Unit 5: I like to move it!
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
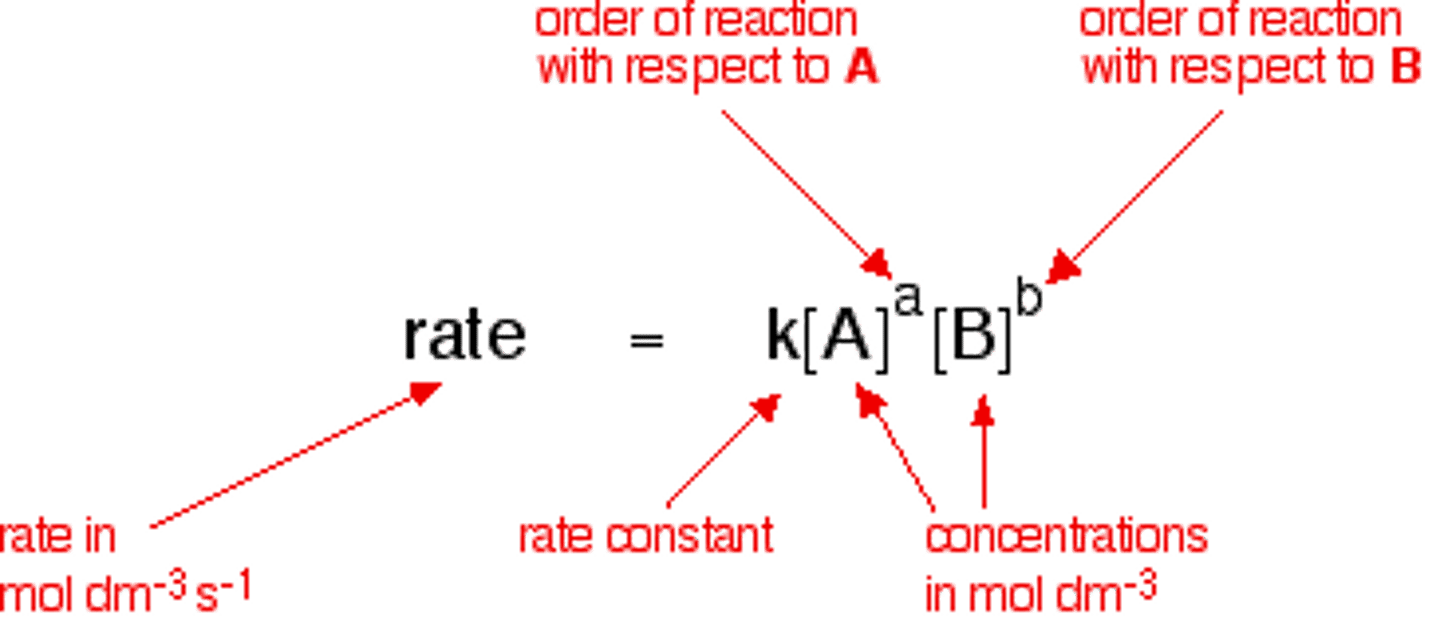
rate law
an expression relating the rate of a reaction to the concentration of the reactants
order of reactant
The power to which the reactant's concentration is raised in the rate-law expression.
overall reaction order
the sum of all the exponents in a rate law expression
rate constant
a constant of proportionality between the reaction rate and the concentrations of reactants that appear in the rate law (ie a constant created to hide the other factors that impact reaction rate, such as temperature)
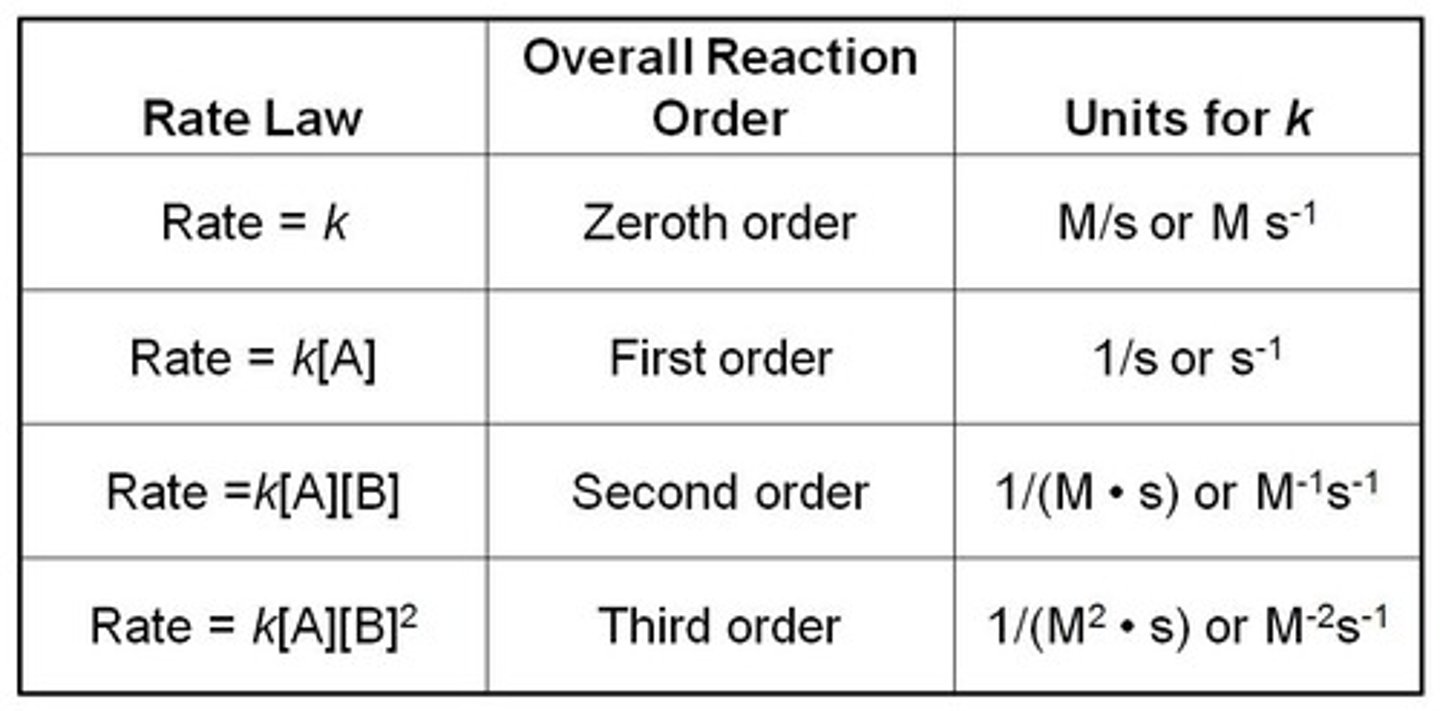
0th order reaction
Reaction rate is independent of the [reactant];
