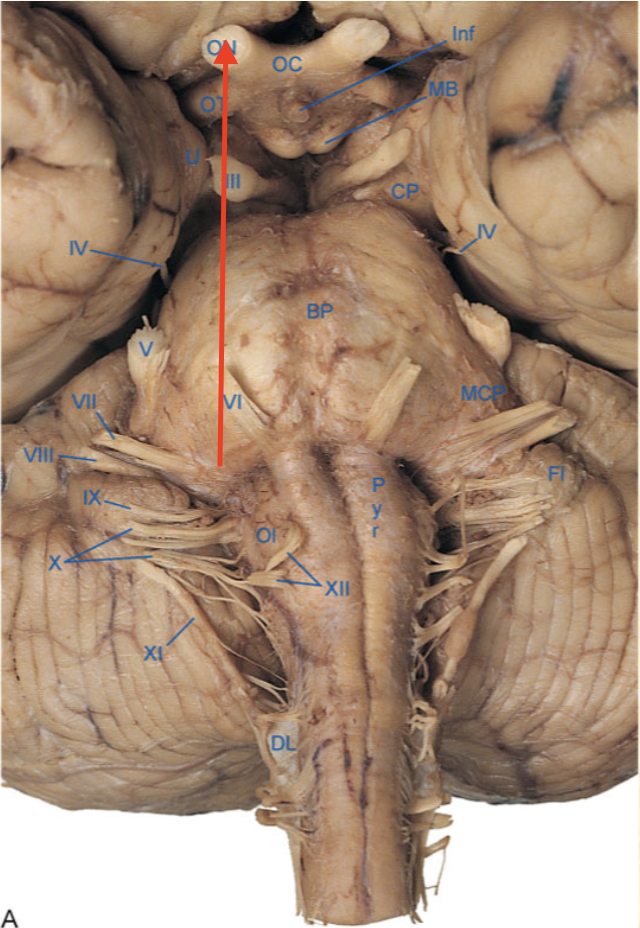
optic tract
lateral ventricle
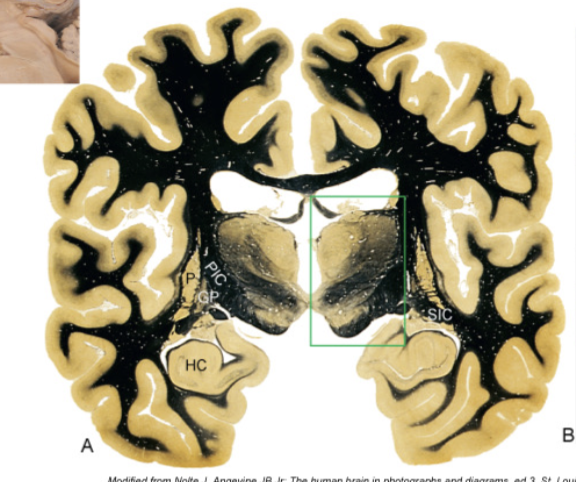
basal nuclei
collection of subcortical nuclei involved in motor movement
internal capsule
whole band of myelinated axons where information is relayed between cerebral cortex and thalamus and some other structures
parenchymal pineal tumors
causes excess melatonin; hypogonadism and therefore delayed puberty
Non-parenchymal pineal tumor
low melatonin production, precocious puberty (6-7 years old)
hydrocephalus
pineal tumors can block cerebral aqueduct preventing the CSF from draining
capsular stroke
caused when a pineal tumor cuts blood flow off from internal capsule