Venkata Unit 4
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What structure is this?
Epinephrine
What structure is this?
norepinephrine
What defines a catechol?
1,2-dihydroxybenzene
What kind of selectivity is displayed by E and NE?
E and NE are non-selective agonists. (even though NE doesn’t affect B2 receptors but still)
What effect does MOA have on catecholamines?
oxidative deamination of the primary amine into an aldehyde.
What effect does COMT have on catecholamines?
methylation of the meta hydroxyl group on the catechol
What role does the size of the group attached to the amine have?
Hydrogen (epinephrine) imparts alpha selectivity
Methyl groups create a nonselective agonist, still preferential alpha agonist
larger groups (i-propyl, t-butyl, aralkyl) produce beta selective agonists.
What is the difference in beta-receptor specificity for molecules with t-butyl and aralkyl groups compared to isopropyl groups?
t-butyl and aralkyl groups will show greater Beta-2 selectivity
isopropyl groups bind to both B1 and B2

What is the answer to this question?
molecule number three is preferential for alpha selection. It contains only hydrogens for its R1 group which imparts greater alpha selectivity.

What is the answer to this question?
Molecules 1 and 2 are both beta selective, but molecule 2 is the most selective as it only binds to Beta-2 receptors due to the larger t-butyl group.
What effect does methyl or small alkyl substitution of the alpha-carbon have on catecholamines?
addition of small alkyl groups imparts resistance to MAO.
What does substitution at the R3 position (beta position) have?
hydrogen substitution increases CNS entry due to non-polar nature
hydroxyl substitution decreases CNS activity due to polarity.
What is the cause of catechol instability in vivo and in vitro?
catechol is subjected to COMT in vivo
catechol is exposed to photooxidation in vitro.
What is the issue with monophenol substitution of catecholamines?
(technically not a catechol) these groups reduce direct action compared to catechol.
What is the selectivity difference between m-phenol (R4) and p-phenol (R5)
R4 substitution retains some alpha-1 receptor activity
R5 substitution retains some beta-receptor activity
What molecule is this?
phenylephrine
What is the difference in metabolization of monophenols compared to catechol?
Monophenols have more resistance to COMT but are vulnerable to glucuronidation.
What effect does hydrogen substitution at R4 and R5 have on adrenergic molecules?
reduction in direct action due to hydrogen bonding (especially at B-receptors)
allows for CNS action, especially in compounds with no R3 OH and an alpha-methyl at R2.

What molecule is this?
methamphetamine
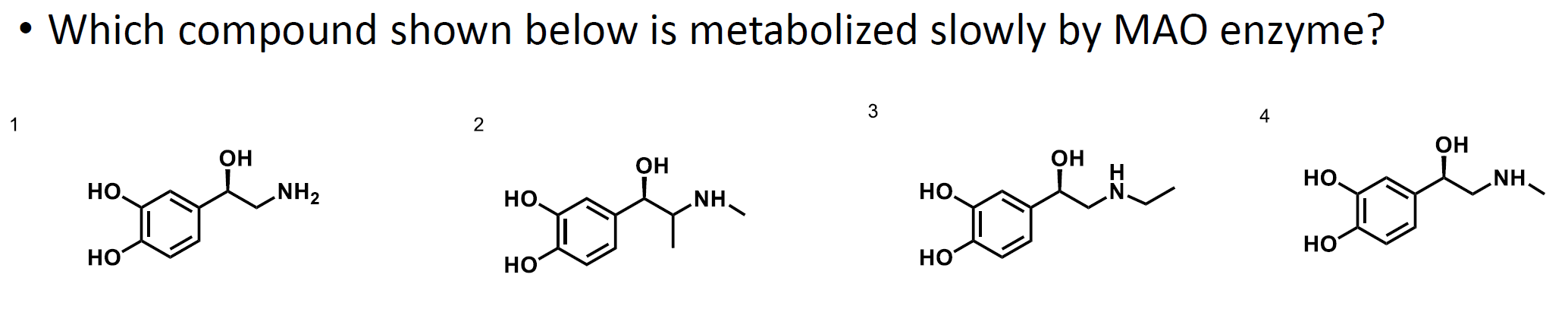
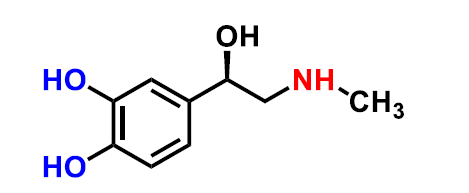
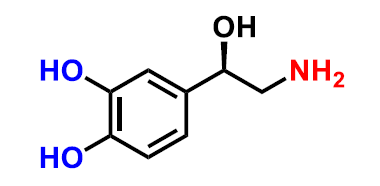
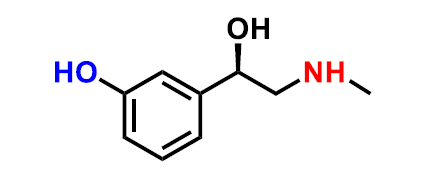
What is the answer to this question?
The methyl group present on molecule 2 will impart resistance to action via MAO