2x [reactant] --> no change in rxn rate
![<p>Reaction rate is independent of the [reactant];</p><p>2x [reactant] --> no change in rxn rate</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c2a2948d-5538-4ef1-8e59-87e8f6daa04c.jpg)
1st order reaction
Reaction rate is directly proportional to concentration of reactant [R];
2x [R] --> reaction rate doubles
rate=k[A]
![<p>Reaction rate is directly proportional to concentration of reactant [R];</p><p>2x [R] --> reaction rate doubles</p><p>rate=k[A]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a9bb5426-d66d-4303-96a6-02ae43995a1d.png)
2nd order reaction
The concentration of a reactant is raised to the second power. If the concentration doubles, the rate is multiplied by 4. If the concentration is tripled, the rate increases 9x
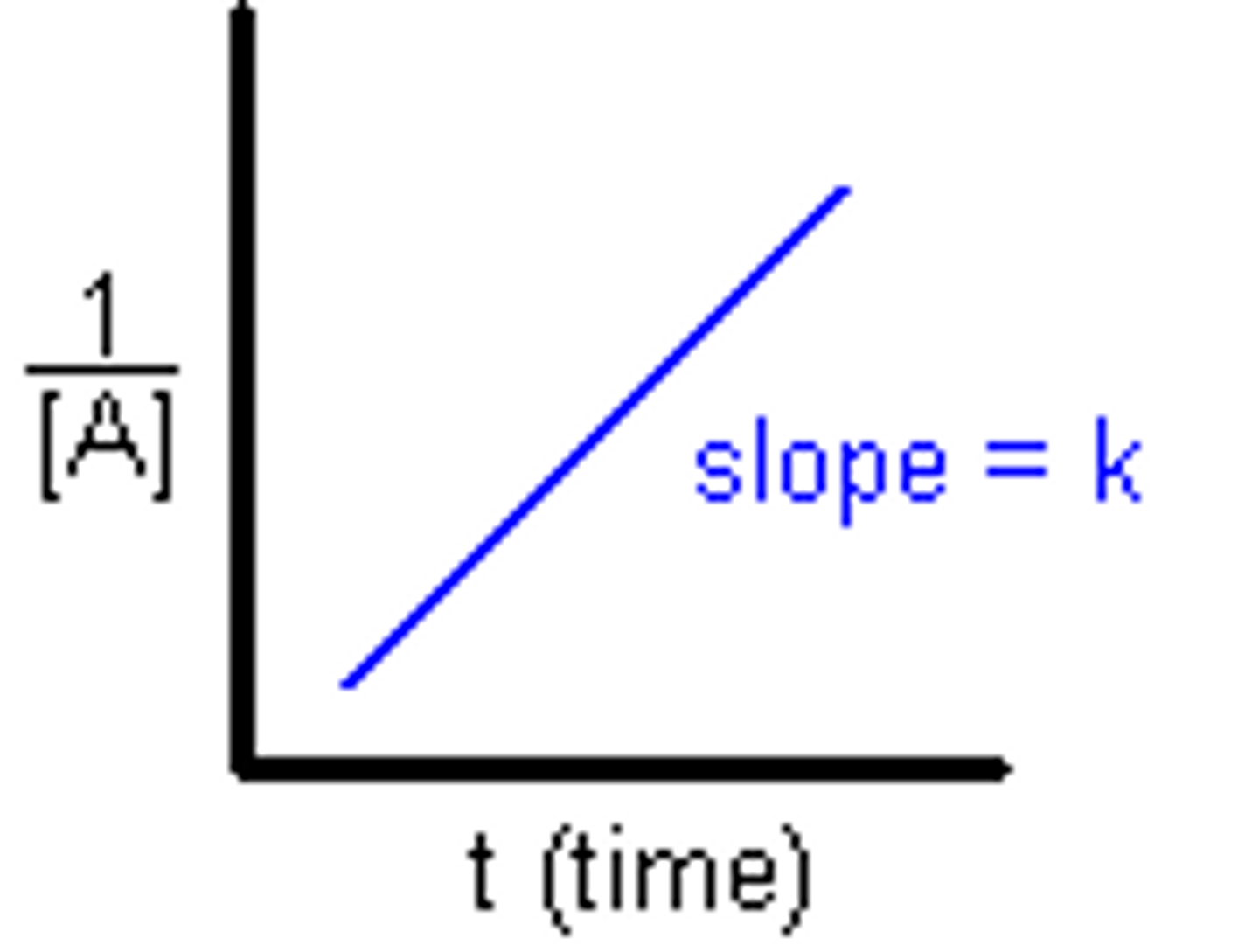
rate law equation
rate = k [A]^x [B]^y
half-life
The time required for one half of the atoms of a radioisotope sample to decay
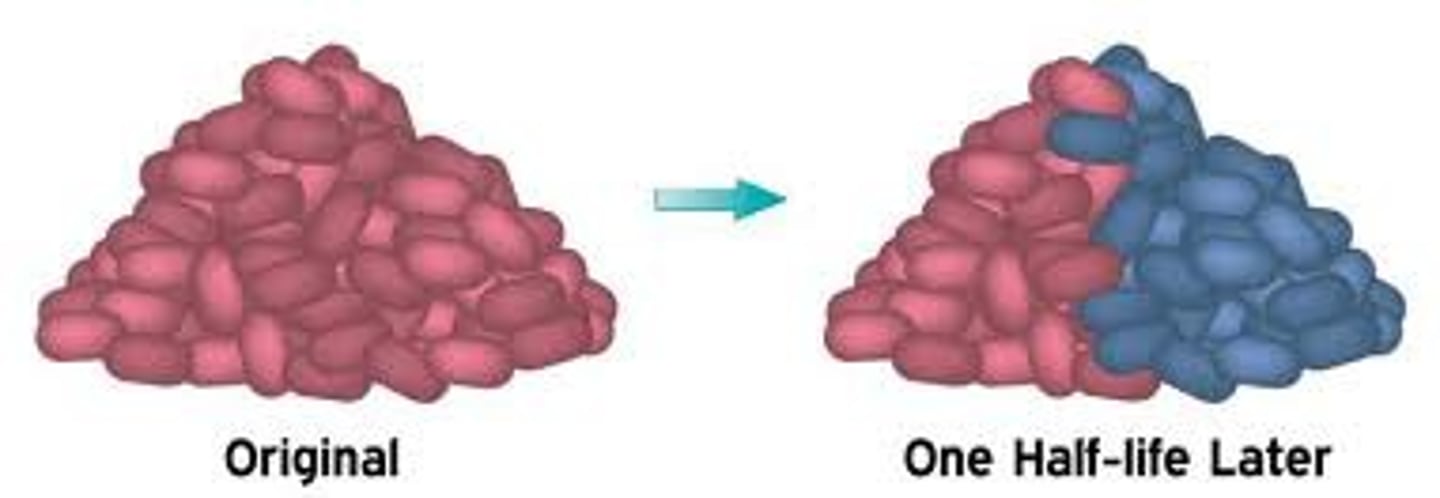
Half life and rate of decay
t 1/2 = 0.693/k
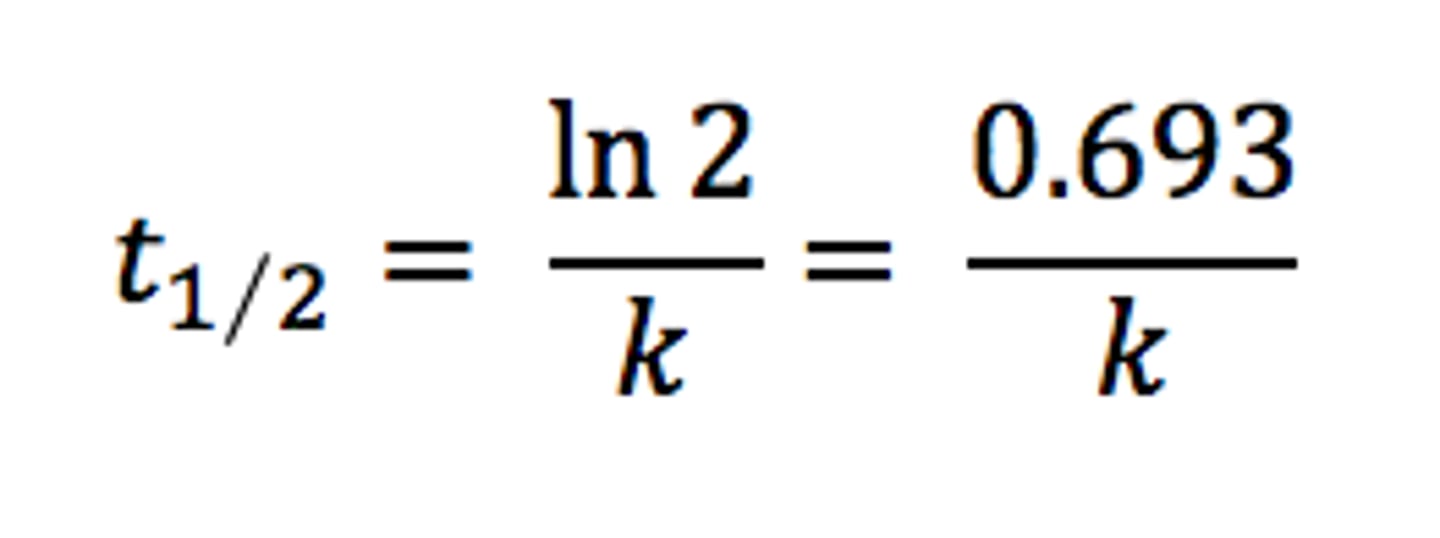
elementary reaction
a single step in a reaction mechanism; describes an individual molecular event
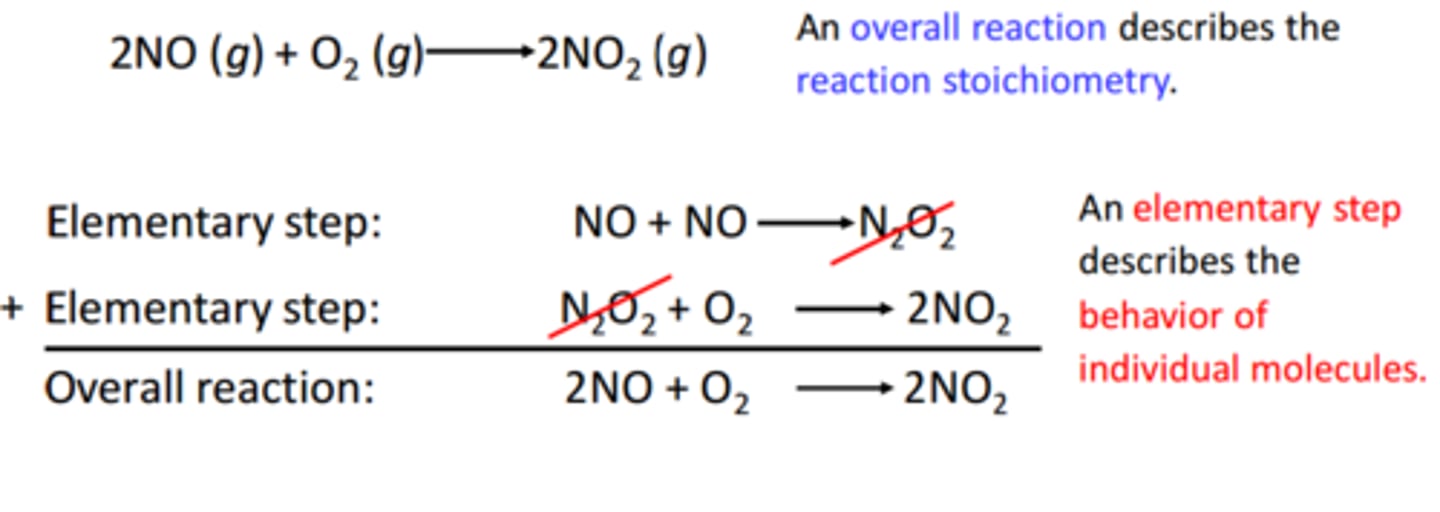
reaction mechanism
the step-by-step sequence of reactions by which the overall chemical change occurs
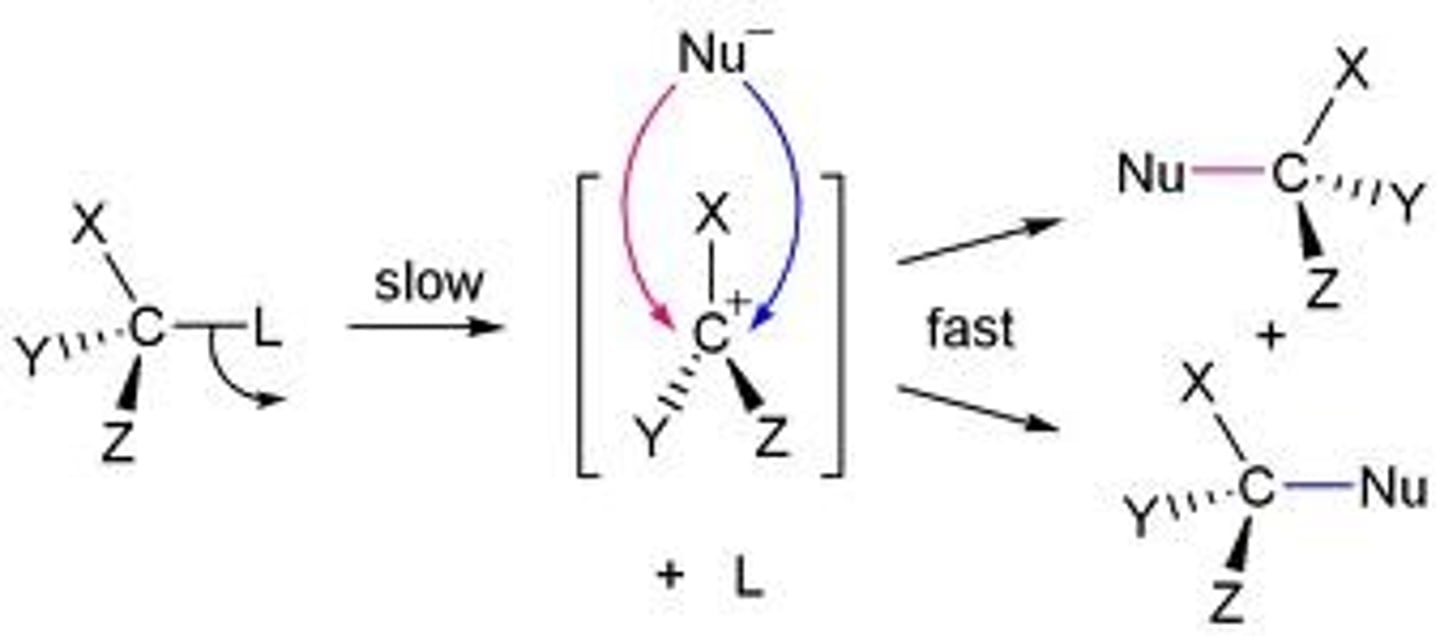
reaction intermediate
temporary substance formed and consumed in a chemical reaction; also known as a transition state
unimolecular reaction
an elementary reaction that involves a single molecule
bimolecular reaction
An elementary reaction involving the collision of two reactant species
termolecular reaction
elementary reaction involving the simultaneous collision and combination of three reactant species - this is very unlikely
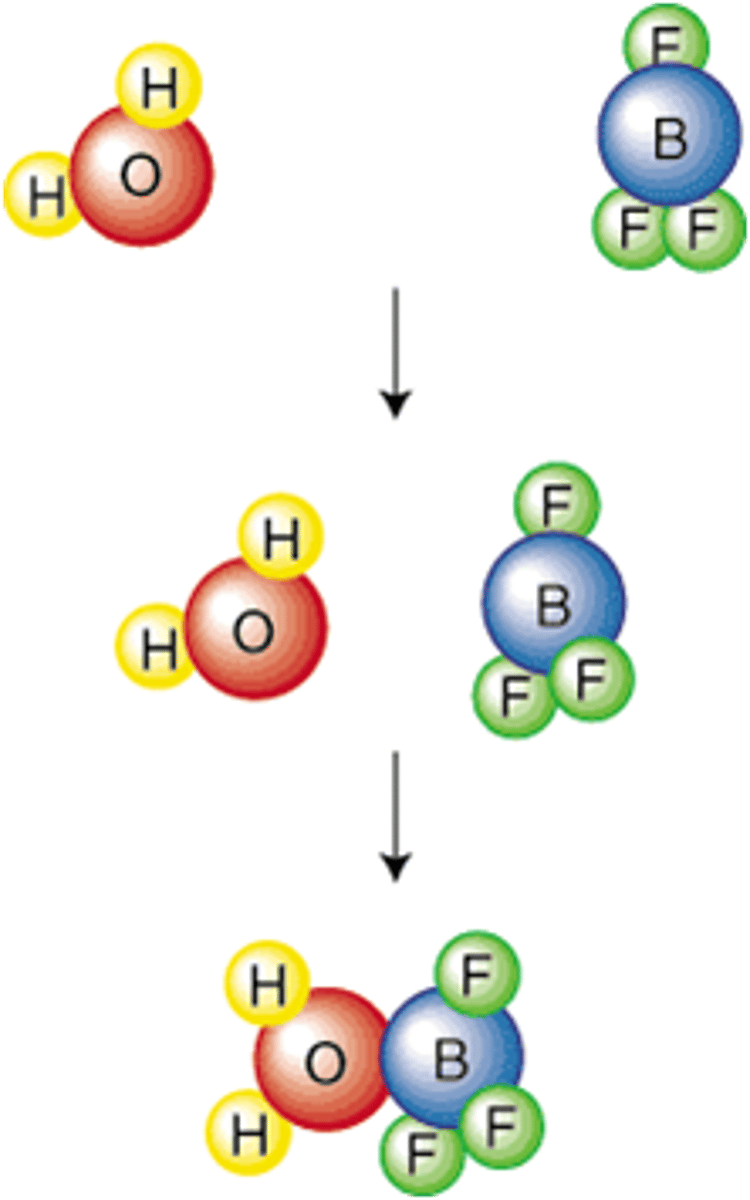
collision theory
For a reaction to occur, the particles must collide, they must collide with the appropriate orientation, and they must collide with sufficient energy.
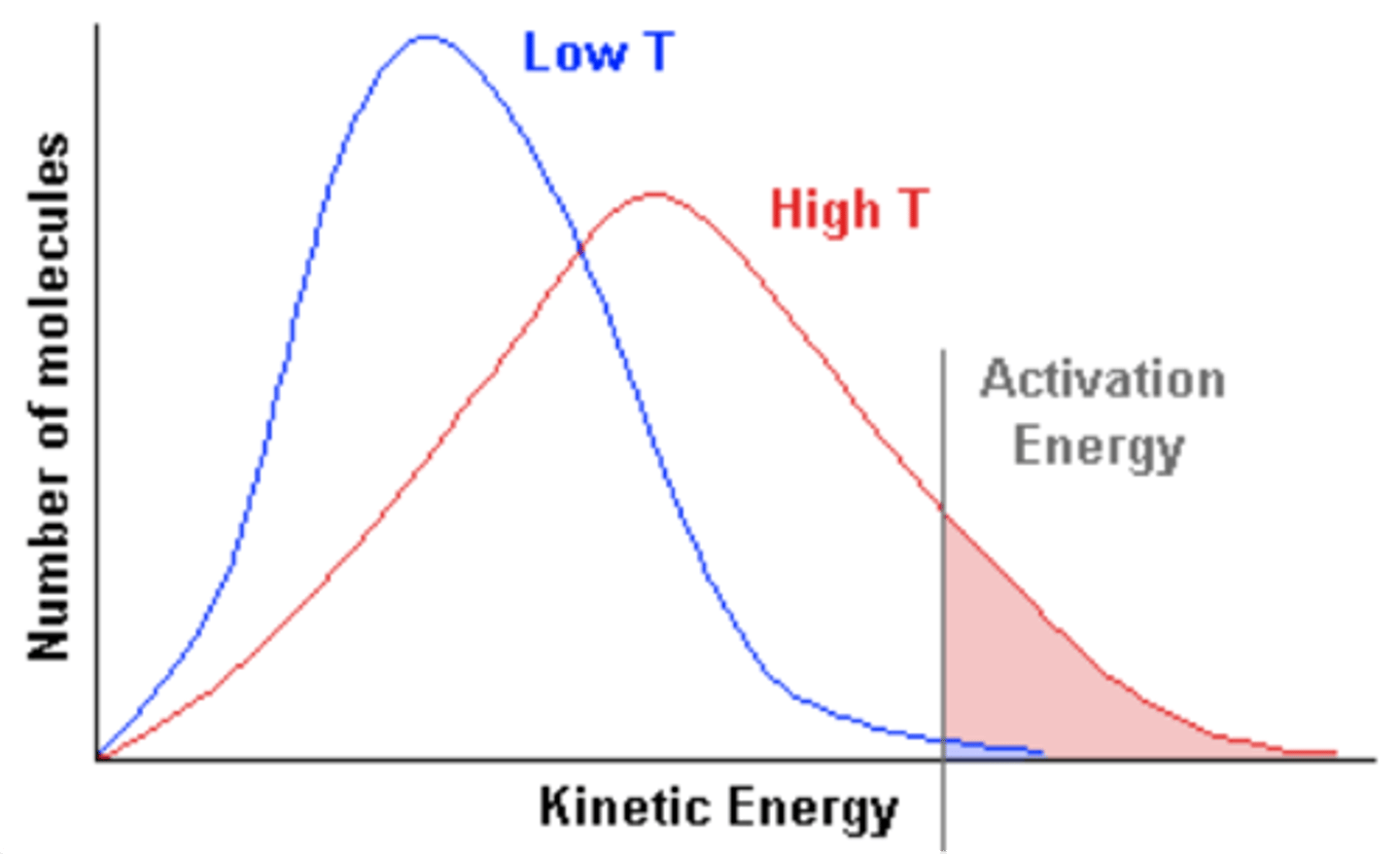
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
The distribution of energies (and therefore speeds) of the molecules in a gas or liquid.