What is the answer to this question?
Answers 2 and 4 are correct.
option 2 has the a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene ring
option 4 is also, technically correct.
a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene ring with an additional ethoxy group.
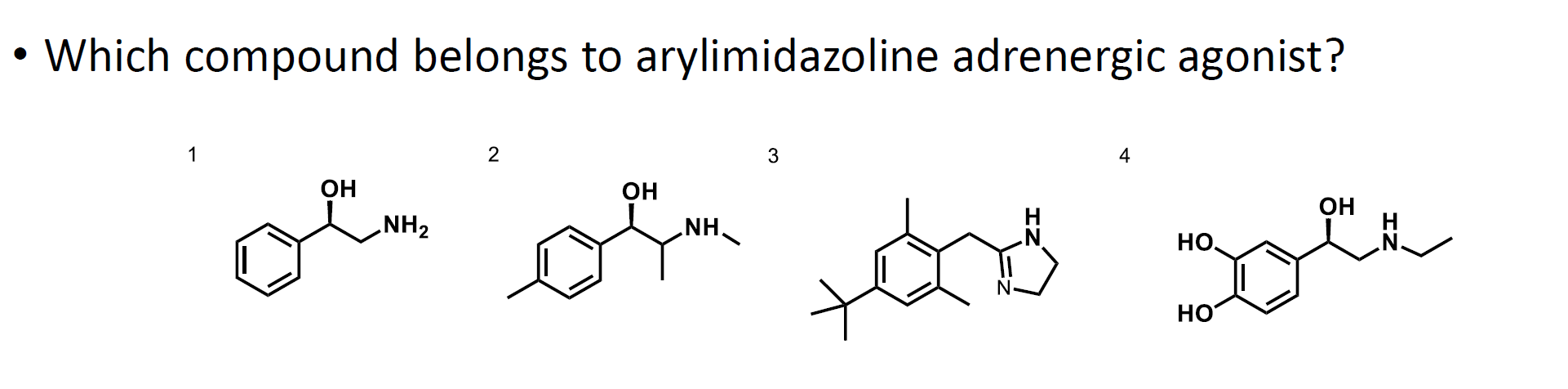
What is the answer to this question?
Option 3 is the answer.
This drug contains an arylimidazoline group
Why does clonidine behave like a non-polar substance despite having a charge?
The positive charge is shared between the three nitrogen atoms of the guanidino group.
Clonidine has two chlorines. What is the function of a single chlorine, and the function of two?
One chlorine atom is required for it to be a potent alpha-agonist
Two chlorine atoms augments the lipophilicity of the drug and allows it to enter the brain.
What is methyldopa?
Methyldopa is a pro-drug that functions as an alpha-2 agonist in the brain
What compounds may be added to methyldopa to counteract its susceptibility to oxidation?
Metabisulfite or sulfite groups may be added.
What is methyldopa susceptible to?
photooxidation
changes in pH
air
What is the fundamental pharmacophore of Beta-adrenergic agonists?
Substituted phenyl-ethanolamine
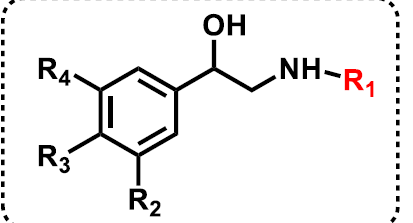
What occurs as a result of bulky substitutions on the R1 position of beta-agonists?
The larger the substituent on the R1 position, the more selective the drug will be for beta receptors.
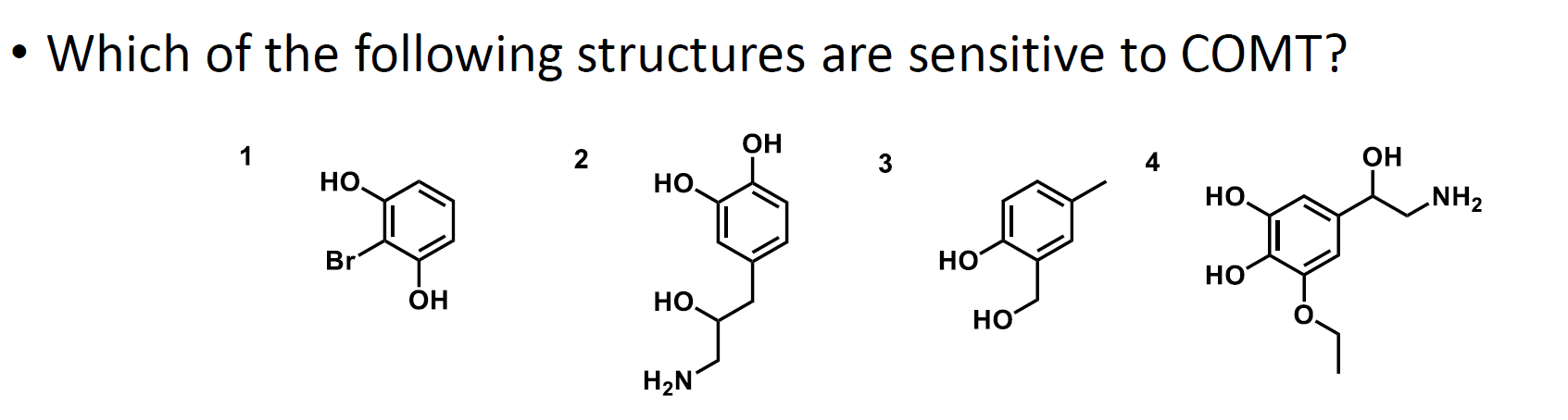
What is the answer to this question?
Structures 2 and 4 are sensitive to COMT because they are catechol rings.