kinetic energy
the energy an atom/molecule has due to its motion
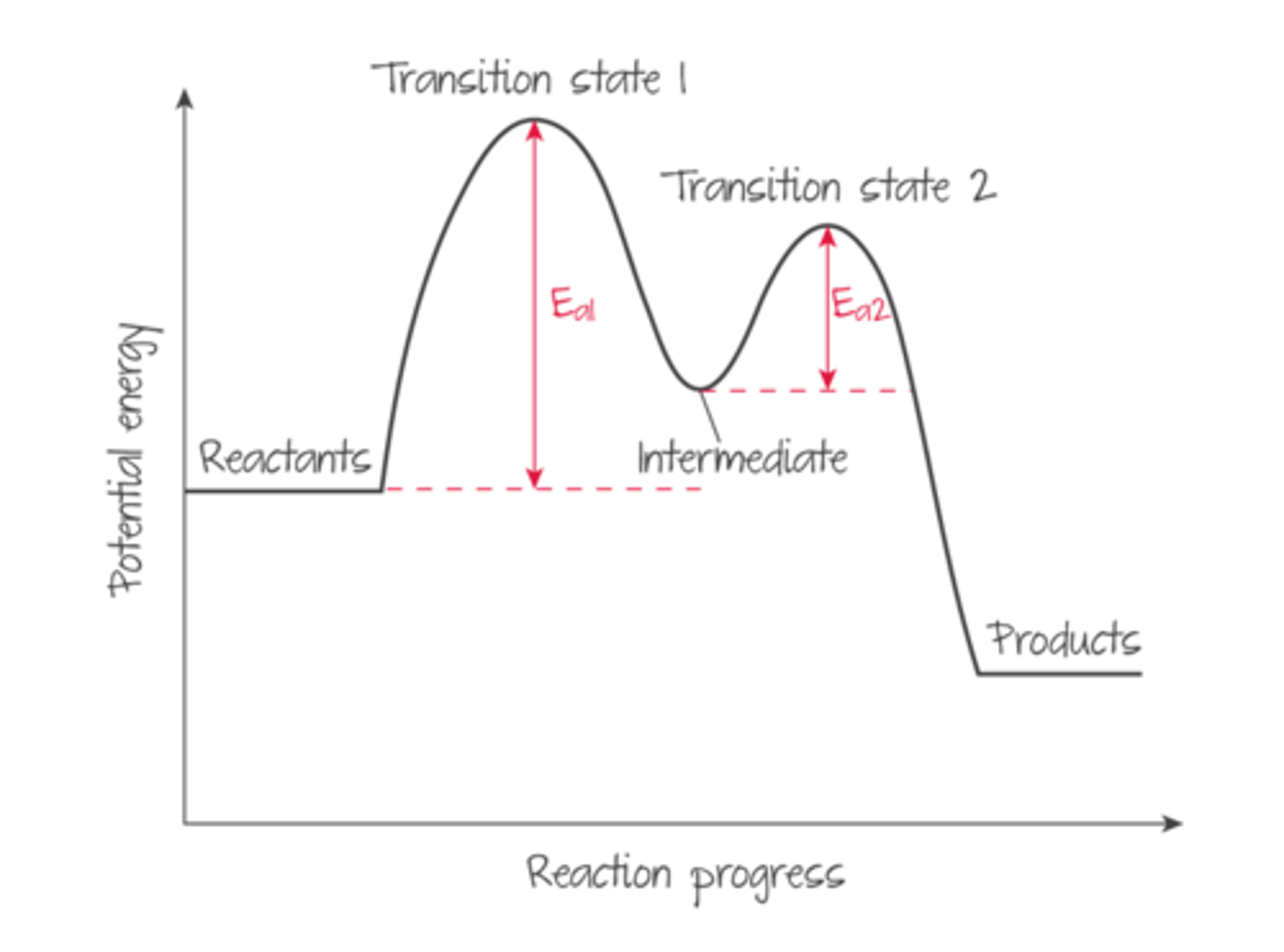
reaction energy profile
A graph showing the relative energies of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction, with the horizontal axis representing the progress of the reaction and the vertical axis representing the energy of the reaction
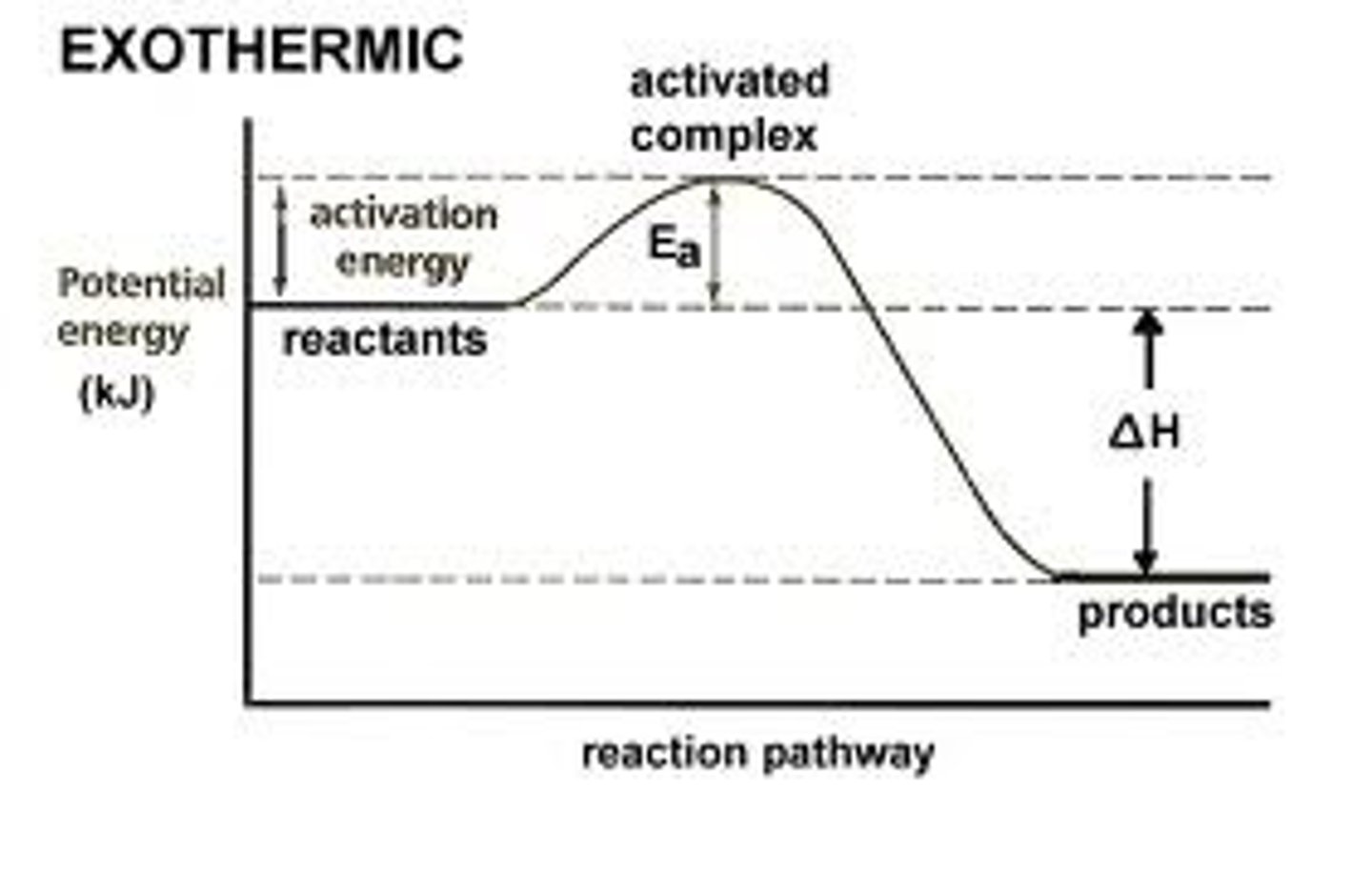
activated complex (transition state)
the arrangement of atoms found at the top of the potential energy barrier as a reaction proceeds from reactants to products
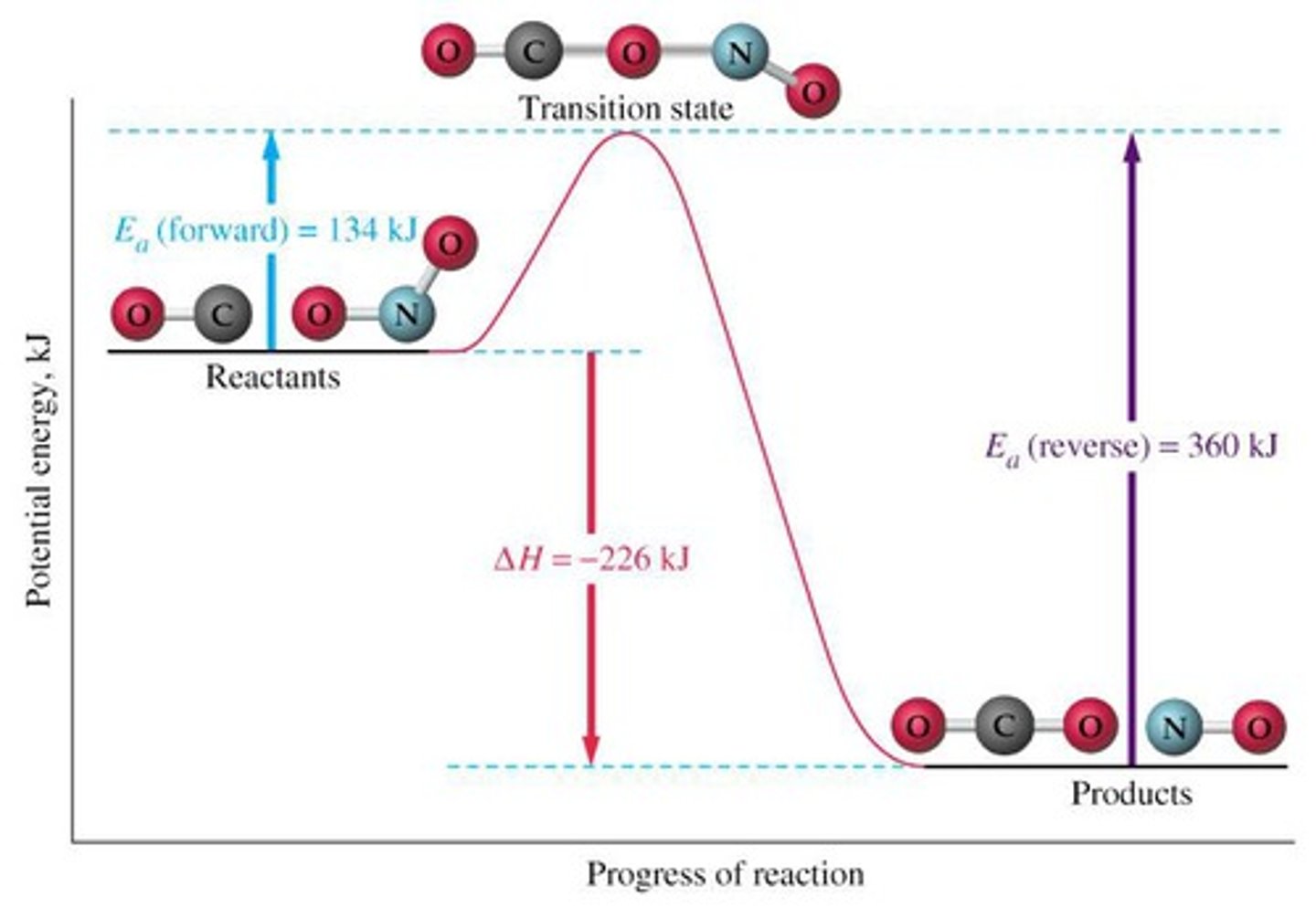
reaction coordinate
A visual representation of a chemical reaction and the accompanying energy changes (ie the progress of a reaction)
activation energy (Ea)
the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction
catalyst
substance that increases reaction rate by stabilizing transition state, decreasing the activation energy
How does a catalyst work?
1. Forms more stable activated complex
2. Increases number of molecular collisions
3. Improves molecular orientations
elementary steps (elementary reactions)
proposed steps where particles actually collide
rate-determining step
the overall reaction cannot occur faster than the slowest reaction in the mechanism
equilibrium
state where rate of forward reaction is equivalent to rate of reverse reaction
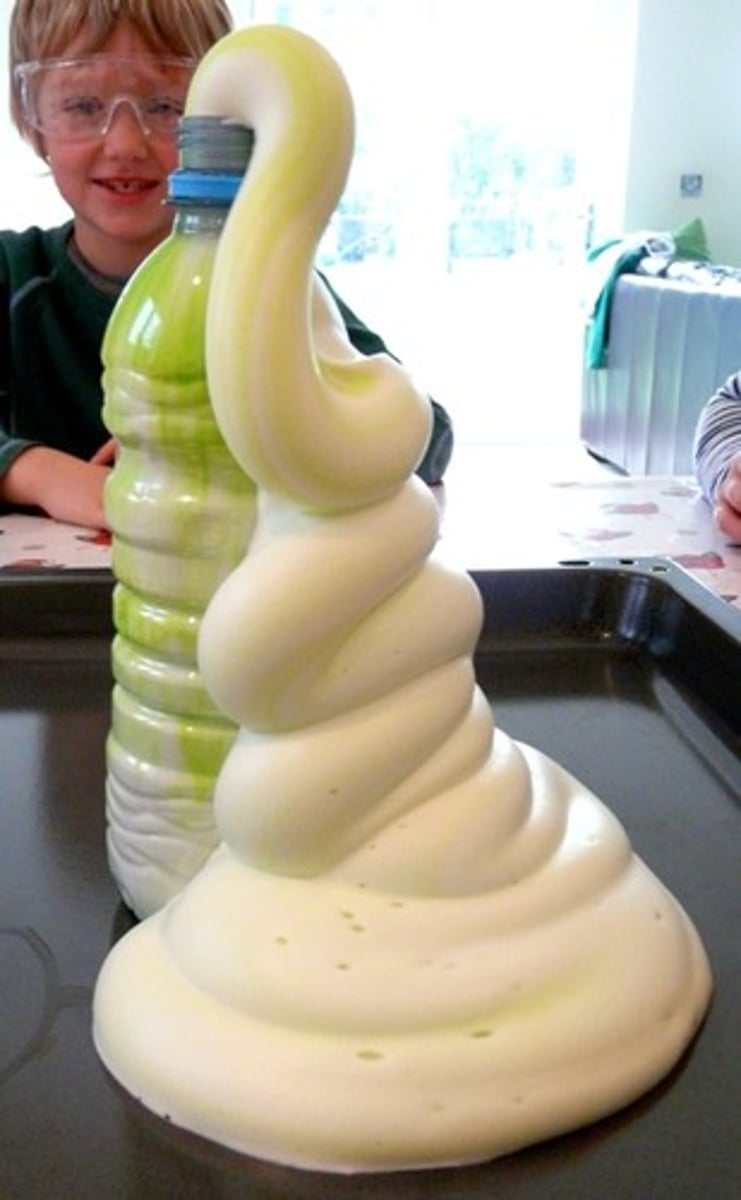
homogeneous catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst and reactants are in the same physical state (ie reactants in the elephant's toothpaste demo are liquids + liquid catalyst)

heterogeneous catalyst
A catalyst in a different phase from the reactants.
adsorption
The process of binding or sticking to a surface.