What is the answer to this question?
Options 3 and 4 are both beta 2 selective
Why is phenoxybenzamine irreversible?
It spontaneously generates an electrophilic aziridinium ion that is readily attacked by alpha-receptor nucleophiles
What are the three key groups for a selective alpha-1 antagonist?
a quinazoline
a piperazine
and an acyl group
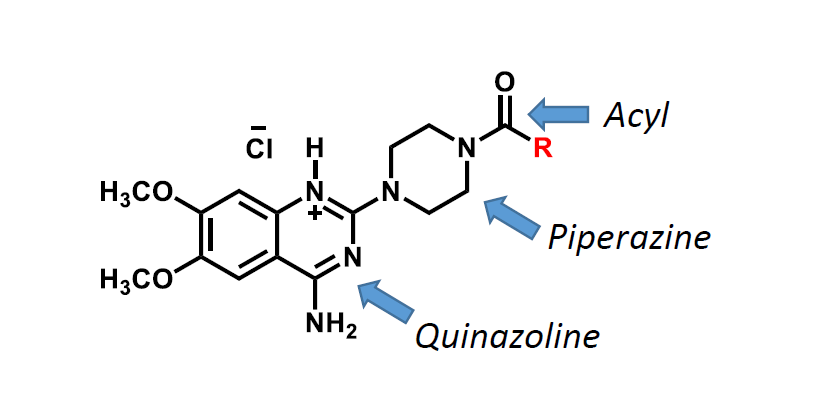
What is this?
That is the general structure of an alpha-1 selective antagonist.
Prazosin, terazosin, and doxazosin are what kind of drugs and have what kind of heterocyclic core?
These drugs are all alpha-1 selective antagonists and contain quinazoline cores.
What is the key component of a non-cancer inducing beta antagonist?
An oxymethylene bridge (OCH2)
What effect do ortho substitutions have on Beta-antagonists?
Small ortho substitutions don’t have major effects on selectivity.
larger substituents will reduce selectivity

What is this?
This is the general structure of a beta-antagonist
What effect does para substitution of a beta-antagonist do?
single substitutions of the phenyl ring at the para position confer beta-1 selectivity.
What does the R1 substitution of a beta-antagonistdo?
The R1 substitution is a directing group.
bulky directing groups (i-propyl, t-butyl) confer beta selectivity.
What group is essential for beta antagonist function?
The hydroxyl group present