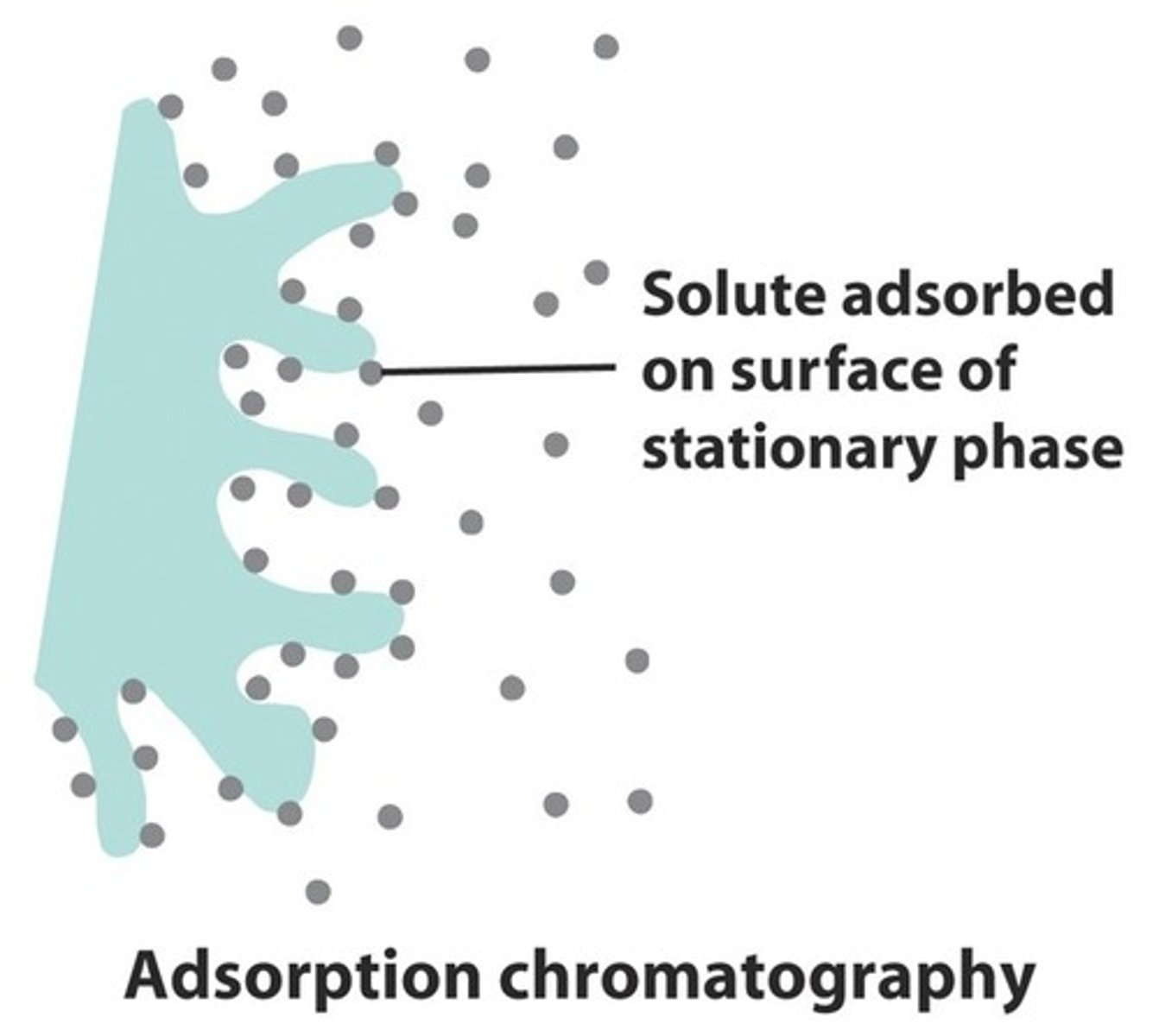
desorption
Release of an adsorbed substance from a surface
steady state approximation
can be used when the differential rate law for an intermediate is equal to zero...Means the change of concentration of a species is zero, which happens if the intermediate is consumed as quickly as it is formed
0th order reaction
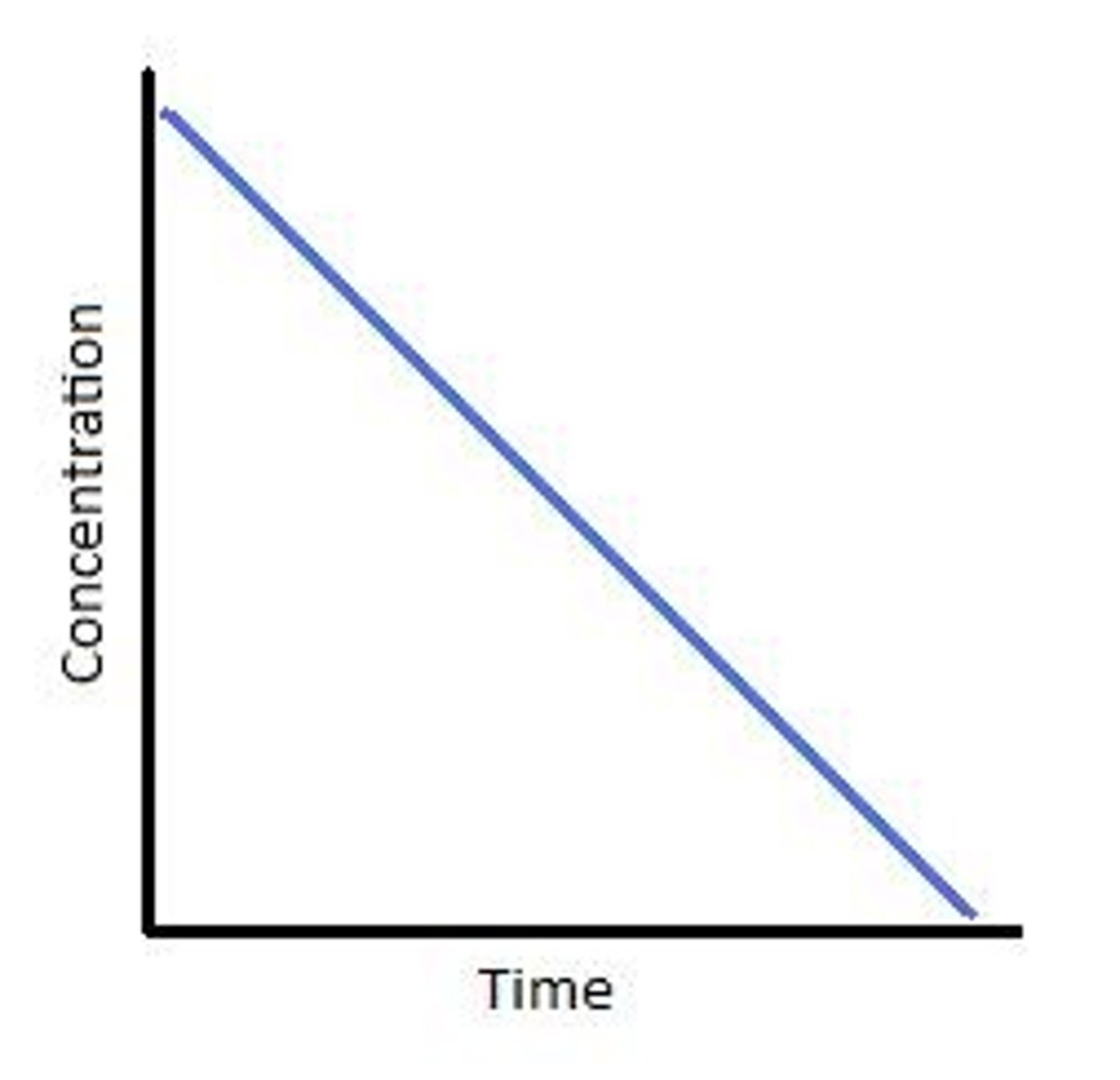
1st order reaction
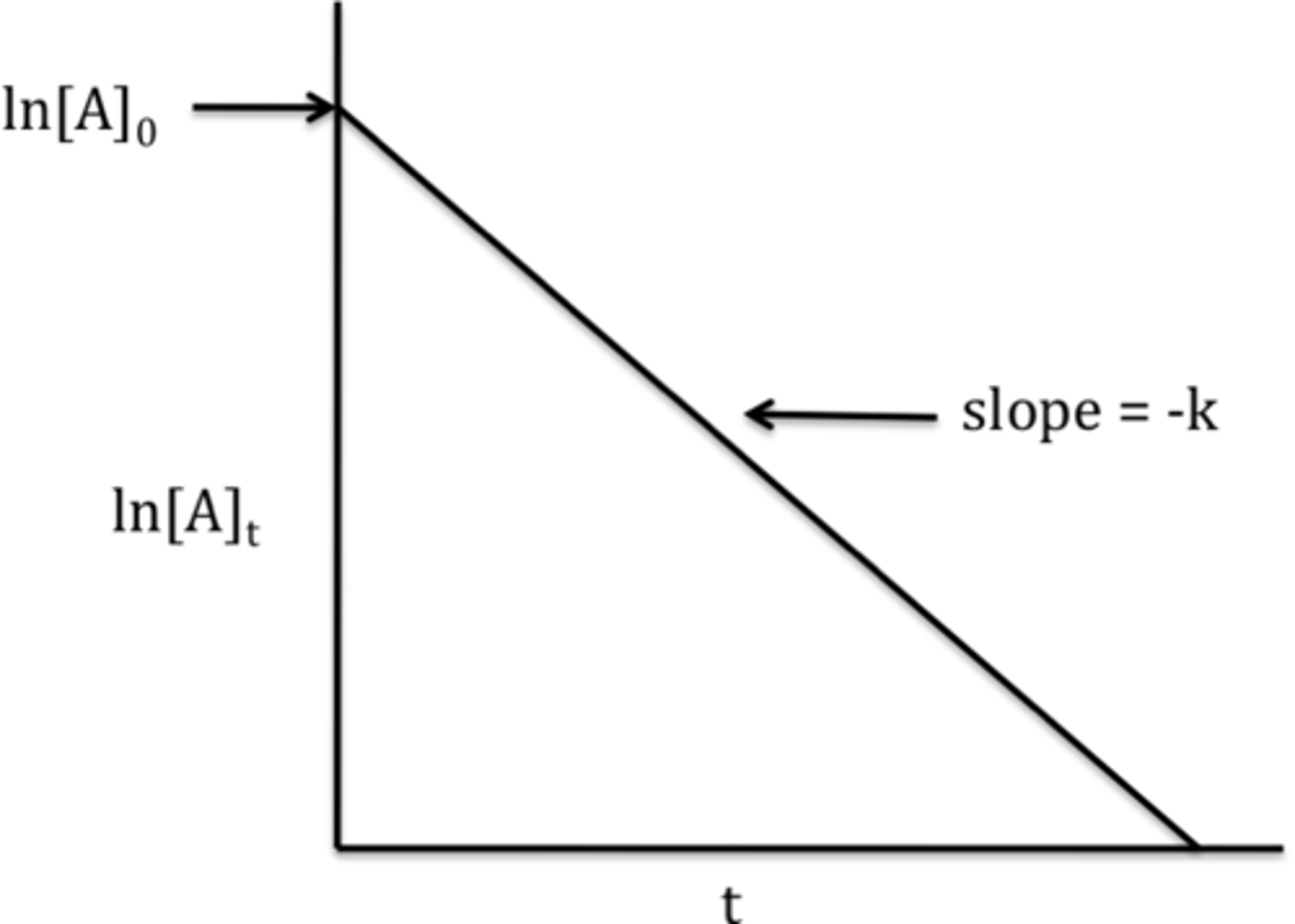
2nd order reaction
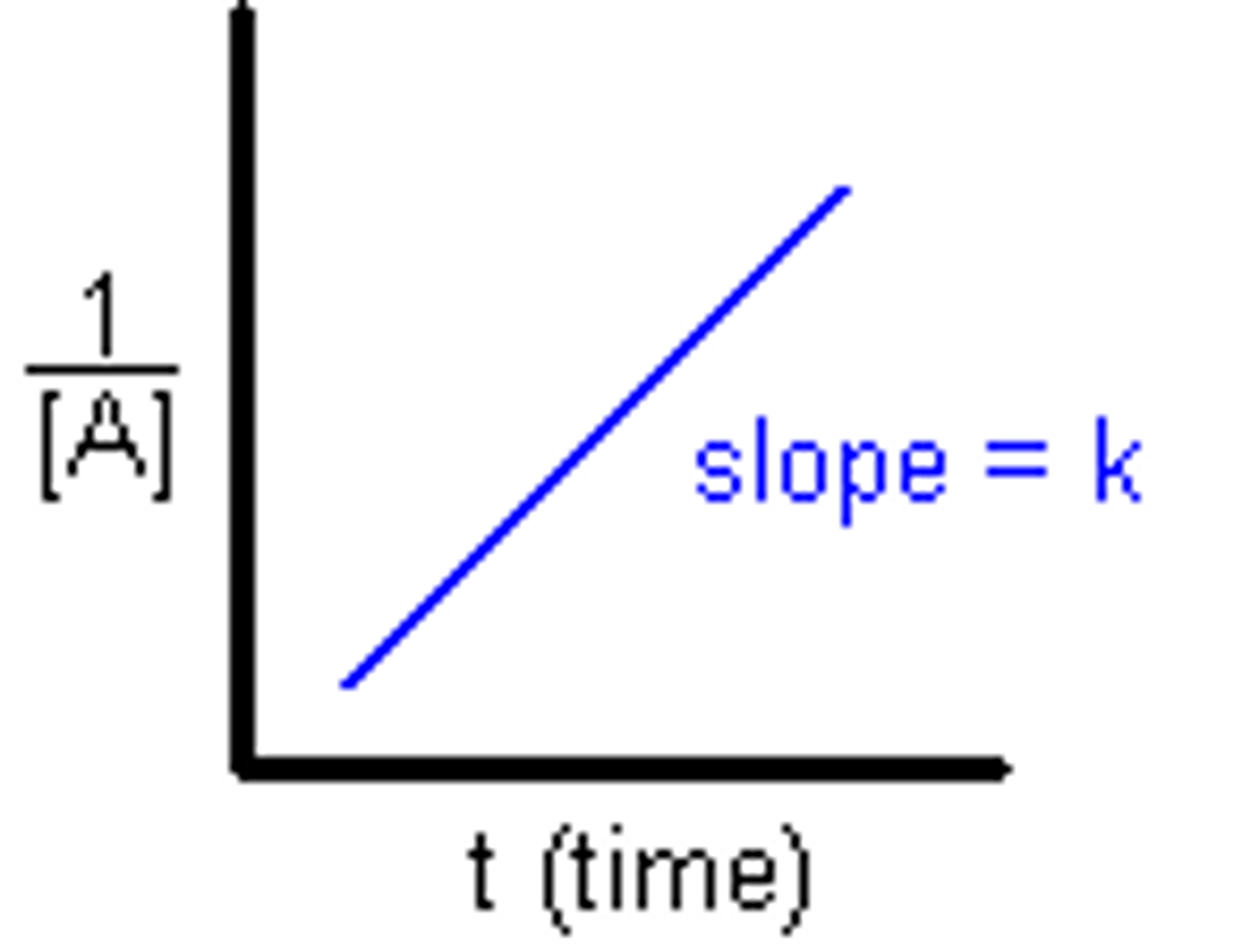
Multi-step reaction profile